With a wide variety of offers from dental clinics about a full range of services, it is worth knowing which doctor can perform tooth extraction and visiting only such specialists.
Every person at any age needs dental treatment, and sooner or later it becomes necessary to have a tooth removed. Our price in Dolgoprudny for this type of service is optimal, taking into account the availability of many drugs for pain relief and the work of real professionals. Often, in search of a specialist who can perform this manipulation, patients end up with inexperienced doctors. This can lead to complications. And only then, having understood the issue, it turns out that not every dentist actually has the right to carry out such manipulations. Therefore, if it is necessary to remove a tooth, price should not be a fundamental factor in choosing a doctor; it is important to know who exactly you need to contact.
Specializations in dentistry
There are different areas in dentistry, but they are all united by one task - maintaining the health and proper functionality of the dental system. The basic area is therapeutic dentistry, but there are other highly specialized areas.
For example, the tasks of a dental therapist include primary diagnosis, treatment of teeth and gums without the need to use highly specialized skills. Most often this is the prevention and treatment of caries and pulpitis, gum inflammation or, for example, tongue diseases. Along with the therapist, other specialists also work on the health and beauty of our smile:
- periodontist – works with diseases of gum tissue, periodontal and periodontal tissues,
- orthodontist – helps to correct the correct bite and straighten teeth,
- orthopedist – restores damaged and missing teeth by using various prosthetic methods,
- hygienist – specializes in the prevention of dental diseases, carries out comprehensive oral hygiene with the removal of plaque, supra- and subgingival deposits,
- a surgeon, including an implant surgeon, performs complex operations on the mucous membrane and jaw bone, implants implants, etc.
There are different directions in dentistry
. Important! Separately, we can distinguish a pediatric dentist who specializes in the treatment of temporary baby teeth and diseases of the oral mucosa in children.
A dental surgeon is a doctor who removes teeth. However, if a simple extraction is required, a general practitioner can successfully cope with this task. Many people also confuse an orthodontist and an orthopedist, but these are two completely different specializations. As mentioned above, the first one works with anomalies of the dental system - it is he who supervises the correction using orthodontic plates, braces and other corrective systems. As for the orthopedist, he is engaged in the restoration of teeth using removable and non-removable prosthetic devices - starting with crowns and ending with the installation of complete dentures on the entire jaw, including implants.
So, the surgeon is the same doctor who pulls out teeth. To understand the issue in more detail, we will consider possible indications for extraction and features of the procedure.
Dentist-therapist
This doctor is needed by almost everyone who is preparing to correct their bite. The fact is that a mandatory requirement before treatment is the elimination of all foci of caries, even superficial ones, and they are often impossible to notice on their own. It is also necessary to treat the common fissure caries (those that form in the recesses of the chewing teeth). After treatment, you need to carry out ultrasonic cleaning to remove tartar and Air Flow cleaning to completely remove soft plaque and polish your teeth. After such preparation, maintaining hygiene with braces or aligners will be easier.
In what cases is tooth extraction prescribed?
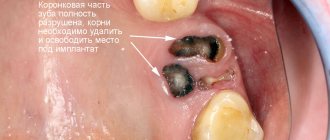
Such a radical measure is usually resorted to in cases where it is no longer possible to save the causal element. As part of the procedure, the doctor carefully removes the tooth along with the root. Moreover, it is important that this is done extremely carefully, with minimal trauma to the surrounding bone tissue and mucous membrane. Thus, the procedure is prescribed if the following indications exist:
- pronounced mobility with destruction of periodontal bonds as a result of the development of periodontitis, periodontitis or the formation of an extensive cystic formation,
- serious injury with root fracture,
- complete destruction of the crown with inflammation of the root,
- problematic eruption of eights (wisdom teeth),
- the need to correct the bite in case of severe crowding - in such a situation, it is sometimes necessary to remove one or more healthy elements in order to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the entire jaw apparatus.
Extraction may be prescribed for a severely damaged tooth.
Timely extraction saves from the uncontrolled spread of the inflammatory process to healthy mucosal tissue and neighboring teeth. To avoid the development of complications after the procedure, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. In the future, it will be possible to fill the gap in the series with the help of a bridge or prosthetics on an implant - the second option is more preferable.
Otolaryngologist
Cases where there is a direct connection between problems with the respiratory system and bite are not frequent, but sometimes a consultation with an ENT doctor is necessary. This is especially true for those who, before contacting an orthodontist, suffered from chronic ENT diseases with frequent exacerbations and impaired nasal breathing.
At the first appointment, the orthodontist collects information about the patient and asks about other diseases. A complete picture of your health condition will help you prescribe comprehensive treatment to achieve the best result and minimize the risk of regression.
How the procedure is performed - extraction options
First, the specialist must examine the oral cavity, select the appropriate anesthesia method and extraction method. In some cases, due to an acute inflammatory process, removal is postponed until the next appointment. In the meantime, the doctor prescribes the patient a course of antibiotics to relieve acute symptoms and normalize the condition.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. If a patient has a strong, overwhelming fear of dental treatment (dental phobia), deep sedation may be offered to relieve anxiety. In rare cases, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia, but recently experts are more often giving preference to deep sedation as a safer and no less effective alternative.
To extract a tooth from its socket, the doctor may use one of the following techniques:
- simple extraction: using special forceps, the surgeon grabs the crown and then carefully removes it along with the root. Incisors, canines and molars are first rotated, double-rooted molars are swung,
- complex – if the tooth needs to be extracted in parts or the remaining root must be removed. The doctor has to saw the crown and root system, cut out the root using different attachments for a drill, make incisions on the gum if the element is impacted,
- atypical - first, the specialist makes a trapezoidal incision on the surface of the gum and peels off a flap of the mucous membrane to open access to the alveolar socket. Next, he saws the crown and roots with a bur and then carefully pulls them out piece by piece. By the way, the same technique is relevant for cases of fracture of the root apex1.
For simple removal, the doctor uses special forceps.
After removing the tooth from the socket, the specialist carefully cleans the wound from small fragments, treats the tissue with antiseptics and places a sterile swab in the socket. If necessary, applies sutures or fixes the drainage system to ensure the outflow of purulent masses. Finally, the patient receives explanations on how to care for the socket after removal. You can read more about them in our special article.
Orthopedic surgeon
An orthopedic surgeon deals with all problems of the musculoskeletal system.
If your posture is poor, the lower jaw shifts and it “pulls” the bite along with it.
All muscles and ligaments in the body work harmoniously. If bite asymmetry occurs, compensation inevitably occurs in the cervical or shoulder region, hence muscle strain and poor circulation. Almost all orthodontic patients have some degree of scoliosis or stooping. Although it is almost impossible to completely correct this problem in adults, it can be compensated for, thereby supporting treatment. Often, treatment aimed at relieving muscle spasms helps progress in correcting the bite, in addition, an integrated approach reduces the risk of relapses in the future, after treatment is completed.
An orthopedic surgeon can prescribe treatment that will help relieve muscle tension and eliminate tension in the shoulder, thoracic, and lumbar spine. This could be massages, physical therapy or physiotherapy.
Features of complex extraction
First, the doctor conducts a visual examination and palpation, studies x-rays and uses them to assess the condition of the bone tissue and periodontal tissue. Only after a thorough examination of all aspects of the clinical picture can a specialist make a final verdict. Based on the same X-ray image, he determines the number of roots, the shape and depth of their occurrence, and assesses the complexity of the work ahead.
Further, the procedure in most cases is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the surgeon makes an incision on the mucosa to provide direct access to the cervical area,
- if it is necessary to separate the teeth, the doctor saws the crown and root system, after which he literally saws it out of the bone tissue in order to remove the tooth in parts,
- then he lowers special forceps to the very edge of the alveolus, clamps the instrument, fixes it and, carefully twisting or rocking the tooth, removes it from the socket,
- the flap of tissue is returned to its place and sutures are applied.
Complex tooth extraction is a full-fledged operation.
As mentioned above, the procedure can be performed both under local anesthesia and with additional deep sedation. And only in exceptional cases is the use of general anesthesia allowed.
Maxillofacial surgeon
This specialist is needed for those whose bite pathology requires surgery. Usually this is a pronounced mesial bite or a combination of several disorders, especially with a pathological narrowing of the jaw. The operation itself is only one of the stages of treatment; in preparation for it and after it, you still need to wear braces to stabilize the occlusion (closing of the teeth) and improve the aesthetics of the smile.
Surgical correction of the bite: the jaws are given the correct shape, but the teeth still need alignment
Where does he receive it?
You can get a free consultation, take an x-ray, and treat some diseases free of charge in public dental hospitals if you have a medical insurance policy. You must first make an appointment through the receptionist or nurse.
In private clinics, medical centers and offices, appointments and treatment by a dentist are paid. Prices for services vary greatly, on average the cost of a consultation is from 500–600 rubles, treatment – from 1.5–3 thousand rubles.
Experience, cost of appointment and treatment largely depends on the category of the dentist. Reviews on the website and forums will help you choose a good private clinic.
Table of dentist categories in ascending order
| Category | Experience, skills |
| Second category | At least 3 years of experience, good theoretical and practical training, knowledge of modern methods of treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of major dental diseases. |
| First category | Work and practice experience of at least 7 years, knowledge of related disciplines, participation in scientific and practical activities. |
| Highest category | More than 10 years of experience, high practical and theoretical training, knowledge of all modern methods of treating dental pathologies. |
If you consider your case to be unusual, it is recommended to choose a doctor of the highest category
Strengthening the root with copper
In people over 40, situations are quite common when a tooth simply breaks and only one root remains. The situation is usually further complicated by inflammation of the gums, because the tooth broke for a reason, but due to a lack of elements that ensure its strength. Usually in such cases the root is removed, but now doctors suggest trying the depophoresis procedure before removal.
Tooth depophoresis is a procedure for saturating the roots with copper. It reliably disinfects open canals and prevents their inflammation. Copper ions penetrate very deeply, into the most remote areas of the root and make them sterile. What is important is that the antiseptic effect of copper is not temporary. It allows you to protect the root from inflammation almost forever. Therefore, such a treated root, regardless of the degree of damage, can be used as a basis for building a new tooth or installing a crown.
Types of dental abscess
Pyogenic bacteria enter healthy gum tissue through the bloodstream or due to mechanical damage. An abscess appears in the area of the affected element. When the abscess matures, the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint, and a whitish spot or characteristic bubble appears. With its rupture, a fistula is formed in the periodontium, through which the contents flow out. This phenomenon does not lead to the disappearance of the problem, the inflammation remains. The pathology is indicated by the flow of pus from the gums when pressing on the affected area. There are several types of abscess:
- Desnevoy. The lesion is on the surface of the soft membrane and interdental papillae. The cause of infiltration is associated with the ingress of food debris and mechanical injuries. If detected early, it responds well to treatment.
- Periapical. A common type of pathology that develops as a result of untreated carious lesions or periodontitis. Infection of the dental root system leads to the accumulation of exudate in the upper part of the root. When immunity decreases, the periosteum of the unit and the mucous membrane are affected, a fistula is formed, purulent sacs appear above the gum, and pus is released.
- Periodontal. The infiltrate develops inside the gum tissue. Infected contents accumulate in the mucous membrane, forming a protrusion in the periodontal pocket. Due to the lack of a channel for fluid to flow out, damage occurs to the bone and soft tissue surrounding the diseased element. There is a high probability of developing periodontitis.
- Pericoronal. The pathological process is characteristic of erupting units. Bacteria and food debris fall under the “hood” of the mucous membrane. As a result, pus accumulates above the tooth, the gums swell and cause pain. The disease is dangerous due to complications: swelling of the neck, angina pectoris.
- Periodontal-endodontic. Infectious damage to the pulp and periodontal tissues occurs. There is a risk of periodontitis.
Flux is characterized by several stages of development, which have characteristic manifestations:
- Serous. Lightning current. The inside of the cheek and mucous membranes swell within a couple of days.
- Purulent. Continuous, debilitating, throbbing pain in the unit. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Hyperthermia.
- Diffuse. Swelling and soreness of the entire surface of the oral cavity, affecting the nose, lips, and outer cheeks.
- Chronic. Gradual progression over months or years. Long-term remissions are followed by relapses. As the swelling decreases, the inflamed areas remain firm.
Why does pus come out of the gums?
The pathological process is of infectious origin and develops when food particles enter the gum pocket and decay begins. Dead microbes and dead immune cells (exudate) gradually accumulate inside. An abscess indicates infection of deep tissues. The human body strives to protect itself and cleanse the affected area from the pathogen. When pathogens spread, blood circulation increases. As a result, immune cells are rapidly transported to the source of infection to detect and neutralize bacteria.
Then pus accumulates on the upper or lower gum and a purulent sac is formed. Gradually, the flux expands, reaches the periosteum, causing swelling, swelling of the gum tissue and the inside of the cheeks. The mucous membrane of the jaw becomes red and a fistula forms on it. A fistula is a kind of channel through which there is a copious flow of exudate from the source of infection to the outside.
Folk remedies
The effectiveness of treatment depends on proper diagnosis and strict adherence to medical prescriptions. Dentists at the Dentika clinic are able to correctly diagnose the problem and correctly select therapy. It is worth remembering that any disease is easily eliminated at the initial stage.
If it is not possible to immediately visit a doctor for dental diseases, the use of traditional medicine methods is allowed.
Pus under a tooth or above the gum can be an independent disease or signal the development of periodontitis or gingivitis. These are serious pathologies that do not go away on their own.
The use of antiseptic rinses helps to temporarily relieve inflammation:
- You can dissolve a teaspoon of soda, table salt or two furatsilin tablets in 200 ml of water.
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution and warm water in a 50/50 ratio.
- Chamomile decoction. Two tablespoons of the plant are poured with boiling water and allowed to brew.
- Miramistin or chlorhexidine biglucanate solution.
The key manifestation of the disease is pain. Taking analgesics will help ease the wait for a medical consultation.
For applications, use an aloe leaf cut in half.