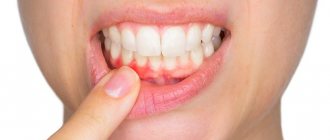
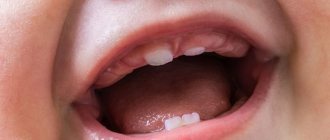
Tooth extraction: swelling
Tooth extraction is a difficult operation that traumatizes the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, it is not surprising that unpleasant consequences occur after tooth extraction: the most common of them is swelling. Patients often complain that after tooth extraction, the gums become swollen, swelling of the cheek or a slight gumboil appears. This is caused by partial destruction of the soft tissue around the tooth. This is unpleasant, but if the tumor is small, it goes away on its own in 2-3 days. To relieve swelling after tooth extraction, ice can be applied to the cheek for about 10 minutes. If the swelling has not gone away after a day, apply heat. Keep the heating pad for 20 minutes, then take a break for 10 minutes and put the heating pad back on.
Sometimes swelling can be caused by an allergy to the anesthesia. In this case, histamine, an antiallergic drug, will help. But if the swelling increases, then it may be a sign of inflammation that has arisen after tooth extraction. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
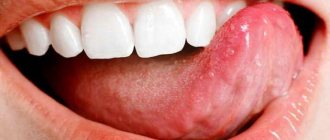
Plaque in the mouth and bitterness as signs of disease
Bitterness in the mouth can be a sign of gastritis and peptic ulcers.
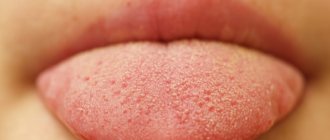
During the examination at the appointment, the doctor will definitely ask the patient to show his tongue: based on plaque, if it is combined with a feeling of bitterness in the mouth and abdominal pain, the doctor will receive more accurate information about the existing pathology.
For various diseases of the digestive system, the following clinical picture may be observed:
- A variation of the norm is the appearance of white plaque, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush. It usually indicates an excess amount of sugary foods in the diet and an increased amount of bacteria in the mouth. However, he speaks of the absence of serious pathologies in the digestive process.
- A feeling of bitterness combined with the appearance of a dense white-gray plaque is a sign of gastritis and gastric ulcer; such plaque often accompanies heartburn. A characteristic sign is the absence of plaque on the tip of the tongue.
- If a dense white coating accumulates at the base of the tongue, it usually indicates chronic gastritis. It is often accompanied by bloating, constant heartburn, and a bitter taste in the mouth.
- If there is a yellow coating with a greenish tint, this is clear evidence of liver pathology and gallbladder function. This is an alarming sign and the patient needs immediate medical attention.
A coating on the tongue also often appears in smokers; it also occurs along with an unpleasant taste in the mouth after drinking alcoholic beverages.
If unpleasant sensations occur systematically, it is necessary to consult a therapist for examination: the doctor will refer the patient to a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist, after which appropriate treatment will be selected.
Pain after tooth extraction
Another common complaint is that after tooth extraction, the gums, adjacent tooth, jaw, and throat hurt. As a rule, these are common symptoms after a traumatic procedure. They are caused by damage to the periodontal tissues and nerves, which goes away on its own after a few days. For example, if a temporary aching pain appears after tooth extraction, this is normal. To relieve discomfort, you can take painkillers. But if the pain intensifies, it is still worth visiting a doctor.
What to do if a crown falls off
The reasons why a crown falls off a tooth can be very diverse:
- With prolonged use, the cement on which the crown was strengthened dissolves.
- Secondary caries, leading to the destruction of the tooth stump and a violation of the tightness of the connection between the tooth and the crown.
- Damage to the denture due to heavy load when chewing solid food.
You cannot try to put the crown in its original place on your own and continue to use the prosthesis. This is very dangerous, since the crown, unexpectedly jumping off the tooth, can enter the windpipe and cause suffocation.
It is impossible to properly strengthen the prosthesis at home; only a dentist can do this.
The dentist, after examination and diagnosis, will decide what to do next.
There are several options:
- If the crown is only slightly damaged, it can be repaired and replaced.
- In case of significant damage or if the service life of the orthopedic structure has come to an end, the prosthesis must be replaced.
- If the cause of crown loss is caries, the tooth is treated, and then a decision is made about the possibility of prosthetics.
- If a tooth is severely damaged and cannot be restored, it is removed, and then implantation or a bridge is installed.
Bleeding after tooth extraction
Immediately after a tooth is removed, there is bleeding from the socket. This is quite normal, since blood vessels rupture during surgery. In this case, the doctor will provide you with the necessary assistance. But sometimes bleeding occurs a few hours after surgery. To stop the bleeding yourself after tooth extraction, apply a small gauze swab to the hole and lightly bite it. After 15 minutes the blood stops flowing. But if the bleeding does not stop for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
What complications does bitterness in the mouth lead to?
Bitterness in the mouth may indicate serious inflammatory processes in the digestive tract.
If you ignore an alarming sign, you may soon encounter very unpleasant consequences of the development of pathology.
Bitterness in the mouth may indicate serious inflammatory processes in the digestive tract: cholecystitis, gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.
Lack of timely treatment leads to the fact that the disease becomes chronic, and it becomes much more difficult to cope with it.
A constant bitter taste leads to loss of appetite, which results in weight loss to the point of exhaustion. Eating habits change; over time, a person may almost completely lose the ability to taste food. All this, in combination with other symptoms of the disease, leads to the development of depression and a general deterioration in well-being.
Pus after tooth extraction
Suppuration of the socket and periodontal tissues is caused by their infection. It can happen for several reasons. Firstly, if you did not follow the dentist's instructions regarding individual oral hygiene after surgery. Secondly, the cause may be a tooth fragment remaining in the tissues after removal. Thirdly, there is a high risk of suppuration after a complex wisdom tooth extraction, for example. If the inflammation is not treated in time, then some time after removal, suppuration, a fistula on the gum, and even a cyst may appear. If pus appears at the surgical site, consult a doctor. He will find and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process.
Symptoms for an urgent visit to the dentist
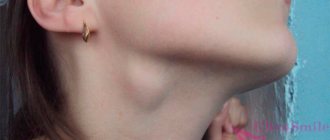
When such an unpleasant symptom as pain and bad breath intensifies, the temperature rises, the gums swell, and dental surgery may even be required. It is important to see a dentist on time.
- The doctor will carefully examine the oral cavity and the surgical area.
- A small spoon is used to diagnose the hole.
- If alveolitis develops, special therapy is prescribed. First, anesthetics are introduced, then plaque and pathogenic microbes are removed.
- Then the wound is treated with an antiseptic, and the necessary medications are applied.
- Stitches may be needed.
You should contact the dentist when the gum tissue is swollen, you feel severe pain, your cheek and neck are swollen. In such a situation, pus collects in the wound area. The dentist prescribes rinsing, disinfection procedures, painkillers, and antibiotics. With severe tissue injury, an abscess may develop. At risk are those patients who do not follow the doctor’s recommendations. Remember that timely contact with a doctor is the key to quick treatment.
Dry socket after tooth extraction
A blood clot should remain in the socket after surgery. This is a very important part of the healing process. This clot protects the bone and nerve endings and serves to form bone tissue after tooth extraction. Therefore, you should not rinse your mouth for a day after the procedure and eat hot food - this will help the clot dissolve. But sometimes it does not form, and a dry socket appears.
Dry socket is considered a complication. It most often occurs after complex removals accompanied by significant trauma. If there is no blood clot, then the hole after tooth extraction hurts, and sometimes it seems that the ear also hurts. Often there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The consequence of a dry socket after a traumatic tooth extraction can be inflammation of the gums or alveolitis. Therefore, if you experience acute pain in the socket, consult a doctor immediately. He will place a tampon with a special anti-inflammatory gel on the hole. Tampons are changed until healing begins.
The most common causes of bitterness in the mouth
The cause of bitterness in the mouth is the ingress of large amounts of bile.
The main reason for the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth is the entry of a large amount of bile into the gastrointestinal tract.
This is a secretion that is produced by the liver and is used when digesting food; normally, bile flows through the bile ducts into the duodenum.
Some foods, such as pine nuts, and medications have a choleretic effect, so they promote the production of increased amounts of bile. If it penetrates the esophagus and stomach, there is a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
Bitterness is a sign of trouble in the digestive system; most often it appears after eating fatty, fried and other hard-to-digest foods. Normally, it should not enter the esophagus; digestive disorders occur for several common reasons:
- Digestive disorders. Usually, bitterness in the mouth is associated with stagnation of bile, in this case it is accompanied by the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue, a metallic taste, and the urine becomes dark. An additional sign of liver dysfunction is yellowness of the skin.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a disorder of the stomach in which its contents begin to leak into the esophagus. The disease is accompanied by heartburn, nausea, belching after eating, and chest pain.
- Infestation with parasites. Parasitic infestations lead to numerous disorders of the digestive tract: intestinal function is disrupted, and signs of vitamin deficiency often appear. If a parasite infestation is detected, the doctor will prescribe special anthelmintics.
- Biliary dyskinesia caused by hormonal disorders. Disruption of the thyroid gland provokes spasm of the biliary tract, resulting in a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- Another hormonal disorder that can provoke this unpleasant symptom is diabetes.
- A short-term feeling of bitterness in the mouth can occur after taking antibiotics due to increased load on the liver; sometimes this feeling occurs after consuming pine nuts, medications, and often occurs during pregnancy.
Alveolitis after tooth extraction
This is a serious complication caused by tooth extraction, which has several causes. This may be the presence of chronic inflammation of the tissues around the tooth - periodontitis, or a dry socket. In addition, alveolitis occurs if, after tooth extraction, a dental fragment remains in the tissues. All these factors cause infection of the hole and the development of its inflammation. 1–3 days after tooth extraction, pain occurs, followed by a specific smell from the mouth. Then these symptoms intensify, the hole becomes covered with a gray coating, and it becomes impossible to eat due to severe pain.
In this case, only a doctor will help you, who will carry out the necessary treatment and clean the hole from infection. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances - alveolitis can develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), causing an abscess and phlegmon.
Painful sensations after the removal procedure are unpleasant, but inevitable. Remember, if these sensations intensify, then in this case, complications after tooth extraction should be treated by a specialist. Do not delay visiting the dental clinic, dulling the pain with analgesics. Correct and timely treatment will help you avoid more serious complications.
Methods for treating bitterness in the mouth
To treat this disease, you can use freshly squeezed juices.
In all cases, treatment of bitterness in the mouth should begin with a visit to a specialist and a comprehensive examination.
This symptom indicates various pathologies in the body, so it is important to accurately determine the cause of the disorders so that the treatment is effective.
In almost all cases, the success of treatment largely depends on the efforts of the patient himself. First of all, you will need to adjust your diet: you will need to exclude any hard-to-digest food and alcoholic drinks from your diet, and you will need to follow a diet.
Compliance with the diet also requires stopping smoking and consuming any substances that can irritate the mucous membranes. In addition to the medications that the doctor will prescribe to treat the identified disease, it will be useful to use the following folk remedies:
- Constantly drinking plenty of fluids helps improve the functioning of the digestive system. You need to drink at least 2-2.5 liters of water per day; in addition, drinking rosehip or currant decoction is beneficial.
- Drinking freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices - carrot, orange, apple, etc.
- Natural juices help improve appetite, provoke salivation, and in addition, the body receives a sufficient amount of vitamins.
- Use of sedatives. Many digestive disorders occur against the background of a constant remedy, so the use of sedatives will be required. This is an infusion of valerian, motherwort decoctions, and also the use of sedative tea.
- It is also necessary to normalize the functioning of the intestines: for this it is necessary to consume sorbents, as well as foods rich in fiber to get rid of constipation.
It is important to remember that bitterness in the mouth is not an independent disease, but only one of the alarming signs that requires mandatory diagnosis and correction of the diet. Only with an integrated approach will treatment be successful and avoid possible complications.