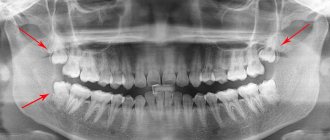
Causes and mechanism of caries in pregnant women
The main reason that provokes the destruction of hard dental tissues is the acids secreted by cariogenic bacteria of the coccus family and lactobacilli that live in dental plaque.
The possibility of the formation of carious lesions increases significantly under the influence of various provoking factors:
- lack of oral hygiene;
- the presence of various dental defects on the outer shell of the teeth;
- a large amount of sweet, sour and hard-to-digest carbohydrate foods in the diet;
- frequent snacking;
- dysfunction of the salivary glands, leading to impaired salivation;
- consumption of water with low fluoride content.
There are a number of prerequisites for the development of caries in the dental tissue of pregnant women.
- Changes in the biochemical parameters of saliva . For the tissue formation of the fetus, volumetric consumption of fluoride and calcium is required. They reach the fetus from the mother's body. In the body of a pregnant woman, a deficiency of minerals is created and the biochemical composition of saliva changes, which leads to the cessation or slowdown of enamel mineralization. The surface of the tooth becomes vulnerable to the action of bacteria that provoke decay processes (caries).
- Decreased immune activity . Any foreign body in the body is rejected by it. To prevent this from happening, the immunological status of pregnant women undergoes restructuring, significantly reducing its activity. As a result of weakened immune defense, the bactericidal functions of saliva also change, which is no longer able to fully stop the aggression of cariogenic bacteria.
- Changing taste habits. Pregnancy is characterized by a craving for pickles, sour or sweet foods. The main environment for bacterial growth is foods rich in carbohydrates, which ferment glucose (sugars) during the fermentation process. The situation is aggravated by the acidic environment formed by pickles and canned foods.
The main mechanism for the development of caries in pregnant women is the influence of acids produced by bacteria from food.
Bacterial flora of the oral cavity, the number of which increases significantly in pregnant women, settles on the protective film of the teeth (pellicle) in the form of a soft plaque. Microorganisms begin the fermentation process - the conversion of food sugars into organic acids, which, penetrating into the solid structure of tissues, wash fluoride and calcium from the enamel layer.
The rapid development of caries in pregnant women compared to non-pregnant women is explained by a violation of the mineral saturation of tooth enamel due to a significant change in the biochemical composition of saliva during pregnancy.
Other causes of tooth decay in expectant mothers
There are some other reasons that also lead to tooth decay in a woman during pregnancy. So, one of the additional issues may be gingivitis , that is, inflammation of the gums. With gingivitis, symptoms such as pain, bleeding, and redness are often observed. Bleeding gums occur when brushing your teeth and even while eating. These inflammatory conditions in the mouth promote the accumulation of microorganisms that begin to destroy teeth and worsen the symptoms of gingivitis. Also, in places called periodontal pockets, hard tartar begins to accumulate, on which even more pathological bacteria settle. Such processes, if treated insufficiently or completely absent, can lead to the loss of diseased teeth.
The infectious component present and accumulating in the mouth creates a permanent focus of the disease,
which can spread not only to neighboring teeth, but also to many other organs of the female body. Women who have inflammatory gum diseases, such as periodontal disease, gingivitis, periodontitis and others, can lead to the development of late toxicosis in the last weeks of pregnancy.
Knowing all this, a woman should immediately consult a doctor when the first symptoms of dental and gum disease appear.
Forms and stages of development of caries
The systematization of various forms of caries is based on several parameters:
- time of detection of pathology;
- specific histological features of the pathological process;
- location and depth of the lesion.
The clinical picture of the disease in pregnant women can be either primary , diagnosed for the first time, or secondary , as a consequence of continued destruction (destruction) of dental tissue with the formation of carious cavities in previously filled teeth.
According to the severity of damage to dental tissues, various types of caries are distinguished: enamel shell, hard dentin tissue, bone tissue, or caries with a suspended destructive process.
To manage pregnant patients, the tactics of topographic systematization of the destructive process are used. There are several stages of development.
Initial stage of caries
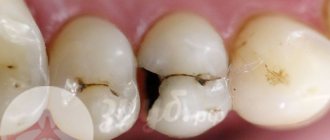
Superficial demineralization of the hard structure of teeth is focal in nature, manifesting itself in the form of spots. The formation of white spots characterizes an active destructive process, brown spots - slow destruction. In treatment, the use of minimally invasive techniques is permissible.
Superficial caries
The process of destruction of tooth tissue does not extend beyond the outer protective enamel shell and does not disrupt the structure of the enamel-dentin junction. At this stage of the disease development, the first clinical symptoms appear. Treatment consists of mechanical treatment of the damage.
Average caries
It is characterized by the formation of carious cavities without signs of deep damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, and a pronounced clinical course. The basis of treatment is the removal of damaged tissue.
Deep stage caries
The destructive carious process spreads to the internal tissues of dentin, accompanied by the development of intense pain. Lack of timely treatment threatens pulp damage with a high probability of developing complications in the form of periodontitis or pulpitis.
While carrying a child, women usually develop moderate-intensity caries, which is explained by a decrease in immune defense, a pronounced deficiency of essential minerals, and sometimes a lack of proper dental hygiene. Systemic and multiple formation of carious cavities is rarely diagnosed.
How to prepare for pregnancy to save your teeth
Among the many causes of pathology of the gums and chewing organs of women in labor, there is a lack of sanitization of the oral cavity on the eve of pregnancy. That is, the expectant mother ignored professional hygienic cleaning when she planned to bear the child. Many did not treat existing dental diseases at all before pregnancy. Therefore, such women first of all develop problems in the oral cavity. Of course, therapy can and should be done while the baby is pregnant. But in order to minimize the risks of damage to the fetus, it is better to eliminate all problems on the eve of pregnancy.
Today, dental treatment during pregnancy is possible with anesthesia. The doctor selects a gentle drug that does not harm the embryo. But, surgical operations could have been avoided if the expectant mother had diagnosed the oral cavity and completed a therapeutic course before pregnancy. Sometimes it happens that dentists even recommend removing wisdom teeth in advance, so as not to carry out such serious manipulations after conceiving a child. Therefore, it is better to put the oral cavity in order before pregnancy, even at the stage of planning conception.
It is necessary to visit the dentist at least 2 times during pregnancy. Dentists often recommend that women take dental vitamins during pregnancy. Such courses will help eliminate mineral deficiency. If a woman has not prepared for pregnancy, the antenatal clinic will offer her not only the necessary tests, but also a visit to the dentist.
Clinical signs (symptoms) of caries in pregnant women
The manifestation (onset) of the disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course. In most cases, pathological processes in the form of formations of light or dark spots on the surface of teeth are detected during preventive examinations.
The main sign of the development of caries with the formation of cavities is increased dental sensitivity to the effects of cold, hot, salty, sweet or sour in the diet.
Symptoms of deep localized caries are manifested by short-term pain in the affected tooth when chewing, pain under the influence of chemical and thermal irritants, which goes away when they are eliminated.
Persistent intense pain indicates deep damage to the internal tissues of the tooth.
Can X-rays and anesthesia be used?
Does radiation affect pregnancy during caries, how to protect the baby in the womb from harmful effects?
Sometimes this method cannot be avoided during therapy, but it is contraindicated during pregnancy. In rare cases, exceptions are possible, but doctors still try not to address them. Modern equipment used in the Dentika clinic provides minimal radiation doses when using special sensors. If the dentist nevertheless decides to carry out the procedure, the pregnant woman is put on a special lead apron to protect the little person inside. And even with such protective measures, such diagnostics are categorically not recommended.
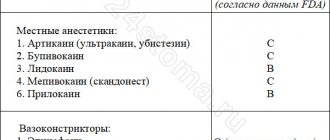
As for anesthesia, everything is more flexible here. During the gestational period, local agents (external gels and ointments, injections into the gums) are welcome. They are indicated no earlier than from the 14th week, that is, upon completion of the process of formation of the placenta, which protects the baby from external factors.
The effect of caries on pregnancy and the fetus
Uncomplicated caries does not affect pregnancy and fetal development, but the manifestation of pain can cause increased irritability and emotionality in patients, which can already have a negative impact.
The high rate of development of destructive processes in pregnant women contributes to the development of various complications:
- pulpitis,
- periostitis of the lower or upper jaw,
- formation of abscesses,
- development of phlegmon in facial tissues,
- sepsis or osteomyelitis.
The direct impact on the fetus due to caries can be provoked by infectious and septic complications, which increase the risk of intrauterine infections in the fetus, causing infection of the amniotic fluid and premature birth.
Oral care during pregnancy
The oral cavity during pregnancy and lactation requires increased care and careful care. Basic hygiene rules do not differ from typical standards. But when a woman does not properly care for her teeth, she has serious problems. Gums may bleed and teeth may break off. At an appointment with a dentist, they identify and draw up a therapeutic plan, which includes activities to teach proper care. Observations have shown that insufficient hygiene activates the processes of crown destruction. When toxicosis occurs, many people undergo formal teeth cleaning. In addition, to get rid of nausea, women in labor constantly eat something. In such a situation, pathogenic bacteria quickly multiply, hard tissues are destroyed, and not only caries develops, but also periodontitis and pulpitis.
Today, dentists offer pregnant women caries treatment using the Icon system. Infiltration is used when the tissue is affected by no more than 1/3 of the thickness of the dentin layer. Pregnant women tolerate this therapy well. It does not harm the embryo, since no anesthesia is used. Caries of several units can be removed in one session. The procedure is painless and lasts 20-30 minutes. Basic principles of proper oral care:
- Since the enamel becomes thin and vulnerable, use a brush with soft or medium bristles.
- The brush must be changed after 2 months.
- It is not recommended to use pastes that contain a lot of fluoride, so as not to harm the little one.
- It is better to use pastes with a high calcium content.
- You should brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after eating.
- Once every 6 months you need to have your teeth professionally cleaned using approved methods.
- Promptly carry out therapy of masticatory organs using gentle technologies.
At the time of pregnancy, treatment of caries, non-carious lesions, periodontitis, and tooth extraction for medical reasons is allowed. The principles of hygiene during pregnancy do not change. But the procedures must be performed carefully, taking into account the processes that occur in the body of the expectant mother.
Methods for diagnosing and treating caries in pregnant women
Diagnosis of the carious process in pregnant patients is not difficult. The main goal of diagnosis is the timely identification of destructive processes in the structure of dental tissues that require urgent treatment, and carrying out differential diagnostics to exclude non-carious pathologies.
A feature of the diagnostic examination of pregnant patients is the exclusion of radiographic diagnostics in the first gestational trimester. The use of radiography in this period is justified only in cases of severe clinical signs (severe pain, purulent inflammation).
Diagnostic search for carious processes in pregnant women includes:
- visual examination using a dental probe and mirrors, a caries detector and thermal stimuli;
- electroodontodiagnostic examination (EDI) , which allows to assess the depth of damage to dental tissue;
- dental transillumination method , which allows identifying pathology at an early stage;
- laser diagnostics , revealing early signs of tooth decay in inaccessible places and signs of secondary caries.
Procedures that should not be done
- Installation of veneers or aesthetic fillings
Although it is not considered a risky procedure, it is nevertheless not recommended. The reason is that any medical interventions during pregnancy should be carried out only when indicated. Aesthetic problems can be solved after the birth of a child.
- Whitening
The reason is the same - the procedure is not therapeutic - it can be postponed until later. In addition, now all medical drugs and equipment are certified; for this purpose, studies are carried out, in which pregnant women usually do not participate. Therefore, there is a formal ban.
- Treatment by an orthodontist
It would seem that wearing braces while on maternity leave is a great idea, because you don’t have to go to work or communicate with colleagues. But in fact, many orthodontists are against this decision. Firstly, during pregnancy and subsequent breastfeeding, bone tissue density may temporarily decrease and the course of treatment will differ from the standard. It is difficult to predict this, so to some extent such a procedure is risky. Secondly, immediately after the birth of a child, a woman cannot always leave him to go to the clinic for an appointment on the appointed day. And it is very undesirable to postpone visits to the orthodontist - it is not recommended to violate the treatment schedule.
It is much easier to choose clear aligners that are invisible to others, and undergo treatment when it is truly convenient for you.
There is no need to “hide” with aligners; the treatment goes unnoticed by others
Thus, the general opinion of dentists is:
- Treatment should be carried out before pregnancy or after 12 weeks.
- Do not put off treatment until later.
- On the contrary, all aesthetic procedures can be completed after the birth of the baby.
Other articles:
- What is more profitable – aligners or braces?
- Reflections braces - their advantages
Treatment of caries in pregnant women
A key feature when choosing treatment tactics for pregnant women is the limitations in the use of a number of techniques and medications traditionally used for tissue restoration.
Therapeutic treatment is selected individually for each specific case. The duration of pregnancy, the dynamics of pathological development, the severity of clinical signs and the presence of possible complications are taken into account.
Recommended methods for treating caries for pregnant women
- Remineralization. Used for caries at the stain stage. The lesion is saturated with fluoride and calcium-containing agents through medicinal applications and sessions of therapeutic electrophoresis. In addition to the procedures, it is recommended to use fluoride-containing dental hygiene products.
- Filling is the optimal method for restoring teeth with any severity of carious lesions.
What dental treatment is prohibited during pregnancy?
When treating teeth during pregnancy, you need to know what is strictly prohibited for expectant mothers.
As a substance for local anesthesia, it is prohibited to use those compositions that contain adrenaline and any of its derivatives. General anesthesia during pregnancy is also strictly prohibited.
Teeth whitening is prohibited. Dental prosthetics cannot be performed. It is prohibited to perform dental treatment using arsenic during pregnancy. Dentists are aware of all the restrictions and your task, in case your pregnancy is short, is to warn the doctor about pregnancy before starting dental treatment.
Until how many weeks of pregnancy can teeth be treated?
Many restrictions on dental treatment and pain relief during pregnancy are associated with myths. But there is a basic recommendation - to perform certain manipulations during pregnancy in the second and third trimester.
There is a generally accepted schedule for visiting the dentist, which is recommended to be followed while carrying a child:
1st visit: 6–9 weeks of pregnancy
2nd visit: 16–18 weeks of pregnancy
3rd visit: 26–28 weeks of pregnancy
4th visit: 36–38 weeks of pregnancy
Is it possible to take dental x-rays during pregnancy? The doctor will tell you during your appointment. As a rule, specialists assess potential risks and only then prescribe treatment.
Pregnant women are allowed to treat caries and periodontal diseases, inflammatory processes in the gums and teeth, non-surgical tooth extraction and installation of braces if there is no tooth mobility.