Types Causes Treatment methods Diagnostics Prevention
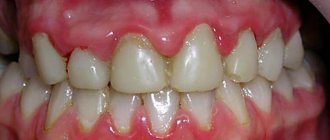
Toothache does not always bring us to the dentist. Quite often, problems are caused not by teeth, but by unpleasant sensations in the mouth, red spots on the tongue, and a burning sensation. These signs are characteristic of a variety of diseases, often systemic, but can serve as symptoms of glossitis - inflammation of the tongue.
Causes of the problem
A red spot on the tongue can be a manifestation of a variety of pathologies, for example:
- Vitamin deficiency
Redness of the tongue is caused by a deficiency of B vitamins and niacin.
- Allergy
Response to food, drinks, drugs
- The burn is
not only thermal, but also chemical. The Internet is full of different, sometimes strange, advice. Experimenting on yourself can have sad consequences.
- Hormonal imbalance
Red spots on the tongue often appear in women during pregnancy and menopause.
- Infections of various etiologies
Bacteria and viruses provoke inflammatory processes, one of the symptoms of which is discoloration.
Red spots on the tongue are not yet a diagnosis. A doctor needs to conduct an examination to determine the exact cause.
Redness of the tongue may indicate various diseases.
What does this mean?
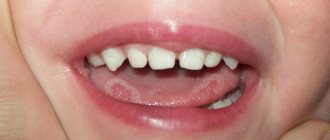
The appearance of red dots on the tongue can be caused by a number of reasons, including those that do not threaten health and life. However, in some cases, such rashes indicate the appearance of a specific disease.
Red dots can have different origins:
- wound, petechiae - slight hemorrhage (with a burn of the tongue, for example);
- telangiectasia, that is, spider veins;
- ulcer;
- erosion;
- epithelial tumor of malignant and benign nature;
- rashes (macula, papule, roseola).
That is why it is of great importance to seek medical help in the case when a person finds red dots on the root of the tongue, as well as on other parts of this organ, in his child or himself.
Diagnosis
It is difficult to independently distinguish relatively harmless manifestations of diseases in the form of red spots from serious disorders. Any rash on the tongue already indicates systemic problems, but some of them indicate serious cases.
Erythroplakia requires immediate surgical intervention. Therefore, it is better not to take the position “it will go away on its own,” but to consult a doctor.
Since spots on the tongue are a symptom of disease, examination is usually aimed at identifying the causes. Laboratory tests, flora tests, histology and medical history allow us to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Why do red dots appear?
Red dots on the tongue most often appear with stomatitis (inflammatory processes of the oral mucosa). There are quite a few direct causes of the development of stomatitis, but most often it is a viral infection, for example, of a herpetic nature.
Other factors also include pathogenic bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci), poor nutrition, fungi (for example, candidiasis), thermal or mechanical injuries, side effects of a number of medications, anemia, hormonal imbalance, decreased salivation, and dehydration.
The next common cause of red dots is allergies. It most often differs in food origin. You can suspect it when keeping a food diary. In this case, it is convenient to note the relationship between the appearance of a rash and the use of a specific product.
What are the reasons for red dots and white coating on the tongue? More on this below.
Disease prevention
Dental measures include:
- Regular thorough oral care.
A properly selected toothbrush, constant flossing, and rinsing your mouth after eating will help avoid inflammatory processes.
- Use a toothpaste that suits the purpose at this stage. You cannot use whitening or medicinal pastes constantly, only in courses.
General preventive measures:
- Healthy lifestyle
- To give up smoking
- Regular medical examinations
Treatment of glossitis of the tongue
First of all, the treatment plan depends on the type of inflammation. It is compiled individually, based on clinical and diagnostic data. For acute catarrhal glossitis, it is important to remove the irritating factor: replace the crowns or, conversely, put crowns on the damaged tooth. Change your eating habits, stop chewing nuts, hard candies, and crackers.
For a folded tongue, oral hygiene comes to the fore.
If lumps and papillomas grow during rhomboid glossitis, they are excised. Laser surgery allows you to do this quickly, with virtually no blood.
The main recommendation for black tongue is treatment of somatic diseases and smoking cessation. Liquid nitrogen is used to remove papillae, as well as applications to keratinized areas.
But there is a general approach to treatment:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- vitamin complexes;
- iron supplements for anemia;
- for pain - light anesthetics in the form of applications;
- for burning - oral baths and irrigation;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- checking for fungal infections.
There are many recommendations on the Internet for treating glossitis with folk remedies. No one disputes the anti-inflammatory properties of chamomile, sage and plantain. When a spot appears on the tongue, applications of sea buckthorn oil and aloe juice can bring relief. But these measures are temporary, they affect the symptoms, but the cause of the disease remains unattended. As a result, it is easy to miss the point when it was not difficult to fix the problem.
Glossitis is closely related to common diseases and psychological causes. Effective treatment is only possible using an integrated approach. How to treat glossitis and what examinations you need to undergo can only be advised by a qualified doctor. Glossitis can be cured quite quickly, but if left untreated, abscesses, tumors, and necrotic tissue changes can form. This is much more serious and the prognosis is not so favorable.
Expert opinion
Roman Borisovich Alekperov
orthopedic dentist
Experience: 24 years
Most often, red spots on the tongue are not accompanied by pain. A slight burning sensation or no symptoms at all creates a dangerous feeling that the problem will go away on its own. This can worsen the condition and cause serious consequences. If you have red spots on your tongue, consult a doctor. It is better to quickly take measures recommended by professionals than to spend a long time on treatment later.
Types of glossitis
All inflammatory processes are divided into chronic and acute, independent and secondary, accompanying other diseases. In any case, problems with the tongue indicate the presence of a disease, so it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Sometimes glossitis occurs without pronounced manifestations, but the doctor will definitely notice changes in the tongue during a routine examination.
Independent diseases (when only the tongue is affected) include several types of inflammation.
Acute catarrhal glossitis
Most often it develops as a result of mechanical damage from sharp edges of decayed teeth, unsuccessful dentures, candies and nut shells. It is a sign of allergies, acute respiratory viral infections or gastrointestinal diseases.
Patients develop red spots on the base of the tongue. Patients experience pain while eating and talking. The tongue swells and becomes covered with a thick coating. Saliva production increases.
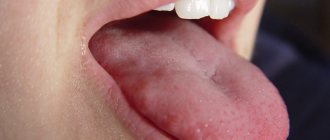
Desquamative glossitis
It has many names: geographic tongue, migrating, exfoliative glossitis. It is he who begins with red spots on the tongue. This occurs due to epithelial detachment (desquamation).
The reasons are not completely clear, but diseases play a certain role in the development of inflammation:
- stomach and intestines;
- edocrine glands;
- hematopoietic organs.
Infectious diseases can provoke inflammation
and
vitamin deficiency
.
All of them disrupt tissue nutrition and, as a result, the epithelium begins to slough off. The red spots are growing. As the spots increase in size, the process of keratinization begins in the center, and the keratinized areas, on the contrary, begin to flake off. This is how glossitis “migrates” from one part of the tongue to another. At the same time, its outline resembles a map, hence the name “geographical”.
In the vast majority, desquamative glossitis is discovered during routine examinations. For a long time it does not cause any inconvenience. But in advanced cases, the tongue begins to react to spices and sours. There are complaints of tingling and burning. The tongue becomes covered with cracks, which can become infected. In this case, the disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, general malaise, and weakness.
Diamond-shaped glossitis
This is an inflammation of the tongue in which red spots have clear boundaries
and
geometric shape
.
Among the reasons are:
- congenital nature of the disease;
- housing and communal services diseases;
- candidiasis of different nature and location.
There are 3 types
rhomboid inflammation. The flat look is the easiest, patients are unaware of it, and only a doctor can see the characteristic red spots on the root of the tongue.
The lumpy and papillomatous types are irritating with the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. Sometimes patients complain of a burning sensation.
Black “hairy” tongue
With desquamative glossitis, the epithelium peels off too much. When the keratinized epithelial cells stop exfoliating at all, they speak of a “hairy tongue.” The size of the papillae increases. They change color as a result of the interaction of iron in food and oral microflora. Most often, the papillae become black or brown.
The reasons may be:
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- infections;
- tuberculosis;
- venereal diseases;
- smoking;
- alcoholic drinks in excessive quantities.
The disease develops gradually and for a long time patients do not pay attention to the changes. Therefore, the sight of a “hairy” tongue can cause a lot of stress. Patients complain of burning, itching, dryness, and foreign body sensation. Sometimes, when talking, gagging occurs. Taste sensations often change.
Folded tongue
This congenital anomaly is detected in children and adults. It is diagnosed less often in children due to the fact that the folds are small. During the period of intensive growth, in puberty, with the growth of muscle tissue, the tongue also increases, the folds appear more clearly. Characterized by changes in the shape and size of the tongue. The transverse folds are smaller, the longitudinal folds are well defined. The main problem of pathology is the accumulation of food debris and bacterial waste products in the folds. This is a favorable environment for microorganisms. They penetrate small cracks and provoke the development of other forms of glossitis. In particular, in 50% of cases, a folded tongue is combined with migrating glossitis. Often inflammation is caused by fungal infections, such as candidiasis.
There is no specific treatment. In the presence of a fungal infection, drugs with a fungicidal effect and ointments against the fungus are prescribed. It is recommended to carefully observe oral hygiene and, along with brushing your teeth, clean your tongue with special scrapers.
Glossodynia
Glossodynia
is a burning mouth syndrome. It usually starts with the appearance of red spots on the tip of the tongue. The tongue is sore and tingling. Pain appears, which subsides while eating, but intensifies in the evening. In 80% of patients, saliva production decreases. The tongue swells, desquamation (detachment of the epithelium) begins. The tongue becomes covered with cracks.
Where to contact
Any dentist will be able to help with advice, but it is still better to contact multidisciplinary clinics. The larger the clinic, the more patients, which means the doctors’ experience is much wider. In addition, high-quality specialists are rarely seen in modest dentistry on the outskirts of the city; they mostly work in large centers. Another reason to contact a multidisciplinary center is that they pay great attention to improving the qualifications of doctors, including in therapeutic dentistry.
The table shows contacts of 5 clinics where you will be advised about red spots on the tongue.
| Dental center | Clinic address | Working hours |
| ROOT | Moscow, st. Rustaveli, 14 building 9 8 800 775–26–37 | 10:00-22:00 seven days a week |
| Your smile.rf | Moscow, Palikha street, 10, building 9 8 | 9:00-21:00 seven days a week |
| Center Family Dentistry | Moscow, Orekhovy Boulevard, 59k2 8 | 9:00-21:00 seven days a week |
| Unident | Moscow, Bobrov lane, 4, building 1 8 | 9:00-21:00 seven days a week |
| CityDent | Moscow, st. Novocheremushkinskaya, 57 8 | 10:00-23:00 day off - Sunday |
Red dots on the tongue and white coating
In some cases, the appearance of red dots is also accompanied by a yellowish or white coating, which is expressed to a certain extent. When it appears on the root of the tongue, the doctor will most likely discover intestinal or stomach pathologies in the patient. These may include, for example, chronic gastritis. In this case, the therapist will most likely refer the patient to a gastroenterologist.
A tongue covered with a white coating and red dots is often accompanied by bad breath. In this case, the cause could be her illness (for example, stomatitis) or diseases of the intestines and stomach. In some cases, the source of pathological signs is insufficient oral hygiene, so you need to brush your teeth on time and use rinses after meals.
How to correctly assess the condition of the tongue?
To independently examine a child’s tongue for plaque or stains, several conditions should be taken into account:
- It is better to carry out an examination in the morning, in natural light and before brushing your teeth;
- the child should stick his tongue forward without straining it, as this will affect the shape and color;
- It is worth remembering that the child ate and drank the day before, so as not to mistake the mark from the eaten cherry for a frightening symptom;
- take into account the fact that you are taking medications, vitamins or sorbents.
During the examination, the parent should pay attention to:
- on the color of plaque;
- its density;
- localization;
- consistency;
- how easy is it to remove?
- How often does it appear again?
Thus, there are only two cases where parents may not worry about their child having plaque on his tongue:
- After a meal, when the child has eaten foods or drunk drinks that temporarily stain the tongue (blueberries, beets, tea, coffee);
- After a night's sleep, in this case, the presence of a light coating is normal and can be easily eliminated through hygiene procedures.
Pale tongue tone
Also, red dots on the tip of the tongue without plaque occur with anemia, but the organ itself turns pale, which is very easy to confuse with deposits. When detecting spots on the tongue, a person does not need to immediately worry and panic. First, you should observe your own condition and check whether such spots disappear within a few days. If there are no changes, even after adjusting the diet and the absence of bad habits, it is advisable to still go to see a doctor and take all the tests required to diagnose the disease, as well as undergo an examination.
Localization
If the tongue has changed and red spots of different shapes and sizes have formed on it, this is a signal about the beginning of the development of a certain disease in the body.
It is important to note on which part of it they appeared:
- At the tip are diseases of the cardiovascular system. A small round spot is formed, the red-blue color of which indicates heart failure, and the dark red color indicates a malfunction of the myocardium.
- On the sides, closer to the base - kidney dysfunction. Small rounded elements are formed.
- On the surface from the middle to the base - changes in the lungs, when redness is complemented by loose plaque, we can talk about the development of bronchitis. Spots with a brown coating indicate pneumonia, and when combined with severe swelling, they are a reason for examination for oncology, tuberculosis or chronic inflammation.
- In the central zone - pathologies of the stomach or spleen. If the surface of the elements is smooth, then we can judge low-acid gastritis. In case of coarsening of the enlarged papillae, gastritis with high acidity is diagnosed.
- Near the root - disturbances in intestinal function. Redness with a whitish coating indicates gastroenteritis, smooth elements in the shape of a crescent indicate problems with the large intestine.
- Along the entire length of the lateral surface - diseases of the gallbladder or liver. Spots accompanied by swelling and a yellow coating indicate liver pathologies. If they appeared only on the left with the same additional symptoms - with the gallbladder.
It is better to examine the surface of the organ on an empty stomach in the morning, after cleaning the mouth and rinsing.
Important: the brighter the color of the spots, the more serious and severe the disease manifests itself.
All the most important things about the treatment of candidal stomatitis, drugs and folk remedies. In this section you will find instructions for using the Panasonic ew 1211 irrigator.
This link https://dr-zubov.ru/ortodontiya/apparaty/kappy/kak-vyrovnyat-zuby-bez-breketov.html contains complete information on how to straighten teeth without braces for adults.
Which doctor should you contact?
Few people know which specialist to contact if their tongue becomes stained. In fact, a whole group of doctors can help establish the cause of the disease and get rid of it: a dermatovenerologist, an ENT doctor, a surgeon, a dentist, a pulmonologist, a gastroenterologist and others. The first thing the patient should do is visit a therapist or dentist, who, if necessary, will refer him to a more specialized specialist.
Any pathology, be it small red dots or redness of the entire surface of the tongue, requires timely consultation with a competent doctor.
Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
One of the reasons that the tongue hurts on the side is Vincent's ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. With this disease, ulcers appear in the oral cavity, which can be located not only directly on the tongue, but also on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, and even spread further:
- on the gums;
- sky;
- tonsils.
The disease is caused by bacteria: spirochetes and fusobacteria. What is especially characteristic of this pathology is that the ulcers are covered with a dirty gray coating. Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis is treated locally with antimicrobial drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are also prescribed.
Homeopathic remedies
| Drugs | Purpose |
| Acidum nitricum | Rashes on the mucous membrane, areas of bleeding, pain and impaired salivation. |
| Mercurius solubilis | For swelling of the tongue, unpleasant odor and impaired salivation. |
| Sulfur | For the treatment of inflammatory processes, impaired taste, symptoms of unquenchable thirst and thick gray plaque on the mucous membrane. |
| Schussler Salze | For the treatment of various types of stomatitis, including desquamative or deep glossitis. |
| Potassium sulfate | With accompanying erosions, ulcers, fungal infections. |
| Borax | Aimed at accelerating regenerative processes when there is damage to the mucosa. |
| Kalium bichromicum | For ulcers and redness on the sides of the tongue and in the root area, it helps to calm. |
| Arsenicum | For the treatment of aphthae, which are accompanied by pain and severe inflammation of the tongue. |
| Acidum nitricum | To eliminate tongue ulcers in young children and adults. |
How can you independently distinguish normality from pathology?
Let us remind parents what is considered normal. This is a language that:
- moderately moisturized and not enlarged;
- has a pink color and a rough texture;
- light white coating, which can be removed with hygienic care.
If during the examination the condition of the tongue corresponds to that described above, then parents have nothing to worry about. When should you be wary? The normal state of the tongue cannot be called a situation where there is a coating:
- lasts for a long time;
- spreads and thickens;
- acquires a certain color;
- gives an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- leads to bad breath;
- reduces olfactory function.
In this case, we can with a high degree of confidence assume the presence of certain disorders in the body. The color will “tell” which ones...