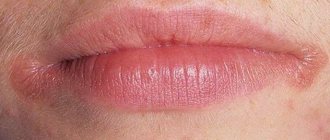
Herpes
is a viral disease. One of the most well-known manifestations of a herpes infection is small, clear, painful blisters on the lips. Previously, in such a case they said “a cold on the lip popped up”, now they more often talk about “herpes on the lip”.
However, the family of herpes viruses is quite large. There are several types of herpes virus that can infect the human body. The most studied types are:
- herpes simplex virus type 1
(HSV-1). It is he who is responsible for pimples on the lip. HSV-1 primarily affects the mucous membranes of the lips, oral cavity and nasopharynx. Herpetic rashes can also appear within the nasolabial triangle (in particular, on the wings of the nose), less often on the cheeks and other parts of the face. Recently, HSV-1 quite often becomes the cause of herpetic lesions of the genital area, where it is introduced through oral sex; - herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) – genital herpes
. Main manifestations: redness, the appearance in the area of redness of bubbles filled with liquid, tending to merge, the appearance of erosions and crusts at the site of the bubbles, itching, headache and muscle pain, increased urination; - chickenpox virus
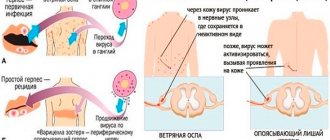
(varicella) is a type 3 herpes virus. In people who have already had chickenpox, this type of virus causes herpes zoster. Therefore, this type of herpes is also called Varicella-Zoster; - Epstein-Barr virus
(Epstein-Barr viral infection - EBVI) is a type 4 herpes virus. It is the causative agent of mononucleosis, causes malignant diseases of lymphoid tissue, and is considered the cause of chronic fatigue syndrome; - cytomegalovirus
– herpes virus type 5. The virus poses a threat to children during fetal development. May affect internal organs.
Causes of herpes
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) can be transmitted through household contact. Airborne transmission is also possible.
The airborne route is the main route of infection with the varicella zoster virus.
Genital herpes and cytomegalovirus are transmitted sexually.
You can also become infected with herpes through blood or saliva. The virus can be transmitted through saliva through kissing. Small children who put things in their mouths every now and then are also very vulnerable. If at least one child in a children's group is infected, a rapid spread of the infection can be expected.
Variety No. 6: boil, or boil
A white sore under or above the lip, which is filled with pus and hurts, is a boil, that is, purulent-necrotic inflammation of the sebaceous or hair gland and the surrounding connective tissue. Of course, the formation does not immediately become purulent. At first, only swelling and redness of the tissues are noted, later a painful abscess appears.
The main causes of the problem: injuries and bacteria entering wounds due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
This is what a boil on the lip looks like
If immunity is good, then the boil forms within 4-5 days, after which it opens spontaneously. Pus and blood come out of it, and all you have to do is carefully treat the wound with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine until complete healing, and also take vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system. To speed up the spontaneous rupture of the boil, you can make applications with ichthyol ointment.
If the immune system is weak due to chronic diseases, and also if you have tried to squeeze out the pus on your own ahead of time, the boil can be complicated by an abscess, phlegmon and even sepsis.
In general, often sores on the lip are a completely harmless phenomenon. They may simply be the result of an allergy to some food product or hygiene product. In this case, it will be enough to eliminate the irritating factor and take an antihistamine like Erius, Suprastin, Zodak. But sometimes they indicate serious problems in the body that require contacting a specialist.
In any case, be attentive to your health. If wounds and abrasions appear on the lips, or if there are injuries, do not forget to treat the tissue with antiseptics. If you find a formation that does not go away for a long time, grows and causes concern, then it is better not to delay contacting a doctor.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 4 ratings, average: 4.25 out of 5)
prevention
- Kazantseva I.A. The effectiveness of acyclovir in the prevention of recurrent herpes of the lips after dental treatment // Bulletin of the Russian Peoples' Friendship University (Series: Medicine). – 2008.
Expert “Do not try to cure aphthous stomatitis on your own, because the set of medications will directly depend on the factor that caused the disease. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. So, for fungal infections, antifungal drugs are prescribed, for viral infections, antiviral drugs. With such a problem, it is better to seek advice from a dentist or general practitioner.” Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Herpes symptoms
Currently, most people are infected with some type of herpes virus. It is believed that antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus can be detected in almost every adult (up to 98% of the adult population of the Earth). Antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 are detected in 90% of the adult population of large cities.
However, as a rule, carriage of a herpes infection does not lead to the development of the disease. The herpes virus is activated when the body's defenses decrease. The weaker the immune system, the more likely the virus is to transition from dormant to active.
That is why the herpes simplex virus type 1 is popularly called “cold on the lip.” The appearance of herpetic rashes is usually preceded by a common runny nose, that is, ARVI. The disease weakens the immune system, which is what the herpes virus takes advantage of.
Symptoms of herpes simplex
When infected with herpes simplex virus type 1, the incubation period ranges from 1 to 8 days. Typical symptoms: chills, fever up to 39-40°C, headache, general weakness and drowsiness. Then redness appears, in place of which characteristic bubbles form. When the oral mucosa is affected, blisters are usually found on the inside of the lips, tongue, and less often on the palate, palatine arches and tonsils. Bubbles appear at the site where the virus enters the mucous membrane. Subsequently, the bubbles burst, leaving behind painful erosions.
The disappearance of symptoms does not mean complete recovery. The virus remains in the body and after some time (in conditions of decreased immunity) a relapse of the disease is possible. Relapses can occur 1-3 times a year for several years and even decades.
Symptoms of genital herpes
The incubation period of genital herpes lasts from 1 to 10 days, after which itching (burning) may be observed in the areas of future rashes. After which swelling appears, and then groups of bubbles appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged. The blisters burst and erosions and ulcers form in their place. The process can last from two to five weeks.
Relapse of the disease is possible within two weeks after the initial lesion. Relapses occur in at least half of those who have recovered from the disease.
Types of stomatitis in adults
Effective treatment of stomatitis in adults begins with the diagnosis of pathology. Identifying the provoking factor is one of the main tasks of the dentist. The situation is aggravated by the fact that many reasons are similar - they overlap each other, distorting the clinical picture. For this reason, only experienced doctors treat stomatitis in adult patients.
There are a variety of classifications of stomatitis:
- according to the course - acute periodic, chronic, recurrent;
- by external manifestation - redness, aphthae, erosion;
- by localization - on the lip, on the tongue, on the palate, in the throat.
When diagnosing and selecting a treatment plan, dentists try to take into account the versatility of the disease - the form, causes, degree of damage to the mucous membranes, stage of the disease, and other classification parameters. Based on these factors, it is customary to identify the most popular types of stomatitis in adults:
- aphthous;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- prosthetic;
- allergic;
- ray.
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of round ulcerative formations covered with necrotic plaque. This is the most common variant of the disease - it occurs in 65-70% of dental patients.
The causes of aphthae formation are viral and bacterial diseases. Localization of ulcers is on almost any mucous tissue of the oral cavity.
Initially, the patient is faced with the fibrinous form, when local blood circulation is disrupted. If left untreated, the disease turns into a necrotic form, accompanied by tissue death, or into a scarring form - the mucosal tissue changes structure.
Ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by the formation of deep, painful ulcers in the mouth. They usually arise due to:
- poor hygiene - a large amount of plaque on the teeth, tartar;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - metabolic disorders;
- chemical burns - abuse of especially spicy foods.
Lesions affect the deep layers of tissue, so treatment of ulcerative viral or bacterial stomatitis in adults is carried out only by a dentist according to a carefully developed plan.
A separate type of ulcerative stomatitis is ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis, Vincent's stomatitis. The cause of the disease is the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, the influence of spindle bacillus and Vincent's spirochete. The disease is observed against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity and is characterized by reactive development. Patients complain of swelling of the gums, suppuration, pain, putrid breath, and loss of appetite. Without treatment, tissue necrosis progresses and tooth roots are exposed.
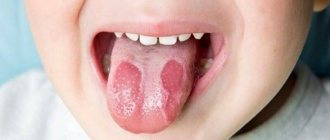
Herpes (herpetic) stomatitis
Viral herpetic stomatitis is a contagious variant of the disease provoked by the herpes virus. Transmitted through hygiene items, through negligence, by airborne droplets.
Externally it differs from other types, since the lesions look like fluid-filled blisters before turning into ulcers.
During treatment, the doctor conducts complex therapy, including taking medications.
Candidal stomatitis
The cause of candidal stomatitis is a fungus that causes the appearance of a cheesy coating on the oral mucosa. Underneath the plaque is a swollen, inflamed area. When the formations are removed, the tissue surfaces begin to bleed.
The causes of the disease are decreased immunity and poor hygiene. Treatment requires careful selection of drugs so as not to aggravate the situation.
Prosthetic stomatitis
The pathology is typical only for adult patients, as it is a consequence of improper prosthetics, individual intolerance to the crown material, and poor quality of care for the orthopedic product.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the soft tissues around the prosthetic structure, turning into ulcers and erosion.
Allergic stomatitis
A distinctive feature of the disease is dryness and itching in the mouth. This is how increased sensitivity to allergens manifests itself. At the site of the inflamed areas, aphthae and ulcers quickly form. In severe cases, an ulcerative-necrotic form may develop.
Pathology happens:
- acute - single manifestation;
- chronic - with constant relapses and complications.
Treatment requires an integrated approach.
Radiation stomatitis
The reason for the appearance is the patient undergoing radiation therapy or chemotherapy and, as a result, a decrease in immunity. It occurs acutely - with inflammation and ulcers. Requires careful attention from the doctor during treatment to avoid worsening the situation.
Methods for diagnosing herpes
Diagnosis of herpes is carried out, first of all, on the basis of examination of the patient, since herpetic rashes have a certain specificity. However, your doctor may order laboratory tests. Laboratory tests can detect infection even in the absence of obvious manifestations.
Herpes test
Be prepared that if you suspect a herpes infection, the doctor will write a referral for a blood test, which will determine the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus in the blood. Based on the results of the analysis, it will be possible to judge not only the presence of the pathogen, but also its activity.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Why do sores form?
An ugly and painful abscess that appears suddenly and seemingly out of nowhere is a fairly common occurrence. Any neoplasm on the body, mucous membranes or inside the body requires a medical examination so as not to aggravate the malaise with further complications.
Only a doctor can reliably determine the reason for the ulcers. They can be located in any part of the oral cavity; white, bloody bumps in the lip area are often observed.
Research has shown the following reasons for their occurrence:
- the mucous membrane is damaged with the formation of microcracks, a favorable place for the development of microbes that cause inflammatory processes
- a consequence of colds, weakening of the immune system, leaving viruses in the form of herpes
- trauma to the mouth from thermal and chemical substances
- from being in the wind, drafts
- allergy or trigger of another disease
- insufficient hygiene care
Each unfavorable manifestation is different in its appearance, has a certain classification of infectious origin, but these inflamed skin, abscessing mucous membranes are united - the treatment has its own identity. The effectiveness of the procedures performed depends on the severity of the infection.
Treatment methods for herpes
Treatment of herpes is aimed at suppressing viral activity, as well as increasing immunity. Oral and topical medications may be prescribed.
The selection of drugs is carried out by a doctor depending on the type of disease (type of infection), as well as on the location of the lesion.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the herpes virus from the body. That is why it is important to always maintain the body’s defenses at a sufficiently high level, and also to prevent re-entry of the virus.
Prevention of herpes
If a person close to you has manifestations of herpes (“a cold has popped up on the lip”), try to ensure compliance with the following hygiene rules:
- use an individual towel and personal hygiene products (soap, toothbrush, etc.);
- be careful with cosmetics: do not use lipstick of a sick person;
- If you have genital herpes, avoid sexual intercourse.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Variety No. 4: lipoma or wen
If a white spot of soft consistency appears on the lip, which does not hurt, but mainly causes aesthetic problems, then we can talk about a normal benign neoplasm, inside of which epithelial cells and fat have accumulated.
The main reasons for the appearance of wen are metabolic disorders, hormonal changes, unbalanced nutrition, and the use of low-quality cosmetics.
This is what a wen looks like
As a rule, wen grow and develop very slowly. It may take more than one year until the problem begins to seriously spoil the aesthetics of your smile. What to do in this case? Do not try to squeeze out the lipoma yourself, as you can introduce an infection inside and also leave deep scars and scars on the delicate skin after the wound heals.
The most correct decision is to consult a doctor who will select the most effective and minimally invasive method of treatment. In some cases, a specialist may prescribe compresses with ointments, for example, “Vitaon”, “Videtim”. If drug treatment for lipomas does not bring results, then a procedure is prescribed to remove them using a laser or piezo knife.