Organization of work of a dental clinic
Among all medical institutions providing dental care, the dental clinic occupies a special place. A dental clinic is a medical and preventive institution whose activities are aimed at the prevention of dental diseases, timely detection and treatment of patients with diseases of the maxillofacial area.
Dental clinics vary:
1. By level of service: republican, regional, regional, city, district.
2. By subordination: territorial, departmental.,
3. By source of financing, budgetary, self-supporting.
4. By category: depending on capacity, which is determined by the number of visits per shift.
A dental clinic is created in accordance with the established procedure and operates as an independent healthcare institution. The boundaries of the area of operation of the clinic, the list of organizations that it serves, are established by the health care authority according to the subordination of the clinic.
The main objectives of the dental clinic are:
a) carrying out measures to prevent diseases of the maxillofacial area among the population and in organized groups;
b) organization and implementation of activities aimed at early detection of patients with diseases of the maxillofacial area and their timely treatment;
c) provision of qualified outpatient dental care to the population.
To carry out its main tasks, the clinic organizes and conducts:
- in a planned manner, according to schedules agreed upon by the heads of enterprises and organizations, preventive examinations of workers of industrial enterprises, construction organizations, students of higher and secondary educational institutions, workers and students of other organized groups with the simultaneous treatment of identified patients;
— implementation of complete sanitation of the oral cavity for all persons applying to the clinic for dental care;
— complete sanitation of the oral cavity in pre-conscription and conscription contingents;
— provision of emergency medical care to patients with acute diseases and injuries of the maxillofacial area;
— dispensary observation of certain groups of dental patients;
— provision of qualified outpatient dental care with timely hospitalization of persons in need of inpatient treatment;
— examination of temporary disability of patients, issuance of sick leaves and recommendations for rational employment, referral to medical labor expert commissions of persons with signs of permanent disability;
— the whole complex of rehabilitation treatment of pathologies of the maxillofacial area and, above all, dental prosthetics and orthodontic treatment;
— analysis of the incidence of dental diseases in the population, including incidence with temporary disability of workers and employees working at industrial enterprises located in the territory of the serviced area, as well as the development of measures to reduce and eliminate the causes contributing to the occurrence of diseases and their complications;
— selection of patients in need of sanatorium-resort treatment;
— introduction of modern diagnostic and treatment methods, new medical equipment and equipment, medicines;
— sanitary and educational work among the population with the involvement of the public, the Red Cross and Red Crescent Society and the use of all media (print, television, radio broadcasting, cinema, etc.);
— activities to improve the qualifications of doctors and nursing staff.
The dental clinic may include the following units (Diagram 1):
- registry;
— departments of therapeutic and surgical dentistry (including, in appropriate cases, children’s);
— department of orthopedic dentistry with a dental laboratory;
— auxiliary units (radiology rooms, physiotherapy);
— mobile dental offices;
— emergency dental care office;
— administrative and economic part;
- accounting.
The structure of dental clinics provides for the creation of examination rooms. The doctors working in them ensure reasonable referral of patients to clinic doctors who provide specialized dental care. Dentists in examination rooms can themselves provide assistance to patients if it is not possible to refer them to the appropriate department.
In addition, the clinic can organize departments and rooms to provide highly specialized care to dental patients. These include rooms for prevention, periodontology, orthodontics, a room for receiving patients with pathological changes in the oral mucosa, a room for functional diagnostics, and an allergy room.
In the structure of republican, regional, city dental clinics, organizational and methodological offices are created, the employees of which, together with the main specialists, carry out organizational and methodological work on dentistry, its planning, analysis of the activities of institutions, and develop measures to improve the quality of dental care for the population.
Dental clinic of republican, regional, regional subordination:
— carries out organizational and methodological management of dental clinics, departments and offices located in the relevant territory;
— analyzes the incidence of disease in this territory, the need for dental care and develops measures aimed at its improvement;
— ensures, in necessary cases, visits of specialists to rural settlements to carry out the entire range of treatment and preventive measures.
The direct management of the dental clinic is carried out by the chief physician, whose rights and responsibilities are determined by the relevant regulations. The administration of the clinic, together with public organizations, establishes internal labor regulations. The operating hours of the clinic are determined by the health authority of subordination, taking into account the needs of the population and specific conditions.
The dental clinic, equipped with modern equipment, staffed with qualified personnel who are proficient in modern methods of diagnosing and treating dental diseases, provides the highest quality of medical care.
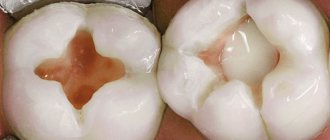
An important part of dental care is preventive work. In order to actively combat dental caries and other most common dental diseases, dental clinics carry out routine sanitation of the teeth and oral cavity for children in schools and preschool institutions, university students and students of technical schools, vocational schools, teenage workers, workers associated with occupational hazards, conscripts, pregnant women and other populations.
The registry plays a big role in organizing receptions and regulating the flow of patients, which is carried out by issuing coupons or pre-registration for appointments. Primary coupons are issued for an appointment with a surgeon or for a planned appointment with a therapist or a specialist (periodontist, specialist in diseases of the oral mucosa). The orthopedic and children's departments, as a rule, have their own registries.
In addition to regulating visits, the registry performs a number of important functions: registration and storage of outpatient medical records, their selection, delivery to offices and layout after the appointment, execution of temporary disability certificates and their registration; has a reference and information service; carries out financial settlements with patients for payment of paid medical services.
In organizing the reception of patients in a dental clinic, a large role belongs to the dentist on duty. If necessary, he provides emergency dental care, examines the patient and determines the amount of further dental care he needs, and refers patients to other clinic specialists.
Repeated visits to the clinic by patients are prescribed and regulated by attending physicians. With proper organization of work, the patient is observed by one doctor until complete rehabilitation. Some dental clinics work on a local basis, which increases the responsibility of each doctor, allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of his work and monitor the quality of care.
In a number of clinics, improving the quality of dental care is ensured by introducing a guarantee service system: upon completion of treatment and complete sanitation of the oral cavity, the patient is given a so-called “sanitation” coupon, which gives the patient the right, if defects are detected, to consult a doctor at any time out of turn during the year from the date of issue of the coupon.
The main sections of the work of a dentist working in a clinic are::
— provision of therapeutic and preventive, surgical or orthopedic care upon request;
— conducting consultations for doctors of other specialties;
— dispensary observation of certain groups of dental patients;
— carrying out planned sanitation of the oral cavity in certain groups of the population;
— sanitary educational work.
The children's dental department works primarily using the method of planned sanitation.
This method is implemented in two stages:
Stage 1 - examination of the oral cavity, determining the need for various types of dental care and its volume;
Stage 2 - providing the necessary medical and preventive care in the shortest possible time until complete rehabilitation. In some cases, planned sanitation also includes a third stage - subsequent systematic active monitoring of patients, i.e. dispensary observation.
Planned reorganization of organized children's groups is carried out according to a special schedule. Not only the dental clinic, but also the administration of schools and kindergartens is responsible for the implementation of this schedule.
Planned sanitation also covers some contingents of the adult population: disabled people of the Great Patriotic War, pregnant women, pre-conscripts, somatic patients under medical supervision by a therapist, students of vocational schools, technical schools, university students, representatives of some professions.
The organization of the work of the orthopedic department deserves special attention. Dental care is provided at the final stage of treatment of dental patients, after complete sanitation.
The orthopedic department has its own registry, examination room, offices of prosthetists, a dental laboratory, and may have an orthodontist’s office. A patient in need of dental prosthetics contacts the reception desk of the orthopedic department.
If there is a certificate of complete rehabilitation, a special outpatient card is created for him and a coupon is issued for an appointment with a doctor in the examination room. In the examination room, a plan for prosthetics is drawn up, after which the patient is sent to an appointment with the attending dentist-orthopedist, who examines the patient, gets acquainted with the plan for prosthetics and issues an order for the manufacture of prostheses. After payment for denture work, the production of dentures begins in the laboratory.
In addition to the manufacture of new dentures, the orthopedic department repairs and replaces old dentures, and provides consultations on dental prosthetics and orthopedic treatment of dental diseases. Some large clinics provide specialized orthodontic care.
Free dental prosthetics are provided to disabled people of the Great Patriotic War, disabled people of groups I and II, personal pensioners, children and some other groups of the population.
Dental clinics provide, if necessary, assistance to patients at home on call from doctors from territorial clinics. To provide dental care at home, the clinic has portable equipment. All necessary types of assistance are provided at home, including dental prosthetics. Room calls are handled either by doctors specially designated for this purpose, or by all doctors of the clinic in order of priority.
Emergency dental care is provided by dentists on duty during the clinic's opening hours, on weekends and holidays, as well as at night - in special emergency dental care centers, which are organized in several clinics in the city.
A large place in the work of a dental clinic is occupied by medical examination of dental patients. Under dispensary observation are patients with active dental caries, periodontal diseases and oral mucosa, chronic osteomyelitis of the jaws, malignant neoplasms of the face and oral cavity, congenital cleft lip and palate, abnormal development and deformation of the jaws, etc. The selection of such patients is carried out as follows: during preventive examinations and planned sanitation, as well as when visiting dentists for medical care.
The clinic operates according to plans that provide for specific organizational, treatment and preventive measures. Accounting for the activities of the clinic is carried out in the manner established by health authorities according to accounting and reporting documents approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Standards and requirements for organizing a dental office.
Ministry of Health of Ukraine
Zaporozhye State Medical University
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry
Abstract on the topic:
EQUIPMENT OF A DENTIST'S WORKPLACE: UNIVERSAL DENTAL UNITS AND CHAIRS. SAFETY.
ETHICS AND DEONTOLOGY IN DENTISTRY. IATROGENIC DISEASES.
Prepared by:
3rd year student, 1st group
Faculty of Dentistry
Aliyev Hashim
Zaporozhye-2015
Plan
- Equipping a dentist’s workplace…………………………..3
- Standards and requirements for the organization of a dental office……………………………………………………………….……….3
- Safety precautions in the dental office…………..….…..5
- Ethics in dentistry……………………………………………………8
- Deontology in the work of a dentist………………………..………9
- Iatrogenic diseases……………………………………………………………10
- References……………………………………………………….13
Equipping a dentist's workplace
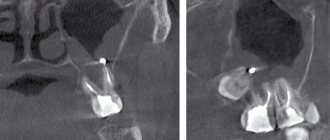
The performance of the duties of a dentist largely depends on the organization of the workplace. Currently, great importance is attached to its technical equipment, since without laboratory and functional methods it is sometimes impossible to make an accurate diagnosis.
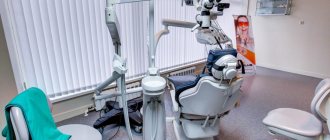
The dentist's workplace is equipped with sophisticated equipment and apparatus, which allows him to successfully solve the problems of diagnosing and treating diseases of the teeth, periodontal tissues and oral mucosa. According to the current situation, a dental office per doctor must occupy at least 14 m2 of area. If several chairs are installed in the office, then its area is calculated according to an additional standard - 7 m2 for each chair. If the additional chair has a universal dental unit, its area increases to 10 m2.
In connection with the use of amalgam when filling teeth, special attention is paid to the finishing of the floor, walls and ceiling of the office. The walls of the dental office should be smooth, without cracks. Corners and junctions of walls, floors and ceilings should be rounded, without cornices or decorations. Walls and ceilings are plastered or rubbed with 5% sulfur powder added to the solution, and then painted with silicate or oil paints. The floor of the office is first covered with thick cardboard, and rolled linoleum is laid on top, which should extend onto the walls to a height of 10 cm. The dental office must have natural light. It is advisable to orient the office windows to the northern directions in order to avoid significant changes in light in the workplace due to direct sunlight in other types of orientation, as well as overheating of the premises in the summer. In offices that have incorrect orientations, in the summer it is recommended to darken the windows using curtains, blinds, awnings and other devices.
General lighting lamps are placed so that they do not fall into the field of view of the working doctor.
Dental offices, in addition to general lighting, must also have local lighting in the form of a reflector on dental units. The dental office must be provided with supply and exhaust ventilation with an air exchange rate of 3 times per hour for exhaust and 2 times per hour for inflow, and also have vents and transoms.
The equipment of the workplace of a dentist conducting a therapeutic appointment includes:
1) dental unit and dental chair of anatomical shape with synchronous movement of the seat and backrest for positioning the patient without the “pulling effect”. Ideal positioning of the patient's head is achieved thanks to the presence of an anatomically configured headrest with complete freedom of movement for treatment on the upper and lower jaws. Greater freedom for placing the legs of the doctor and assistant is provided by shifting the upper part of the chair in relation to the base. The correct bend of the lower part of the chair allows even elderly patients to be comfortably positioned;
2) auxiliary table and instrument holder (doctor’s unit), combined into one group, they can be installed in the desired position with one hand in any medical situation. All tools can be taken from any position. The doctor's instrument holder is equipped with two micromotors (electric or air), a turbine, a 3-function gun, an attachment for removing dental plaque, an electrocoagulator, and an electro-odontometer. The assistant's tool holder is equipped with a saliva ejector, a vacuum cleaner, a curing lamp, a 3-function gun;
3) operating lamp with adjustable brightness, which does not heat up and does not glare; porcelain spittoon with automatic rinsing and glass filling; screen for viewing x-rays; autonomous device for distilled water.
In addition, there are height-adjustable work chairs for the doctor and assistant, which can be easily moved on casters.
The dental unit must be installed in such a way as to allow ergonomic four-handed operation. The patient's position is more flexible, the doctor's workplace is to the right of the patient, and the assistant's is to the left.
In the auxiliary area of the office there is an office table for maintaining documentation, chairs, sinks for washing hands and instruments, a table with a set of sterile instruments, cabinets for storing medications, instruments, filling materials, etc.
It is necessary to distinguish between the equipment of offices designed for the work of one doctor or a group of doctors, for mixed or specialized treatment of patients, for the work of a dentist at a therapeutic appointment, a dental surgeon, an orthopedist or an orthodontist. In addition, dental equipment must meet the requirements of technical aesthetics, safety regulations (for the doctor and the patient), occupational hygiene of the dentist and all medical personnel. And naturally, offices must be provided with the necessary minimum of basic dental materials, medications and instruments for each medical position per 1 year of work
The successful operation of a dental office largely depends on the strict performance of duties by the nurse and nurse.
The nurse is responsible for the safety and condition of the office equipment, the technical serviceability of equipment, installations and chairs; before starting work, she sterilizes instruments and materials, and prepares the doctor’s workplace. Her responsibilities include managing the flow of patients into the office during appointments, providing the doctor with the necessary tools and materials, the nurse is fully responsible for storing medications, in particular groups A and B, and monitoring the sanitary condition of the office.
The nurse carries out wet cleaning of the room every day after completion of the appointment. During the work of the office, she carries out thorough mechanical processing and washing of used ones. trays and tools.