What is Priestley plaque on teeth?
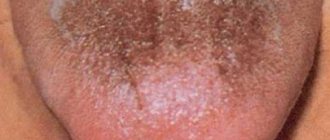
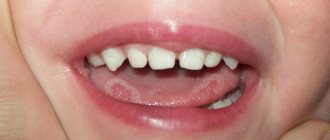
This is a dental problem that occurs in children. In this condition, deposits are found on the enamel of the teeth. Dark plaque on a child’s teeth can be black or brown, sometimes with a light or pearlescent tint. As a rule, it is located as a thin border along the lower edge of the teeth closer to the gums. But plaque can also cover a large area of the tooth or look like a small spot on the enamel. Most often, dark deposits appear on the inside of the teeth, less often in the interdental space or on the outer surface of the teeth.
Photo courtesy of InWhite Medical Clinic
Provoking factors
The main reason why tartar forms in young children is poor oral hygiene. Even parents are not always able to thoroughly clean children’s teeth, so, as a rule, large plaque accumulates in hard-to-reach places.
The provoking factor may be:
- lack of solid food in the child’s daily diet;
- bite pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
It is not always possible to eliminate the provoking causes of tartar in a child, so dentists recommend that parents constantly monitor the quality of their teeth cleaning.
How to detect dark plaque in time
- regularly examine the child’s oral cavity independently;
- do not postpone scheduled visits to the dentist.
It must be taken into account that Priestley plaque on the teeth often accumulates slowly, which is why the child gets used to the stains on the enamel and does not tell his parents about them. Darkening of teeth can occur quickly, literally overnight. Reactive appearance most often occurs during illness, accompanied by intoxication, dehydration and increased body temperature. This is due to the fact that the child’s body reacts sharply to various changes in diet, the functioning of internal organs and in external conditions.
Deposits most often occur at the age of 2-3 years. However, they can also appear on the very first milk teeth of a one-year-old child. Or it could affect the baby teeth of a younger teenager who haven’t had time to change. The darkening may also spread to permanent teeth.
Methods for removing tartar
The dental procedure for removing tartar from teeth is painless and safe. This can be a separate manipulation or a stage of professional cleaning of tooth enamel.
Removal of supragingival tartar can be performed by two methods:
- hygienic cleaning - with professional toothpaste and a special brush;
- Airflow method - a hardware technique for cleaning teeth with soda crystals flowing through a nozzle under pressure with an air flow).
It is more difficult to get rid of subgingival deposits, so more effective methods are used:
- manual cleaning - the doctor uses a tool to separate the tartar from the enamel;
- ultrasonic cleaning - deposits are destroyed by ultrasonic waves and then removed with a tool.
The procedure is completed by polishing the tooth. To strengthen damaged tooth enamel, a remineralizing composition and fluoride varnish are applied to the surface of the tooth.
Why does a child have black plaque on his teeth?
The main problem with the appearance of Priestley plaque on teeth is not that it causes bad breath, looks unsightly, or cannot be removed independently without the help of a hygienist. Priestley's plaque is a signal that something has changed in the child's body, due to which non-dangerous bacteria began to actively multiply, creating deposits. And for high-quality treatment and prevention of the development of diseases, it is necessary to find out why black plaque forms on the teeth, the reasons for the appearance of beneficial living conditions for bacteria.
Possible causes of plaque:
➢
diabetes;
➢
genetic feature or hereditary predisposition;
➢
thyroid diseases;
➢
incorrectly selected hygiene products;
➢
parasite infection.
Dysbacteriosis.
Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract can occur due to malnutrition, food poisoning, immaturity of the digestive system, taking antibiotics or chronic diseases of the stomach, liver, and intestines.
Caries.
Due to the fact that parents usually do not brush their baby’s first teeth, yellow plaque begins to accumulate on the enamel, which over time can cause caries. Irregular or insufficiently high-quality tooth brushing by the child himself also leads to the formation of caries. Carious lesions create a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria, which causes Priestley plaque to appear on baby teeth.
Dehydration.
Due to dehydration due to various reasons, the body cannot produce enough saliva to wash the teeth and remove food particles. Because of this, bacteria begin to multiply faster, and a dark plaque forms on the child’s teeth. Therefore, it is important to ensure that your baby gets enough fluids, especially in hot weather or during illness.
Hypoplasia of tooth enamel.
Some children have underdeveloped top layer of enamel. It is weakened and unable to perform a protective function.
Disorders of dental development in the prenatal period.
Dental buds may be damaged during development due to viral infections suffered by the mother, calcium deficiency, iron deficiency, or taking certain medications.
Improper functioning of the immune system.
Malfunctions in the immune system can affect the body's ability to suppress bacterial activity.
Malocclusion.
If a child has a malocclusion, the load on the jaw when chewing is distributed unevenly, which is why some of the teeth receive increased load, but are cleansed with solid food: carrots, apples. And unused teeth become covered with plaque.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the development of dental diseases and the formation of plaque should be applied from the moment the baby first starts teething. The risk of unpleasant problems occurring can be significantly reduced by the following simple measures:
- Gentle oral care. Infants up to one year old can clean their gums with a cotton pad soaked in a decoction of chamomile, string, oak bark or sage. Special silicone attachments are also widely popular, which adults put on their fingers and thus clean the baby’s oral cavity. From the age of two, children must be taught to brush their teeth with a brush and toothpaste, and it is also advisable to rinse the mouth after each meal.
- Proper nutrition. This does not imply following any diets, but the child’s nutritional system should be designed in such a way as to limit his intake of sweets, sugar, confectionery and increase the consumption of healthy natural products. Sweets from the store are an excellent substitute for candied fruits, fruits and dried fruits.
- Timely abandonment of pacifiers and bottles. With prolonged use of a bottle or pacifier, an incorrect bite develops, dependence on accessories appears, and a black plaque forms, which in dentistry is called “bottle caries.” You should not delay in weaning your child off devices that he no longer needs.
- Maintaining the immune system. It is important to ensure that even in winter, the child has enough vitamins to maintain healthy teeth and the body as a whole.
By following these simple recommendations, you will ensure your child’s dental health and the beauty of a child’s smile.
return to list of articles
Diagnosis of Priestley plaque on teeth
If darkening is detected on the enamel of a child’s teeth, you must contact a dental clinic.
The specialist will:
✔
inspection;
✔
laser diagnostics to determine the depth and size of the lesion;
✔
anamnesis collection.
After a conversation with the parent and child and collecting an anamnesis, the pediatric dentist will immediately prescribe treatment or conduct an additional examination. You should not neglect it - it is important for a specialist to find out why the child has black plaque on his teeth. Only after this will he be able to provide quality treatment.
How to prevent it?
The main task of parents is not to cure the disease, but to prevent it! Therefore, certain measures should be taken to prevent mineral deposits on teeth:
- As soon as the first teeth appear, you need to teach the child to eat solid food, do not follow the lead of the little lazy person - do not chop carrots and apples;
- You should brush your teeth with a children’s brush, which is better to buy on the recommendation of a dentist;
- You need to change the brush every 2-3 months;
- Teach your child to brush their teeth correctly. The doctor will give you all the necessary recommendations at your appointment.
- purchase pastes with pyrophosphate (but strictly in accordance with the age of the baby).
But the most important rule is to bring your child once every six months for a dental examination. This will not only help get rid of tartar, but also prevent serious diseases in the future that are caused by mineral deposits: periodontitis, gingivitis, stomatitis.
Additional protective measures for Priestley's raid
It is possible that Priestley's plaque on the teeth appeared due to an infection and, as a result, a temporary deterioration in the functioning of the immune system. But it is necessary to make sure that there are no serious and dangerous deviations in the child’s health. Therefore, if dental plaque is detected, the dentist will recommend taking additional measures:
- get tested for the presence of parasites in the body;
- consult a gastroenterologist;
- take tests to check the level of iron and calcium in the body;
- check your blood sugar levels.
These measures will help identify the problems that are causing plaque to form on your teeth.
DIAGNOSTICS
Priestley's plaque itself is not dangerous to the body, but dark spots can also occur for other reasons. Therefore, you should always rule out risks and check with a dentist.
In cases where a stain appears on a tooth, diagnostics is carried out using a laser. This helps the specialist determine how deep the caries has spread, as well as its stage. After diagnosis, individual treatment is prescribed based on the data obtained.
If the dark plaque was not caused by caries, the specialist will prescribe additional tests that will identify the problem.
How to remove black plaque on teeth
It is impossible to remove dental plaque at home. Moreover, the use of abrasive agents and intense exposure to teeth with a brush can cause an increase in dental problems: thinning or damage to the enamel, trauma to the gums or mucous membrane.
Priestley's plaque on children's teeth can only be removed in a well-equipped dental clinic. The specialist will:
- professional teeth cleaning;
- If necessary, treat the teeth with a remineralizing composition.
If plaque formation is caused by dental problems, additional treatment may be prescribed, including bite correction.
The doctor will also select a home hygiene kit that is ideal for the child: a toothbrush of the correct shape and hardness, toothpaste with the optimal composition, and mouth rinse. Additionally, the hygienist will teach the child how to brush their teeth correctly and will talk about the need for quality oral care.
Taking into account the causes of the disease, the dentist may prescribe additional treatment measures, for example, recommend dietary supplements, dietary nutrition, avoidance of drinks and foods with dyes that affect the color of the enamel.
What kind of stone is there?
There are two types of tartar:
- supragingival;
- subgingival.
They differ from each other in location.
Supragingival calculus is easy to see, it is grayish or yellowish in color, and is easy to scrape off from the tooth. The appearance of such a stone can be blamed on the minerals found in saliva. Most often, this type of deposit is based on the front teeth and buccal surfaces of the molars of the upper jaw.
Subgingival stone can only be detected by a dentist. At Family Dentistry, the doctor will definitely conduct a diagnosis in order to detect deposits or make sure that they are absent. This type appears due to gingival fluid containing minerals. This stone is either greenish or dark brown, attached to the neck of the tooth, on the root cement, in the periodontal pocket.
Visually, it can only be seen if the disease is advanced - the deposit covers the neck of the tooth, and protrusions form.
Reasons for appearance
When you eat, bacteria settle and build up on your teeth's enamel. In the absence of regular teeth cleaning, the number of accumulated microorganisms increases, which leads to the appearance of pigmented plaque .
In an adult
The orange tint is due to the accumulation of waste products of chromogenic bacteria. Microorganisms are colorless, coloring pigments are deposited nearby, in the form of tiny drops, crystals, coloring the environment.
Bacteria have the ability to cause fermentation and decay processes, which leads to loosening and loss of teeth, and the appearance of caries.
Orange plaque is localized in the cervical area of the teeth (usually incisors); the color varies from light orange to brick-red.
In adults, the appearance of such plaque can be caused by the following reasons:
- taking medications, in particular antibiotics;
- rinsing the mouth with solutions of Ethacridine, potassium permanganate and others;
- eating food with coloring components (coffee, tea, red wines);
- disturbance of intestinal flora, dysbacteriosis;
- smoking - nicotine forms a thin film, as a result of which food particles stick to the tooth surface more intensely.
The child has
The reasons that contribute to the formation of an orange plaque in a child are also the waste products of chromogenic bacteria. Children from 5 to 15 years of age are more susceptible to microorganisms than adults due to the composition of saliva (low bactericidal properties due to a small amount of lysozyme) or the onset of puberty. The appearance of a bacterial film can also be influenced by :
- A pathological change in the composition of saliva formed at the stage of intrauterine development.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, inflammatory processes of the biliary tract.
- Frequent drinking of sweet, pigmented drinks, excessive consumption of chocolate, fruits and vegetables containing carotenoids (plant colorants) - carrots, tomatoes, peaches, melons and others.
- Regular consumption of food that does not require thorough chewing, malocclusion.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa, leading to thinning of the pellicle (protective film), enamel and, as a result, the appearance of microcracks in which bacteria accumulate and multiply.
A bright orange plaque with a reddish tint may indicate that the child has a hereditary disease - porphyria, which is associated with a violation of tissue pigmentation.