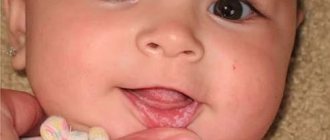
What does thrush look like in a child?
Any part of the oropharynx can be affected: tongue, lips, corners of the mouth, gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tonsils. White grains (spot coating) appear, reminiscent of curdled milk, or a film (solid coating) of a cheesy appearance. These elements are easily removed by scraping with a spatula, revealing a bright red base, sometimes with a bleeding surface. As a rule, the course of the infection is painless and has only local manifestations. General health is not affected.
Prevention of thrush in newborns
To prevent thrush from returning, as well as for preventive purposes, you should follow simple rules:
- boil bottles, nipples and pacifiers if the child eats formula after each feeding;
- cleanse your baby’s skin daily using hygiene procedures;
- wash your hands before playing or interacting with the child, before feeding;
- pay enough attention to mother’s breast hygiene if the newborn receives mother’s milk as food;
- after feeding, clean the mouth with water or special products sold in pharmacies or children's stores (foam, solutions, etc.);
- strengthen the child’s immunity (long-term breastfeeding, hardening procedures, daily walks, massage, etc.);
- Toys should be washed at least once a week;
- monitor the condition of the baby’s intestines.
Thrush is an unpleasant phenomenon, but it is quite treatable, provided that therapy is started on time and carried out after consulting a doctor. Complications after suffering from candidiasis almost never occur, so preventive measures and close attention to the hygiene and well-being of the baby are quite enough to avoid relapses and re-infection.
To learn how thrush manifests itself in infants and how to get rid of it, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.antibiotic.ru/cmac/pdf/6_2_168.pdf
Rate how useful this article was
5 5 people voted, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
How to treat thrush in a child?
The disease is treated at home. Local medications are used and only as prescribed by a doctor: pediatrician or dentist! Special antifungal agents are used in the form of solutions, sprays, gels, and drops. For maximum effectiveness of therapy, the drug must remain in the oral cavity (on the mucous membrane) for as long as possible. Therefore, the main way to use them is by rinsing or lubricating.
Treatment is long, up to 2-3 weeks.
It is important!
Often thrush in the mouth of infants is associated with candidiasis of the skin of the nipples and areola in the mother. In this case, the woman experiences redness, irritation, and a burning sensation on her chest. In this case, treatment should be comprehensive, for mother and baby.
How to distinguish thrush from the consequences of regurgitation
Some parents (especially if the child is the first-born) mistakenly mistake the plaque for the remains of curdled milk after the baby has burped. Indeed, it can be very difficult to visually determine the nature of the contents of the oral cavity.
To understand what exactly caused the symptom, you can do a small test. You need to moisten a piece of clean cloth with boiled water or chamomile decoction and try to remove the plaque.
If this is the remains of milk after regurgitation, then the baby’s mouth will be easily cleaned, and all the contents will end up on the tissue. If you have thrush, it is not so easy to remove plaque (after the procedure, irritated areas will remain at the site of inflammation).
Child nutrition
Simple carbohydrates are the main nutrient medium for fungal growth. Therefore, sweets, sugar, cookies, etc. must be excluded from the patient’s diet. Breastfeeding certainly continues.
If the child is bottle-fed or mixed-fed, then preference should be given to formulas containing probiotic microorganisms, which have the largest evidence base for their effectiveness. These are LGG and BB-12 from Chr. Hansen. It has been proven that LGG and BB-12 inhibit the growth of opportunistic microorganisms and fungi, protect against the development of caries and infections, and effectively prevent atopic eczema. Nutrilak Premium Comfort is enriched with LGG probiotic.
Symptoms of thrush in the mouth in infants and children
Signs of candidiasis in babies vary depending on the stage of the disease and may appear 5-10 days after birth.
Symptoms of the first phase of the disease are disturbances in the psycho-emotional state (tearfulness) and the appearance of plaque. It is difficult to remove pathological formations that look like small white dots. The child refuses to take the breast and is capricious.
As thrush develops, deposits spread beyond the mouth and become localized in the throat.
The plaque acquires a cheesy consistency, looks like dense white plaques, and cannot be removed. The child's mouth smells unpleasant.
Stage three thrush in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- deposits cover the throat, lips, tonsils, palate, gums, cheeks;
- upon palpation, enlarged lymph nodes are felt;
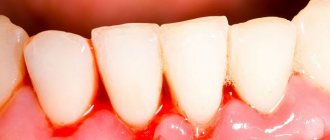
- identified ulcers are characterized by increased bleeding.
The baby is worried, constantly cries, and refuses to eat. Additional signs include fever up to 37.5 °C, lethargy, the presence of allergic reactions, and a strong odor from the child’s mouth. The disease spreads to the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract and manifests itself in the genital area. The plaque may take on a yellow or brown tint.
Symptoms
The symptoms of thrush cannot always be identified the first time. Parents often confuse it with the usual plaque that occurs after feeding a child artificial milk formula. The presence of thrush can be determined by specific signs:
- the plaque has a cheesy character and is difficult to remove from the mucous membranes;
- when it is removed, hyperemic areas of the mucosa are exposed , which can bleed;
- the appearance of plaque is accompanied by irritability and tearfulness of the child, since the affected areas are characterized by severe pain;
- the baby refuses to eat ;
- As inflammation grows, plaque gradually covers the entire surface of the oral cavity , forming a thin film. It then spreads to the lips and larynx;
- the disease is accompanied by stool disturbances and fever .
Treatment of candidiasis
The main method of treating the disease is the use of local antifungal and antibacterial agents, as well as antibiotics. Antimycotic (antifungal) drugs can not only eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but also destroy the fungus in the oral cavity, as well as in other organs and tissues. For this purpose, antibiotics of the polyene series (levorin, nystatin, etc.), as well as clotrimazole, econazole and other imidazoles, are used. Fluconazole, Diflucan, and Nizoral also have a pronounced antifungal effect.
A significant part of antibiotics has a number of side effects and has a negative impact on the immune system. Therefore, when treating children, antibiotics are used only in the most severe cases, as well as in cases where there is a risk of complications and generalization of the process. At the initial stages of the disease and with a mild course of the disease, preference is given to local remedies. We recommend using ASEPTA series rinses, which contain chlorhexidine and other active ingredients that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. To remove plaque, you can use special ASEPTA Baby wipes. The individually packaged finger wipe is made of hypoallergenic materials and allows you to carefully clean the mucous membranes without the risk of damaging them or causing additional infection. It is also recommended to regularly treat the oral cavity with Lugol or silver solution. This procedure must be repeated every three hours.
For the prevention and treatment of candidiasis in children, diet and oral hygiene are also of great importance. It is recommended to exclude or strictly limit the amount of food containing simple carbohydrates - these are, first of all, confectionery and flour products. Make sure your child brushes his teeth regularly - it is best to use a special toothpaste for this, for example - ASEPTA Baby, Kids, Teens. The components contained in these pastes help prevent caries and, as a result, reduce the infectious load on the child’s immunity.
Causes
There can be many causes of thrush in infants, but it is worth considering that all people on Earth are carriers of this type of fungus. If immunity drops, then the fungus begins to develop. All infants have weak immunity, and it takes some time for the child to get stronger, this is especially noticeable in premature babies.
In addition to the fact that a baby can become infected with thrush from his mother during childbirth, thrush can also lie in wait for him at home. Fungi love an acidic environment, and a newborn's regurgitation is an excellent breeding ground for them. Babies also like to put their hands and various objects in their mouths, which means that the cause of thrush can be improper hygiene and dirty objects.
Candida mushrooms also love sweets, and if the mother gives the baby a sweetened formula or water, they will begin to multiply. When breastfeeding, taking antibiotics by the mother also causes thrush in the baby.
Until about
six months, thrush on a baby's tongue is considered normal , so it needs to be looked after and monitored.
Do not forget that sometimes a more dangerous disease is hidden under the guise of thrush, so you should never self-medicate, but rather consult a pediatrician. The doctor will determine the cause of the disease and then prescribe proper treatment. Thrush on the tongue and mouth is treated by a pediatric dentist. Another cause of oral candidiasis is a condition after surgery, chronic indigestion, hypovitaminosis, anemia, pronounced rickets, dysbacteriosis (in this case, the intestinal microflora is disrupted, and its habitat changes, which contributes to the development of harmful bacteria). This also includes chronic infections, diabetes, improper metabolism and all other diseases that lead to a decline in the protective functions of the body of a small child.
Many mothers begin adding other foods and formulas that are known to contain sugar too early into their newborn's diet. The level of sugar in the baby’s body increases, and at the same time the acidity of the normal environment of the body changes, which contributes to the proliferation of fungi.
In some cases, the cause of infection is medical personnel or other people who are near the newborn. People can be carriers of any form of candidiasis, and infants quickly become infected with the disease. Harmful fungi can be transmitted through hands, ventilators, pacifiers, diapers and endotracheal tubes.
Help
A peculiarity of the treatment of thrush in infants is that most drugs and agents that are effective against Candida fungi cannot be used at this age. Therefore, therapy should be prescribed only by a doctor. This applies not only to local or general treatment, but also to the use of traditional methods.
Local therapy
Local therapy is the most preferred option for treating thrush in infancy. It does not have an overall negative effect on the body, but at the same time effectively fights the symptoms and cause of the disease. The following agents are mainly used for local treatment:
- A slightly diluted solution of potassium permanganate. Used to treat the baby’s oral cavity at least 5 times a day.
To do this, wrap the finger in a bandage and moisten it in the solution, after which the entire mucous membrane is treated, paying attention to the inflamed areas. Potassium permanganate has aseptic properties, which stops the growth of fungi. - Nystatin ointment , which has an antifungal effect. It is used to treat inflamed areas at least 2 times a day.
- Holisal. This gel is recommended for use to relieve pain in the mucous membrane; in addition, it has an anti-inflammatory effect. After application, the drug begins to act within 2 minutes. Most often it is used to facilitate the feeding process.
- Aqueous solution of 1% tannin. It is used to disinfect mucous membranes by applying to the affected area.
For infants, the solution should not be used for more than 5 days. After each treatment, it is necessary to apply iodinol, gentian violet or lugol to the mucous membrane. The treatment is repeated every 3 hours. - A suspension of levorin with an antifungal effect. It is prepared independently by crushing the tablet into 100 thousand units. and fill it with 5 ml of boiled water. The entire oral cavity is treated with the suspension every 6 hours. This remedy can be replaced with a suspension of pimafucin.
- Canesten in the form of a solution. It has pronounced antifungal activity. Used to treat mucous membranes no more than 3 times a day.
General therapy
As a rule, general therapy in infancy is prescribed only for advanced thrush or its chronic form, when local drugs have not had the desired effect. The following antifungal drugs can be used as general treatment in this age period:
- Fluconazole or its derivatives: diflazone, diflucan. In case of pronounced symptoms, a single dose is prescribed on the first day in a dosage calculated at 6 mg of the drug per 1 kg of the child’s weight.
In the following days, the dosage is reduced by half. To facilitate the administration of the product, it is mixed with milk or water. On average, the treatment period is from 3 to 5 days. - Amphotericin B. Available in powder form, from which a suspension is prepared.
Indicated for the treatment of children from one year old, but under the supervision of a doctor it can be used at a younger age. The dosage is determined depending on the child’s weight: per 1 kg there should be no more than 75 units of the drug. The drug is taken 1 time per day for 3 days. - Flucytosine. It is a powder used to prepare a suspension that can be used to treat thrush from the moment the child is born. The average daily dose is 100 mg per kg. The course of treatment lasts about 7 days.
What timing of baby teeth eruption is considered optimal? Data table.
How much does it cost to silver baby teeth? Here are approximate prices.
This article https://zubovv.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/d-zubi/prorezyivanie-z/kak-imenno-rastut.html contains photos that show how molars grow in children.
Folk recipes
To alleviate the symptoms of the disease, traditional methods of treatment are also used. But before using them, you must definitely consult a specialist. The most popular means are:
- solution of baking soda , which is prepared as follows: dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled water at room temperature. The resulting mixture is used to treat the inflamed mucous membrane 5 times a day;
- a decoction of a mixture of medicinal plants : oak bark, calendula, chamomile, sage.
A tablespoon of each plant is poured with a glass of boiling water and allowed to cool. When treating the mouth, it is necessary to use a small amount of liquid to prevent its ingestion, as these plants can cause allergies; - paste made from raspberry juice and honey. To prepare it, you need to take both components in equal volumes and boil 3 times. The cooled mixture is applied to the areas of inflammation.
Despite the fact that this recipe has become widespread, doctors do not recommend using it, since raspberry juice contains acid, which leads to additional irritation of the mucous membrane.In addition, honey is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria, the proliferation of which will only worsen the overall clinical picture.
Diagnosis of thrush
Oral candidiasis is diagnosed based on clinical findings, and additional mycological testing usually does not need to be performed. The positive effect of local specific therapy confirms the correctness of the diagnosis.
A complete diagnosis of candidal lesions is based on data from the clinical picture, microscopic and cultural studies, and serological reactions.
During a microscopic examination, scrapings are made from the mucous membranes and the material is examined under a microscope. This method allows you to identify yeast-like cells and filaments of mycelium of Candida fungi.
During a bacteriological examination, a culture is performed to determine the number of colonies of Candida fungi, the type of Candida fungus and its susceptibility to antifungal drugs. To do this, fungal colonies grown on a nutrient medium are treated with various antifungal drugs and see which drug is more effective.
Sometimes the reason for ineffective treatment of candidiasis may be the insensitivity of the fungal species to treatment with certain drugs. In this case, such a study must be carried out.
In a serological test (a test in which antibodies are tested in human serum), the most reliable test is the complement fixation reaction (CFR) with yeast antigens. The study detects antibodies to Candida fungi. In most patients, RSC is positive even with a small amount of antibodies.
Advertising
Clinical treatment
The success of treatment of candidal stomatitis in children can only be said if all sources of infection have been completely eliminated. When the cause of oral disease is the use of antibiotics, in parallel with general treatment, a course of antifungal therapy may be prescribed.
The principle of treating candidal stomatitis in children comes down to creating an alkaline environment in the oral cavity - it is this pH value that is detrimental to fungi. In addition, in an alkaline environment, most pathological microorganisms die, including those that cause carious tooth decay.
The child’s oral cavity can be treated with a solution of baking soda (the optimal concentration will be determined by the attending physician). The procedure for treating candidal stomatitis in children is quite simple: a gauze swab soaked in a solution is used to treat the oral mucosa of the gums and cheeks.
In severe cases, your dentist may prescribe oral medications.
The Doka-Dent dental clinic provides quick and safe diagnostics for effective treatment of stomatitis in infants and older children. Branches in Moscow are located at two addresses:
- Teply Stan district, Leninsky Prospekt, building 131, 1st and 2nd floor. One minute from Troparevo metro station in a building located between Leninsky Prospekt and Academician Bakulev Street.
- Tverskoy district, 1st Tverskaya-Yamskaya, building 27, 2nd floor. Three minutes from any exit from Belorusskaya station in a building located between the first Tverskaya-Yamskaya and the first Brestskaya streets.
Specialists from both clinics conduct examinations free of charge and help urgently prevent the development of complications and the spread of the disease!
Treatment
Fungal diseases in children can be treated by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of oral thrush, then therapy can also be carried out by a dentist.
The diagnosis of candidiasis is determined in most cases based on an examination of the oral cavity performed by a specialist. If there is any doubt, the doctor refers the patient for additional examinations. More often, to confirm the disease, a laboratory test is used to test a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children requires an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe cases, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local agents and compliance with preventive recommendations.
Possible deviations
All infectious diseases in children tend to quickly spread to other organs and systems. Girls, even in infancy, can develop vaginal candidiasis. Vulvovaginitis is dangerous because in girls, who at this age have extremely delicate mucous membranes, there may be fusion of the vagina or labia. This problem can only be solved surgically. That is why the mother should regularly check the condition of the child’s genitals: for redness and discharge. In addition, against the background of thrush, other, much more serious and dangerous conditions can often develop - generalization of the process and the development of sepsis (an infectious disease caused by the spread of bacterial or fungal flora from the source of infection into the blood, lymphatic tract, and from them into all tissues and organs). Therefore, a serious approach to prevention, early detection, effectiveness and timely treatment of thrush is necessary. The process may be complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection, spreading to the gastrointestinal tract.
With insufficient treatment, oral candidiasis can take a chronic, relapsing course. The child may begin to refuse to eat, sleep is disturbed, and the baby becomes irritable. Changes occur in the protective function of the child’s body, allergic reactions develop, and a predisposition to the development of various diseases, such as bronchial asthma, is formed.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Most often, candidiasis occurs in newborns and preschool children.
The older the child, the less often the disease is diagnosed. The favorite place for thrush to appear is the oral mucosa. A cheesy coating appears on the gums, palate, and inside the cheeks, and the baby feels pain and itching when eating. Along with these symptoms, candidiasis in children is also characterized by other signs:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- ulcers that open after removing the cheesy plaque;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- white coating on the tongue.
The child does not eat well and is often capricious, since any touch to the mucous membrane causes pain.
In advanced cases, bleeding wounds open at the site of the removed plaque. There is another common form of candidiasis - fungal tonsillitis. It develops as a result of improper treatment of protracted sore throat. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are a cheesy coating on the tonsils and a burning sensation in the throat.
When the skin is infected with fungi, dense spots, redness, and blisters appear on it. In adolescents, thrush often affects the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and the disease is more typical for girls. Vaginal discharge becomes white and thick. In boys, the head of the genital organ turns red, and a discharge similar to sour cream appears in the area of the urethra. Cystitis and urethritis may develop.
If fungi infect the digestive tract, the child begins to suffer from colic, and food is difficult to digest. The baby suffers from constipation and pain in the lower abdomen. If fungi colonize the respiratory organs, the child often suffers from bronchitis, pneumonia, and ARVI. If internal organs are damaged, treatment should begin immediately, in consultation with a pediatrician.
To prevent your baby from getting thrush
To prevent thrush from reaching the baby’s mucous membranes, special precautions must be taken:
- Regularly care for your child’s mucous membranes, monitor their condition when the baby is sick, and especially when he suffers from infectious diseases;
- If your child is prescribed antibacterial drugs, be sure to remember to use special means to protect the microflora;
- If candidiasis occurs during pregnancy in an expectant mother, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment. In addition, on the eve of birth, maternity hospitals carry out special prophylaxis for newborns with an increased risk of candidiasis. Thrush is especially susceptible to infants whose mothers suffer from chronic candidiasis and those who have foci of infection already in the immediate vicinity of birth. Mothers with inflammatory gynecological diseases or difficult childbirth can also transmit the risk of fungal infection to the newborn.
Forecast
The prognosis for candidal stomatitis is favorable; with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, complications rarely occur.
Severe consequences of the disease can occur in children with weakened immunity, chronic diseases of the endocrine and digestive systems. In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease becomes chronic, which is fraught with frequent relapses even with the slightest hypothermia.
Complications
The main complication is the spread of candidiasis to other parts of the body and organs, as well as the transition of acute thrush to chronic. Thrush from the oral cavity can spread deep into the throat and internal organs.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
A pediatrician usually has no problems diagnosing thrush on the oral mucosa.
This is a common disease with characteristic symptoms, so an experienced specialist can easily identify it. In particularly difficult cases, when diagnosing a sore throat, sputum analysis may be required to identify the pathogen. The situation is more complicated with the diagnosis of candidiasis on the genital mucosa. In this case, you will have to take a smear for microflora, which will show the presence of inflammation and help identify the causative pathogen.
Thrush on internal organs is even more difficult to detect: external symptoms may be absent. Blood, urine, and stool tests may be required to detect mycosis.
Features of treatment of children, depending on age
When choosing medications, be sure to consider the child’s age and weight and the severity of oral candidiasis.
How to treat oral candidiasis in children:
| Age | Effective and safe drugs |
| Newborns | Candida solution. |
| From 6 months to a year | Treat problem areas with Fucis DT solution. Dosage – 3 mg/kg. Dilute the required amount with water. In severe cases of the disease - Diflucan and Fluconazole tablets. |
| Since the year | For treating inflamed areas - Miramistin, Lugol, nystatin ointment, Triderm ointment (from 2 years), Pimafucort (from 1 year). For rinsing - a solution of saline solution and Nystatin tablets. Antihistamines for severe itching - Erius, Fenistil. Additionally - B vitamins, calcium gluconate, Ferrum-Lek. |
| 5 years and older | Vfend is an effective antifungal agent, but can be used to treat children over 5 years of age. Sprays and solutions with antiseptic action - Stomatidin, Stopangin. If complications are detected, use Nystatin. The dosage is calculated by the doctor. |
Disease prevention
To get rid of candidiasis completely, you need to adhere to a number of simple preventive measures. Among them:
- compliance with basic hygiene rules: wash your hands thoroughly, care for the skin and mucous membranes of the child;
- maintaining an optimal microclimate in the apartment;
- strengthening the child's immunity.
Thrush in a baby is a serious disease, the recurrence of which can only be avoided by timely consultation with a doctor. It is prohibited to independently treat childhood candidiasis, without undergoing the necessary examinations, based on knowledge obtained from newspaper (magazine) articles.
Causes
The cause of thrush is a fungus of the Candida . It is found in the body of every person and is activated when immune functions decrease . Since infants’ immunity is not yet fully formed, the fungus, when it enters their body, quickly begins to multiply, leading to the appearance of thrush.
There are several options for infecting a baby:
- during childbirth , when the child becomes infected with urogenital candidiasis, passing through the birth canal;
- by airborne droplets.
There are several factors that provoke the development of the disease:
- dysbacteriosis;
- prescribing antibiotics to a child;
- oral acidosis;
- acute respiratory infection;
- allergy;
- frequent regurgitation;
- regular failure to comply with hygiene rules by the mother : licking the pacifier, using unsterilized bottles, etc.