Every person experiences tooth extraction sooner or later. The first experience was with baby teeth, but, as a rule, no problems arise with them, and they fall out safely even without medical assistance. But with permanent teeth the situation is different. Due to their complex root system, it is sometimes very difficult to remove them, and various additional techniques have to be used. Fortunately, modern dentistry has a whole range of modern methods that are low-traumatic and allow you to cope with even the most complex cases.
What is the tooth extraction procedure?
Removal or extraction is a dental surgical operation during which a tooth is removed from the alveolus of the jaw in whole or in part. In the first case, the crown and root part are removed, in the second, resection or hemisection is performed while preserving the dental unit.
- Complete removal - removal of the crown and roots after separation of the soft tissues and rupture of the ligaments. It is indicated in cases of loosening, significant tooth decay, jaw fractures, or the need for orthodontic (for example, braces) or orthopedic treatment.
- Resection is the excision of the apex of the affected root; it is performed when a granuloma or cyst is detected on it. Access is carried out microsurgically through the soft tissue and jaw bone in the projection of the inflamed area or neoplasm.
- Hemisection is the amputation of one of the roots of multi-rooted (chewing) teeth along with the adjacent part of the crown. It is used for inflammatory processes, the impossibility of tooth-preserving treatment, pathological features or root fractures.
Complete tooth extraction
Does it hurt to remove?
A typical mistake made by patients before tooth extraction is the desire to start the procedure faster in order to “get over it” faster. In this case, the anesthesia does not have time to completely dissipate through the tissues and the patient will face a painful procedure. Therefore, you need to wait a certain time, which is suggested by the dentist.
Stress factors can also affect pain during surgery. During the effect of anesthesia, you need to remain as calm as possible, which will allow you to carry out the procedure quickly and with the least risk.
When does a tooth need to be removed?
Removing a wisdom tooth or any other tooth is a last resort measure, used only when it is not possible or advisable to preserve the dental unit. In this case, extraction can be carried out either urgently, on the day of treatment, or delayed - according to an individual schedule.
Indications for emergency removal
It is urgent to remove a tooth in the following cases:
- extensive carious lesions, impossibility or inappropriateness of caries treatment;
- inflammatory diseases of periodontal tissues, odontogenic sinusitis;
- pathological processes accompanied by acute pain, fraught with serious complications;
- injuries to the teeth and jaw (fractures).
Indications for the planned procedure
Removal is delayed if:
- teeth become loose due to weakening of the ligaments and periodontitis;
- there are supernumerary, impacted (unerupted) or dystopic (severely displaced) dental units;
- orthodontic treatment was prescribed to correct the bite (braces);
- the tooth interferes with prosthetics, including implantation;
- The baby tooth prevents the eruption of the molar tooth.
Root removal
How is the root of a tooth removed if the tooth is completely destroyed? Despite this situation, extraction is not always recommended. If, after diagnosis, the doctor determines that the root can be used for an inlay, then the tooth is restored with a crown. But if there is pain, an unpleasant smell and taste, or swelling has developed, then dental care is required urgently. In this case, the question of whether to remove the roots of the teeth is decided in favor of the operation, since the neglected condition can also lead to the loss of neighboring elements.
Regardless of the chosen technique, pain relief and X-ray control are required after removal. This allows you to make sure that there are no root fragments in the cavity, since it is often loose and can crumble under slight pressure from the forceps.
Contraindications
Even if a wisdom tooth (or another) hurts, removal may be contraindicated. Contraindications are divided into absolute (complete prohibition) and relative, when the operation can be performed under certain conditions. The first include blood diseases accompanied by reduced blood clotting (hemophilia, for example), oncological processes in the jaw area, as well as a recent history of a heart attack or stroke.
Relative contraindications include any acute conditions and pathological processes in the body (extraction is allowed after the exacerbation has stopped). The list includes:
- renal failure;
- cardiovascular pathologies (hypertension, arrhythmia, angina pectoris);
- infectious inflammation of any localization;
- stomatitis;
- blood diseases (agranulocytosis, leukemia);
- radiation sickness;
- circulatory disorders;
- cancer at the stage of therapy.
There are additional restrictions for women. Thus, it is not recommended to remove teeth during menstruation (due to decreased blood clotting), as well as in the first and last trimesters of pregnancy.
Existing indications for surgery
With a radical method of solving dental problems, the tissues of the oral cavity are inevitably injured. Due to damage to nerves and blood vessels, the patient experiences moderate pain, the injured area turns red and swells.
To minimize the consequences of removal and eliminate possible complications, the patient needs to have a strong immune system. The procedure is contraindicated for physically weakened people and those in whose body pathological processes are detected.
That is why in a number of situations surgery under a certain set of circumstances is excluded.
All indications should be divided into two subgroups:
- events in which surgical intervention must be performed urgently;
- when the extraction can be scheduled for a specific time, eliminating rush.
Immediate measures
When figuring out “when and why it is necessary to remove a tooth and in what cases this should not be done,” it is important to know that urgent removal is carried out in the presence of an inflammatory process. When inflammation has already led to the appearance of a tumor. Such complications may include granuloma, cyst, phlegmon, abscess, etc. In addition, emergency surgery is performed in case of injury to dental tissue or a fracture of the crown, which leads to the development of neuritis and other damage.
Pulpitis or periodontitis are not indications for mandatory tearing out. Sometimes, with these pathologies, an element of the series can be preserved. This largely depends on the size of the affected area and the individual characteristics of the patient. However, when there is a risk of spreading infection, radical action is inevitable.
Only timely elimination of the source of infectious agents can protect a person from serious consequences in the form of many dangerous diseases.
In what case is it necessary to extract a tooth as planned?
If there is no obvious danger to the body, but damage to dental tissues is 70% or more, pathologies are identified in the root zone and pulp, surgical intervention is planned for a certain time. Typically, the removal procedure is prescribed for advanced periodontitis or degree 3-4 mobility of elements. Sometimes they resort to pulling out before installing braces. Eliminating one or more units frees up space for subsequent movement during leveling.
Third molars are found in many people and are rudiments that have no functional significance. Often their growth occurs in the wrong direction, they do not fully erupt and contribute to the curvature of neighboring elements. This should be kept in mind when asking the question: “is it necessary to remove a wisdom tooth?” The consequences of the formation of molars are naturally inflammatory processes and the appearance of caries. Due to possible serious complications, figure eights are most often pulled out at the first alarming manifestations.
Planned indications also include cases when the patient has excess elements or unformed parts in the oral cavity.
It is up to the dentist to decide whether to perform surgery or not. Only he is able to correctly assess the condition of the patient and his mouth. Dentika specialists consider the clinical picture as a whole, take into account the likely consequences and make a decision. If it is impossible to avoid surgery, they plan to perform a removal procedure.
The essence and types of tooth extraction surgery
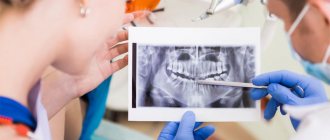
Both emergency and planned removal of a wisdom tooth (as well as any other) is performed after diagnosis. In order to determine the shape and location of the roots and identify neoplasms, an x-ray is prescribed. The information obtained allows the doctors of the Yulistom clinic to perform an operation of any complexity as efficiently and painlessly as possible, and also completely eliminate the risk of complications.
Pain relief before surgery
The extraction can be simple or complex, based on which the dentist chooses the appropriate type of anesthesia. In the first case, complex manipulations are not required, so local anesthesia is performed using the application or infiltration method. In the second, two options are possible: local conduction or intraosseous anesthesia with potent drugs; general anesthesia is also possible. The latter is contraindicated if the patient is diagnosed with:
- exacerbation of respiratory system diseases;
- acute renal failure;
- diabetes;
- stage of decompensation of pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- hemophilia;
- colds.
General anesthesia is also not done on a full stomach. Indications for this type of anesthesia when removing wisdom teeth are an uncontrollable fear of pain, as well as an allergy to topical medications and a strong gag reflex.
Simple tooth extraction
This term refers to extraction that does not require the use of complex instruments or additional manipulations. This method removes teeth with one straight root, a strong crown, as well as dental units that are mobile due to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus.
Dentists distinguish four degrees of mobility, determined by its intensity and direction:
- The first is that the tooth can be rocked back and forth when the forceps are applied.
- The second is that the medial-distal direction (in different directions) is added to the vestibulo-oral direction of movement.
- Third, the crown and root part additionally move freely up and down.
- Fourth, the tooth not only sways, but also partially rotates around its own axis.
Indications for extraction are grades 3 and 4. In such a situation, chewing food becomes difficult, and moving roots can injure soft tissues and provoke an inflammatory process.
Simple removal is performed after pain relief according to the following algorithm:
- peeling of the gum from the neck of the tooth is carried out - ligamentomy;
- the forceps are applied and securely fixed;
- the dental unit is dislocated by the method of luxation (swinging) or rotation (rotation around an axis);
- the tooth is removed from the alveolus;
- the hole is inspected and treated with an antiseptic;
- a gauze pad is applied.
The procedure, excluding the time required for pain relief, takes no more than 5 minutes.
Complex tooth extraction
It is carried out when the dental roots are curved or there are several of them, the crown is destroyed, completely or partially hidden under the mucosa. The technique is also used to remove lower and upper wisdom teeth, atypically located units, in the presence of cysts.
The operation is performed according to the same algorithm, but additional manipulations may be required. These include cutting the gums, bone tissue, sawing the tooth, and suturing the wound. For example, extraction of a tooth with crooked roots is done in the following order:
- anesthesia;
- sawing the crown with roots into several parts;
- extracting fragments;
- inspection, antiseptic treatment of the hole;
- suturing.
Complex tooth extraction
The duration of the operation depends on the extent of the surgical intervention, so it can range from a few minutes to 2-3 hours or longer.
Strengthening the root with copper
In people over 40, situations are quite common when a tooth simply breaks and only one root remains. The situation is usually further complicated by inflammation of the gums, because the tooth broke for a reason, but due to a lack of elements that ensure its strength. Usually in such cases the root is removed, but now doctors suggest trying the depophoresis procedure before removal.
Tooth depophoresis is a procedure for saturating the roots with copper. It reliably disinfects open canals and prevents their inflammation. Copper ions penetrate very deeply, into the most remote areas of the root and make them sterile. What is important is that the antiseptic effect of copper is not temporary. It allows you to protect the root from inflammation almost forever. Therefore, such a treated root, regardless of the degree of damage, can be used as a basis for building a new tooth or installing a crown.
Features of extraction of different types of teeth
Milk and permanent teeth are removed in different ways. The methods for extracting one or more dental units located on the upper or lower jaw also differ. The removal of wisdom teeth has its own characteristics due to pain, improper eruption, and atypical location.
Removal of baby teeth
Baby teeth can be removed at any age if it is not possible to save them. The manipulation is usually performed under local application anesthesia (painkillers are applied to the gums) or an injection is given. In cases where the child is not contactable due to age - up to one and a half years - or for other reasons, general anesthesia is given.
Indications for simple removal are:
- extensive carious lesions;
- inflammatory processes – periodontitis, pulpitis;
- the baby tooth prevents the eruption of the permanent one or does not fall out after it;
- pronounced dystopia.
The features are due to the fragility of the enamel and the weak expression of the neck. For extraction, a special tool with a loose grip is used; the extraction itself is performed in one movement.
Removal of upper teeth
Incisors and canines with one root are removed in a simple way, and multi-rooted molars and premolars are removed in a complex way. Removal of upper dental units has a number of the following features:
- teeth are removed from the alveoli more easily, since the structure of the jaw bone tissue is more porous;
- the roots are usually straight, which also makes manipulation easier;
- anesthesia acts faster and stronger;
- due to less trauma, healing after removal of a wisdom tooth (or another) is faster.
During the operation, the patient's head should be tilted back. This gives the doctor a full overview and access to the desired tooth.
Removal of lower teeth
By analogy with the upper ones, simple removal is used for single-rooted teeth of the lower jaw, and complex removal is used for chewing teeth. Due to anatomical features during the procedure, the doctor may encounter the following difficulties:
- often there are dental units with curved roots;
- increased bone density, making surgery difficult:
- low effectiveness of anesthesia (does not work for a long time, insufficient pain relief).
The patient's head should be tilted forward during removal. When removing front teeth, a straight head position is possible.
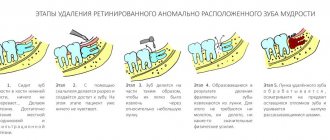
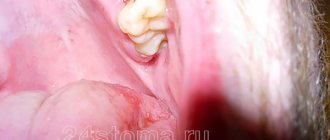
Wisdom tooth removal
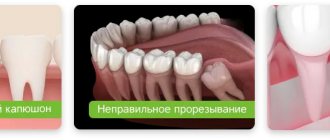
This is the name given to third molars, which usually erupt in humans between the ages of 15 and 25. They are considered a rudimentary formation, therefore they often grow with displacement, quickly collapse, injure the mucous membrane, have a non-physiological crown shape, and curved roots. These teeth may remain impacted (unerupted); in case of incomplete eruption, they form a fold in the gum (“hood”), which often becomes inflamed.
Removal of a wisdom tooth with a “hood”
The listed features of wisdom teeth are a recommendation for removal. Their extraction is a complex operation for the following reasons:
- difficult access due to location;
- the need to cut the gums due to retention or destruction of the crown;
- the need for longitudinal sawing of the tooth for its gradual extraction due to curved roots.
After wisdom teeth are removed, stitches are often needed. Also, sometimes a bandage soaked in medicine is placed in the hole; it must be changed regularly when visiting a doctor.
Removal of several teeth
Simultaneous extraction of a significant amount or all dental units is carried out according to indications - before prosthetics, for periodontal disease. The order of complex and simple extraction during the operation is determined by the dental surgeon individually for each patient. The exact number of teeth that can be removed in one visit also varies individually and is determined by a combination of several factors:
- type of anesthesia - under general anesthesia, a larger volume of surgical intervention is permissible, and local drugs have restrictions on the duration of action and dosage;
- client comfort - gradual removal is possible (first on one side, then on the other, after healing, which makes it easier to eat) or simultaneously, if it is more convenient for the patient;
- difficulty of removal - when it is necessary to saw a lot of teeth, cut a significant area of the gum surface, extraction is performed in several stages;
- general health, absence of specific contraindications (reduced blood clotting, vascular and heart diseases, hypertension) - after the removal of a wisdom tooth and others, an extensive wound surface is formed, which is fraught with bleeding and infectious inflammation.
Pulling out milk elements
The first incisors and canines fall out on their own with age. This happens during the period of change in the temporary bite. However, there are often cases when it is necessary to resort to extraction before the onset of natural loss. The need for it is determined by a dental specialist. Parents just have to listen to his recommendations and not put off solving the problem until “later.”
It is a big mistake to consider that various pathologies of milk samples are insignificant and that it is not necessary to take action to eliminate them. Yes, teeth will certainly fall out on their own over time, but pathological deviations may well be transferred to the developing permanent elements. As a result, they will erupt already sick.
Premature tearing is resorted to when inflammation occurs, which is provoked by an advanced form of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. In all these cases, it is no longer possible to restore the crown. If there is more than 1 year left before the bite changes, the installation of dentures is necessary. Otherwise, the series will inevitably become distorted, which is fraught with consequences.
The most difficult thing in working with children is dealing with fragile dental walls. The child should not be in pain during the procedure. It is very easy to crumble a thin coronal surface with large forceps, so instead they use a special smaller and lighter version.
Recommendations after tooth extraction
Immediately after the wisdom tooth is removed, the hole is treated with an antiseptic and a gauze swab is placed in it. It is necessary to stop bleeding and form a protective blood clot. You need to remove the tampon after 20-30 minutes.
What to do to prevent tooth pain after extraction
Eating is allowed no earlier than two hours after surgery, and chewing should be done carefully so that food particles do not damage the blood clot. You can drink drinks at a neutral temperature earlier, immediately after removing the gauze swab.
During the healing period of the postoperative wound, which lasts from 3 to 5 days, it is recommended to eat only pureed warm food. Rough foods, too hot or cold foods should be avoided. You need to chew on the side of the jaw that has not been operated on, so as not to destroy the blood clot.
After the wisdom tooth is removed and the anesthesia wears off, pain may occur. To relieve pain, it is recommended to take Ibuprofen, Ketorol, Nimesil. To prevent bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed, especially for periodontitis or after the extraction of a significant number of teeth. To avoid swelling, you can apply cold in the first hours.
It is not recommended to rinse your mouth in the first few days after surgery, so as not to damage the blood clot in the socket. Oral baths using Chlorhexidine and Miramistin are acceptable. You can brush your teeth after 24 hours, using a brush with soft bristles and not touching the operated area of the gum.
It is strictly forbidden to eat or smoke in the first 2 hours after the removal of a wisdom tooth or any other tooth. Over the next 3-5 days you cannot:
- eat food and drinks of contrasting temperatures;
- drinking alcohol;
- eat viscous, hard foods;
- touch the hole with your tongue;
- allow increased physical activity.
Contrary to popular belief, you should also not drink liquids through a straw during this period. This method of drinking drinks promotes the formation of a vacuum in the oral cavity, which leads to the destruction of the blood clot.
Extraction of problematic eights
Most often, molars initially have an incorrect position or are bent during the process of formation. When asking a specialist whether “it’s worth pulling out a tooth,” keep in mind that such elements must be eliminated. Without timely surgical intervention, they can interfere with the normal functioning of neighboring units, destroy their root system, lead to the curvature of an entire row of teeth and the development of harmful bacteria in the oral cavity.
Removal is a complex process. First of all, the doctor cuts the gum and moves it back. Then he carefully loosens and “turns” the figure eight using an elevator. Often, initially he has to saw the crown with a drill, which involves further extraction in parts. Only after all necessary actions have been completed, the dentist proceeds to suturing.
How does socket healing proceed after tooth extraction?
The healing process goes like this:
- After a wisdom tooth is removed, a socket filled with blood is formed. Within 2 hours, the blood clots and a blood clot is formed, which is necessary to protect the wound from infection. The postoperative socket at this time has a dark red color.
- In the first 2-3 days, the blood clot decreases in size, darkens and thickens. The process of formation of granulation tissue begins, which is necessary for the restoration of the gum mucosa.
- Within three days to a week, the clot lightens and becomes whitish. Young connective tissue fills the hole almost entirely. At the same time, pain and swelling completely disappear.
- On days 7-10, the thrombus resolves, and the hole with light granulation tissue decreases in size. The process of bone tissue formation begins, which completely fills the defect within six months.
- After 15 days, superficial healing is complete, the gums are covered with a pink mucous membrane.
Thus, the postoperative wound usually heals within 2 weeks. Recovery from a complex wisdom tooth extraction may take longer as the tissue is usually more damaged. The healing time is also influenced by the condition of the oral cavity, the presence of infectious diseases, individual characteristics of the body, and correct adherence to medical recommendations.
Stages of healing
Norm and pathology
Immediately after extraction, the patient does not feel anything, as the effect of the anesthetic continues. As the effect of the drug wears off, pain of moderate intensity appears. Normally, they completely disappear no later than three days.
After wisdom tooth removal, swelling of the gums is possible, especially if the soft tissues were significantly injured during the operation. Within three days, the swelling goes away without causing much discomfort.
The blood stops within half an hour, a blood clot forms, completely covering the hole, so there should be no bleeding during normal healing. However, if you touch a clot, slight bleeding may occur.
The listed phenomena are natural for the postoperative period and should not cause concern. Reasons for urgently contacting a doctor are:
- Intense pain that increases over time. If the gums hurt very much after wisdom tooth removal for more than three days, and analgesics do not help, an inflammatory process is likely.
- Persistent swelling of the gums and the development of swelling of the face on the operated side are also symptoms of inflammation.
- Bleeding that lasts several hours or re-opens after stopping indicates vascular damage.
- Elevated body temperature is a sign of infectious inflammation, which is fraught with serious complications.
- A deep empty hole covered with a yellow-gray coating with a bad odor indicates alveolitis, an inflammatory complication.
- Purulent discharge from a wound, especially in combination with pain and swelling, is a sign of tissue infection.
- Runny nose and nasal discharge are the result of perforation of the maxillary sinuses during surgery.
- Paresthesia - numbness of the cheeks, tongue, lips, after the anesthesia has worn off, indicates nerve damage.
Features of hygienic care after surgery
For patients undergoing surgery to remove one or more teeth, it is recommended:
- stop eating food for 2.5 hours;
- do not chew food on the side of the postoperative wound until it is completely healed;
- temporarily stop consuming too hot drinks and food;
- refrain from brushing for 1.5 days;
- give up active physical labor for 3 days.
If complications develop (the appearance of prolonged bleeding, inflammatory processes, purulent discharge, etc.), you must immediately contact specialists at a dental clinic and undergo a course of therapy according to the regimen they have developed.
How to avoid complications
Inflammatory processes in the postoperative period usually occur due to the fault of patients who do not follow several basic rules. The dentist will tell you what to do after removing a wisdom tooth or any other dental unit to prevent negative consequences. Standard recommendations are as follows:
- Do not touch the blood clot in the first three days so as not to damage it. This clot naturally reliably prevents infection from entering the wound.
- Follow the advice on nutrition and oral care - eat only approved foods, brush your teeth carefully.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, especially in case of periodontal disease or after removing a significant number of teeth.
Complications can also arise due to the fault of the dentist. In addition to infection of the wound with unsterile instruments, there is a risk of jaw fracture, damage to nearby teeth, and incomplete removal. Such situations can be avoided; you just need to choose a clinic with an impeccable reputation. Yulisty employs highly qualified dental surgeons, so the possibility of medical error is completely excluded.
We remove the problem, not the tooth
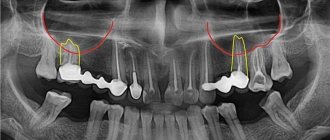
Very common problems are cysts or granulomas. They are a type of tumor that not only can be a source of pain, but also destroy bone tissue. Cysts become especially painful during a cold or after experiencing stress. It is then that the problem appears in all its glory on the X-ray.
The cause of the appearance of a cyst or granuloma can be an infection in the gum, most often due to careless tooth filling. The consequences of an untreated cyst can be anything. Since it is a source of infection, there is a high risk of infection entering the blood and spreading throughout the body. Such disorders are neurological in nature. Peri-, myo- and endocarditis may occur. Another common consequence is rheumatism of the joints. preventive cleaning and treatment should not be neglected
Previously, in order to clean out the cyst bubble, the tooth was actually removed. This makes it much easier to treat the gums and control the further course of the disease, but now, basically, three other, more progressive methods are offered.
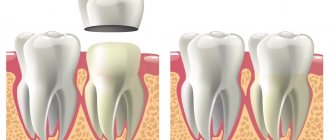
- Cystectomy. During this procedure, the doctor cuts out the cyst and the damaged part of the root. The resulting hole is cleaned and filled with special medications, which should promote the growth of new bone tissue. If everything goes according to plan, the hole will heal and infection will no longer accumulate in it. Full recovery usually takes at least three weeks.
- Hemisection. If one of the tooth roots can no longer be saved, it is removed along with the cyst. After this, the hole is cleaned, treated with disinfectants and closed with a crown. This manipulation is simpler, so the functionality of the tooth is restored faster.
- Laser dialysis. This procedure is not carried out in all clinics, but it is quite effective. The cyst is “killed” using a laser beam that is injected directly into it. This also disinfects the root itself, eliminating the need for additional procedures.
If the granuloma is small, you can try the same tooth depophoresis . In 2-3 procedures you can defeat the infection at the root. It will be practically painless, but you need to strictly follow the procedure and properly care for your oral cavity between them.
Tools used
If a simple elimination requires only two main tools - forceps and an elevator, then in the case of a complex elimination everything is a little different and much more auxiliary devices are required. The instruments are specially developed for dental surgery, which allows all manipulations to be performed without causing severe harm (the level of mechanical damage is minimized).
To extract a molar or premolar, forceps, a bur, an excavator or an elevator are used, and during surgery a scalpel, hammer, scissors, and chisel are used. Let's take a closer look at what the role is and in what situations each of the tools is used.
- forceps. They are used in situations where the coronal part has been preserved and the roots are located in such a way that they can be grasped with an instrument. The specialist sets the axis of the crown to align with the axis of the forceps. For each group of teeth, forceps of a certain shape are designed, having a working part - cheeks, handles, lock;
- elevator. It is used in relation to molars (particularly the eighth) and premolars in the upper jaw. If necessary, using this instrument, the dental surgeon loosens the tooth (or its remains) along with the root, after which it is dislocated with forceps and removed from the gums;
- excavator. According to the principle of operation, it is similar to an elevator; it is used for deep fractures of a molar or premolar. It has an angular working surface, making it easy to penetrate into the hole;
- bit. It is used to eliminate the outer wall of the alveolar process. It is often necessary in a situation where a tooth breaks off and it is not possible to get it out using an elevator or excavator;
- hammer. Its help is resorted to in cases where a tooth is removed using a chisel. The dentist places the instrument in the area between the root and the hole, and at this time his assistant, using a hammer, makes several blows to this area;
- scalpel. Often, complex removal requires making a small incision with minimal trauma. For this purpose, a scalpel is used;
- drill. A drill is usually used during separation, removal of multi-rooted teeth, or removal of bone tissue surrounding a molar or premolar. In such situations, the dental tissue is sawed and removed piece by piece. This is not a simple procedure; it requires sufficient qualifications of a specialist. It is more advisable to resort to it if the root canals have already been previously filled or when the last molar is growing incorrectly (in a horizontal position).
A-Medic dentistry practices complex tooth extraction in Moscow. Qualified specialists work here. For high-quality removal during surgical intervention, the above-described instruments are used. Additionally, the clinic provides all necessary manipulations and services: hemostatic sponge, anesthesia (conduction, infiltration, application), preparation, dressing (using Trichopolum or Alvogil), removal and application of sutures. To make an appointment, just call the numbers provided or fill out an application on the clinic’s official website, after which the administrator will contact you.