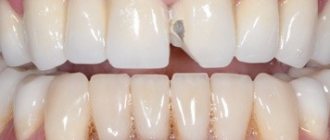
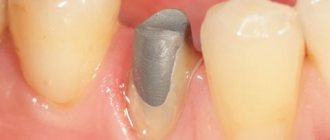
Metal ceramics cause gums to turn blue
Each metal in the alloy has its own reaction to the body. Most often, standard alloys oxidize over time, which leads to gum subsidence and discoloration, which can occur over time. This occurs if standard crowns with an uncovered lower metal part were used. When using crowns with shoulder mass, or, as they are also called, increased aesthetics, the place where the metal adheres to the gum is closed, which helps prevent swelling of the mucous membrane, discoloration, and rapid subsidence.
What is a metal-ceramic crown?
A metal-ceramic crown is a permanent dental prosthesis that is fixed to the remaining tooth. Consists of a metal frame and layered ceramic coating. More than 500 alloys are used in dentistry; alloys based on:
- gold from 70% in alloy;
- gold and other precious metals (25-50%);
- palladium (more than 50%).
The strength of the finished product depends on the frame; if it is thin, the overall resistance to occlusal load will decrease. A thick base worsens the appearance, because... over time we will shine through the ceramics. Dental technicians adhere to the rule that the minimum thickness of the frame is 0.3-0.4 mm, the maximum depends on the tooth being replaced. The thickness of the metal-ceramic prosthesis is 1.1-2.0 mm.
These crowns are designed to cover individual teeth, as well as to secure bridges in visible areas of the dentition. They are installed as a replacement for the front and chewing teeth.
Attention: if part of the crown veneer breaks off, it will not be possible to restore the integrity of the patient’s oral cavity. She is being removed.
Metal-ceramic dental crowns are not stained by food and do not have a harmful effect on surrounding tissues. The approximate service life is 5 - 15 years, depending on the materials used and manufacturing technology. The more expensive the materials and the more elaborate the manufacturing technique, the longer the crown will last (a gold-platinum alloy as a frame increases the service life to an average of 20 years).
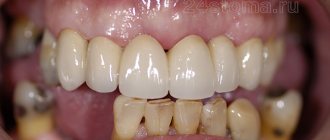
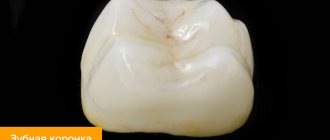
Metal crowns with ceramic coating
Is it possible to remove a denture?
How are metal-ceramic crowns removed from teeth? It all depends on the method of fixation. If the prosthesis is “planted” on cement, then it is first sawed and removed in parts - such a product cannot be repaired (but the implant itself remains unharmed, of course). But the orthopedic construction needs to be made new.
If screw fixation is initially chosen, the dentist drills a composite filling that covers the screw. Then he unscrews the screw itself and removes the prosthesis - here the removal is done without destroying the prosthesis, and it can be fixed to the implants again, if necessary.
You cannot remove prosthetic structures on implants yourself! The only case when this can be done (but not always necessary) is if the prosthesis is conditionally removable and fixed on certain abutments - spherical or “locators”, that is, the system provides for independent removal.
Indications and contraindications for installing metal ceramics
These dental crowns are used for aesthetic prosthetics. Main indications:
- Destruction of the natural crown of a tooth by caries, trauma, non-carious lesions, etc., which cannot be restored with filling.
- Traumatic tooth fracture.
- Darkening of color or hypoplasia of enamel.
- Dental abnormalities.
- Fluorosis.
- Restoration of the lower part of the face with pathological abrasion.
- How to fix a prosthesis (removable, bridge).
- When splinting teeth for periodontitis.
- Replacing dentures.
Contraindications for installing metal-ceramic crowns are relative (sometimes it is enough to carry out preliminary treatment):
- Age up to 16 years (intact pulp).
- Teeth with fragile, thin crowns (often this applies to the lower incisors).
- Blocking bite, when the lower incisors completely overlap the upper incisors.
- Pathological abrasion of teeth and a decreasing bite (will lead to breakage of the metal-ceramic crown if the bite was not corrected and myostatic reflexes were changed before installation).
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles (for example, bruxism).
- Diseases of marginal periodontium due to possible functional overload of teeth.
Allergy sufferers and people with gastrointestinal diseases need to be very careful when choosing a metal frame, since the constant presence of metal can cause a deterioration in well-being over time. For such patients, a gold base is recommended. Doctors also do not recommend nickel-chromium alloys even for healthy people, since there is a tendency for general immunity to decrease and a surge in autoimmune diseases and the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the alternatives?
As already noted, cermets can be replaced with products made from zirconium dioxide. Moreover, it can be used as “pure”, i.e. without facing, or facing with ceramic mass, and then firing. This is necessary if very white zirconium dioxide with minimal transparency is used - then the zirconium cap, after applying several layers of ceramics, will be indistinguishable from natural teeth and will last more than 20 years.
If the patient needs an extended bridge, then zirconium dioxide will make the restoration very expensive. In this situation, you can pay attention to cheaper, but lightweight and high-quality materials, for example, ceramic composite.
Stages of installing a metal-ceramic crown
Prosthetics are more the work of a dental technician than an orthodontist. The crown will be made in 7-10 days. However, before installation, it is necessary to prepare the patient, carry out appropriate treatment if necessary, and also prepare the tooth. Therefore, you will need to visit the clinic 4-5 times (it is possible to combine several stages in one visit). If problems are discovered, the number of visits to the doctor will increase.
The presence of a pain symptom during installation of a prosthesis depends on the tooth:
- on the pulpless one the pain is not felt. However, if you ask for additional anesthesia, they will give it;
- on “living” teeth, with the root preserved, there is an unpleasant sensation, pain is felt during grinding. Anesthesia solves the problem, but it is advisable to do a test to avoid an allergic reaction.
When installing dental crowns, when a temporary prosthesis is installed, the edge of the gum may be damaged and discomfort may be felt, but this is a normal process - no medications are required. If there is increased nervous excitability, the pain threshold is low - you can take sedatives and painkillers (be sure to discuss this issue with your dentist!).
Diagnostics before installing crowns is necessary
Diagnostics
Clinical assessment of the oral cavity and tooth damage is a mandatory step before installation. This is an examination, the manipulations are painless. Orthodontist:
- examines the tooth, checking the severity of the midline (equator), the degree of destruction;
- notes fillings, degree of tooth mobility;
- identifies defects in bite and dentition;
- checks the distribution of occlusal load;
- pays attention to periodontal disease.
An x-ray may also be needed if there is inflammation or a suspected tumor. If there is no inflammatory process (it must be eliminated before installation), the tooth is cleaned of plaque and caries is treated. They are filled, if necessary, removing the nerve and additionally filling the canals.
Tooth preparation
Preparing a tooth for a metal-ceramic crown means grinding off part of the tooth so that the crown placed on top is in line with the rest of the teeth and does not interfere. The walls are shortened and smoothed, the tooth shape becomes cylindrical.
If the tooth root is healthy, the nerve is not removed. They try to keep the tooth alive, then it will not “dry out” under the crown - the service life of the metal-ceramics will increase. The abutment tooth for a metal-ceramic crown is prepared much more than when preparing to install an all-ceramic crown. Focus on the rules:
- The color of the structure, close to the natural tooth, is obtained by distributing the thickness of the ceramic: center - 1.3-1.4 mm;
- cutting part - 1.5-1.6 mm.
Like any dental procedures in the mouth, preparation is not the most pleasant, but it does not cause severe pain. At the patient’s request, the doctor will always inject an anesthetic to make him feel comfortable. When the preparation is not gentle, a significant amount of enamel and dentin (about 2 mm of hard tissue) is ground off; full anesthesia is performed with a living (intact) pulp.
Taking an impression, installing a temporary prosthesis
The orthodontist needs an impression of the upper and lower jaws to correctly make the crown so that the prosthesis is not perceived as something foreign. On the model made in plaster according to the cast, the height of the product, the angle of inclination, and the evenness of the dentition will then be checked. Sometimes an impression is made of the antagonist teeth and only the jaw where the crown will be installed.
Impression of teeth for making crowns
When making such crowns, impressions are used consisting of 2 layers:
- indicative (basic);
- clarifying (correcting).
First, gum retraction is performed under anesthesia to move it away from the tooth. The most painless method is mechanical, when the gum tray is opened using a thread soaked in a retraction compound. The groove opens, exposing the space between the tooth and the soft tissue.
An inlay is placed on the tooth, since any crown can be installed on it. The first impression is made using impression material and a special tray with perforations. Then the retraction thread is removed, a second layer (corrective) is applied, and the impression tray is again placed on the dentition according to the dental impressions. While the crown is being made, the orthodontist will install a temporary composite, and the patient will wear it for 1-2 weeks.
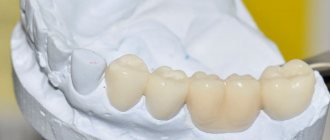
Manufacturing of a metal-ceramic crown
Stages of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown:
- Creating a Casting Mold
- Formation of a metal frame
- Application and fixation of dentin, enamel, transparent layers
- Retouching with dye does not imitate carious lesions, only the necessary natural darkening.
The frame is modeled using different methods. For example, the Adapt method. The metal base is obtained by pressing a stamp. A more “jewelry” method is wax modeling. To make a metal-ceramic crown, a mock-up is first prepared from wax that accurately depicts the contours of the finished crown. Then the wax is cut off (this creates a platform for the ceramics), and a fireproof mold is prepared for casting.
The frame of the metal-ceramic crown, which has cooled after casting, is carefully removed and cleaned of the remains of the molding material, dissolving them in an acid solution. The sprue channels (through which the melt was poured into the mold) are removed and sent for a 10-minute firing. The temperature in the oven is 950-1000°C. After cooling, the metal base is adjusted to the required dimensions on the supporting tooth and ground.
Features of manufacturing a metal frame depend on the type of material:
- Soft alloys with a gold content of more than 70%. To prevent the appearance of bubbles on the surface, the finished area for ceramics is treated with a cutter or carbide boron, cleaned with steam, a solvent (for example, carbon tetrachloride or chloroform).
- Alloys of gold-palladium, gold-palladium-silver, palladium-silver and palladium-copper. Their peculiarity: they can change the color of the finished crown. Silver can “color” ceramics yellowish; copper will give a greenish tint. The finished area for the ceramic mass is treated with corundum grinding heads, cleaned in a sandblaster, and small deposits and dust are removed with steam or an organic solvent. Palladium in the base of most alloys absorbs (absorbs) air; when fired, oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen are released, forming bubbles on the surface. Therefore, the formation of the frame includes the stage of vacuum heat treatment (degassing), when the temperature is maintained at 1000°C. The surface darkens to black.
- Nickel-chromium alloys. Corundum heads are used in processing. The ground frame is then heated to form an oxide film on the surface. Next, the metal base is polished with aluminum oxide particles using a microsandblaster and cleaned with a solvent or steam cleaner.
An opaque mass is applied in thin layers to the prepared metal-ceramic crown frame, which forms the dentin layer. For a natural depth of color, as in a healthy tooth, the first layer is the contour of the crown, setting the shape by cutting off the excess.
Further production of the metal-ceramic crown and ceramic superstructure is divided into 2 volumetric stages:
- Application of dentin coating followed by modeling.
- Condensation, i.e. vibration (for uniform distribution), blotting off excess moisture with special napkins and drying under a stream of hot air.
Manufacturing of metal-ceramic crowns
“Finger-shaped” grooves, which are very clearly visible under the enamel of a real tooth in young people, are obtained by cutting off small sections from the workpiece and smoothing the cuts with a brush. To give the metal-ceramic crown the effect of opalescence (dispersion of light), a lighter enamel mass is applied in the next layer. The final layer is colorless; it is this layer that gives the crown transparency and depth comparable to natural tooth enamel. The technician can even draw cracks (relevant for older patients), darken some areas (intertubercular space and cervical area) so that the metal-ceramic crown in the dentition looks natural.
Fitting and fixation of a metal-ceramic crown
Before installing a metal-ceramic crown, the patient wears a temporary one. All this, together with the temporary cement, is cleaned and the stump is dried. To prevent saliva from getting onto the base, a retraction thread is used. First, simply put on the crown to check the tightness of the fit. Only then does the final fixation of the metal-ceramic crown take place.
Each orthodontist has its own quality control. Some use a strip of paper, others check the installation with dental floss (a piece of paper, thread is held tightly between the teeth). After installing the crown, it is advisable to refrain from eating for 2-3 hours.
Possible problems and complications
Installation of a metal-ceramic crown is a mini-operation in the oral cavity, with local anesthesia at the request of the patient, possible (but unlikely) problems. The more positive the clinic’s reputation, the lower the risk of complications, since this is based on the doctor’s mistake.
The most common occurrence is the development of caries under the crown. Causes:
- drying of the tooth if the nerve is removed;
- violation of tightness.
Prevention is considered to be proper dental care. Visiting the dentist once every six months will also prevent complications.
Although metal ceramics are considered biocompatible with the tissues of the human body, another complication that can appear both immediately after installation and several years after installation is toxic or allergic stomatitis. Without ulcers, but with swelling of the tongue, difficulty breathing, drooling, burning of the tongue. With toxic stomatitis, there will be a deterioration in health (pain, heaviness in the liver, kidneys), itchy skin, and urticaria. Please note: if the frame is made of gold or silver-palladium, cases of such stomatitis are rare.
Sometimes patients complain of chipping of the ceramic coating. Most likely reasons:
- incorrect frame modeling;
- improper processing of the area for ceramics (the surface is too smooth, poorly polished, without an oxide film, etc.);
- selection of materials without taking into account physical and chemical characteristics;
- violation of the technology of applying layers, firing and cooling;
- too many firings to change color or shape (ceramics shrink);
- uncorrected occlusal interlocking contacts;
- internal stresses in the metal part of the crown due to improper preparation of the supporting teeth and fitting of the frame.
If the ceramic part breaks off, you need to contact an orthodontist. If a piece is swallowed, it is advisable to immediately rinse the stomach.
At the dentist's appointment
- Try to listen carefully to the dentist about possible prosthetic options. Do not hesitate to ask questions (your understanding of the treatment process is very important).
- Make a decision on one or another prosthetic option. Ask about the timing and total cost of treatment. Ask for a detailed treatment plan indicating the full cost, payment schedules and treatment time frames.
- Check the warranty period. Read the contracts carefully. If something worries you or you have doubts, do not hesitate to take a time out.
Remember! It is better to consult several doctors before starting anything.
Avoid! Promises and bravado, if you have previously consulted with several doctors and only one promised you what others refused, then we advise you to contact those who refused.
Carefully! If the clinic lures you into paying the full amount of treatment immediately REMEMBER that you will not get it back. Try to avoid clinics with this approach to taking money despite the discounts offered.
Caring for metal and ceramic crowns
Metal ceramics do not require special care. Enough:
- brush your teeth regularly to remove food debris;
- rinse with rinses (for example, “One Drop Only”, “Paro Chlorhexidine 0.12%”), intended for daily care for gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis, as well as after surgical operations on the oral mucosa;
- rinse with warm decoctions of herbs (for example, chamomile, lemon balm, rosemary, sage, bloodroot, witch hazel), which reduce bleeding gums.
To care for the crown, it is better to purchase a toothbrush specially designed for people with implants, dentures, or orthopedic structures (especially if no ledge is created during preparation). They clean the interdental spaces, gingival areas of the teeth, and the space under the crowns well. The brushes are small, the working part is usually a bundle of fibers collected into a cone, or 1 row of bundles.
Caring for metal-ceramic crowns
The most popular orthodontic toothbrushes:
- "Antiplaque". The bristle profile is V-shaped. Designed for patients with various orthodontic structures (crowns, braces).
- Oral-B Interdental. There is a removal-fixation system with a “volcano-shaped” tip, which makes it easier to replace cone-shaped or cylindrical brushes.
- "StaiNo Interdental Brush" ("Sultan"). Aluminum oxide abrasive bristles are used. The brush cleans well the interdental spaces and the space around bridges and braces. The brush designs and color markings are different.
- Lacalut Interdental. There are 2 replaceable heads for cleaning interdental spaces and effectively processing orthodontic structures and bridges. Used without toothpaste.
The dental floss recommended by dentists for cleaning a metal-ceramic crown without the risk of damaging it is Oral-B Super Floss. This is a triple thread, which includes:
- a short, rigid tip for ease of entry into the interdental space and under the body of a bridge or orthodontic structure;
- A section of soft nylon fiber (sponge floss) cleans areas around and in wide spaces between teeth;
- regular floss removes plaque in the periodontal sulcus.
Superflosses are specially designed for patients who have permanent orthopedic crowns. It is not recommended to use regular threads.
Electric toothbrushes and irrigators cannot damage a high-quality metal-ceramic crown. However, if the manufacturing technology is violated, the supply of water under pressure, as well as pulsating or reciprocating movements can lead to microcracks.
When choosing a toothpaste, you should pay attention to products that provide the prevention of caries, periodontal diseases and oral mucosa. Remember: tooth ceramics are dense, not porous. There is no point in using special whitening pastes; you can continue to use the one you are used to.
How much do metal-ceramic crowns cost?
The cost of metal ceramics consists of:
- metal base (a gold frame, of course, costs more than a palladium alloy);
- ceramics (the price of ceramic mass depends on the manufacturer. For example, a jar of MC Emotions Opaque powder - 3200 rubles for 20 g);
- volume of work of a dental technician;
- electricity costs (firing);
- depreciation;
- additional expenses (taxes, rent, payment for third-party services).
As a result, the approximate cost of manufacturing a fixed metal-ceramic prosthesis is from 5,000 rubles. And then you need to add the price for diagnostics, preliminary treatment, preparation, installation. The total cost of visiting a dental clinic (1 crown) can reach 250 thousand rubles.
Prices on the website of any clinic are approximate. Each case is individual, so it is better to prepare in advance for an increase in costs by about a third.