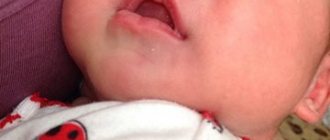
The appearance of herpetic rashes on the lips of a baby can alarm any mother. Some believe that colds on the lips or herpes in children are a simple disease that does not require special treatment. However , herpes in children has many faces. There are 8 strains of herpes viruses, the activation of which causes the appearance of infectious symptoms. The best known are herpes viruses types I and II, which cause the appearance of blisters filled with transparent contents on the lips and genitals, accompanied by itching and mild tingling. Different types of herpes viruses can manifest themselves in the form of such diverse and sometimes dangerous diseases as cytomegalovirus infection, chickenpox, herpes zoster, and infectious mononucleosis.
How is herpes transmitted to children?
The herpes virus is very common and lives in almost all living things. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact . Once the herpes virus enters the body, it remains there for life. However, it can be in a “sleeping” state and not bother a person. If the herpes virus in a child has made itself felt, parents need to pay attention to this problem, because some herpes infections can take forms that are dangerous to health.
Children become infected with the herpes virus more often than adults, but overprotecting a child from infection is pointless and harmful. immunity to it . But the body is safe only in a situation where the infection is easy and without complications.
Enteroviral stomatitis
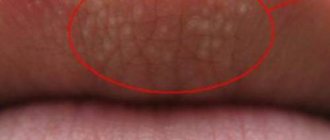
Enteroviral stomatitis (hand-foot-mouth syndrome) is also characterized by the formation of painful aphthae on the tongue, under the tongue, on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips, on the soft palate and at the base of the gums. Accompanied by a blistering rash around the mouth, on the palms, back of the hands, feet, back of the thighs and buttocks of the child, fever, sore throat, headache, loss of appetite.
The causative agents of enteroviral stomatitis are the Coxsackie virus and other enteroviruses. The disease is very common among young children in the summer and is transmitted through contact with an infected person through the airborne or fecal-oral route: through dishes, hygiene items, bedding, toys.
The incubation period (from infection to the onset of symptoms) is 3 to 6 days. Fever is often the first sign of illness. Painful aphthae in the mouth appear 1–2 days after the onset of fever, then rashes are observed on the arms, legs and buttocks. Enteroviral stomatitis does not require special treatment, all signs and symptoms of the disease usually disappear after a week, and the child’s condition returns to normal.
Types of disease in children
There are 80 types of herpes virus, of which 8 are dangerous to humans. The nature of the disease and the type of herpetic rash depend on the type of herpes simplex virus (HSV):
- Type 1 HSV - looks like cold-like rashes in the form of blisters on the lips, causes herpetic stomatitis and herpetic encephalitis.
- Type 2 HSV – manifests itself as a rash on the genitals (genital herpes).
- Type 3 HSV – causes chickenpox and recurrent herpes zoster.
- The 4th type of HSV - Epshane-Barr virus, causes malignant lymphoma and infectious mononucleosis - an acute viral disease with fever, damage to the respiratory tract, lymph nodes, liver, spleen and blood.
- Type 5 HSV – cytomegalovirus; affects the respiratory system, internal organs, intestines, eyes, brain, nervous and urinary systems.
- Type 6 HSV - causes viral eczema - exanthema - pseudorubella-type rash;
- The 7th and 8th types of HSV have not been sufficiently studied. Source: A.G. Lateral Herpesvirus infections in children - an urgent problem of modern clinical practice // Children's infections, 2010, No. 2, pp. 3-7
Infectious mononucleosis
Another disease of viral etiology with severe “cold” symptoms. The main causative agent of infectious mononucleosis is the Epstein-Barr virus (rarely other viruses). The infection spreads through saliva.
The disease is typical for adolescents and young adults (the so-called “kissing disease”), but young children can also become infected with infectious mononucleosis through contact with objects touched by an infected person (for example, through dishes). Most adults already have antibodies to IM because they have been exposed to the infection, so they are immune and do not get sick. In people with a weakened immune system due to concomitant pathologies or organ transplantation, MI can cause serious complications and other diseases (anemia, meningitis, encephalitis, myocarditis, etc.).
Symptoms of MI appear approximately 4–6 weeks after infection and may develop slowly and not all at the same time. They include severe sore throat, weakness, fatigue, fever, loss of appetite, enlarged neck and axillary lymph nodes, inflammation of the tonsils with white plaque, headache, muscle pain, skin rashes, abdominal pain, enlarged spleen or liver.
Most patients recover within 2–4 weeks of onset of symptoms, but some continue to experience symptoms of MI (eg, fatigue, enlarged lymph nodes, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly) for several weeks or even months.
The disease is diagnosed based on symptoms, their duration and specificity, as well as a physical examination. A blood test for antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus and a general blood test to determine the level of leukocytes (prescribed if necessary) help confirm the diagnosis.
The symptoms of MI are quite unpleasant and cause significant discomfort to the patient, but the disease goes away on its own, without treatment or any consequences. Drinking plenty of fluids, rest and a healthy diet are recommended. To relieve symptoms (sore throat, headache, muscle pain, fever), it is recommended to use paracetamol or ibuprofen, or gargle with salt water. The addition of a secondary infection (streptococcal, for example) requires the use of antibacterial drugs. If the airways are severely narrowed and there is difficulty breathing, corticosteroids may be prescribed. To reduce the risk of rupture of the capsule of an enlarged spleen or liver, it is recommended to avoid exercise, heavy lifting, and contact sports for at least a month, or until the liver and spleen return to normal size.
Virus activity
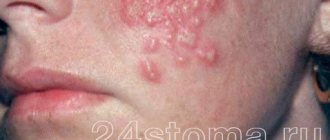
Most often, children are faced with the herpes simplex virus, which manifests itself in the form of that same cold on the lips.
Herpes on the lips or chickenpox are not as dangerous for a child as herpetic lesions of the eyes, genitals, and internal organs.
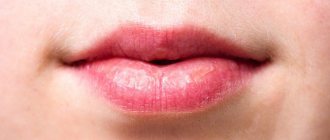
Externally, herpes appears as a rash on the skin or mucous membranes. It usually looks like small blisters that eventually burst and become sores. In addition to the rash, there is burning and itching.
How often the herpes virus is activated is influenced by hereditary predisposition and the state of the immune system. The weaker the child’s immunity, the more susceptible he is to virus attacks.
Newborns up to 1 year of age are protected by maternal antibodies. The peak incidence is observed at the age of 2-3 years. By the age of 15, up to 90% of adolescents are infected with HSV. The pathogen is in an inactive state in the body and does not cause discomfort. Under unfavorable conditions, HSV is activated. Source: A. Taieb, N. Diris, F. Boralevu, C. Labreze Herpes simplex in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnostic value of clinical signs, clinical course // Ann Dermatol Venerol, 2002, v.129, No. 4, p.603—608
Causes of exacerbations and relapses of herpes in children:
- decreased immunity due to severe and prolonged illnesses;
- severe shocks and chronic stress;
- systematic fatigue;
- hypothermia;
- taking hormonal medications;
- endocrine pathologies;
- hormonal changes in adolescence;
- systematic unbalanced diet;
- complicated seasonal colds;
- chemical and radiation anticancer therapy;
- excessive physical activity. Source: M.N. Kankasova, O.G. Mokhova, O.S. Pozdeeva Frequently ill children: the view of an infectious disease specialist // Practical Medicine, 2014, No. 9(85), pp. 67-71
Flu
An annual flu vaccination is the most reliable way to prevent severe disease and complications (otitis media, pneumonia) of the disease.
Vaccination of children against influenza is permitted from the age of six months.
Influenza is an acute respiratory viral disease caused by influenza viruses (usually types A or B; type C rarely causes serious symptoms). It is very easily transmitted from person to person, as confirmed by annual epidemics of the disease. People with the flu are most contagious in the 24 hours before symptoms appear and until symptoms subside (about a week).
The flu can be confused with a cold, but most often it is more severe. Symptoms - fever, chills, headache and muscle pain, runny nose, sore throat, cough, ear pain, loss of appetite, weakness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea - appear approximately 2 days after exposure to the virus.
Most children with the flu recover at home, but if the disease is severe or has complications, they will need hospital treatment.
There are no effective cures for the flu; it is necessary to ensure that the child drinks plenty of fluids and is not dehydrated, gets plenty of rest and sleep; in general, the same tactics are followed here as with any ARVI. To relieve flu symptoms (reduce fever and reduce pain), you can use paracetamol or ibuprofen, rinse your nose with saline solution (for infants, saline solution is dripped into the nose, an aspirator is used to remove nasal discharge), and monitor the level of humidity in the room.
Important: antibiotics are not used to treat influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections.
Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms worsen, severe cough, difficulty breathing, fever in children under 3 months of age that lasts longer than 3 days, headache that does not go away with paracetamol or ibuprofen, stiff neck ( meningeal symptom).
More details
Flu
Treatment of herpes in children
It is impossible to eliminate the herpes virus from the body, so the goal of treatment is to reduce its activity , eliminate symptoms by activating the immune system, achieve stable remission and prevent complications.
The most effective medicine against most manifestations of the herpes virus in children is the substance acyclovir. Treatment uses both oral and local medications. Source: I.F. Barinsky, L.M. Alimbarova, A.A. Lazarenko, F.R. Makhmudov, O.V. Sergeev Vaccines as a means of specific immunocorrection for herpetic infections // Questions of Virology, 2014, pp. 5-11
A comprehensive treatment regimen for acute herpetic infection includes:
- antiviral-antiherpetic drugs - tablets, injections and ointments - based on acyclovir;
- surface antiseptics for the prevention of secondary bacterial infections;
- immune stimulants – herbal and interferon derivatives;
- multivitamins and vitamins in therapeutic doses;
- antipruritic antihistamines;
- antipyretics;
- hepatoprotectors – in case of severe intoxication;
- diet therapy with sufficient amounts of protein and exclusion of foods that are sources of arginine.
In severe general condition, bed rest is recommended. Only a doctor can decide how to treat herpes in a child.
Which doctor treats a rash on the lips
A rash near the lips can be a dangerous symptom. If such manifestations occur, you should definitely visit a doctor, undergo prescribed tests and, if necessary, a course of treatment. First, you should visit a dermatologist, who will prescribe diagnostic procedures to identify the disease.
Even if the test for herpes is positive, many more parameters are taken into account when prescribing therapy: the number of antibodies, the stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body. This disease has 8 varieties, and appropriate treatment is selected for each.
If a reaction to certain substances and products develops, consultation with an allergist is required. There is often a need to visit an immunologist, since most diseases associated with a rash on the lips progress against a background of weakened immunity. But you should not visit the dentist if you have such symptoms. During dental treatment, the vesicles can become damaged and become infected, which causes inflammation and complications.
Possible complications
Without timely and adequate treatment, herpes infection can cause severe complications:
- disruption of internal organs;
- eye diseases;
- deafness;
- sore throat;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- infertility.
Sources:
- A.G. Side. Herpesvirus infections in children - an urgent problem of modern clinical practice // Children's infections, 2010, No. 2, pp. 3-7.
- Taieb, N. Diris, F. Boralevu, C. Labreze. Herpes simplex in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnostic value of clinical signs, clinical course // Ann Dermatol Venerol, 2002, v.129, No. 4, p.603-608.
- M.N. Kankasova, O.G. Mokhova, O.S. Pozdeeva. Frequently ill children: the view of an infectious disease specialist // Practical Medicine, 2014, No. 9(85), pp. 67-71.
- I.F. Barinsky, L.M. Alimbarova, A.A. Lazarenko, F.R. Makhmudov, O.V. Sergeev. Vaccines as a means of specific immunocorrection for herpes infections // Questions of Virology, 2014, pp. 5-11.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy 1 element | 700 rub. |
| Setting up functional tests | 190 rub. |
| Excision/removal of cutaneous/subcutaneous elements and formations (1 element) | 2550 rub. |
| Removal of milia of one unit using electrocoagulation | 350 rub. |