21.07.2021
Author: Dentist-periodontist, therapist Stopinskaya Ulyana Yurievna
Modern dentistry is impossible without reconstructive surgical interventions. Almost all of our patients undergoing dental rehabilitation have encountered one type of surgical treatment or another: implantation, closing recessions, replanting grafts, etc. The success of such treatment depends on many factors. We will look at some of them in more detail.
To begin with, it should be noted that for quick and high-quality healing, the doctor must meet the following conditions:
- Healing by primary intention (bringing together the edges of the wound with sutures). Wound healing refers to all the physiological and regenerative processes that occur when restoring the integrity of damaged tissues. Surgical wounds are created under relatively controlled conditions, i.e. The surgeon can influence certain factors to a certain extent, for example, the type of incision, the method of creating the flap, the width of the receiving bed, and the method of suturing.
The photo shows a view of the wound on the 14th day after surgery. The seams are visible. Healing by primary intention.
- Good blood supply to the intervention area . The difficulty of healing after implantation or plastic periodontal surgery is often due to the fact that the wound is located in the projection of the surface of the tooth or implant, which does not contain blood vessels. This reduces local immunity and makes it difficult to deliver nutrients.
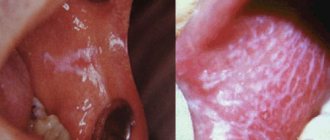
- Cleanliness in the intervention area. The oral cavity is colonized by a large number of bacteria that can directly affect wound healing. The doctor must ensure that on the eve of the operation the patient undergoes professional hygiene and is trained in postoperative oral care.
The photo shows the view before and after professional hygiene
Now let's take a closer look at the factors influencing wound healing. They can be divided into general and local.
Causes of sores in the mouth
The oral mucosa has increased sensitivity to adverse environmental factors. Wounds appear for the following reasons:
- Aphthous stomatitis refers to chronic diseases of the oral cavity. Manifests as ulcers, aphthae on the mucous membrane. With pathology, many ulcerative defects develop on the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue, and palate.
- Herpetic infection affects the skin, membranes, and internal organs. Herpetic stomatitis is manifested by numerous small ulcers, which are located in groups at the bottom of the oral cavity.
- The appearance of wounds on the mucous membranes of the mouth is caused by poor hygiene. Failure to comply with hygiene procedures is more common in children. Babies may suffer from Bernard's afte. They represent ulcerative defects that form on the hard palate from the mechanical impact of foreign objects.
- The wound appears from an accidental bite.
- A hard toothbrush, dentures, dentures, pointed crowns, the habit of biting the lips, and strong blows to the cheeks cause the defect.
- During treatment and dental procedures, the patient may receive minor injuries to the gums, lips, and cheeks from instruments. Dental implantation can also lead to various types of damage to the oral cavity. This is why, among other things, it is so important to trust the installation of implants to qualified specialists.
- The proliferation of fungi on the inner surface of the oral cavity is manifested by ulcers with white cheesy deposits. The first symptoms of candidiasis.
- Lack of vitamins and strong feelings lead to a decrease in local immunity and the appearance of pathological lesions in the mouth.
- Necrotizing periadenitis is manifested by compactions in the submucosal layer, which over time degenerates into painful ulcers. Healing of defects takes a long time.
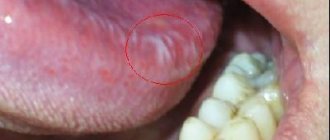
The occurrence of ulcers due to diseases/damage to the soft tissues of the mouth and tongue
1. Recurrent
aphthous stomatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by periodic eruptions of aphthae (small ulcerations) on the oral mucosa. Aphthae can be localized on the tongue, buccal mucosa, hard and soft palate, and also on the mucous membrane of the lips. They are painful. In some cases, with constant injury, aphtha can turn into a long-term non-healing ulcer, after epithelization of which a scar is formed.
Patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis usually suffer from colitis. Nervous strain, minor injuries to the mucous membrane, for example, when brushing teeth, as well as menstruation, can also predispose to the onset of the disease. The aphtha heals within 7 - 10 days. In case of complications of the disease, the number of ulcerations may increase, then the healing period is extended by 2 - 4 weeks.
2. Herpetiform stomatitis
characterized by the appearance of numerous small ulcers. In appearance they resemble the sores of herpes simplex. As a rule, they occur in women under 30 years of age. They are localized mainly on the lower surface of the tongue and in the area of the floor of the mouth. They do not have clear boundaries, the base is gray. The healing process is completed largely without scarring within 7 to 10 days. In simple forms of stomatitis, white ulcers in the mouth are observed (or rather, the center of the ulcer is covered with a thin, loosely fitting white or grayish film). Also, a white ulcer in the mouth can form in children in cases where there is candidal, or fungal, stomatitis.
As for the treatment of stomatitis, in this case the form of the disease and the severity of the lesion are taken into account. General and local treatment depends on this. But for almost all forms of stomatitis, vitamin C is prescribed to improve immunity.
3. Recurrent necrotizing peryadenitis
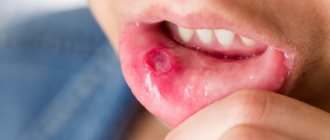
(Setton's aphthae) is characterized by the formation of a compaction in the submucosa, then painful ulcers with raised and compacted edges form in this place, as well as the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate (accumulation of cellular elements mixed with blood and lymph). Ulcers are localized on the upper and lower lips, cheeks, and lateral surfaces of the tongue. Eating food becomes extremely difficult for many patients, even to the point of giving it up. The same severe pain can be observed when talking. The ulcers do not heal until several months, and the disease lasts for years.
4. Afty Bednar
occur exclusively in children and are defined as traumatic erosions (ulcerations). The cause is poor oral hygiene or rough mechanical rubbing of the mucous membrane of the palate (this is where they are located). Covered with a whitish-yellow coating.
5. Traumatic ulcer
in the mouth is most often the result of physical impact, hence its name. As a rule, such an ulcer occurs as a result of an accidental or intentional bite of the mucous membrane, damage by a toothbrush. The presence of a traumatic ulcer in the oral cavity can provoke dental treatment (with careless use of dental instruments or, for example, with pointed temporary crowns).
Also among traumatic ulcers are the so-called prosthetic ulcers, which arise from exposure to complete or partial removable dentures, the dimensions of which are larger than necessary, or their surface is poorly processed and has sharp edges. Such ulcers can be located directly under the prosthetic structure. As a rule, healing takes place within 10 - 14 days, provided that the traumatic factor is eliminated. Treatment may not be necessary, since traumatic ulcers are often painless and small in size. In the case of the opposite, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the use of an ultrasonic brush is recommended, which not only cleans, but also has an antibacterial effect.
Also, the presence of ulcers can be caused by the effects of alkalis, acids, and certain medications on the oral mucosa.
How and what to treat wounds on the oral mucosa
Defects in the mucous membrane are manifested by typical symptoms: pain that intensifies during eating, unpleasant odor, metallic taste. Pathology disrupts the normal rhythm of human life. He gets tired quickly and cannot eat due to severe pain.
Cheap antiseptics (iodine, brilliant green, peroxide), which are available in every home, will help remove unpleasant symptoms.
Gargling with hydrogen peroxide treats symptoms of acute tonsillitis. An antiseptic disinfects the oral wound from microorganisms that cause disease. The instructions for the drug indicate only external use. Representatives of traditional medicine advise diluting the medicine with water to avoid unpleasant consequences. Hydrogen peroxide is diluted: take 1 tsp per 120-150 ml of water. antiseptic. The solution should be warm to reduce irritation of the mucous membrane.
Before using the medicine, you should consult a medical specialist. Thus, specialists from the Ibn Sina dental clinic https://stomatologis.ru/ will help identify the true cause of the disease and determine the tactics for treating a wound in the mouth. Hydrogen peroxide is effective if the ulcers have a traumatic, bacterial etiology.
The medicine will not cope with fungi.
The medication can be used 4-5 times a day for 7-14 days. It's important not to overdo it. Incorrect dilution and frequent rinsing can lead to chemical burns of the mucous membrane. Following medical recommendations will help you avoid this pathological condition.
Ulcers as local manifestations of general diseases on the oral mucosa
- Oral tuberculosis
is usually a secondary manifestation of pulmonary tuberculosis. It occurs as a result of penetration of tuberculosis bacteria into the oral mucosa through damaged epithelium. The membranes of the cheeks, tongue, and floor of the mouth are affected. First, typical tuberculous tubercles are formed, and then, after their disintegration, small ulcers are formed, which increase in size over time. The ulcer itself is not deep, with a loose bottom, which is covered with easily bleeding granulations (young tissue), uneven edges are observed, soft to the touch. With this disease, there is a sharp pain in the ulcer. In addition to the local manifestation in the form of an ulcer, there is a general deterioration in the well-being of patients: emaciation is noted, the amount of plaque on the tongue increases, sweating and body temperature increase. General treatment of tuberculosis of the oral mucosa is carried out in specialized anti-tuberculosis institutions. As for local treatment, in this case, sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out during the period of remission (weakening of the disease), treatment of the mucous membrane with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents. - Syphilis
is a chronic infectious disease caused by the so-called Treponema pallidum. All periods of development of this disease (in addition to the incubation period, which lasts 21 - 24 days) are characterized by the presence of ulcers in the oral cavity. At the initial stage of development of the disease, the presence of a painless ulcer is observed, which has a round or oval shape with raised, smooth edges and a cartilage-like specific infiltrate. The bottom of the ulcer is bright red, shiny or covered with a grayish-dark coating. The ulcers heal in 3 to 12 weeks with or without scar formation. Even with tertiary syphilis, there is no sharp pain, as, for example, with a tuberculous ulcer. The ulcer is surrounded by a powerful infiltrate, which is a dense bluish-red ridge that rises above the level of the mucosa. Its edges are smooth, bright red, covered with granulations, and bleed easily. After the ulcer heals, a retracted star-shaped scar forms. This process lasts 3 - 4 months. After the ulcers heal, scars remain, which are a sign of previous syphilis. General treatment of syphilis is carried out in a venereology hospital, local treatment is carried out during the period of remission or recovery (sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of local traumatic factors). - Acute necrotizing gingivostomatitis
is a viral infectious disease. Most often, ulcers are localized on the mucous membranes of the gums, cheeks, soft palate, arches and tonsils. Favorable factors for the development of this disease are a decrease in the overall resistance of the body, a violation of the integrity of the oral mucosa, and a deficiency of vitamins in the body. There are also cases of this disease occurring against the background of cooling or overwork. It can also be a complication of viral infections, as well as allergic stomatitis. Usually young people (under 30 years of age) are affected, more often men.
Among the symptoms it is necessary to highlight: pain when eating; extremely unpleasant odor from the mouth; increased salivation; elevated body temperature. The gum mucosa becomes swollen, painful, and bleeds when touched. The epithelium of the gingival margin and gingival papillae becomes cloudy. The surface of the gingival margin is covered with a grayish-yellow coating, which is easily removed. The ulcers have soft, uneven edges and are covered with a dirty green coating (with a foul odor), which is easily removed. In this case, a loose bleeding bottom is detected. The surrounding tissues are swollen.
Treatment of necrotizing gingivostomatitis is carried out in accordance with the general condition of the body, taking into account its location and severity of the lesion. In moderate and severe stages of the disease, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, as well as drugs that prevent or reduce the manifestation of allergies. At any stage of development of the disease, vitamins C and P, high-calorie foods, juices are prescribed, and in some cases, according to indications, taking cardiac medications.
Local treatment is carried out under anesthesia (removal of necrotic tissue). The oral cavity is treated with warm solutions of antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The ulcer is also sprinkled with white clay powder. After acute inflammation has been relieved, professional oral hygiene is carried out.
Mouth ulcers can also form due to HIV (gum ulceration occurs in approximately 30% of people infected with HIV). How to cure mouth ulcers in this case? Treatment is specific and carried out by infectious disease doctors. Dental care is provided in all dental institutions with careful adherence to safety precautions.
Prevention of all of the above oral diseases consists of eliminating the causes of their occurrence. For example, to prevent infectious diseases that manifest themselves on the oral mucosa, such as syphilis, measures are necessary that prevent infection from entering the body. In other cases, wellness measures are very important, which include systematic independent and professional oral hygiene, which is offered by almost all dental clinics in Moscow.
Methods for treating mouth wounds
Before starting treatment for wounds in the mucosa, you should understand the causes of the condition. If ulcerative defects are caused by another disease, it is necessary to fight the underlying pathology to reduce the size of the ulcers.
Wounds that appear from mechanical irritation with a brush or teeth are treated with antiseptic agents. They reduce the risk of bacterial flora attaching.
Therapy for the pathological condition is supplemented by diet, prescription of B vitamins, prevention of exacerbation of chronic pathologies, and elimination of stressful situations.
A patient with recurrent ulcers in the oral mucosa in the absence of treatment effect must undergo a set of tests to exclude a systemic disease of viral etiology (HIV, hepatitis).
Medication
- Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic solution that helps quickly treat wound defects in the mouth. The drug has antimicrobial and disinfectant abilities. Allergic reactions to the composition of the drug are rare. It is suitable for children. Wounds treated with Chlorhexidine can heal in 5-7 days. Rinsing should be done 3-4 times a day.
- Xikain gel has three main effects: reduces pain, destroys pathogenic flora, and relieves inflammation. The medicine is not used in children.
- Asept is a popular spray based on Lidocaine. The drug simultaneously anesthetizes and disinfects the inflammatory focus. The spray is used 2-3 times a day.
- Stomatidin destroys pathogenic microorganisms and disinfects the oral mucosa. The drug is widely used to combat the symptoms of stomatitis. It has a healing effect if you simply bite your lip.
Folk
- Representatives of traditional medicine recommend treating a wound in the mouth after a bite with decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, and calendula. They can be mixed or cooked separately. Take 1 tablespoon of the plant per glass of boiling water. The oral cavity should be rinsed with warm infusion 3-4 times a day.
- Furacilin, soda, and salt will help get rid of the problem. To prepare the solution you will need 5 tablets of the drug, 1 tsp of kitchen ingredients. The listed components of the solution are mixed in a glass of water. You will need 4-5 rinses per day to achieve rapid healing of ulcerative defects.
- A recipe with propolis helps with painful scratches. Take 1 teaspoon of alcohol solution per glass of water and rinse. Propolis relieves discomfort and promotes rapid healing. The soreness goes away within a week.
- Rinses with carrot, horseradish, and cabbage juice are used against stomatitis.
- Kombucha treats wounds in the mouth that form after injuries to the mucous membrane. Improvement occurs after the first rinse.
Review of effective ointments
- Bonafton is used in patients with herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The drug has a negative effect on the herpes simplex virus. Suppresses the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The ointment is applied three to four times a day for 2 weeks.
- Solcoseryl is a medicine that is intended to improve metabolism and accelerate regenerative processes. The drug is prescribed for the treatment of inflammation of the cornea and blood vessels of the lower extremities. It fights the manifestations of stomatitis and gingivitis. The drug should be applied to the inflammation site 2 times a day. A positive effect is achieved 2-5 days after the start of treatment.
- Pimafucin has an antifungal effect. The active components of the cream suppress the vital processes of the microorganism. Pimafucin is intended for external use.
- Metrogyl Denta is an ointment for the treatment of wounds in the mouth. Consists of metronidazole and chlorhexidine. The products have disinfectant and antimicrobial properties. The gel is applied 2 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
Features of getting rid of a purulent wound
A purulent wound in the mouth occurs as a result of the active activity of microbes. The condition is accompanied by severe pain and an unpleasant odor. Doctors recommend treating defects in the mucous membrane with antiseptic rinsing solutions and antibacterial ointments. It is contraindicated to pierce or squeeze out the pathological focus on your own to release the purulent contents.
Metrogyl Denta and Cholisal are used for treatment. Rotocan, Chlorhexidine, Givalex are suitable antiseptics. The products are used in dentistry to treat problems of the oral mucosa.
If the pathological process is accompanied by a prolonged increase in temperature, the appearance of pus in the wound, the question of systemic administration of antibacterial agents is raised. They suppress the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, promoting a speedy recovery. The selection of effective antimicrobial therapy is carried out by a family doctor or therapist.
Rules for processing and treatment in children
Ulcerative defects on the mucous membrane in children appear when personal hygiene rules are not followed. Children can injure the inner surface of the oral cavity with foreign objects. Before starting treatment, it is better to consult a pediatrician. Pharmaceutical drugs, when used incorrectly, cause allergic reactions in children's bodies. You can treat a wound in the mouth using special ointments, gels, and powders.
Children are prescribed Solcoseryl, Chlorophyllipt, Stopangin, Furacilin.
At home, you can use an infusion of calendula or chamomile to wash ulcers.
Pain syndrome in children older than six months is relieved with Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
When treating the oral mucosa, you must adhere to the following rules:
- You cannot independently increase children’s doses of medications or the frequency of administration.
- If the child does not know how to rinse his mouth, then it is necessary to lubricate the wounds with antiseptics. Do not allow your baby to swallow the medicinal solution.
- If allergic rashes appear, stop treatment and consult a doctor.
- When treating a wound, it is necessary to follow the rules of using aseptic techniques. Before treatment, wash your hands and lubricate the inflammatory areas with a clean cotton swab with the applied medication.
Why do wounds appear on the roof of the mouth?
Among the variety of causes that provoke the occurrence of wounds (ulcers) on the roof of the mouth, special attention should be paid to factors that can be divided into three categories.
Oral diseases
These common oral diseases include:
- Gingivostomatitis of necrotic type. The development of this disease is facilitated by oral injuries, weakened immunity, hypothermia, lack of vitamins, and the presence of allergic stomatitis. The gums, tonsils, palate, cheeks and tongue are affected. With this disease, the wounds may have a yellow or greenish coating, which causes an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. Shallow wounds have uneven outlines. Very often, with this disease, the appearance of wounds is accompanied by minor bleeding. The treatment process must necessarily take place in a hospital setting and with the help of drug therapy.
- Herpetiform stomatitis. This disease is characterized by the appearance of sores very similar to herpes sores. In this case, damage to the palate and tongue occurs. The course of the disease usually takes no more than a few days. However, if the wounds do not heal on their own within seven days, you should definitely contact a specialist.
- Necrotizing periadenitis. The initial stage of this disease is characterized by the appearance of small compactions, which after some time become wounds (ulcers). The localization of the disease covers the lips, palate, cheeks and tongue. This causes difficulty while eating and talking.
- Recurrent stomatitis. The localization of wounds and ulcers in this disease covers the palate, the area around the lips, cheeks, and also the tongue. The disease is characterized by the presence of pain when eating, as well as a feeling of discomfort in the mouth. Treatment of this type of stomatitis must begin immediately when the first nonspecific symptoms appear.
- Oral tuberculosis. The course of this disease is characterized by the formation of ulcers (wounds) affecting the entire oral cavity, including the cheeks and surface of the tongue. There is no pain during the formation of such ulcers, but over time the ulcer can grow. During this type of tuberculosis, the wounds are not deep, but have a loose structure. Often the formation of wounds, as with necrotizing gingivostomatitis, is accompanied by bleeding. The wounds have uneven outlines. Treatment of this disease should take place exclusively in a hospital setting and under the close supervision of medical personnel.