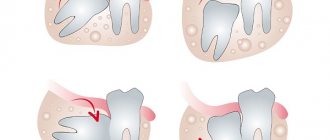
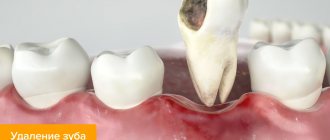
Alveolitis is an inflammation of the socket (alveoli) left after tooth extraction. This pathology does not always develop; its development depends on many factors. The disease is characterized by severe pain in the area of the hole formed after surgery, general weakness, fever, headache, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, bad breath and other unpleasant symptoms.
Alveolitis is not only physically painful, but also a dangerous disease. In the absence of proper treatment for several days, the inflammatory process can result in limited osteomyelitis, purulent melting of the jaw bone, and then surgical intervention will be required again.
With timely diagnosis of pathology and proper sanitation of the socket, the treatment prognosis is favorable. The main thing is to detect the symptoms of the disease in time and begin to treat it.
Situations in which swelling is not a cause for concern
In many cases, swelling that occurs after tooth extraction is normal and should not cause alarm.
There is no need to worry if:
- The swelling is mild and does not increase over time. If tooth extraction turned out to be traumatic or was carried out against the background of severe inflammation, then slight swelling is allowed to appear, which should go away on its own in a couple of days.
- Body temperature is slightly elevated, but does not increase over time, or is completely within acceptable values. Removing a tooth when it is inflamed can cause a slight increase in temperature, which, if the source of pain has been eliminated, quickly subsides.
- There is no increasing pain. A sign of normality is the presence of slight pain (after all, removal is a surgical procedure during which soft tissues are injured), gradually decreasing over time. If the pain does not go away, or its strength increases, then this indicates either increasing inflammation or the occurrence of any complications.
- The hole left after the operation is closed with a blood clot. Naturally, after the procedure, the hole is filled with rapidly clotting blood. This clot reliably protects the tissue, preventing the development of an inflammatory process.
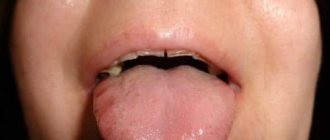
After removal, the cheek may look swollen for one day - this is a period during which you should not worry. If after 24 hours there is no obvious deterioration and the swelling decreases, there is no need to waste time on a visit to the dentist. But if at least one of the symptoms listed above is present, this indicates the need to make an appointment with a dentist as quickly as possible in order to prevent the situation from worsening.
Signs
The appearance of a bruise on the gum is accompanied by a host of other unpleasant symptoms: the formation of a compaction (nodule), swelling of the soft tissues, increased body temperature, and weakness. The patient may experience pain directly at the site of the surgical intervention, but the pain can also radiate to neighboring teeth and radiate into the jaw.
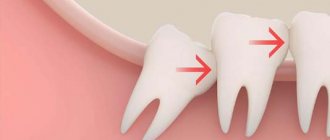
Hematoma after extraction of a wisdom tooth is a common phenomenon due to the “inconvenient” location and, accordingly, difficult medical access to this unit, as well as the high risk of damage to soft tissues during surgery. In an empty socket, there is often a feeling of tingling, pressure, tightness, and numbness.
When you can't do without a doctor's help
If any of the situations listed below arise, you need to go to the dentist, who will take the necessary measures (wash the hole, put in medicine, take measures to release pus, etc.).
So, you can’t do without a trip to the dental clinic if:
- The swelling that appears after removal does not subside, but, on the contrary, grows. In this case, there is no point in continuing to wait, since it is obvious that the situation will not resolve itself. Swelling may indicate inflammation or suppuration. In some cases, swelling can develop to large sizes, affecting the area under the eye.
- There is pain that does not decrease over time. Severe pain for a couple of days is acceptable only with a particularly difficult removal, accompanied by sawing out the bone: in all other situations, the pain should decrease and completely disappear after 1-2 days.
- The temperature rises.
- Feeling unwell does not go away.
- There are difficulties opening the mouth and making swallowing movements.
- There is no blood clot in the hole left after tooth extraction. Perhaps the clot simply fell out or was washed out when rinsing the mouth. If there is no clot, then the risk of inflammation increases, which is accompanied by very severe pain. It is useless to wait patiently for the pain to go away on its own: the dentist, having assessed the situation, will administer the required medicine, which will quickly relieve the discomfort.
Sometimes swelling does not appear immediately, but 3-4 days after surgery. Typically this is due to the fact that:
- the blood clot in the socket has festered;
- inflammation began in the hole.
This condition is called alveolitis. With this inflammatory lesion, self-medication using antibiotics and other medications is pointless. Only a doctor can alleviate the patient’s condition by clearing the hole of small food debris and placing medicine inside.
Sometimes a hematoma may form on the gum. In the first few days after its appearance, it may not cause attacks of pain or lead to swelling of the cheek, however, when obvious signs of suppuration are visible, leading to pain, you should consult a dentist, who will most likely open the hematoma.
Treatment
Oral injuries can vary in nature and severity. No matter how painful a tooth bruise seems, treatment must be carried out in a specialized dental clinic. We at Natadent often encounter such cases. After the initial diagnosis, visual examination, interviewing the patient and collecting anamnesis, an x-ray is taken - this is the only way to clearly determine which tissues are damaged and prescribe the correct treatment.
By studying an x-ray, the doctor can determine what kind of damage the tooth has received (this could be a fracture, dislocation, crack, various deformations and other pathologies).
Only after a correct diagnosis can treatment be prescribed. If a tooth injury has caused serious damage, electrodiagnostics is prescribed - a special procedure that allows you to determine the condition of the pulp, detect hemorrhages and necrotic areas in it. If diagnostic actions show that the damage is not very serious, a set of preventive measures is prescribed, which includes:
- application of compresses;
- use of decoctions for mouth rinsing;
- exclusion from the diet of hot dishes and foods that require chewing; exclusion of this area of the dentition from the chewing process by applying a bandage or protective splint.
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
If a more serious tooth injury is diagnosed, treatment may include surgery to the structure of the tooth and surrounding tissue. The sequence of actions is determined by the complexity of the injury, but in most cases includes the following steps:
- ;
- Local anesthesia is performed (or general if complex and painful treatment is involved).
- If the pulp sac is damaged, even if the tooth enamel has retained its structure, the doctor drills a hole in it and removes the nerve.
- The canals and cavity are cleaned, treated and filled, as in conventional caries treatment.
;
;
A tooth bruise is a dangerous injury that can lead to undesirable consequences and complications. Even if pulp removal and filling have been performed, it is advisable that the patient undergo a course of therapeutic treatment, and after some time come for additional examination. Only after this can it be said that the consequences of the injury have been completely eliminated and there will be no complications.
When should swelling occur?
There are situations when the development of noticeable edema is inevitable. They arise:
- After an operation of increased complexity. Removal accompanied by damage to nearby tissues (for example, when it is necessary to saw out bone or incisions in the mucous membrane) leads to the appearance of edema. In some situations (for example, when the eighth tooth is removed), facial asymmetry is likely to occur.
- When removed due to severe inflammation. Then an infection remains in the hole, which can become the main cause of swelling. If the operation is carried out in compliance with all the rules, then the dentist, seeing inflammation, is obliged to thoroughly rinse the wound with an antiseptic solution, and then apply the medicine. Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed. However, even then it cannot be said that the inflammatory process will not begin.
- When cutting the gums on which there is an abscess, the dentist makes an incision to release the pus located in the soft tissues. If there was already a slight swelling during the procedure, it may increase slightly in size, which is normal.
- When contacting people suffering from certain diseases. Quite often, according to the observations of dentists, patients who have high blood pressure complain about swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction, leading to the accumulation of a subcutaneous fat layer on the face. In such people, swelling may well appear even with normal removal, which proceeds without any complications.
How to get rid of swelling at home
If there is no reason to see a doctor, but you want to get rid of the swelling as soon as possible, you can try the following methods:
- Immediately after removal or surgery, apply a cold compress (water bottle, wet cloth). The application must be repeated throughout the day once every half hour for 5 minutes. ATTENTION! Using a cold compress on the second, third, etc. day is unacceptable.
- Use special decongestant ointments.
- Sleep with your pillow raised high.
- After a few days, cold compresses are replaced with warm ones. A single session of the procedure should not exceed half an hour. Vasodilation and increased blood flow promote faster recovery.
- use corticosteroids. Since this type of drug has many side effects, it is better to consult a doctor before taking it. You should resort to these medications only in cases of extreme necessity, when pain due to swelling interferes with normal daily activities.
- These methods should be used if there are no complications: in other cases, it is recommended to consult a doctor for a detailed examination.
Complications of edema and methods of dealing with them
Often, swelling is accompanied by one or more complications from the list below:
- bleeding. A little bleeding is normal. If there is more blood, the wound can be pressed with a gauze pad moistened with an antiseptic (for example, Chlorhexidine). If bleeding does not go away for more than 2 days, you should not delay visiting a doctor;
- numbness. After any dental procedure, the area around the mouth may lose sensation. There is nothing wrong with this if the side effect goes away within 12 hours;
- the occurrence of pain, which is acceptable even after surgery. The main rule is that pain should decrease within a couple of days. In some cases, the pain can be so severe that a person cannot chew food (the condition should last no more than 5 days). To alleviate this condition, you can take painkillers (for example, paracetamol);
- the occurrence of a dry socket after surgery (especially important for smokers). In this case, a blood clot, without which the healing process is impossible, does not form. The condition is often accompanied by a feeling of pain and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The most effective way to combat it is to wash the wound several times a day, followed by applying an antiseptic bandage.
Accelerated rehabilitation
For patients who want to quickly overcome the period of operational inconvenience, our Center provides an accelerated rehabilitation complex.
- Injections of lymphatic drainage drugs The composition of the drugs includes biostimulants, peptides, a complex of microelements and vitamins. They improve blood and lymph circulation and have anti-inflammatory properties. Minimize swelling and hematomas, accelerate wound healing.
- PRP plasma therapy Blood plasma is rich in platelets, which use the body's reserve forces. The work of the immune system is enhanced, regeneration processes proceed faster. Swelling and bruising disappear, soft tissues heal faster.
- Microcurrent therapy Exposure of facial skin to weak currents activates cell function. Recovery processes are accelerated, blood circulation improves. Swelling and pain go away, spasms of the muscles of the face and neck decrease.
Minimizing swelling and bruising, reducing muscle tension is possible on the day of your visit
After restorative procedures, the condition improves instantly. You can lead your usual lifestyle - walking, going to work and visiting. But do not forget to follow postoperative recommendations to avoid complications!
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
Diseases that occur after tooth extraction and cause swelling
When teeth are removed (in particular, molars, canines and incisors), the following diseases may occur:
- alveolitis, when suppuration of the hole occurs. Accompanied by swelling of the cheeks and cheekbones. The temperature rises, general weakness occurs, and bad breath appears;
- osteomyelitis is a disease in which the jaw bone becomes inflamed (the process is accompanied by the formation of pus). The cheek swells at the site of inflammation, and the pain affects the entire row of teeth. It becomes painful for a person to open his mouth and talk. The disease is accompanied by severe headache and fever; in some cases, blood poisoning is possible (if you do not consult a doctor in time);
- neuritis. The facial nerve is affected, which is accompanied by acute pain. Quite often it occurs when teeth with long roots are removed. With neuritis, the cheek becomes swollen and numb; numbness also affects the palate, larynx and tongue.
How to prevent complications?
To avoid swelling and subsequent treatment, it is recommended:
- Keep your head held high for at least 12 hours after surgery (or better yet, 24 hours). To do this, while lying down, you need to place several pillows under your head;
- do not touch the hole with your tongue or fingers;
- do not use warm compresses for 36 hours after surgery;
- do not smoke or drink alcohol for 72 hours after surgery.
Correct behavior after surgery is no less important than the procedure itself: if you adhere to the above rules, the swelling will go away either in the shortest possible time or will not occur at all.
Preventive measures
Since the likelihood of swelling after tooth extraction is quite high, the following recommendations should be followed to minimize the risk of cheek swelling (the same rules apply in cases where swelling has already formed and needs to be removed as soon as possible):
- use oral baths (the salt liquid is only kept in the mouth without rinsing, since otherwise infection of the hole may occur);
- use anesthetics to relieve pain. As a rule, these are Ketanov, Ibuprofen and other similar drugs that reduce the inflammatory process and relieve pain. The most important thing is to follow the dosage indicated in the instructions;
- follow the diet. If an operation has been performed, then on the first day you should not eat hard or hot food, as it can cause injury to the already damaged gum. During the week after surgery, the basis of the diet should be soft and non-spicy foods. Until the swelling goes away, it is better to chew on the other side of the mouth, doing it slowly;
- Avoid taking hot baths, as this may cause bleeding from the socket;
- When brushing your teeth, skip the operated area until the swelling goes away.
- On average, swelling subsides within 2-3 days from the date of surgery: if this does not happen, you will have to contact the dentist again for an examination and additional research if necessary.
Tooth bruise - what to do?
Please note that it is impossible to determine the severity of the injuries yourself. A complete diagnosis must include an x-ray and a professional examination in a dental office. At home, an experienced dentist can examine the damage and make certain assumptions, but even without the necessary tools, he will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
If it is obvious that the tooth bruise is quite serious, self-treatment is unacceptable. To ease the pain, you can apply ice or just a cold object and go to the dentist as quickly as possible. If it looks like the jaw is damaged, it is advisable to fix it with a bandage. It is advisable that someone accompany the victim, since he may lose consciousness on the road.