Since the creation of the modern structure of dental care, the medical record of a dental patient has been its basic element. It existed when there was no trace of other documents, without which it is impossible to imagine the work of a modern clinic (contract, protocol of voluntary informed consent, insurance policy, etc.).
At the same time, many dental clinics completely or partially ignore the role of the dental patient’s medical record: they either do not use it at all, or they modernize, modify, or invent their own versions. And if the use of various variations on the theme of a dental patient’s medical record can be understood (in many ways, the existing form already lags behind the requirements of the time), then the complete absence of a medical record is completely unacceptable.
What is a dental patient's medical record?
A medical record of a dental patient is a document that properly identifies the patient and contains information characterizing the characteristics of the condition and changes in the state of his health, established by the doctor and confirmed by laboratory, instrumental and instrumental research, as well as the stages and features of the treatment.
Registration of a medical card for a dental patient –
The medical record of a dental patient is drawn up in accordance with orders of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 1030 of October 4, 1980 and No. 1338 of December 31, 1987. At the same time, the Ministries of Health of the USSR and the Russian Federation managed to create extreme confusion with the medical record. In 1988, an order of the USSR Ministry of Health was issued (No. 750 dated 10/05/1988), according to which the Order of the Ministry of Health No. 1030 became invalid. However, another, newer Ministry of Health, now the Russian Federation, since 1993 began to regularly refer to the provisions of Order No. 1030 of the USSR Ministry of Health, introducing appropriate changes and additions to it.
There are no later basic orders or other acts of the Russian Ministry of Health establishing the form of a medical record. Therefore, although many provisions of Order No. 1030 have lost force, new regulatory documents periodically contain references to those parts of the order that relate to the maintenance of medical records. In particular, the requirement remains that all medical institutions (note, regardless of their form of ownership) are required to maintain medical records in the established form. In dentistry, this is Form No. 043/у “Medical record of a dental patient.”
What does a medical card include?
Medical record No. 043/u contains three main sections.
1) The first section is the passport part. It includes:
- card number;
- date of its registration;
- last name, first name and patronymic of the patient;
- patient's age;
- patient's gender;
- address (place of registration and place of permanent residence);
- profession;
- diagnosis at initial visit;
- information about past and concomitant diseases;
- information about the development of the present (which became the reason for the initial treatment) disease.
This section can be supplemented with passport data (series, number, date and place of issue) for persons over 14 years of age, and birth certificate data for persons under 14 years of age.
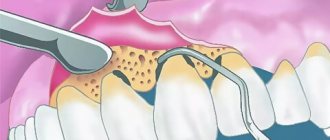
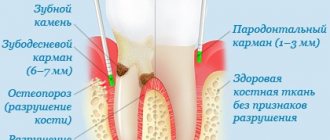
2) The second section is data from objective research. He contains:
- external inspection data;
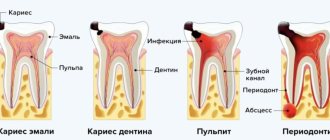
- oral examination data and a table of dental condition, filled out using officially accepted abbreviations (absent - O, root - R, caries - C, pulpitis - P, periodontitis - Pt, filled - P, periodontal disease - A, mobility - I, II, III (degree), crown - K, artificial tooth - I);
- description of bite;
- description of the condition of the oral mucosa, gums, alveolar processes and palate;
- X-ray and laboratory data.
3) The third section is the general part. It consists of:
- examination plan;
- treatment plan;
- treatment features;
- records of consultations, consultations;
- clarified formulations of clinical diagnoses, etc.
Dear Colleagues! In this article I answer all the questions that doctors and managers of dental clinics ask me at seminars and consultations.
IMPORTANT: The medical record of a dental patient is a key link in disputes with the patient, since it is used to assess the quality of the patient’s treatment through a forensic medical examination of the case materials (including the clinic’s medical record and other medical documentation of the patient) and examination of the patient by experts.
Therefore, regardless of whether it is a printed card or an electronic one, in form 043/u or in a free form, the dental patient’s medical record must perform a protective function, that is, the card entries must be readable and reflect the progress of the treatment performed.
Now let's look at all the subtleties.
Historically, the so-called “U” forms familiar to all dentists were approved by Order of the USSR Ministry of Health dated October 4, 1980 N 1030 “On approval of forms of primary medical documentation of healthcare institutions.” However, after 8 years, by Order of the USSR Ministry of Health dated October 5, 1988 N 750, Order No. 1030 was canceled. Thus, since 1988, no laws formally oblige doctors to adhere to the established form of the Medical Card of a Dental Patient (043/u) . 13 years after the order was cancelled, since everyone continued to use the old approved forms, especially in general medicine, the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation in Letter dated November 30, 2009 N 14-6/242888 reported that before the publication of a new album of samples of registration forms of health care institutions, on the recommendation of the Ministry of Health of Russia use in your work to record your activities the forms of Order No. 1030 (all the same familiar forms).
Since then, there have been advances in the management of dental patient records, when everyone could develop and maintain their own form of cards, because up to the present time, the Ministry of Health and Social Development recommends (but does not oblige) the use of forms /y.
In March 2015 The medical record of an orthodontic patient 043-1/u was put into effect, which was officially approved and mandatory for maintenance, including in private dentistry. It is important to clarify that for other dental specialties everything remains the same - you can use any form of cards.
This means that it is reasonable to develop your own forms, convenient for printing and recording, based on form 043/у. What should a medical record include (required sections)? In parentheses, I indicated optional sections that have neither medical significance nor legal significance for protection against claims (in case of a dispute, the patient always confirms that assistance was provided to him, therefore passport data, etc. information can be neglected if the patient does not wants to communicate them). The first section is the passport part: 1. card number (optional); 2. date of its registration; 3. last name, first name and patronymic of the patient; 4. age of the patient; 5. gender of the patient; 6. address (optional); 7. profession (optional);; 8. diagnosis at initial visit; 9. information about previous and concomitant diseases; 10. information about the development of the present (which became the reason for the initial treatment) disease. 11. Preferred method of appointment reminder (tel, SMS, etc.). The second section is objective research data: 12. external examination data; 13. data from an examination of the oral cavity and a table of the condition of the teeth, filled out using officially accepted abbreviations (absent - O, root - R, caries - C, pulpitis - P, periodontitis - Pt, filled - P, periodontal disease - A, mobility - I, II, III (degree), crown - K, artificial tooth - I); 14. description of the bite; 15. description of the condition of the oral mucosa, gums, alveolar processes and palate; 16. X-ray and laboratory data. The third section is the treatment part: 17. examination plan (optional) 18. treatment plan; 19. treatment records; 20. consultations of related specialists 21. consultations; 22. clarified formulations of the clinical diagnosis 23. information on radiation doses received by the patient during X-ray examinations (based on the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation “On the introduction of state statistical monitoring of radiation doses of personnel and the population” No. 466 of December 31, 1999); 24. X-rays of the patient’s teeth and maxillofacial area, taken in this dental clinic. The following can be pasted into the medical record: 25. test results, 26. extracts from other medical institutions where dental care was provided, medical reports.
Let's analyze judicial practice in dental cases on the issue of the legality of using free-form patient cards . First of all, you need to understand that the dental patient's chart has the role of evidence of quality; the quality component is proven mainly by detailed, readable records in the chart and examination of the patient at the time of the dispute. In this case, what is important is the content of the records and their completeness, and not the form of presentation (in which type of card the records were made). “ consumer” component of quality is proven by the text of the Agreement, Treatment Plan, Informed Consent, Memo and Refusal of Treatment, for example, refusal of alternative prosthetic options. Therefore, information about the diagnostic and therapeutic procedures performed must be readable and complete, i.e. abbreviations must be understandable to dental experts, records must unambiguously interpret the manipulation according to a standard or accepted rule, without guesswork (not just “the root is sealed to the anatomical apex,” but all stages of endodontics),
A well-written chart is when a dental expert is forced to write during the review “according to the records in the medical record, the treatment was carried out of adequate quality,” which automatically removes the clinic’s guilt and leads to the patient losing the claim.
What is practice? Here are excerpts from the court decision regarding the conclusions of the forensic medical examination: “An analysis of the presented materials of the civil case and medical documents showed that during the observation and treatment of K., the medical record of the dental patient was not filled out (form N 043/u). Instead, an “Individual Outpatient Card” N *” was compiled, which is not provided for by the relevant orders of the USSR Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. In the document “Individual Outpatient Patient Card” N * presented to the expert commission, the following entries are missing: anamnestic data on previous and existing diseases; information about allergy history; dental status, including dental formula; description of radiographs, orthopantomograms, CT scans; basic treatment plan for the dental system; alternative treatment plan (signature of the patient agreeing with the proposed treatment plans); the state of the radiographic picture of the alveolar process of the upper jaw (height, thickness) in the areas of proposed dental implantation, bone tissue; justification for the use of the dental implantation method in the upper jaw in this patient; the condition of dental implants after the first implantation (since during the second implantation three implants are installed in the projection of the implants already installed earlier in the projection of teeth 1.2, 2.2, 2.5); information about orthopedic work and the manufacture of therapeutic orthopedic devices (except for taking impressions, adjusting a complete removable denture of the upper jaw); diagnosis of dental disease (pathology). In Appendix No. 1 to the Agreement for the provision of paid medical services for each point of treatment there is a short entry limited to the word “yes”, which does not allow us to determine what exactly was planned to be done. Thus, the lack of necessary entries in the medical document, as well as the incompleteness of the entries in Appendix No. 1 to the contract, do not allow us to objectively and reliably answer the questions posed.”
Based on the fact that the card did not reflect the progress of treatment, and not because it was not written in accordance with the form, the Clinic was unable to prove the proper quality of the service and lost the trial.
I would like to add that experts are usually older people who are accustomed to certain patterns and naturally “resist” innovations. Therefore, it is better to adapt form 043/у to your needs, and, most importantly, do not forget about the “consumer” component of the service,” which can be proven by having anti-claim documentation (specially drawn up agreement, consent, plan, memos).
As for the issue of keeping records and the card itself in electronic form , including using various programs, the approach to it is similar. Using the basic principle of law “everything that is not prohibited is permitted,” we can keep a map on a computer. It is important to resolve two main issues. The first is to prove the legal significance and time of recording (during the patient’s appointment, and not before the court hearing). Secondly, the content of the records must prove the quality of the services provided to the patient.
With regard to the legal significance of electronic documentation, documents can be divided into two groups. The first are documents that require a mandatory signature, so they must be printed and signed by the patient and the clinic representative. These include: an agreement for the provision of paid medical services, informed voluntary consents, a treatment plan and a certificate of services performed. Typically, the patient's regular written signature is used, as I have not yet encountered a dental clinic that is an authorized user of an enhanced qualified electronic digital signature. For documents of the second group, no requirements are established at the legislative and regulatory level (medical records and medical records), and in this case, the procedure for using such documents can be established by agreement of the parties in the contract. Thus, if the contract contains a provision for maintaining a medical record in electronic form, then the electronic record will have legal significance in court . In most clinics, they simply print out the card and put the patient’s signature at the end (when the treatment plan is completed), which will certify the time of making entries in the card. You can check the quality and completeness of the patient’s documentation by ordering a free audit of the medical clinic’s documentation. Conclusions : 1. for an orthodontic appointment, you must use the template “Medical record of an orthodontic patient,” form 043-1/u, filling in only the necessary fields (if your clinic does not work in compulsory medical insurance), 2. for other areas of dentistry, you can use any templates, including incl. own, based on the classic form of a medical record of a dental patient (form N 043/у), 3. maintaining dental records in electronic form is allowed, including using various programs for dentistry, subject to storage in printed form signed by the patient for the implementation of the plan treatment, 4. evidence of the proper quality of paid medical services provided to the patient is the content of the entries in the medical record, and not the form of the record itself.
For convenience in work, at the request of dental clinics, I have developed, BASED on form 034/u, a dental patient card in A4 format (for a tablet). The card has been reviewed by my regular clients - dental clinics and has been used by them in their work for more than three years. The cost of the card is 1000 rubles. The card is sent by email. mail in Word format. The card can be maintained electronically (printed during verification) provided that the patient’s signatures are collected in the required places (informed consents, agreement, plan, certificate of services performed).
To order documentation:
- use the Services section
- write to email mail
- You can immediately pay 1000 rubles. to the Sberbank card: 5469300238629783, Recipient - Artem Valerievich Voropaev ), in the message indicate 1. “Medcard” 2. Your email. mail. 3. Required by email. send a letter by email stating that you have paid, and you will receive a letter with documentation.
Some features of the medical record
The material and type of medical record of a dental patient does not matter much.
It can be produced in a clinical setting or by printing and, as a rule, is an A5 notebook. The main requirement is that it be in paper form and have records in the form approved by law. The passport part is prepared by a medical registrar, clinic administrator or nurse. All other entries in the medical record are made only by the doctor, legibly, without corrections (a printed (computerized) option for making entries is possible), using only generally accepted abbreviations. The formulations of diagnoses, anatomical formations, names of instruments and medications are indicated in full, without abbreviations, taking into account the officially used terminology. The entry made is confirmed by the signature and personal seal of the doctor.
In addition to the records, the following must be included (pasted) in the medical record:
- test results (if any) - originals or copies;
- extracts from other medical institutions where dental care was provided, especially if the provision of dental care in other institutions occurred after the patient first applied (began to be observed) in this dental clinic;
- medical reports, expert opinions, consultations received in connection with the diseases for which the patient is observed in this clinic; medical reports, expert opinions, consultations received in connection with other diseases, the course of which may affect the characteristics of the dental disease;
- information on cancer examinations (based on the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation “On measures to improve the organization of cancer care for the population of the Russian Federation” No. 270 dated September 12, 1997);
- information on radiation doses received by the patient during X-ray examinations (based on the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation “On the introduction of state statistical monitoring of radiation doses of personnel and the population” No. 466 of December 31, 1999);
- X-rays of the patient’s teeth and maxillofacial area, taken in this dental clinic.
Let's take a closer look at the last point. Of the entire evidence base that is used by the parties when considering consumer claims in court in connection with the quality of services provided, X-ray images are of the greatest importance. Why? As an example, let’s look at a controversial situation that arises most often.
The patient had his teeth treated in several clinics and collected his x-rays from everywhere after the treatment was completed. At the same time, of course, in all clinics there were certain documents confirming the fact of treatment (service agreements, entries in the medical record, payment receipts, checks, etc.). In one of the clinics, an instrument broke off in a tooth canal during treatment. However, the patient sued not the clinic where the instrument was broken, but the richest of those where he was treated.
At the same time, it is almost impossible to prove the absence of fault of the clinic specified in the claim if the clinic cannot present an x-ray taken after completion of treatment. That is why the clinic is extremely interested in keeping all the images taken on the patient. However, certain legal difficulties arise here.
The fact is that radiography is usually included by clinics in the price list as a separate type of service. And on the basis of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the patient has the right to regard the x-ray performed as a service paid for by him, the material expression (result) of which is an x-ray. Accordingly, the patient acquires the full right to take this image for himself.
Of course, this situation does not suit the clinic at all. Therefore, the clinic usually uses the following exit options:
- include in the Contract for the provision of dental services a clause according to which x-rays taken in the clinic are an integral part of the medical record of the dental patient. In this case, all images taken at the clinic remain its property on the basis of an agreement concluded with the patient.
- They give the patient not the image itself, but its image on paper or other media - for example, a copy from a visiograph, or a printout of a scanned image.
However, all of the above applies to the medical record of a dental patient, form No. 043/u. If a dental clinic uses its own form of medical records, then it may face serious problems in court proceedings. The fact is that the patient can submit a request for the clinic to provide evidence of a medical record of a dental patient in the form established by law (form No. 043/u).
In this case, the provision of a medical card of a different form by the dental clinic may be interpreted by the court as a formal basis for recognizing this form as not meeting the requirements of the law, and on this basis the card may not be accepted as written evidence. And this will allow you to ignore all the entries made in the card and give the patient grounds to accuse the clinic of improper record keeping.
Since this form of card is truly outdated and does not fully reflect both changes in civil legislation and new diagnostic and treatment standards, its certain modernization becomes inevitable. Therefore, in dentistry, as a way out of this situation, they use a loose leaf for the medical record (information sheet), taking into account the specific features of a particular clinic. It is much worse for a dental clinic if the dental patient’s medical record is not maintained at all.
1).Medium caries:
Complaints: short-term pain from cold, sweet foods in …..(tooth formula)
Objectively: on…..(name) surface …..(tooth formula) is carious
cavity ..... Black class, made of softened dentin. Probing is painful along the dentinal-enamel border. Short-term pain from temperature stimuli. Percussion is negative.
RVG:
Treatment: under topical anesthesia (………………….. (name)) and
infiltration (conduction) anesthesia (…… (name)) is formed
and the cavity was treated with medication. ….(description of the
manipulations - filling (number of surfaces). restoration, tab, etc., with the name of the material and color indication)
FAQ -
- Who makes entries in the medical record? The passport part is filled out by the registrar, administrator or nurse; all other entries are made only by the doctor.
- How are entries entered into the medical record? Legibly, using only generally accepted abbreviations, without corrections, handwritten or printed, certified by signature and the doctor’s personal seal.
- Why do you need a medical card? To reasonably protect the interests of the dental clinic, first of all, in court.
- Can dentistry issue a medical card to a patient? Formally yes, in fact no.
- What problems can there be for using the wrong card options? An incorrect version of the map may not be recognized by the court as written evidence, and the resulting lack of documentation required by law may become the reason for legal claims.
- Does the patient have the right to collect x-rays? Yes, at least copies of photographs on paper or other media.
- How do dentists update medical records? Use the medical record insert – information sheet.