How to determine?
There are several signs by which you can immediately understand that a tooth is growing in the wrong direction. This is evidenced by:
- Pain at the end of the dentition.
- Pain and bleeding from mechanical stress, such as brushing teeth or chewing hard food.
- Swelling and hyperemia of the soft tissues near the inside of the cheek.
- Most often, the teething process is delayed for several months or even several years.
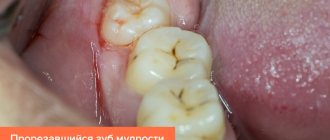
- It is visually noticeable that the apex of the tooth is located abnormally.
Symptoms of the problem
The reasons for the incorrect eruption of third molars are the lack of ready-made conductive canals, since there are no milk analogues. However, formation begins as early as five years of age, causing discomfort and pain.
Malposition and pain during growth are usually caused by the following reasons:
- jaw abnormalities, including hereditary ones;
- the position of the molars is incorrect;
- there is an excessive number of ones in the row, there is not enough space for eights;
- the shape and size of the molars are non-standard;
- hormonal disorders of the patient, metabolic problems;
- early removal of a tooth, the appearance of large gaps.
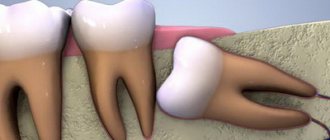
In the normal position of the teeth and jaw, eruption occurs almost imperceptibly, there is no pain or inflammation, and the figure eights take their position. But with a narrow jaw, severe pain and swelling appears, the tooth begins to grow sideways, growing into the surrounding oral tissues. This is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bleeding, pain also occurs when brushing or flossing;
- discomfort during chewing loads;
- mucosal tissues are swollen, discoloration is observed;
- the inner surface of the cheek is injured, it is constantly bitten, and swelling appears when ingrown;
- swelling and signs of inflammatory processes appear in the gums and tongue;
- headaches, fever appear, and the condition worsens.
In especially severe cases, eruption lasts for several years, during which the patient constantly feels pain and discomfort. This requires contacting a doctor, who, after examination, chooses a treatment method.
What to do?
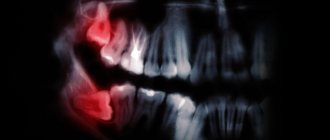
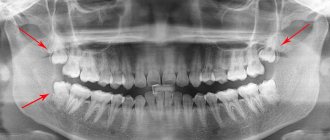
If a wisdom tooth causes severe discomfort and erupts in the wrong position, it will most likely have to be removed; there is no other solution to the problem. It is better to entrust such complex dental removal to a real professional so that the procedure is carried out according to all the rules. First you need to carry out diagnostics to understand the exact location of the unit. For this purpose, an X-ray of the jaw is performed. Let's consider a step-by-step algorithm for surgical intervention:
- Use of local anesthetic. High-quality long-acting medications are needed, since wisdom tooth removal can take several hours.
- Excision of soft tissue is performed.
- Using a drill to create access to the tooth root.
- Using special forceps, the tooth is removed from the oral cavity.
- The wound is carefully treated with antiseptic agents.
- Stitches are required to stop the bleeding.
Many patients ask the same question: is it possible to leave a tooth in the mouth and not remove it? Experts say that this is quite possible if the new unit does not cause pain or discomfort and does not interfere with neighboring teeth.
Removal
If complications occur, severe pain and incorrect position, the doctor may recommend removal. This is done under local anesthesia after a preliminary examination. It is necessary to undergo a series of studies; the doctor will evaluate the condition and structure of the jaw, the presence of interlacing or curvature of the roots, and other problems. This makes the operation less traumatic for the patient and forgives the dentist’s actions. But even with a preliminary examination, removing eights can become a rather complex process, including the following steps:
- the oral cavity is prepared, the doctor uses local anesthesia for pain relief;
- an incision is made at the site of growth and the tissue is pressed away from the bone;
- using a drill, the doctor drills holes in the bone around the figure eight, which facilitates access and facilitates subsequent removal;
- interroot partitions are sawed (if the roots are entangled, the unit is large);
- all fragments are removed, the wound is washed, a drug is applied to the hole to prevent the development of inflammatory processes and infection;
- stitches are placed on the fabric.
The duration depends on the complexity of the intervention and the condition of the tissues. After the operation is completed and the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel pain and discomfort. But if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, the pain quickly goes away, and the soft tissues heal quickly.
Recommendations after removal
After removal, the patient must follow a number of recommendations:
- the cotton swab is removed only after twenty minutes after tooth extraction to avoid infection;
- it is necessary to measure the pressure, if it increases, you should take medications to lower it (only under the supervision of a doctor);
- To reduce swelling and pain, you can apply ice compresses to the cheek;
- after the operation, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, which must be taken strictly according to the prescribed regimen, without skipping doses or exceeding the dose;
- It is allowed to take painkillers and injections of lincomycin (as prescribed by the dentist);
- Once a day, the mouth should be rinsed with special products containing chlorhesidine, but this should be done carefully so as not to wash out blood clots;
- It is not recommended to use herbal infusions, as they have little benefit;
- Do not rinse your mouth with hot solutions or use hot compresses, as this will worsen the condition.
On the day after removal, you must give up physical activity and solid food. It is not recommended to disturb the removal site in order to speed up healing and eliminate swelling.
Recommendations after tooth extraction
Removing a complex tooth is considered a full-fledged operation. For this reason, dentists recommend carefully observing the rehabilitation period so as not to provoke the development of complications:
- At the end of the dental procedure, the doctor places a gauze pad. Do not rush to remove it from your mouth; keep the turunda in your mouth for at least 15 minutes.
- When you get home, apply a cool compress to your cheek. This will help avoid severe swelling and soothe the aching pain.
- Do not self-medicate, take only those medications prescribed by the doctor.
- Rinsing the mouth is only permissible on the recommendation of a doctor. As a rule, short-term antiseptic baths are done to prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microflora.
- Monitor your body temperature. If it increases, you should see a dentist.
- Do not heat your tooth under any circumstances. Don't take a bath and limit strenuous physical activity for a week.
- Eat soft foods that can be consumed through a straw.
- If you experience disturbing symptoms, do not ignore going to the doctor.
- If after the end of the painkiller you are in pain, you are allowed to take a painkiller tablet in accordance with the instructions.
Consequences
Launched processes cause serious complications, including the destruction of neighboring units and their loss. In addition, the consequences include:
- destruction of the roots of adjacent units;
- damage to the enamel of the seventh units, development of caries;
- signs of inflammatory processes and severe swelling appear on the cheek;
- facial asymmetry appears;
- the development of inflammatory processes in bone tissue, the appearance of phlegmon, periostitis, pericoronitis and other diseases;
- soft tissues become denser, degeneration occurs, which can cause the appearance of malignant and benign tumors.
You can exclude complications by consulting a doctor in a timely manner. After diagnosis and external examination, the doctor will assess the condition, predict eruption and choose treatment methods. In some cases, serious intervention is not required, but if it grows sideways or in the cheek, the doctor recommends removal.
Causes of abnormal growth
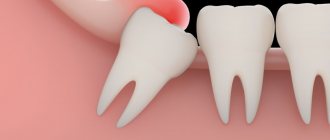
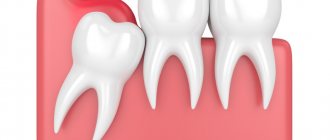
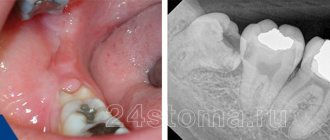
“Eights” or, as dentists call them, third molars, are a vestige left over from our ancient ancestors - the Neanderthals. The structure of their skull was different, and their jaw was more elongated, so there was enough room for 16 teeth. Over time, the structure of the head changed, human food became softer, and the jaws stopped protruding strongly forward - the “eights” simply became cramped. Sometimes they literally have nowhere to grow, so they erupt wherever there is at least a little free space. There are frequent cases when a dystopic wisdom tooth begins to grow towards the cheek in both the upper and lower jaws) - you can understand what kind of anomaly this is from the visual photo below.
The pathological process of eruption also arises because the “eights” do not have milk precursors, and therefore, no ready place for growth and location, like the other units of the series. Therefore, they have to pave the way with difficulty, in several stages. For the same reason, in some people, third molars do not grow at all - they either remain in the thickness of the bone or do not form at all.
For your information! In some European and American clinics, doctors remove third molars at the stage of their formation, thus saving patients from the painful periods of eruption of “eights” and possible complications with their growth. Russian dentists do not adhere to this practice, believing that there is no point in removing a healthy “eight”: sometimes when other molars fail, it can become a support for an orthopedic bridge during prosthetics.
Sometimes the cause of a dystopic “eight” can be a pathology of the jaw structure (as a rule, such a defect is inherited) or a non-standard shape of the third molar (too large a crown). You can see in detail what a wisdom tooth looks like growing into the cheek in the photo.
Indications and contraindications
The attending physician (therapist) or orthodontist directs the removal of a molar in the lower jaw. In any case, the patient is sent for a panoramic photo, where the location of the teeth is visible. This procedure facilitates the work of the surgeon who has to deal with a complex operation. Contraindications for removal are as follows:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding. After such a complex removal, the mother will have to stop breastfeeding, because antibiotics and painkillers can get into the baby along with the milk.
- People of the older generation with a diseased heart, hypertension of the 2nd or 3rd degree should be attentive to their health and not rush into surgery, but it is better to refuse it altogether.
- Malignant formation in the tooth growth zone.
Tooth extraction is also done as a preventive measure in advance, so that later they do not hurt and do not interfere with others.
Advantages of treatment at Aurora
Removing the lower wisdom tooth is a complex procedure that requires high specialist competence. Due to the inconvenient location and improper growth of the last molar, neighboring teeth suffer. Highly qualified specialists of our center easily and quickly carry out complex operations of this level. In addition, Aurora dentistry has other important advantages over its competitors:
- the possibility of receiving installments from Pochtabank or Renaissance Credit;
- individual approach;
- work on weekends, including for residents of the region by appointment;
- The doctor is assisted by an assistant, which allows him to carry out manipulations 2 times faster;
- modern, 100% high quality, imported materials.
Our dentistry offers the following promotions for the removal of the lower wisdom tooth:
- If you found out about us through 2GIS, we provide 5% on services;
- 10% discount on your birthday and the next 3 days
- For pensioners there is a “Golden Watch” promotion - a 10% discount on tooth extraction from 9-00 to 11-00
If you need complex and long-term dental treatment in Blagoveshchensk, we have an individual discount policy and a flexible payment schedule
To make an appointment, just call. On the appointed day, the doctor will see the patient and tell him how the lower wisdom tooth will be removed without pain after the procedure and fear.
In order to answer this question, let’s figure out what kind of wisdom teeth they are.
It is not without reason that wisdom teeth received such an interesting name; many beliefs and legends are associated with them. The ancients believed that a person develops these teeth (17 - 25 years old) only when his soul has strengthened, become mature, and life wisdom has appeared. The eruption of all 4 teeth indicated the protection of the clan, so they were practically not removed - because then the person was deprived of protection.
These teeth are also called “eights”, as they are the eighth in the dentition. Wisdom teeth are unique because they are the only group of teeth that do not have a clear anatomy, and for the most part they are all different. It is impossible to be unambiguously sure of the number of root canals and their patency.
Nature has endowed humans with “figure eights” so that the teeth are located closer to each other and to make chewing hard food easier. Now this problem has lost its relevance. In the modern world, we eat softer food, so wisdom teeth began to grow much later than others and not in all people, so “eights” are considered to be rudiments. According to data, 15 - 20% of the population have no wisdom teeth at all, not even the rudiments. The rest have rudiments, but often they prefer to remain in the thickness of the jaw and not rise to the surface. And only some “lucky” ones can experience the beauty of teething already in adulthood.
The unpleasant sensations that wisdom teeth sometimes cause can be safely blamed on the process of evolution. Over the millennia, the human body has transformed, and the jaw is no exception. Gradually it decreased, but the size of the teeth did not change. Because of this, wisdom teeth, which are the last to grow, do not have enough space in the mouth.
Wisdom teeth, indeed, are almost not involved in the chewing process. But you shouldn’t neglect them either, since a fully erupted wisdom tooth in the event of loss of other teeth can “save” a person from removable dentures.
In what cases is it worth fighting to preserve a wisdom tooth?
Arguments for"
A wisdom tooth that has completely erupted and is affected by caries can and should be treated. If the canals are well passable, not curved and can be filled with high quality, even complications of caries (pulpitis, periodontitis) are not a “sentence” for these teeth.
There is one advantage in the “eights”, because of which some patients try to save them. Erupting later than others, wisdom teeth can become a support for a bridge prosthesis - instead of damaged teeth. Without the figure eight, such permanent prosthetics will only be possible with the help of implants.
A wisdom tooth may definitely be required for prosthetics if: the seventh tooth in front is missing, both the sixth and seventh teeth are missing, or the sixth and seventh teeth have not yet been removed, but will soon be removed.
Definitely delete!
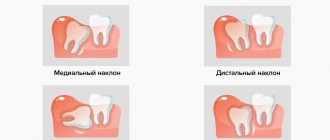
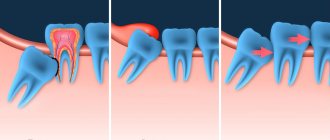
Delayed eruption (retention), incorrect position (dystopia) of the wisdom tooth
As a rule, this is a partially erupted wisdom tooth, lying horizontally or with its crown tilted towards the lingual, buccal, medial (inclined towards the “seventh” tooth), distal (towards the angle of the jaw) sides. The value of such a tooth for prosthetics and chewing food is zero. It happens that the crown of a wisdom tooth has a pronounced slope towards the cheek area. This leads to the person biting his cheek all the time. Chronic injury to the buccal mucosa can even lead to the development of an oncological process in this area. There is no point in preserving such teeth.
2) Destruction of the front (“seventh”) tooth
As mentioned above, wisdom teeth often erupt at an angle. The front cusps of the crown sometimes rest against the seventh tooth in front. Lack of adequate hygiene and constant pressure from the wisdom tooth on the enamel of the nearby tooth can cause its destruction and the occurrence of caries. Preserving the seventh tooth and its full treatment is sometimes not possible without removing the wisdom tooth.
3) Orthodontic indications (bite anomalies).
Previously, to correct the bite, “fourth” teeth (less often “fifth” teeth) were often removed for subsequent orthodontic treatment. These teeth are located in the smile line and from an aesthetic point of view, it is currently more advisable to preserve them. Therefore, removal of wisdom teeth is the right decision, since they can provoke relapse after early orthodontic treatment, due to later eruption. In addition to removing impacted wisdom teeth, orthodontists recommend removing even the rudiments of these teeth.
4) Pericoronitis (inflammation of the mucous hood).
A fully or partially erupted wisdom tooth occupies such a position that part of its crown is covered with an overhanging hood of mucous membrane. In this case, a space is formed between the hood and the tooth in which microbes multiply, which leads to inflammation. In such cases, patients, as a rule, note aching pain in the jaw, discomfort when opening the mouth (sometimes limited mouth opening caused by inflammatory muscle contracture), pain when swallowing, enlarged lymph nodes, and sometimes swelling of the cheek appears. In this case, to stop the inflammatory process, the mucous hood is excised, followed by anti-inflammatory therapy. Such inflammations can happen more than once, so the only correct solution is to remove the wisdom tooth.
There are situations when it is impossible to maintain the “eight”, and inaction is dangerous!
These are inflammatory processes caused by wisdom teeth. Periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw). Initially, complaints appear of aching pain in the tooth, which intensifies when biting (a symptom of an “overgrown” tooth). If the patient ignores these pains, the inflammatory process spreads to the periosteum. In such cases, swelling appears and general health worsens. At the same time, pain in the tooth decreases. In case of extensive destructive process on the roots, the tooth is removed with dissection of the periosteum (periostotomy) and subsequent drainage of the lesion.
More serious complications are osteomyelitis (inflammation of the jaw), abscesses and phlegmons (limited and widespread purulent processes of soft tissues), abscessing lymphadenitis (purulent melting of the lymph nodes) and others. These diseases are an indication for the removal of wisdom teeth, followed by serious treatment in a hospital.
Summarizing all of the above, I would like to focus on the fact that everything is very individual, and only after carefully weighing all the pros and cons, having received a comprehensive consultation with a doctor, should you make a decision regarding treatment or removal of a wisdom tooth.
Causes of pathology
The formation of the structure of the future jaw apparatus and the formation of hard tissues occur in the prenatal period. And anomalies and individual characteristics appear with age, when the eruption of a specific unit begins. Experts identify typical violations during the growth of “eights”:
- development proceeds incorrectly if the rudiment has an abnormal shape and direction;
- the last tooth stands out from the general row due to its large size or unusual shape. There is not enough space for it to be positioned correctly on the jaw;
- There are not enough minerals for normal tooth growth due to general metabolic disorders;
- jaw pathologies can also provoke disruption of the hormonal system;
- there is crowding, an increased number of units in a row. There is simply no room for a figure eight on the jaw arch;
- Sometimes jaw pathology is observed in the opposite situation: excess space for a wisdom tooth provokes its incorrect position.
Whatever the cause of the pathology, it is impossible to correct it at home. If you have such a problem, it is recommended to immediately seek medical help to correct or surgically remove the unit.
Make an appointment for lower wisdom tooth removal
Byshlyaga Dmitry Yurievich
Byshlyaga Dmitry Yurievich Orthopedic dentist
Extensive practical experience. Regularly undergoes internships and advanced training courses.
Working hours: from 9.00 to 20.00, daily, seven days a week, by appointment
Make an appointment
More details
Asatryan Alexander Aramovich
Asatryan Alexander Aramovich Dentist therapist - orthopedist - surgeon
Extensive practical experience. Regularly undergoes internships and advanced training courses.
Working hours: from 9.00 to 20.00, daily, seven days a week, by appointment
Make an appointment
More details
×
When is it better not to remove a wisdom tooth?
It seems that removing the lower wisdom tooth is the best solution to all problems, but this is not always true. In many patients, the eruption of “eights” occurs without complications, and in the future these teeth do not cause inconvenience, so there is no need for surgery. Also, you should not pull out your lower wisdom tooth if:
- dental prosthetics are planned and the third molar can become a support for a bridge;
- "seven" is missing. In this case, the wisdom tooth will take its place;
- caries affects only the upper part of the wisdom tooth. Then, instead of a traumatic removal operation, you can perform a regular filling, the price of which will be lower.
Relative contraindications to wisdom tooth removal are:
- infectious and inflammatory processes affecting the oral cavity
- for example, periodontal disease. In this case, you first need to stop the inflammation and take a course of antibiotics, and only then proceed to remove the molar; - respiratory diseases
- influenza, ARVI. They can provoke postoperative complications; - pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- cardiovascular diseases
in the acute stage.
Causes of injury
The lining of the oral cavity is very delicate. Even a slight impact violates its integrity. Any damage leads to infection. The severity of the damage, as well as the clinical picture, depend on the strength of the impact and on the characteristics of the body. The most common type of damage diagnosed is mechanical. Constant injury to the cheek by teeth is dangerous. Based on the depth of the lesion, the following types of pathologies are distinguished:
- Hemorrhage inside tissues, that is, hematoma, when their integrity is not broken;
- Erosion after injury;
- Decubital ulcer;
Most often, erosions occur in irregular shapes. They are covered with a thin whitish-yellow coating. Ulcers, as a rule, are single, there is no swelling around them, they become moderately painful. Their bottom and edges are covered with a fibrinous film. The usual localization of ulcers is the inner side of the cheeks, tongue. With prolonged absence of therapy, their bases and edges become denser. Common causes of damage:
- In babies in the first months of life, the mucous membrane is affected due to premature eruption of the masticatory organs. Since their dentin, the enamel layer, is underdeveloped, the frenulum, the lower part of the tongue, is injured when sucking. Disruption of the epithelial layer causes inflammation.
- Biting lips and cheeks after anesthesia form abnormalities. In addition, children are often injured by stuck plates of apple cores.
- People with increased nervousness may bite their cheeks, tongue, or lips. They often bite pencils and pens.
- The provoking factor for injury may be the sharp edge of the crowns.
- Damage occurs from overhanging edges of fillings, from wire splints, from ligatures, from wearing orthodontic systems.
- Mechanical damage occurs in people who wear improperly installed veneers.
- Accidental biting occurs when eating in a hurry.
- Patients often consult a doctor with occlusion problems, carious cavities, and dilapidated crowns.
- The causes of injury include chips, fractures of masticatory organs, and remnants of roots.
The oral cavity in children can be damaged by sharp toys, household items, and exposure to various bad habits. Defects occur during coughing, when the tongue is pressed tightly against the sharp parts of the lower units.
Safe and high-quality removal of wisdom teeth in Balashikha
The Berezka dental clinic offers qualified assistance to anyone who, for certain reasons, requires the removal of a wisdom tooth from above or below. The operations are performed by experienced surgeons using safe anesthesia and modern instruments.
Before the procedure, the dentist collects the patient’s medical history, conducts all the necessary examinations, and only if the clinical picture is present is it possible to extract the wisdom tooth.
The operation is performed in a comfortable environment for the patient. Innovative equipment and professional dentists ensure successful and safe removal of the most complex teeth.