Why does a child's color change?
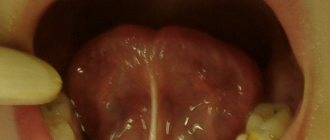
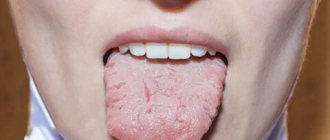
The tongue is a human organ that tends to clearly demonstrate ongoing changes in the body. If its surface acquires a different shade from normal, then it is worth monitoring the baby’s behavior and condition.
If a slight whitish coating appears, there is no need to panic. Most often, these tiny particles of food settle on the receptors, which leads to this appearance. You can eliminate this tone with a simple toothpaste and brush.
A blue tint is a rather dangerous sign of illness. Therefore, when a child’s tongue is blue, this indicates the presence of a serious disease in the internal organs. It is strictly forbidden to start the process; if such a symptom occurs, it is possible to bring the disease to critical situations.
What are the symptoms in babies?
Symptoms may range from mild to severe. This depends on the level of bilirubin in the blood and the duration of the disease. The causes and consequences of jaundice in newborns can vary, but there is one common characteristic - jaundice of the skin and sclera. It is worth noting that the eyes show symptoms faster. The baby may experience increased drowsiness with a decreased sucking reflex. Convulsions may occur. Without treatment, advanced jaundice can cause deafness, mental retardation and paralysis.
Does your newborn have symptoms of jaundice?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Causes of turning blue
If a child’s tongue turns blue, then only a doctor can identify the problems that helped provoke the development of such a process. The following reasons are identified due to which a bluish tone is observed on the surface of the organ:
- Kidney diseases, such as total or diffuse cyanosis. There is a decrease in the required volume of oxygen in the body, which provokes the appearance of a blue tint not only on the surface of the papillae, but also on the walls of the oral cavity.
- Diamond-shaped glossitis - with its development, the surface becomes dense in structure and turns blue. The disease tends to occur without symptoms. Therefore, identifying a non-standard color should not be ignored.
- Iron deficiency anemia - a deficiency of vitamin B12, iron, and folic acid is detected in the body. The signal for treatment is not only a specific tone in the mouth, but also excessive pallor of the skin;
- Pathological processes with the lungs or heart muscle - a bluish tone appears on the surface or a deep purple color of the external receptors. If the abnormal color occurs on the lower part of the organ, then the problem lies in the blood circulation, which leads to cardiopulmonary failure.
- Kidney failure - a bluish tint is fixed on the edge of the root, in front of the pharynx.
- A sharp bluish discoloration of the surface may indicate poisoning with heavy metals, especially mercury.
- Inflammation of organs in the abdominal cavity - in addition to the non-standard color of the baby’s mouth, increased body temperature and painful discomfort in the lower abdomen are added.
If the baby begins to feel unwell and becomes capricious, you should more closely monitor not only his well-being, but also carefully examine the oral cavity. In some situations, a child's blue tongue may indicate problems with the respiratory system.
Treatment
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
In each individual case, the treatment complex is selected individually based on the reasons for the formation of black deposits on the tongue, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Treatment of black plaque:
- If the cause of the formation of black deposits is dental problems , treatment should be performed by a dentist.
- In cases where plaque has formed due to prolonged antibacterial therapy, the doctor cancels it or prescribes another drug.
- For candidiasis, antifungal drugs are prescribed (Fluconazole, Pimafucin)
- If you have stomatitis and fungal infection, rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions (Chlorophyllipt, Hepilor).
- For gastritis, antacids (Maalox) and drugs to enhance the protective properties of the gastric mucosa are prescribed .
- In case of vitamin deficiency, are prescribed .
- If the cause of the black plaque is poisoning, it is recommended to take sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional medications:
- probiotics (Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin) and prebiotics (Duphalac, Lactusan) to populate the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and stimulate the production of your own healthy microflora;
- interferons to strengthen the immune system (Cycloferon, Kagocel).
Important! The specialist also gives mother and child recommendations on nutrition and oral hygiene, which must be strictly observed during the period of active treatment and after it.
Associated symptoms of pathology
If the organ necessary for conversation acquires a specific tone, then most often the baby will additionally exhibit the following symptoms:
- Swelling in the mouth and face;
- Specific secretions;
- The presence of cracks, weeping ulcers;
- Soreness in the mouth when talking or eating;
- There are pimples, growths, and bumps on the surface.
If, when sticking out your tongue, not only a blue tone is visible, but also additional signs of illness, such as an unpleasant odor, then it is recommended to immediately consult a pediatrician. There is no need to prolong the baby’s condition until it becomes critical. It is better to start treatment at the first symptoms.
conclusions
- there are both pathological and non-pathological causes of darkening of the tongue in a young child;
- plaque formation may be accompanied by alarming symptoms, such as vomiting and fever, or may occur without the appearance of additional symptoms and complaints;
- if the plaque does not disappear on its own, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment for the child to see a doctor;
- Treatment can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the causes of darkening of the tongue;
- the appearance of the taste organ will return to normal when the causes of the formation of black plaque are eliminated.
What to do if your tongue changes color?
If you notice a plaque of a specific tone in a child that does not go away for a long period of time, you should contact your pediatrician. Self-administration of medications is unacceptable. After the examination, the pediatrician will recommend an additional consultation with specialized specialists: a dermatologist, an infectious disease specialist, a gastroenterologist, a toxicologist, and a dentist.
Only after the examination, all doctors have the opportunity to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Typically, when a child has a purple tongue, the following therapeutic intervention is recommended:
- Problems with the digestive system - antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antispasmodics are prescribed;
- If there is a lack of vitamins in the body, the pediatrician will prescribe the required fortified complexes that will replenish the lack of nutrients in the internal organs;
- If a fungal infection is detected, antifungal drugs or antibacterial substances are required for treatment.
You should definitely make sure that your baby cleans his mouth with toothpaste that contains antibacterial ingredients. During therapy, as well as after the treatment process, it is recommended to rinse the mouth for a long period of time with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, soda-saline solution or Furacillin.
In addition to medications, you can use infusions of medicinal herbs to irrigate the oral cavity: a collection of cinnamon and cloves, calendula and medicinal chamomile.
The doctor will develop a special therapeutic diet for the baby that will prevent the condition from worsening and prevent the possibility of such a dangerous symptom from appearing in the future. It is required to give up fast food products, not to consume smoked meats, pickles and other heavy foods, as well as concentrated juices and carbonated drinks.
In what case should you consult a doctor and undergo an examination?
If the deposits disappear on their own after rinsing your mouth or drinking, there is no need to go to the hospital, since the cause of the darkening of the tongue is most likely food.
If the plaque does not disappear when rinsing, but appears again after cleaning the tongue, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician.
If the blackening of the surface is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, diarrhea or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
You should not try to treat your child yourself or try folk remedies without consulting a specialist and finding out the reasons for the blackening of the tongue.
You should know! Self-medication can cause serious harm to the baby's health.
Possible complications
If the pathology is not detected in time and the baby lives for a long period with purple or blue color in the oral cavity, then there is a possibility of causing various complications:
- Development of heart failure;
- Problems with the respiratory system;
- Improper kidney function;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Malocclusion, which leads to the inability of the baby to close the teeth when talking or eating food;
- Problematic pronunciation of words;
- Teeth move in different directions.
At the same time, a small person may develop an inferiority complex and mental discord due to the abnormal appearance of the oral cavity.
Thus, the appearance of a bluish tint indicates health problems. To prevent such complications, you need to monitor your own child’s condition and consult a doctor in time to prescribe treatment.
What does tongue position affect?
Language takes part in many important processes:
- determines the taste and temperature of food;
- helps in mixing food and saliva, starting the digestion process;
- facilitates swallowing;
- participates in the formation of speech.
And also, making several thousand movements per day (swallowing movements alone are about 2000), the tongue participates in the formation of the arch of the palate and bite.
The relationship of the jaws in the bite has a close relationship with the position of the head relative to the body and posture in general.
Bite is the relationship between the dentition of the upper and lower jaws during their tight closure. Depending on age, the bite can be milky, replaceable or permanent. Classification of occlusion is not the topic of this article, so I will focus only on the description of physiological occlusion, which is characterized by the following features:
- does not interfere with the process of eating;
- does not distort speech;
- does not spoil the external characteristics of the face.
When the teeth are completely closed, the physiological occlusion meets the following indicators:
- the upper dentition covers a third of the lower dentition;
- all opposing chewing teeth of the upper and lower jaws fit well together;
- a conventional central line drawn vertically along the face divides the jaws into equal halves.
I apologize in advance to orthodontists for such a simplified description of the physiological bite and there may be some other inaccuracies. I hope the meaning of the article did not suffer from this.
For proper growth of teeth, the so-called myodynamic balance must be formed in the oral cavity, that is, the pressure of the tongue from the inside on the dentition of the upper jaw must correspond to the pressure of the muscles of the lips and cheeks from the outside.
Normally, the tip of the tongue is in a neutral position, located behind the upper incisors, without touching them. Where the tongue is when we pronounce the sound “H” is the so-called “resting point”. During each swallowing movement, the back of the tongue is pressed against the palate, stimulating the growth of the upper jaw in width, improving blood supply to the nasal and oropharynx and thus increasing local immunity. The correct position of the tongue at rest and when swallowing is only possible with nasal breathing, while the mouth must be closed. When breathing through the nose, all the air inhaled has time to be purified and warmed up. The air flow passing through the nasal turbinates also stimulates the growth of the upper jaw in width and the harmonious growth of the entire middle third of the face.
Now I will dwell a little on the changeable bite and the problems of the formation of a physiological bite, which become obvious precisely during the change of teeth. Usually this age ranges from 4-5 years to 12-14 years. During the mixed bite, the most intensive growth of the jaw bones occurs, so bite correction is also most effective at this time.
In children who breathe through their mouth, the so-called “adenoid” type of face is formed, the face becomes narrow and long - elongated. Narrow jaws cause a lack of space for permanent teeth, that is, they are crowded. The Gothic palate and lack of space for the back of the tongue creates problems with sound pronunciation.
Children with malocclusion often breathe through their mouths, even if the nasal passages are clear. They develop habitual mouth breathing and begin to get colds more often. It has been proven that mouth breathing reduces blood oxygenation, as well as the transfer of oxygen to tissues. The brain suffers more than other organs from hypoxia. Children become irritable, not assiduous, and not attentive.
The tongue in such children is in the middle (interdental) or low position - between the palate and the lower jaw. When swallowing, it does not rest against the roof of the mouth, but against the teeth. The tongue is a powerful muscular organ and when it is pressed, the teeth deviate from their normal position.
Very often this is combined with weakness of the orbicularis oris muscle, which normally should balance the pressure on the teeth from the outside.
Normally, swallowing should be visible only by the movement of the thyroid cartilage, the face should not tense. If the position of the tongue is incorrect and the orbicularis oris muscle is weak, the child has to use additional muscles to keep the mouth closed when swallowing. He begins to help himself when swallowing with the corners of his lips, facial muscles, neck movements, shoulders, and sometimes even his stomach.
The tongue, in the middle or lower position, blocks the airways and, in order to somehow open them, the child is forced to move his head forward and raise his chin. This unnatural position of the head and neck also changes the upper chest. Orthopedists, seeing such a picture, talk about poor posture.
So, a change in the position of the tongue leads to a change in the position of the head, a distortion of the anatomically correct location relative to each other of the cervical vertebrae, hyoid bone, cartilage of the larynx and soft tissues of the neck, trachea and esophagus, vessels supplying the brain, and nerve trunks that ensure the functioning of all internal organs.
Thus, during a mixed dentition, it becomes extremely important to form nasal breathing and create conditions for the anatomically correct position and functioning of the tongue, because this will contribute to both the normal development of the dentofacial system and the child’s entire body.
- normal chewing, facilitates the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract;
- normal swallowing forms a correct bite and harmonious facial features;
- nasal breathing reduces the risk of colds (the air is purified, warmed, lymphoid tissue is not subject to additional stress and does not hypertrophy);
- improves central nervous system function due to sufficient oxygen supply;
- communication function improves due to clear and understandable speech;
- Due to correct posture, a sense of balance, dexterity, and coordination develops.
Correct bite and anatomical position of the tongue are the key to the health and well-being of your child.
I would like to briefly list the factors that can lead to incorrect position and functioning of the tongue:
- Intrauterine factors (multiple pregnancy, abnormalities in the structure of the uterus, increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy, genetic conditions, etc.);
- Traumatic childbirth;
- Prematurity;
- Artificial ventilation in the first year of life;
- Artificial feeding;
- Untimely introduction of complementary foods;
- Lack of solid food in the child’s diet;
- Bad habits: thumb, tongue, cheek, and various objects sucking, prolonged pacifier sucking (more than 1.5 years);
- Premature loss of baby teeth;
- Frequent diseases of the ENT organs, enlarged adenoids.