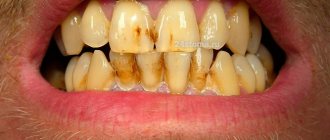
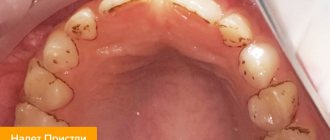
In most cases, dental plaque is the cause of insufficient oral hygiene. But it also happens that people who are very sensitive to hygiene issues develop black plaque on their teeth.
The reasons for its appearance in adults and children differ : if in the former it is a consequence of drinking large amounts of tea and coffee, as well as smoking, then in the latter it may be associated with the activity of certain bacteria, the use of mouthwashes and the use of chewable vitamins.
Types of plaque
Plaque on teeth is divided into two large groups:
- the occurrence of which is associated with external contamination of the tooth;
- appearing due to the deposition of pigments.
If oral hygiene is not maintained, plaque may appear on the teeth:
- soft microbial;
- mineralized;
- hard, often called tartar.
If everything is in order with hygiene, then black plaque is a consequence of:
- regular consumption of tea, coffee and nicotine;
- use of medications with high iron content;
- vital activity of chromogenic bacteria;
- use of certain types of rinses and antiseptics.
Symptoms of a cracked tooth
A tooth crack is a split in the enamel, which causes the main symptoms:
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold.
- Aching pain for no apparent reason.
- Unpleasant sensations when closing the jaw.
It is important to understand that small cracks may not be noticeable, but over time they increase, and the tooth itself is destroyed. In order to prevent destruction, it is better to seek help in a timely manner if you discover one or another sign of a condition deviating from the norm. After all, in this case, treatment will be faster and will cost you less.
Bacterial plaque on teeth: causes
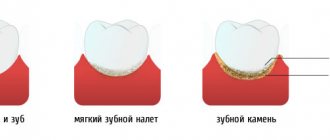
Soft or, as it is also called, bacterial plaque has a soft consistency, so it is easy to get rid of it with the help of an ordinary toothbrush. The main place of its accumulation is the neck of the teeth.
Harder plaque that cannot be removed with a brush is called tartar. It occurs during the mineralization of soft plaque with phosphorus and calcium salts present in saliva.
Why does plaque form?
There are constantly a huge number of bacteria in the mouth, which, firstly , multiply, and secondly , leave behind waste products. Even if you brush your teeth regularly, plaque cannot be avoided: within 6 hours after thorough brushing, you can easily notice, without resorting to the use of specialized equipment, a bacterial mass on the surface of the tooth enamel. A surge in microbial activity is observed immediately after eating: leftover food in the mouth forces bacteria to begin intensive processing.
At the same time, even small pieces of food that are invisible to the human eye are enough for microorganisms: they can feed on a film consisting of carbohydrates and proteins that invariably remains on the surface of the teeth after eating, and on food debris that gets into the spaces between the teeth. In this regard, it is imperative to brush your teeth for 15 minutes after each meal, since the mass of bacterial plaque can increase several times in volume in 1-2 hours. Plaque accumulates especially intensely on the necks of teeth in people who like to snack on a bun or something sweet between main meals.
Almost immediately after the soft plaque appears, the process of mineralization begins, as a result of which it gradually hardens. The period of primary mineralization (i.e., when the plaque, in simple terms, “sets” but still remains loose) is 10-15 hours. When the plaque finally hardens, its surface becomes ideal for the formation of deposits.
If the tooth has darkened
If one tooth has darkened and this is not a superficial plaque, but a change in the color of the tooth enamel, this means that we are talking about the death of the dental nerve and damage to the pulp. Perhaps the nerve was killed or removed during dental treatment, or the patient was in no hurry to see a doctor during an acute inflammatory process that led to the death of the nerve. Be that as it may, if a tooth is blackened from the inside, it means that only intra-canal whitening, installation of a crown or veneer will help it. In this case, the dentist must first find out why the tooth turned black and rule out the inflammatory process.
As a rule, an experienced specialist, when treating a tooth with nerve removal, knows that it will change color and immediately advises the patient to think about installing a crown or veneer. Therefore, if you don’t know exactly why your tooth turns black, remember if your doctor warned you about the possibility of such consequences.
Sometimes the reason a patient goes to the dentist is that the tooth has turned black under the filling. In this case, the cause of the tooth discoloration is most likely due to poor quality treatment. In particular, the filling may turn black if blood gets into it during installation - for example, because the doctor injured the gum. Also, a tooth under a filling may turn black if the dentist has not completely removed the damaged tooth and the carious process continues under the filling. In this case, the filling will have to be removed and a new one installed. This is a good reason to think about the professionalism of the doctor who performed the dental treatment.
In any case, the first thing to do if a tooth has turned black is to contact a reliable, highly qualified dentist.
Pigmented dark plaque on teeth
The main reason for the appearance of such plaque in adults is smoking, drinking coffee and tea. Maintaining hygiene guarantees the absence of bacterial plaque and tartar, but if you neglect it, black plaque will not take long to appear. Pigments adhere very well to enamel covered with bacterial plaque formed as a result of infrequent brushing of teeth.
Types of pigment plaque include:
- brown coating that occurs from regular consumption of tea and coffee in large quantities;
- accumulation of nicotine deposits;
- darkening of the enamel as a result of taking medications containing iron;
- proliferation of bacteria that form dyes (they are called chromogenic);
- change in enamel color after using antibiotics;
- blackening due to diseases of internal organs.
If plaque is caused by bacterial factors, then regular thorough brushing of teeth, the use of rinses and floss reduce the likelihood of its occurrence to a minimum. However, if the reason for the appearance of plaque lies in the influence of dyes, maintaining hygiene to prevent it will not help.
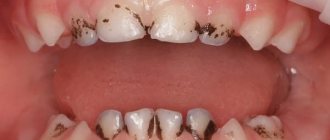
Black plaque on children's teeth , the causes of which are associated with the activity of chromogenic anaerobic bacteria, appears in the form of spots localized in the neck area. Actinomycete bacteria produce hydrogen sulfite, which reacts with iron (found in saliva and red blood cells). As a result, a form of black iron that cannot be cleaned off with a regular brush is deposited on the surface of the teeth. Chromogenic coloration can also be orange, green and brown.
Black plaque on a child’s teeth can also form for other reasons . It appears due to:
- the use of antiseptics that contain chlorhexidine, benzaclonium chloride, as well as essential oils (the latter are found in the popular Listerine product);
- consumption of foods rich in iron, as well as vitamins with a high content of iron.
Removal techniques
So, you have found black plaque on your teeth, what should you do? The first step is to make an appointment with a dentist. Depending on the degree of damage and medical history, the doctor will select a treatment method.
The fundamental factor in choosing therapy is the causes of dark plaque on the teeth, so tests and diagnostics may be required. In some cases, consultation with a specialist may be required (in the presence of chronic diseases).
Ultrasound is recognized as an effective, proven and safe way to remove black plaque on teeth. For the procedure, a special device is used - a scaler. It emits ultrasonic vibrations and transmits them through the tip to the tooth surface. Under the influence of ultrasonic vibration, deposits are destroyed and separated from the enamel.
Ultrasonic cleaning is painless, does not cause health problems, teeth do not hurt after it and you can lead a normal lifestyle. It can be carried out for both adults and children.
A reliable result is demonstrated by the procedure using Air Flow technology. It will return your teeth to their original appearance, eliminate blackening and deposits, and restore the beauty of your smile. Can be used both in the lateral and frontal zones.
This method uses the sandblasting principle of processing sand of a certain dispersion. A mixture of water, air and abrasive particles is applied to the tooth surface under high pressure. The enamel is polished, becomes smooth and is cleared of pigment and solid particles.
These were the basic tips on how to remove black plaque on teeth, but it is wiser to still use preventive measures and not lead to clinical treatment.
How to remove plaque from teeth on your own
Many people do not like to visit the dentist again, especially when it comes to removing plaque, which does not cause much inconvenience. The reasons for this are clear: lack of free time and reluctance to pay for the procedure.
You can try to remove plaque from your teeth at home, but this will only work if there are no subgingival deposits and the plaque layer is thin.
The first method involves using a special toothpaste to remove plaque with abrasive substances. The label of such pastes must indicate the RDA indicator, indicating the degree of abrasiveness. In pastes that eliminate plaque, its value should exceed 100. But such pastes cannot be used on an ongoing basis. If the paste contains pyrophosphates, then it can help get rid of tartar, since they have the ability to dissolve its matrix.
The most effective of these pastes are:
- President White Plus. The abrasiveness index is 200 units; in addition, the composition contains silicon dioxide, which has abrasive and polishing properties. You should not use the paste more than once a week.
- Lacalut White. According to the abrasiveness index (RDA=120), it is more gentle than the previous sample. The composition contains pyrophosphates, which make the plaque loose.
The second method is to use a special toothbrush, which allows you to remove plaque yourself. Recommended use:
Caries in the spot stage: diagnostic measures
The most reliable and effective diagnostic procedure for the initial form of caries is to check the integrity of tooth enamel using special organic dyes. Dentists use:
- carmine;
- tropeolin;
- methylene red;
- methylene blue.
The latter is more often used in dental practice. First, the specialist removes accumulated plaque from the tooth surface. Use cotton swabs to isolate the tooth from saliva and then apply the coloring solution. After a few minutes, the solution is thoroughly washed off and the condition of the enamel is analyzed. If it is stained, this indicates the presence of caries.
There are other ways to diagnose caries in the spot stage:
- drying of enamel. The surface of the tooth is treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, then the enamel is thoroughly dried with a stream of warm air. After drying, areas with white spots will immediately become noticeable;
- radiography. The area affected by caries appears as a small spot on an x-ray. The method is used mainly for contract caries;
- examination with a stomatoscope. First, all accumulated plaque is removed from the surface of the teeth, then the dentition is illuminated with the device. Under ultraviolet radiation, it is not only easy to distinguish damaged tissue from healthy tissue, but it is also possible to determine the boundaries of pathology.
In order to treat caries in the spot stage, it is very important to undergo a timely diagnosis, accurately recognize the presence of pathology and exclude similar diseases that resemble caries.
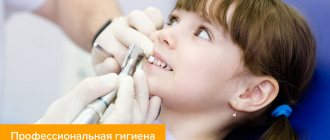
Plaque on a child’s teeth: treatment
Removing bacterial and chromogenic plaque in a child will be no different from a similar procedure recommended for an adult: ultrasonic cleaning and AirFlow are used in the same way.
However, chromogenic staining of teeth may return over time. The only possible solution to the problem is regular professional cleaning by a dentist. To make visits to the dentist as rare as possible, your child should be taught to use an electric toothbrush, the pulsating circular movements of the head of which perfectly break up plaque.
Accelerated formation of deposits is promoted by blood in the oral cavity, so the child’s gingivitis must be treated. The use of chlorhexidine and antiseptics based on it should be abandoned.
Brown spots
Similar manifestations on tooth enamel are also caused by the development of hypoplasia. The disease is generally very common and, according to some estimates, affects up to 40% of children.
The causes of hypoplasia, in contrast to caries, which destroys still growing teeth, are complications during pregnancy or trauma during birth. It can also develop due to poor nutrition, digestive problems and damage to tooth enamel.
For prevention, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the mother’s teeth. You should stop artificial feeding and monitor the child’s nutrition subsequently, as well as regularly visit the dentist.
How do you check the type of stain?
White spots during initial caries should be distinguished from spots of non-carious origin, which can occur with enamel hypoplasia and dental fluorosis. The former can be identified using a special dye solution - a 1% solution of methylene blue. This diagnosis is carried out at a dentist’s appointment and does not take much time. As a result, the foci of demineralization will turn blue, but with hypoplasia and fluorosis, staining of the spots does not occur, because The enamel in these diseases is very dense.
Complications of pigmentation
Stains on teeth can be carious or non-carious. Depending on the etiology of the formation of an area that differs in color from the rest of the enamel, treatment is prescribed. There are also internal and external prerequisites for the appearance of dark or white spots on teeth. The type and size of stains may depend on the region of residence, since the state of the enamel directly depends on the degree of mineralization of drinking water.
Changes in the color of the enamel, if this is not a congenital or hereditary feature, indicates a malfunction in the body and it is short-sighted to leave such a signal unattended. If the cause of pigmentation is not an insufficient level of personal hygiene, smoking or addiction to coffee, then you should definitely visit a dentist. Black, brown, white dots can serve as harbingers of thinning of the upper layers of the tooth.
It is also worth considering the psychological discomfort that a person experiences, especially if his profession involves constant communication with people or speaking in public.