Thrush is one of the most common and not yet conquered infections that affects any person, regardless of age. Today, doctors have enough tools in their arsenal to eliminate pathology - both the most sophisticated and simpler ones, but no less effective. One of these remedies is Sodium tetraborate, which is cheap and has been proven for decades. The drug is not as widely known as other advertised medications, and it is not primarily offered in pharmacies. Nevertheless, Sodium tetraborate helps against thrush in adults and children no worse than other medications used.
Characteristics of the drug
The therapeutic effect of the drug is provided by sodium tetraborate (or borax) - a substance that is a derivative of boric or, more precisely, tetraboric acid.
The compound has strong bacteriostatic and antiseptic properties. The mechanism of its action is to come into contact with pathogenic microorganisms, further blocking their attachment to tissues and destroying fungal mycelium. As a result of such exposure, infectious agents are deprived of the ability to function and form colonies. Despite suppressing the growth of fungi, the boric acid derivative does not have fungistatic or fungicidal properties, and therefore does not directly have antimycotic effects. Borax is often included in combination medications due to its insecticidal and antiseptic properties. In particular, the substance is used for topical use in the treatment of respiratory diseases.
The excipient of the drug is glycerin. It is included in the composition due to its ability to reduce the local irritant effect of sodium tetraborate, as well as to accelerate its transport through the skin and mucous tissues. As a result of drug interaction, the drug easily and quickly penetrates the layers of the dermis, binds to pathogens and suppresses their activity.
The medicinal solution has a bactericidal effect on some types of cocci, as well as bacteria, Trichomonas. Actively suppresses the functioning of yeast fungi of the genus Candida, which are the culprits of thrush.
The drug is well absorbed through the damaged surface of the dermis and into the gastrointestinal tract. When used systematically, it is retained in the bones and liver. It does not form metabolites and is excreted unchanged by the kidneys and through the stomach.
Sodium tetraborate is prescribed for thrush of various localizations (oral cavity, upper respiratory and urinary tract, reproductive system), as well as for the treatment of bedsores and diaper rash.
Thrush: a common problem with improper treatment
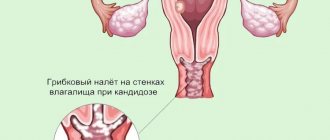
Every woman knows what candidiasis (“thrush”) is. And each has a “proven” remedy. But what if symptoms return? Why can candidiasis persist? And how to find an individually effective medicine?
Why does Candida fungus “grow”?
1. Lactobacillus deficiency
As is known, the basis of female microflora is lactobacilli. The share of which, ideally, is at least 85%.
The remaining 15% are dozens of species of opportunistic bacteria and 4 species of Candida fungi. The presence of which is acceptable and safe, but only in limited quantities.
Control of the number of such pathogens is carried out by lactobacilli, which secrete lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide. And while there are enough of the latter, “conditionally harmful” ones are not capable of reproduction.
To maintain normal activity, lactobacilli need food - glycogen from the surface cells of the vaginal epithelium ("dead from old age").
And the rate of epithelium renewal, that is, “replenishment of food reserves,” in turn, depends on the balance of estrogen.
Thus, a decrease in lactobacilli and the “overgrowth” of fungi and other pathogens against this background is often associated with an imbalance of estrogen and is observed with:
- Diseases or decreased ovarian function,
- When taking certain oral contraceptives;
- Against the backdrop of acute stress
- Against the background of sudden weight loss (fat is needed for the synthesis of estrogens).
Mechanically, frequent douching and other similar procedures that “wash away” the surface layer of cells and a certain amount of beneficial flora can provoke disturbances.
Well, among other reasons:
- inflammatory diseases
- sexually transmitted infections
- long-term and/or “non-targeted” use of antibiotics
- and the use of antibacterial/antiseptic suppositories.
2. Insufficiency of immunity
“Thrush” may also be associated with immune disorders, since Candida is “under the supervision” of local defenses.
And another risk factor for candidiasis are:
- various immunodeficiency conditions
- chronic pathologies that adversely affect the immune system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies, oncological processes, etc.),
- taking glucorticoid hormones.
3. Household reasons
Well, the most “banal” provocateur of the violation may be the regular use of sanitary pads, wearing synthetic underwear and some other factors that create conditions for increased local temperature, oxygen deficiency and high humidity. That is, what fungi of the genus Candida “love”.
Candidiasis or “other”
If you suspect a risk of candidiasis, you can already based on the presence of the listed factors. It is not easy to distinguish candidiasis from vaginosis at first glance.
At the same time, the treatment of one and another pathology is fundamentally different. And the use of non-targeted therapy leads to chronicity of the process and the development of complications, including infertility.
The nature of the discharge can help determine candidiasis by eye - white, cheesy, with a sour odor, accompanied by severe itching. However, not everyone has such “classic” signs and not always.
Vaginosis (bacterial vaginosis) often “has” copious white-gray, sometimes foamy, discharge, with an alkaline (“fishy”) odor, which intensifies after sexual intercourse. Sometimes with itching. However, even here the nature of the symptoms varies greatly. And, among other things, violations can be combined.
Thus, to accurately distinguish candidiasis from other forms of vaginal dysbiosis, a flora analysis will be required.
And the most complete picture can be obtained from the “Florocenosis” analysis.
The study includes calculations:
- lactobacilli,
- causative agents of bacterial vaginosis Gardnerella vaginalis
- and Atopobium vaginae,
- Enterobacteriaceae
- Ureaplasma urealyticum,
- Candida albicans
which makes it possible to differentiate several types of dysbiosis at once and apply the correct treatment.
Typing fungi of the genus Candida allows you to select an effective antifungal drug. After all, not everyone knows, but some of the listed types have pronounced resistance to popular means. You can get the typing result in the “Florocenosis” test or submit a vaginal smear for a separate fungal typing test in order to accurately determine the type of thrush pathogen and select the right antifungal drug.
Prevention of candidiasis
Summarizing all of the above and adhering to national clinical recommendations, we can conclude that the prevention of “thrush” in both women and men comes down to:
- maintaining personal hygiene,
- the use of barrier methods of contraception,
- abstaining from unprotected sexual intercourse with frequent changes of partners,
- avoiding uncontrolled use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs,
- exclusion from the “wardrobe” of tight, synthetic underwear,
- monitoring the state of general, hormonal and reproductive health.
In addition, women should:
- limit the use of sanitary pads to menstruation days only,
- exclude douching, vaginal douche and other similar procedures,
- prevent long-term use of intrauterine devices and vaginal diaphragms.
And pregnant women require special attention, due to physiological weakening of the immune system, changes in hormonal levels and stagnation of lymph in the pelvis due to increased intra-abdominal pressure. Which creates “favorable” conditions for the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
How to use Sodium tetraborate
Like any medicine, it is highly undesirable to use the drug for therapy independently, without medical prescription and supervision. In addition, this is due to the characteristics of borax: the substance does not affect the growth and reproduction of fungi, does not destroy their spores, but only prevents the fixation of microorganisms in mucous tissues. And if, after the use of Sodium tetraborate, only partial washing away of the infection occurs, then the surviving pathogens will inevitably cause a relapse of the disease. To prevent its return, the doctor must monitor the progress of treatment: check how effectively the drug has washed away the infection. For this reason, the specifics of treatment for borax should be determined by the treating specialist.
In pediatrics
For stomatitis in newborns, the product is used to wipe the oral mucosa using a sterile stick or cotton wool. The regularity of procedures for thrush in infants is 2-3 r./s. Course – from 3 to 7 days.
In gynecology
Borax in glycerin for thrush is used for lubrication, applications, douching, applied 2 to 3 times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor in accordance with the woman’s testimony.
Instructions for use recommend using the drug after hygiene procedures for thrush (vaginal candidiasis). After this, it is advisable to douche with chamomile decoction or boiled water at a comfortable temperature and then treat the infected area with medication: wipe with a cotton swab or disk soaked in borax, or place inside as a candle for 20-30 minutes.
The frequency and duration of therapy depend on the severity of candidiasis: for light discharge, procedures are carried out once a day (preferably at night), and for heavy discharge, twice a day (morning and evening). The course of therapy is individual for each woman, on average its duration is 1 week.
Colpitis: vaginal douching is indicated for treatment. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times per day. after hygiene procedures. During hygiene therapy, it is recommended to use slightly alkaline detergents or soaps with a neutral pH balance, and change linens, washcloths and towels daily.
During pregnancy and pregnancy
The drug Sodium tetraborate is prohibited for therapy during pregnancy. If it is not possible to replace it with another medicine, the doctor may consider the possibility of using it on an individual basis.
In addition to pregnant women, the drug should not be used by nursing women, since there is no proven data on its safety for the child.
Sodium tetraborate (borax solution in glycerin) 20% 30g
A country
Russia
The country of production may vary depending on the batch of goods. Please check with the operator for detailed information when confirming your order.
Active substance
Sodium tetraborate
Compound
Bottle 30 ml Borax (sodium tetraborate) 20 g Excipients: glycerol 80 g.
pharmachologic effect
Antiseptic. Sodium tetraborate has bacteriostatic activity. Effective against candidiasis. Removes the mycelium of the fungus from the mucous membranes, disrupts the process of attachment of the fungus to the mucous membranes and inhibits its reproduction (it is not an antifungal drug, because it does not have a fungicidal or fungistatic effect). As an antimicrobial drug, it is included in combination drugs for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Sodium tetraborate has insecticidal properties (class IV in terms of toxicity level).
Indications for use
Candidal lesions of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, pharynx, upper respiratory tract, urinary tract and genital organs; diaper rash, bedsores.
Mode of application
Sodium tetraborate is used for rinsing, lubricating the skin, and douching 2-3 times a day.
Interaction
You should not practice the simultaneous use of topical antibiotics, as well as those drugs that contain boric acid and phenol. Sodium tetraborate should not be used with hormonal agents. When taken simultaneously with other drugs for external use, allergic manifestations may occur.
Side effect
Local reactions: hyperemia and burning sensation at the site of application. With prolonged use, symptoms of chronic intoxication may develop: From the digestive system: anorexia, gastrointestinal disorders. From the central nervous system: weakness, confusion, seizures. Dermatological reactions: dermatitis, alopecia .Other: menstrual irregularities, anemia.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, pregnancy, lactation. Violation of the integrity of the skin (during skin processing).
Overdose
It should be taken into account that when taking the drug orally, the lethal dose for an adult is 10–20 g. In case of an overdose, the following symptoms may be observed: - abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting; - headaches, a feeling of general weakness; - loss of consciousness, dehydration; - convulsions, twitching of the muscles of the face or limbs; - damage to the liver and kidneys; - cardiovascular failure. In this case, it is necessary to immediately rinse the stomach and carry out forced diuresis. For severe poisoning, hemodialysis is practiced. Riboflavin is prescribed intravenously, a mononucleotide. Correction of acidosis and water-electrolyte balance is carried out. Also, a solution of sodium bicarbonate, solutions of sodium chloride and glucose, and plasma-substituting solutions are administered intravenously. If the patient complains of pain in the stomach, he is prescribed a solution of platyphylline and atropine, a 1% solution of promedol, and a glucose-novocaine mixture is injected intravenously. Drugs are also prescribed to support normal functioning blood vessels and heart. Read more: https://medside.ru/natriya-tetraborat
special instructions
Can be used together with boric acid as a buffer and antimicrobial agent in eye drops. Not for internal use.