The state of the tongue reflects the state of the human body. That is why almost any doctor during an examination asks the patient to show his tongue. In a healthy person, the tongue has a pale pink color, pronounced papillae, and a straight fold exactly in the center. It should be soft to the touch, and moving it should not cause discomfort or pain. If you find that you have a white tongue, then there is a high probability of certain problems in the body. In this article we will talk about how dangerous the appearance of plaque on the tongue is, what causes and diseases lead to changes in the condition of the organ, and how this problem can be avoided and eliminated.
Anatomy: what does the tongue consist of?
The tongue is an organ that is part of the digestive system. It performs several functions:
- plays an important role in the formation of speech;
- helps form a bolus of food in the mouth and push it into the esophagus;
- helps us determine the taste of food.
What does language consist of? The organ is conventionally divided into two parts:
- the body of the tongue is the anterior movable part;
- The root of the tongue is the back part located closer to the larynx.
The tongue has a mucous surface on which taste buds are located, thanks to which we distinguish different tastes.
Why are complex teeth treated at PARTNER-MED?
We know how to work!
We have orthopedic dentists with 8-30 years of experience!
We love to work!
We will give you a free consultation and tell you exactly how best to make your teeth better!
We are responsible for the result!
We work conscientiously and will make your teeth LIKE YOURSELF!
Request a call back or dial our number!
+7
This phone call does not obligate you to anything. Just give us a chance and we will help you!
Just pick up the phone and call us!
+7
We will definitely make you an offer that you cannot refuse!
What does plaque on the tongue mean?
At different periods of time, the appearance of the tongue may change, and a coating on the tongue that has a whitish color is acceptable in a small amount. At the same time, the papillae are clearly visible through it. In summer, the thickness of the plaque may increase, and in winter it may acquire a yellowish tint.
When should you worry about tongue coating?
- if the tongue is constantly coated;
- the plaque becomes dense and completely hides the mucous membrane;
- the papillae of the tongue are poorly visible;
- the color of the tongue has changed (excessive pallor, redness, blueness);
- the plaque has a dense cheesy structure;
- unusual color of plaque - yellow, green, brown, gray, black.
With such signs, we can talk about both dental pathologies and more serious problems - acute and chronic diseases of internal organs. To get rid of plaque on the tongue, you first need to find out the reason for its appearance.
The first step is a consultation with a dentist. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will accurately determine whether the coated tongue is associated with caries, diseases of the oral cavity, and if not, he will refer you to other highly specialized specialists.
Liver diseases
The liver is the most important organ of the human body, related in its structure and functions to the endocrine glands. The liver performs a huge number of vital functions, the main one of which is cleansing the blood of toxic, poisonous substances and allergens, as well as removing from the body excess amounts of hormones and compounds hazardous to health: ammonia, ethanol, ketones and their acids, etc.
With any liver disease, a person develops a gray coating on the tongue, which may be accompanied by a change in the color of the skin, mucous membranes, deterioration in general well-being, and pain in the right hypochondrium. The danger of many diseases of the hepatobiliary system lies in their practically asymptomatic course in the early stages, so it is important to know the signs and symptoms of these pathologies and be able to identify them before irreversible changes in the functioning of the liver begin.
Liver cirrhosis disease
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease accompanied by structural changes in the liver with the formation of scar tissue, shrinkage of the organ and a decrease in its functionality. Early symptoms indicating cirrhosis include the following:
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
- In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.
General advice for patients with liver cirrhosis:
- Rest as soon as you feel tired.
- To improve digestion, patients are prescribed multienzyme drugs.
- Avoid heavy lifting (this may cause gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Measure your body weight and abdominal volume at the navel level daily (an increase in abdominal volume and body weight indicates fluid retention);
- If there is fluid retention in the body (edema, ascites), it is necessary to limit the intake of table salt to 0.5 g per day, liquid intake to 1000-1500 ml per day.
Following a diet for liver cirrhosis involves, first of all, avoiding foods that have a high protein content. After all, in patients with liver cirrhosis, the digestion of protein foods is disrupted, and as a result, the intensity of putrefaction processes in the intestines increases. The diet for liver cirrhosis involves periodic fasting days, during which the patient does not eat food containing protein at all.
Why does plaque form on the tongue?
The most common and easily eliminated reason for the formation of white plaque on the tongue is poor oral hygiene.
However, there are other factors that influence the condition of the tongue. Among them:
- infectious diseases in the oral cavity (stomatitis, etc.);
- acute, chronic diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- parasitic infection;
- candidiasis;
- kidney diseases.
Whether it is worth worrying about the health of certain organs can be judged by the color, nature and location of plaque on the tongue.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis of treatment will depend on what initial disease was detected in the patient. In case of dental problems, a few visits to the dentist are enough to get rid of most of the problems that arise. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can lead to bleeding, which requires urgent hospitalization and surgical treatment. The success of treating infectious diseases strongly depends on the patient’s immunity and the timeliness of starting the use of prescribed medications.
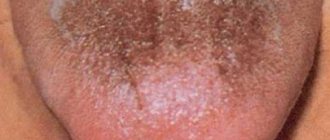
White coating on the tongue - what is it?
The main cause of plaque is poor hygiene and the resulting pathological conditions of the oral cavity. Therefore, first of all, you should see a dentist with such a problem.
In some cases, you can independently differentiate its causes by the color and location of the plaque. For example, why is the tongue white?
- 1
A white coating at the base of the tongue (in the root area) indicates high activity of bacteria or fungi. This may be due to both problems in the oral cavity and disturbances in the functioning of the intestines and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. - 2
A thick white coating on the tongue is usually caused by an infection of the tonsils, respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract.
- 3
A white, cheesy coating on the tongue is a sign of candidiasis (thrush).
- 4
A white coating on the tongue, as well as on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity, indicates stomatitis.
Determining the disease by the color of plaque
The first diagnostician on the condition of the tongue was the Russian doctor M. A. Nechaev, who in 1833 published the book “Recognition of diseases by changes in the language” in the printing house of Kazan University. Several generations of Russian doctors were grateful to him for this unique work, which helped to carry out diagnostics without additional instruments.
Today, the technique is widely used not only among traditional healers, but also among practitioners of traditional medicine. However, the diagnosis must be confirmed after a comprehensive examination carried out in a laboratory, or using ultrasound, CT, MRI, fluoroscopy, etc.
What do you pay attention to during this diagnosis:
- plaque color;
- its consistency.
As for the color of plaque, it can be:
- white;
- grey;
- yellow;
- greenish;
- bluish;
- brown;
- even black.
And the consistency can be:
- almost transparent;
- flaky;
- viscous.
All signs are compared, and a certain diagnostic verdict is made.
Yellow coating on the tongue
If your tongue turns slightly yellow in hot weather, there is no cause for concern. An alarming sign is the formation of a pronounced yellow coating on the tongue, which most often indicates serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gall bladder, and other pathologies of the digestive system.
Why is the tongue yellow?
- A small yellow plaque that appears in the morning and is easily removed during standard teeth brushing may indicate intoxication of the body (metabolic disorders, excess toxins). If the tongue remains clean for several hours after the procedure, then it really is a matter of toxins. To get rid of plaque, the patient needs to change his diet in order to normalize the functioning of the digestive system.
- Yellow plaque, loose in structure, combined with a specific taste and bad breath is a sign of serious disorders in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, requiring appropriate diagnosis and treatment. If such plaque appears, you need to contact a gastroenterologist.
- Yellow plaque in tandem with a high temperature may indicate inflammation of the ENT organs (pharyngitis, sore throat).
In addition, a yellow coating on the tongue inevitably appears in smokers, coffee and black tea drinkers.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines
These organs are directly involved in the digestive processes, so any disturbances in their functioning can lead to the appearance of bad breath, changes in taste perception and the formation of a grayish coating on the surface of the tongue. The oral cavity and pharynx are the initial sections of the digestive tract, and their condition is closely related to the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Listed below are the main pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that can cause such symptoms, as well as traditional treatment regimens for these diseases.
Gastritis
Gastritis – millions of people suffer from this disease in various forms. In fact, the term “Gastritis” includes many diseases leading to inflammation of the stomach. In any case, if pain appears in the upper left region of the abdomen, then everyone categorically diagnoses themselves and their friends as gastritis. In this article we will try to help you understand the causes of gastritis, their symptoms and methods of effective treatment.
In the clinical diagnosis of acute gastritis, everything is obvious:
- Soreness in the left hypochondrium has the character of aching pain, sometimes with periods of cramping exacerbations in the form of cutting attacks.
- Heartburn is usually characteristic of gastritis caused by reflux or increased stomach acidity.
- Nausea and vomiting - sometimes this is the only possible way to reduce excess stomach acidity. However, vomiting is not as common with gastritis as the first two symptoms.
- Bloating. For the digestive system, which operates on the principle of a disassembly conveyor, it is important that all necessary enzymatic and chemical influences are carried out at all stages of digestion.
- Increased appetite is due to the fact that after eating, the acidity of the stomach temporarily decreases. However, in the case of severe damage to the stomach, eating can only increase pain, which leads to a reflex loss of appetite.
Treatment of gastritis should be preceded by a full examination to identify the causes of stomach inflammation. Only by finding out the cause of the pathology will it be possible to adequately treat it. However, in the acute period, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. This is done in order to reduce stomach pain and stop or reduce the body's inflammatory response. To do this, first of all, it is necessary to reduce the aggressiveness of gastric juice. And this can be achieved by following a diet and using drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid or neutralize acidity in the lumen of the stomach.
The traditional treatment regimen for gastritis is shown in the table below.
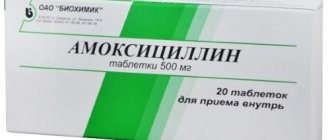
Table. Drugs for the treatment of inflammation in the stomach
| Pharmacological group | Drugs |
| Antibiotics | "Clarithromycin", "Amoxicillin", "Tetracycline". |
| Antimicrobials | "Metronidazole". |
| Bismuth preparations | “Ventrisol”, “Tribimol”, “Vicalin”, “De-Nol”. |
| PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) | "Omeprazole", "Orthanol", "Omitox", "Rabeprazole". |
| Antacids | "Gaviscon", "Gastal", "Rennie", "Maalox". |
| Vitamins | vitamin P, vitamin U. |
Gastritis is a serious precancerous disease, so you should not try to diagnose yourself and treat the pathology at home. In the absence of adequate therapy, the risk of developing gastrinoma (a malignant tumor that produces gastrin) increases 4 times.
Gastroduodenitis
Gastroduodenitis is the most common complication of gastritis, when descending infection occurs and the duodenum is involved in the inflammatory process. In total, there are three forms of gastroduodenitis:
- superficial (the mucous membrane turns red and swells);
- hypertrophic (epithelial membranes thicken, multiple pinpoint hemorrhages appear on their surface);
- erosive (mucous membranes become ulcerated and covered with erosions).
Erosive gastroduodenitis is considered the most dangerous form of the disease, in which the risk of ulcerative damage to the gastrointestinal tract is more than 30%. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to those of gastritis, the only difference is the localization of the pain syndrome: with gastroduodenitis, it can shift from the epigastric region to the abdominal space. Also typical are changes in stool, which can manifest as sudden diarrhea (including profuse diarrhea) or prolonged retention of bowel movements.
The treatment regimen for gastroduodenitis includes drugs used to treat inflammatory processes in the stomach, but when selecting medications, etiological factors must be taken into account. If the cause of the disease is stress, the patient is prescribed sedatives and sedatives. With reduced secretion of hydrochloric acid, replacement therapy with digestive enzymes is indicated.
If the pathology has become chronic, auxiliary treatment is necessary, which is carried out outside of exacerbation attacks. It may include treatment with mud and mineral waters (sanatorium-resort treatment), physiotherapeutic methods, exercise therapy, massage and herbal medicine.
Colitis
Intestinal colitis (inflammation of the large intestine) is another disease in which a gray or off-white thin coating may form on the surface of the tongue. If the pathology occurs over a long period of time, the patient may not have any pronounced symptoms, so it is necessary to pay attention to atypical signs. These may be symptoms associated with a lack of vitamins and minerals due to impaired absorption in the colon: weight loss, dry skin and lips, hair loss, mood instability, loss of energy, anemia.
Almost always, simultaneously with the appearance of an unpleasant odor and changes in the appearance of the tongue, defecation disorders occur in the form of constipation or diarrhea. The smell of feces is fetid (less often sour).
Treatment of colitis in adults depends on the symptoms present and the results of the diagnosis. Drugs for treating uncomplicated colitis are listed in the table below.
Treatment of inflammation in the large intestine
| Pharmacological group | Drugs |
| Antimicrobials | "Nifuroxazide", "Enterofuril". |
| Intestinal sorbents | "Polifepan", "Enterosgel", "Neosmectin". |
| Laxatives | "Bisacodyl", "Magnesium sulfate", "Portalac". |
| Antidiarrheal drugs | "Imodium", "Loperamide". |
| Probiotics | “Normobakt”, “Bion-3”, “Yogulakt”, “Bifiform”. |
| Antibiotics | "Amoxicillin", "Azithromycin", "Tetracycline". |
| Antiparasitic agents | "Vermox", "Pyrantel". |
| Stimulators of regeneration and repair | "Methyluracil". |
| Antispasmodics | “Spazmol”, “Spazmalgon”, “No-shpa”. |
When diagnosed with ischemic intestinal colitis, patients are also prescribed drugs that prevent platelet aggregation and blood clot formation, for example, Pentoxifylline. To identify vascular ischemia of the colon, a coagulogram, intravenous angiography and blood tests are indicated.
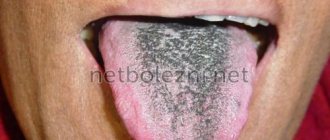
Black coating on the tongue
Black plaque looks especially scary; it can occur with long-term use of antibiotics and a number of other medications, and can also indicate a number of diseases:
- infectious disease, in particular cholera;
- Crohn's disease;
- acidosis – PH disturbance;
- viral sore throat.
A dark tongue may have a purple tint, which indicates blood diseases, including anemia. A plaque with a blue tint is one of the symptoms of dangerous diseases such as dysentery and typhoid.
Professional cleaning at the dentist
Even such thorough self-cleaning of the oral cavity is not enough to be sure that you will be free from periodontal disease or caries. From time to time it is necessary to contact a dentist so that he can carry out professional sanitation. Typically it includes:
- preventive examination and assessment of the condition of gums and teeth;
- removal of tartar mechanically or using ultrasonic devices;
- treatment with a special powder mixture to get rid of food pigmentation of teeth, typical for smokers, lovers of strong coffee and tea;
- final flossing to remove tartar fragments from the most difficult to reach places;
- polishing using a special paste to create the most even surface relief of the teeth.
It is recommended to carry out such cleaning every six months, in case of predisposition to caries and periodontal disease - once every 3 months.
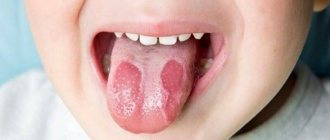
Why does the coating on the tongue have spots?
In most cases, spots on the tongue have nothing to do with dangerous conditions and diseases. However, it is imperative to find out their cause and pay attention to eliminating the causative factors.
What types of spots exist and why do they appear:
- the tip of the tongue turns red and goes numb - most likely this happened as a result of injury (burn from hot, spicy food, smoking), and problems in the intestines and heart are also possible;
- bright pink spots on the tongue - depending on the size and location, they can be caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12, folic acid or the development of scarlet fever, migratory glossitis;
- bright red spots on a pale tongue are a symptom of scarlet fever, but also appear against the background of anemia, in smokers;
- red dots combined with a whitish coating at the root of the tongue most likely indicate diseases of the digestive system.
Treatment of gray plaque
It should immediately be noted that treatment consists of eliminating the root cause of the disease. To avoid dental problems, you should treat your teeth on time, systematically brush your tongue and rinse your mouth. It happens that a muscle organ becomes gray due to an unbalanced diet. It is enough to remove the errors and the layers will disappear. If a pathology of a specific organ is identified, then the disease should be treated by a corresponding specialist.
- For respiratory abnormalities, patients most often undergo a therapeutic course of antiviral drugs or antibiotics. Bronchitis, sinusitis, and tracheitis are often treated with physiotherapy.
- Problems with the digestive organs are solved depending on the nature of the illness. Antacids, enzymes, probiotics, and choleretic agents may be prescribed.
- If dehydration is diagnosed, the drinking regime is normalized and salt is limited.
- When the body's protective functions are reduced, vitamin complexes and immunostimulants will help.
- Candidiasis and stomatitis are treated with antiseptics and antifungal agents.
Do not self-medicate. Trust an experienced doctor. Depending on the illness, you will be prescribed antihistamines, antivirals, antimicrobials and other drugs. You may need a special diet, antispasmodics, or mineral water therapy. After proper treatment, deposits on the tongue disappear.
How to remove plaque on the tongue?
- 1
Contact your dentist for advice. He will examine the oral cavity for dental diseases, carry out treatment if necessary (treatment of dental periodontitis, etc.), if plaque is associated with inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, and give recommendations on proper hygiene.
- 2
If the cause of the plaque is not related to dental health, the doctor will refer you to other specialists for examination.
What absolutely should not be done if plaque appears on the tongue:
- touch it with your hands;
- independently prescribe treatment for yourself, take medications without consulting a doctor;
- use solutions containing alcohol, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green to clean the tongue;
- take vitamins without prior examination and doctor’s prescription.
In case of plaque or rashes on a child’s tongue, you need to be careful when planning your diet and do not introduce new foods, as they can provoke an allergic reaction and aggravate the situation.
How to get rid of plaque on the tongue?
- drink enough fluids, especially in hot, dry weather;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- introduce solid raw fruits and vegetables (apples, carrots) into the diet;
- take care of the health of the digestive system - adhere to a healthy diet, which will restore the intestinal flora, improve the functioning of the liver and pancreas, and normalize the acid-base balance;
- monitor the health of teeth and gums, undergo dental treatment on time;
- observe the rules of oral hygiene.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.