938
The prototype of combined crowns can be considered a design on platinum foil, which was made by the American dentist Charles Land in 1888.
True, the platinum frame was not rigid enough, and the lining was fragile, since at that time they did not yet know how to properly fire dental ceramics.
It was not until 1903 that Land succeeded in producing a relatively strong combination crown.
Product characteristics
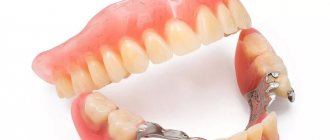
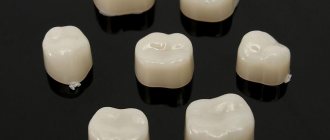
Combined crowns consist of a thin metal frame (MC, base) and a covering material that is close in texture and color to natural teeth. Most often, this material is dental ceramics; less commonly, plastic or composite is used.
MK is usually made of cobalt-chromium and nickel-chromium alloy or stainless steel. Two technologies are used to shape the metal into a crown - stamping and casting. The minimum thickness of stamped products is 0.3 mm. Cast frames, for the manufacture of which less durable nickel-chrome or gold alloys are used, have a thickness of 0.4-0.5 mm.
The cheapest frames are made from industrially manufactured dental sockets from stainless steel. They take a standard sleeve that is closest in size to the tooth stump, stretch it additionally to obtain a more accurate diameter, and forge it on a metal die made from an impression from the prepared tooth.
To make a cast frame, an impression is also taken from the tooth, but not a metal die for forging is made from it, but a wax model, which is used to cast a nickel-chrome, gold-platinum or other frame.
The optimal MC should have an internal diameter 50-100 µm larger than the diameter of the tooth stump. In this case, the highest strength of the connection between the crown and the tooth is ensured using cement. Only cast frames provide such accuracy, so they are considered preferable to stamped ones.
The technology for manufacturing frames for cladding with ceramics or composites does not differ from the standard one. But for plastic, which has only a mechanical connection with the MC, until recently it was necessary to create special retention points in the form of small balls or granules (pearls) fixed to the base, or jagged windows.
But now adhesive liquids have been developed that provide a strong bond between the metal frame and the plastic cladding.
Dental ceramics, plastic or composite, a hybrid material consisting of ceramics and organic resins, are used as veneering materials. Ceramic is considered the best facing material.
The thickness of the veneer varies depending on its material and location on the crown. For example, in a metal-ceramic microprosthesis it is 1.3-1.4 mm in the central part, 0.8-1 mm in the cervical part, and 1.3-1.4 mm in the cutting part. In metal-plastic models, the thickness of the polymer layer is 1.0-1.5 mm.
To prevent the metal from being visible through the ceramics, it is coated with colorless white varnish or yellow titanium nitride.
Gold alloys also have low translucency. In addition, they are biocompatible with human tissues. This explains the fact that gold and its alloys continue to be in demand in dentistry, despite the emergence of many new materials.
Since the main function of the cladding is the aesthetic side, it is not necessary to apply it to all surfaces of the frame; you can get by with just the vestibular one.
Purpose of a metal-free crown and its characteristics.
Come here to take a closer look at all types of coated metal crowns.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/mozhno-li-stavit-na-zhivoy-zub.html we will tell you whether it is possible to put a crown on a living tooth.
How are dentures made?
- Therapeutic treatment of the tooth is carried out after its preparation.
- An impression of both jaws is made using plaster or alginate. Plaster impressions are gradually becoming a thing of the past as obsolete; the use of alginate is preferable.
After this, the dentist begins to work closely in the dental laboratory.
- He is given a model of the dentition of both jaws cast in plaster, on which, in case of problems with the bite, the central relationship for its correction is determined.
- Plaster of Paris is placed in the occluder.
- A plaster stamp is cut out of the wax model that is then created, and then a metal one is made according to its sample.
- The sleeve-blank is selected as precisely as possible according to the size of the cast die.
The fact is that the sleeves are produced according to average parameters, and in order to fit the prepared stamp exactly to the tooth stump, there are two ways: choose the exact size or reduce it from the available ones. The sleeve is put on the second die and the fitting work begins, which includes thermal and mechanical effects on the workpiece.
The final check of the finished crown is done in the clinic, where, after fitting, they look at how tightly it fits (without taking into account the future cement layer) to the neck of the tooth. Defects are identified, then the outer surface is ground. If the patient expresses a desire, titanium nitride will be sprayed onto the steel surface.
At the last stage, the finished crown is dried using alcohol treatment, the cement is diluted and injected inside, and it is forcefully pressed onto the tooth stump. To do this, you just need to clench your jaw tightly. The squeezed out excess cement is removed.
Indications and restrictions
Combined crowns are indicated for all defects in which conventional metal structures are also used.
But only for those teeth that are visible when talking and smiling. These are primarily the frontal maxillary teeth and upper premolars.
Of course, at the patient’s request, any tooth can be covered with a combined crown. But based on financial and functional feasibility, there is no need to cover molars with veneered products. Moreover, the supporting teeth need to be ground down to a greater amount than for purely metal microprostheses, which is undesirable for obvious reasons.
Defects for which combined microprostheses are indicated:
- Severe destruction of the supragingival part of the tooth, which cannot be eliminated by simpler, more gentle methods - filling or inlays. In general, it is believed that if the visible part of the tooth is damaged by 1/3, a filling should be used, from 1/3 to 2/3 - inlays, and more than 2/3 - crowns.
- Reduction in the height of the lower third of the face due to tooth wear.
- Irreversible change in enamel color.
- Mobility of teeth. Crowns are an integral part of splinting devices.
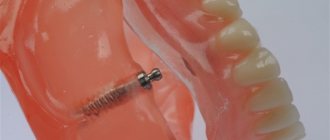
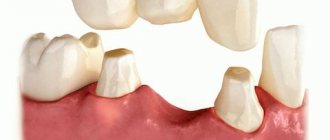
- Edentia replaced by bridges. The veneered crown in this case is part of the MP.
- During dental implantation.
- Other clinical situations include the need to place medication in a tooth, as a support for orthodontic devices, replacing old microprostheses, etc.
Contraindications
The main contraindication to use is the lack of thickness of the tooth wall separating the pulp from the outer surface after grinding. It should not be less than 1 mm due to the risk of pulp burns.
The most serious contraindications:
- Lower front teeth - due to too thin layer of dentin.
- Deep bite with retrusion (backward deviation) of the upper incisors. The small distance between the oral surface of the upper incisors and the vestibular surface of the lower ones does not leave room for installation of the structure.
- Age up to 16-18 years due to immature teeth and close proximity of the pulp chambers to the outer surfaces.
- Bruxism (creates a risk of microprosthesis fracture).
In what cases is the use of a combined crown recommended?
- in case of damage and destruction of the natural crown as a result of tooth damage by caries, the presence of pathological abrasion and wedge-shaped defects, which makes it impossible to use fillings, inlays and porcelain crowns;
- the presence of various anomalies in the shape and color of the tooth;
- the need to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth;
- the presence of deep overlap of the front teeth or a deep bite, which makes it impossible to separate the antagonizing teeth.
All the pros and cons
Combined crowns are the most cost-effective solution to the problem of aesthetics and functionality of individual teeth and their groups. The best option in terms of strength and appearance of teeth are metal-free zirconium oxide models. But they are expensive.
A good option is all-ceramic structures, but only for the front teeth. Due to their lack of strength, it is not advisable to install them on chewing teeth. And they again cost more than the combined ones.
As a result, it turns out that the most economical way to restore the functions and aesthetics of teeth is to install combined products.
The specific advantages and disadvantages of veneered microprostheses depend on the type of veneer and are discussed below.
Advantages
Due to the metal base, combined crowns are stronger than real teeth. With proper care, their service life is 15 years
.
Additional advantages:
- They do not lose their shape or shade.
- Visually close to natural enamel. Therefore, they are invisible against the background of neighboring molars when laughing or talking.
- Reliable protection and functionality - you can safely chew your usual food.
- The risk of allergies is minimal (traditionally, up to 2% of people are sensitive to alloys).
When installed correctly, it adheres to the gum and tooth, protecting the units
Varieties
There are three main types of combined crowns - metal-ceramic, metal-plastic and metal-composite.
The frames are made using a similar technology, the difference lies in the cladding - its material, application methods, type of hardening, and the nature of the connection with the base.
Metal-plastic
Metal-plastic models are microprostheses in which the metal base is lined with polymethacrylate. The facing material is available in different forms, requiring different technologies for applying it to the base.
The peculiarity of plastic as a facing material is that it does not form a chemical bond with the metal. Today the market offers special liquids that increase the adhesion force of plastic to metal. This eliminates the need for mechanical retention.
In general, the technology for manufacturing metal-plastic crowns is as follows. After casting or stamping, the metal frame is sandblasted and degreased.
The plastic crown is modeled with wax on a plaster model of the tooth made from an impression. After packing the model into the molding mass, the wax is removed by heating and the resulting cavity is filled with plastic under pressure.
Other methods of applying plastic cladding are also used. In particular, layer-by-layer application of the polymer mass with a brush or spatula with polymerization of each layer.
The method of applying the material depends on its original shape. Most often, polymer cladding is supplied in the form of a powder (polymethyl methacrylate in various colors) and liquid (methyl methacrylate with additives), which are mixed in certain proportions before use.
According to the curing method, materials of hot and cold polymerization are distinguished. Hot involves placing the cuvette after pressing in boiling water and keeping it there for some time. After polymerization is completed, the cuvette is cooled in cold water.
When using a cold polymerized material, no heating is required. Curing occurs at room or oral temperature.
The main advantage of metal-plastic structures is their relatively low cost with acceptable aesthetics. Disadvantages: low strength, low resistance to abrasion and staining, short service life.
Let's consider the reasons for the appearance of blood from under the crown of a tooth and ways to eliminate the symptom.
In this publication, we will find out what to do if a ceramic chip appears on the crown.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/dostoinstva-farforovyih.html we will find out whether the price of a porcelain crown for the front teeth corresponds to its quality.
Metal-ceramic
As the name implies, the facing material in metal-ceramic models is glass ceramics. The initial form of the material is ceramic powder diluted in liquid.
The creamy mass is applied to the frame in layers, placing it in a firing oven after each layer is applied - first opaque, then dentin and finally enamel.
After sintering and processing are completed, the metal-ceramic product is fitted to the tooth, finished and glazed, after which it becomes ready for installation.
Metal-ceramic crowns are the most popular due to several factors:
- They are durable, thanks to the metal base, so they can be installed on both the front and chewing teeth.
- They have high functionality (restoration of chewing functions is close to 100%).
- Aesthetic.
- Versatile. They can be used as independent prostheses, and be part of orthopedic and orthodontic structures.
- Durable.
- They have a moderate price, considering the high quality.
The disadvantages of metal ceramics include the significant thickness of the crown, reaching 2 mm in some places. Because of this, it is necessary to grind off a large layer of enamel and dentin from the supporting tooth, which leads to its weakening.
Contraindications related to the above feature, for example, lower front teeth , since the metal frame may be visible under some types of lighting.
Metal composite
A composite is a hybrid material consisting of a polymer matrix (organic resins) and small ceramic particles.
The composite mass is applied to a metal frame and cured with light. The first dental composites appeared around the middle of the last century. After this, interest in them either increased or decreased depending on the emergence of new, promising developments.
The disadvantages and advantages of metal-composite models very much depend on the specific material (brand). Therefore, we can only talk about them in relation to a specific brand.
In general, it is believed that the disadvantages of composites are:
- unreliable connection with the frame;
- relatively fast washability;
- colorability over time;
- plaque deposition;
- polymerization shrinkage.
But if you look at the composites of a specific manufacturer, in particular, GC Gradia or TwiNY, you will find that they are not that much inferior to high-quality ceramics. The bending strength reaches 120-240 MPa, with the ISO standard being at least 50 MPa. True, composites with such high characteristics are 1.5-2 times more expensive than standard ceramics.
In addition, hybrid materials have an advantage over ceramics in the speed of manufacturing prosthetic products. The first requires at least 2 hours for sintering, the composite requires only 10 minutes to cure when irradiated with light.
Composites also have such a significant advantage as the possibility of repair in a clinical setting (in the patient’s mouth).
Caring for installed stamped crowns
Since in the process of using such dentures, sooner or later the marginal fit changes and a gap is formed between the neck of the tooth, gum and crown, special care measures are required for them. Among the hygienic rules of care are the following:
- Brushing your teeth – at least 2 times a day. The use of a brush with medium-hard bristles is mandatory. The paste is selected with the appropriate mineral composition.
- Be sure to rinse your mouth after eating.
- Use dental floss to clean the space between your teeth.
- No later than 3 months after the installation of the prostheses, visit the doctor who installed them. Make such visits once a quarter a rule, until the very end of the service life. This way you can notice negative changes under the crown in time: the beginning of the carious process, tartar deposits, inflammation. And take treatment measures before the process goes too far and the crown has to be removed.
Manufacturing technology
The manufacturing technology according to Belkin and Pogodin has features, starting from the end of frame manufacturing. First, a stamped base is made using standard technology, then it is modified, which consists of removing part of the metal.
In Belkin’s model, the vestibular part is removed (cut out), while in Pogodin’s design, the vestibular and oral parts are removed. This, on the one hand, prevents metal from being visible through the plastic; on the other hand, it leaves exactly as much metal as is necessary to reinforce the structure and absorb the chewing load .
Starting from the moment of production of stamped MK, the technology for manufacturing structures according to Belkin and Pogodin is as follows:
- Cutting out windows on the vestibular (according to Belkin) and vestibular and oral (according to Pogodin) surfaces of the frame with teeth along the perimeter (for retention). The metal is preserved in the form of bridges in the neck area and covering the cutting or chewing surface of the tooth.
- Installation of the frame on a plaster model, wax modeling.
- Preparation of the plastic mass (mixing powder with liquid).
- Transfer it to a cuvette.
- Packing models in a cuvette with molding sand.
- Wax removal.
- Pressing (filling a cavity with plastic instead of wax). The exact technology is determined by the material used and the equipment available.
- Polymerization of products. Can be done hot or cold depending on the material used.
- Cooling, modification.
The video shows the technique for making a combined crown.
Installation steps
Manufacturing and installation of a metal-ceramic crown with a solid-cast frame includes the following steps:
- examination and diagnosis of the patient;
- design choice;
- turning the abutment tooth;
- production of a provisional crown;
- obtaining an impression of the prepared tooth and its antagonists;
- installation of a temporary model;
- production of plaster models from impressions;
- casting a solid metal frame;
- fitting the frame to the tooth;
- determining the color of the cladding;
- sintering of ceramic coating;
- fitting and modification;
- glazing and finishing;
- fixation on the tooth with cement.
Alternative Methods
Ceramic-composite metal-free, lightweight crowns with high light transmittance
Zirconium Durable crowns with high aesthetics, suitable for anterior and posterior teeth
Cast Durable and durable one-piece crowns made of metal alloys with the possibility of veneering
Article Expert
Shirokov Ivan Yurievich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
Work experience: more than 16 years
Life time
The service life of veneered products is determined by several factors, including the type of lining material, the professionalism of the doctor, the accuracy of technology, and care of the oral cavity after prosthetics.
The approximate service life of combined models, depending on the type of cladding, is:
- for metal ceramics – 10-15 years;
- for metal composite products – from 5 to 15 years, depending on the grade (brand) of the composite;
- for metal-plastic structures – up to 5 years.
Failure can occur for various reasons. If for metal-plastic products the main danger is the separation of plastic from the metal, then for composite and ceramic products it is cracks and chips.
While composite products can be repaired in the patient's mouth, with metal ceramics there is no other way to correct the problem other than replacing the crown. The same can be said about metal-plastic microprostheses. Detachment of the lining will inevitably lead to food getting underneath and rotting. Therefore, the sooner the prosthesis is replaced, the better.
Contraindications
Relative
the procedure can be carried out with extreme caution
- Bite defects;
- increased abrasion of the enamel of the antagonist tooth;
- gum pathologies (atrophic, inflammatory);
- pregnancy;
- allergy to anesthetics;
- acute infections;
- mental disorders;
- exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Absolute
the procedure is strictly prohibited
- Severe periodontitis with tooth mobility grade III-IV;
- malignant processes of the oral cavity;
- allergy to prosthesis material;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus.
Price issue
The cost is determined mainly by the cladding material (not counting products made of precious metals). Depending on it, the price of microprosthetics can range from several to 2 tens of thousand rubles.
The table shows approximate prices for lined structures. But you need to understand that if you want, you can always find an option a couple of thousand cheaper than the market average.
| Type of crown | Cost, rub. | Features of the instructions |
| Metal-plastic | From 2 500 | Frame made of dental socket (stainless steel) |
| Metal composite | From 7 000 | Material GC Gradia or TwiNY |
| Metal-ceramic | From 8 000 | Nickel-chrome alloy frame |
| Metal-ceramic | From 18 000 | Gold frame |
Materials
Stamped crowns are made from 900 gold or special stainless steel (grade 1x18N9T), which is easy to melt and forge. If the factory stamped sleeve is made of gold, then, due to the softness of this variety, the cutting edge is soldered from a metal of a different standard - harder 750.
But usually gold crowns are no longer placed. And yellow metal crowns, manufactured in modern dental prosthetic workshops, are made by sputtering titanium nitride onto steel blanks, imitating 900 gold.
In addition to steel and gold, blanks made of platinum, an alloy of cobalt and chromium, silver-palladium and titanium can be used.
Reviews
Today, the combined crown can be called “folk” due to its popularity. The time of fashion for gold “fixes” is irrevocably passed.
The main question that worries patients is how long can crowns lined with various materials last? If you have your own experience in this regard, please share it with visitors to our site. The comment form is at the bottom of the page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags dental crowns fixed dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Teeth analogues from the Japanese company Yamahachi are the best solution for removable prosthetics
Next article
Relevance of neuromuscular dentistry