We all know about such a disease as dental caries. And of course we know that dental caries must be treated, since otherwise not only the appearance of the teeth will deteriorate, but various complications may also arise. For example, pulpitis. Dentists use this term to refer to inflammation of the nerve bundle or, more simply, the dental nerve, which is located in each tooth.
How does pulpitis appear, what are the signs of this disease, how is pulpitis treated? Our article will help you find answers to these questions, in which we will tell you in detail about tooth pulpitis.
Definition of the concept in dentistry
Deep caries is the last stage of the carious process occurring in the tooth, which is characterized by extensive damage not only to hard tissues, but also to the deep layers of dentin. In general, the concept of “deep caries” reflects the depth of the lesion.
Caries can be:
- primary - a consequence of untreated secondary caries;
- secondary (recurrent) - the occurrence of a carious process under a filling in a previously treated tooth.
Based on the sensation of pain and clinical examination, the disease is divided into 3 forms:
- Acute form. It is determined by the narrow entrance opening of the carious cavity and the wide base (during examination), as well as by descriptions of the patient’s sensations - reaction to food temperature and chemical irritants.
- Chronic form. It is characterized by a wide (funnel-shaped) inlet and a narrow base. The patient feels pain when the “hollow” is clogged with food and during examination with a probe by the dentist.
- Deep cervical caries. It is characterized by the development of demineralization of enamel tissue and the carious process in the cervical area of the tooth (near the gums).
According to the clinical course, caries is also divided into several forms:
- compensated,
- subcompensated,
- decompensated.
What is a root canal?
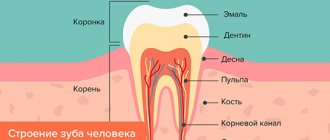
Each tooth, except for enamel and dentin, has an internal space - a pulp chamber, communicating with thin cavities running along the entire length of the roots of the teeth - root canals. Different dental groups have different numbers of roots, and, accordingly, canals. The front group has 1 channel, the side ones - from 2 to 4.
Narrow, winding, thin tubes with many branches - this is how to characterize the root canals of teeth. The entrance to them is located at the apex of the tooth root, it is called the apical foramen. Through it, through each root canal, passes neurovascular tissue, which is responsible for the blood supply and innervation of the tooth.
Endodontic treatment is a procedure for removing infected, inflamed or dead neurovascular tissue, followed by cleaning and disinfection of the resulting space, and completely sealing the dental canals.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which include:
- external inspection using a mirror;
- instrumental examination using a probe;
- voicing symptoms (complaints) by the patient;
- thermal diagnostics (checking the reaction to cold and hot);
- electroodontic diagnostics (testing the reaction to exposure to current);
- radiography (performed if the presence of secondary deep caries is suspected or to exclude it).
If upon examination significant damage (destruction) of the tooth crown is detected, expressed by the presence of a deep carious cavity and accompanied by pain during probing, then this confirms the presence of deep caries in the patient.
In the acute form, the carious cavity is filled with light, softened dentin. In chronic deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with a layer of dense pigmented dentin (from brown to black). Percussion of the tooth is not accompanied by pain.
Diseases that require endodontic therapy
Treatment of tooth canals is performed only if there are strict indications, since as a result of the intervention, the tooth is deprived of the vessels and nerve endings that feed it, which makes the dental tissues less durable and more susceptible to destruction. Indications for intervention include inflammation and infections accompanying caries or traumatic tooth damage:
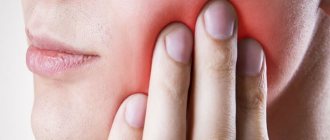
- Pulpitis is inflammation of the pulp (neurovascular tissue) - soft, fibrous tissue, including blood and lymphatic vessels, nerve endings and connective tissue.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the tooth root and surrounding tissues (periodontal tissue).
These diseases are usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Acute, throbbing or aching pain in the tooth, increasing at night or intensifying with load on the tooth.
- Swelling, discoloration of the gums, formation of ulcers and fistulas on it.
- Putrid odor from the mouth.
In some cases, there are no pronounced symptoms and the development of pulp necrosis is detected only during a doctor’s examination. Only a specialist can accurately determine whether endodontic treatment will solve the problem and select the most effective therapeutic regimen.
What are the differences from other forms of the disease?
Deep caries is very similar to some forms of the disease, but there are still visible and invisible differences.
Difference from pulpitis
Pulpitis is a complication of advanced caries. The forms of the disease can be distinguished from each other by their characteristic symptoms:
- Defeat. With pulpitis, the nerve is affected; with caries, the nerve remains unharmed.
- Feelings of pain. With pulpitis, pain can occur spontaneously, even without exposure to irritants on the tooth. With caries, pain disappears along with the disappearance of irritants.
- Night sleep. With pulpitis, sleep can be disturbed due to severe pain; with caries, the tooth does not hurt at night.
Difference from average caries
The similarity between the two forms of the disease is that the patient in both forms feels pain from cold, sour or sweet foods. However, with average caries they go away within 1-2 minutes, with deep caries they last longer.
Medium caries is characterized by the fact that in this form the carious lesion does not affect the tooth pulp and does not cause inflammation of the nerve, as in deep caries.
Causes of dental problems
The occurrence of a problem such as caries is associated with the destructive effect of bacteria on the structure of the teeth. The microflora in the oral cavity includes a huge number of microorganisms. Even proper and thorough brushing of teeth with special means and the use of rinses cannot make the oral cavity completely sterile. The proliferation of pathogenic bacteria begins 2-4 hours after the last cleaning.
What exact reasons can cause tooth damage?
- poor oral care;
- unbalanced diet;
- decline in immunity;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- insufficient amount of minerals (calcium, fluorine) in drinking water.
Stages of treatment
Treatment of deep caries is impossible without anesthesia (pain relief) and it takes place in several stages.
- Anesthesia. It is carried out using injection (infiltration or conduction) administration of an anesthetic substance.
- Drilling out a carious cavity using a drill. In this way, the specialist can reach and remove all affected areas of dentin, which is very important to prevent relapse under the filling.
- Treatment (disinfection) of the walls of the tooth and the bottom of the cavity.
- Installation of a therapeutic insulating pad and temporary or permanent filling.
- The final stage involves grinding and polishing the filling.
The following factors influence whether a filling will be installed - temporary or permanent:
- at what distance from the pulp is the carious cavity located;
- parameters of dentin, which separates the pulp from the tooth cavity;
- degree of pain.
If there is a high probability of inflammation developing in the pulp area, the dentist will place a temporary filling. And only if there are no complaints of pain and discomfort for several days, the patient will have the temporary filling replaced with a permanent one.
Psychological aspect
To prevent children from being afraid of dentists, clinics use distracting maneuvers. While waiting and even during treatment, children can be shown their favorite cartoons. You can read a fairy tale, play games. Some clinics even have special rooms where boys and girls can relax and forget about the fear of an unfamiliar doctor.
The staff in children's clinics dress in bright clothes, and you can see smile masks on their faces. Each office has a thoughtful interior that resembles not a hospital, but a gaming center. The best clinics employ a psychologist who helps the child overcome his fear of dental treatment. The rest of the staff also takes courses in communicating with children.
A child’s teeth can be treated without general anesthesia, but it is better to use this safe method today. The main thing is to make it clear to the child from a very early age that the dentist is not a terrible doctor, but a friend of teeth from childhood.
Author: Zhukov M.A.
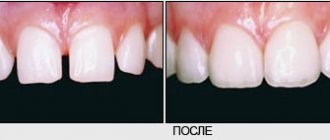
Deep caries of the front teeth. What are the differences in treatment?
Deep caries of the front teeth should be treated as carefully as possible so as not to burn the pulp. The main difficulty in treatment is:
- minimum thickness of all tooth tissues;
- inconvenient location of the cavity, if we are talking about caries located in the interdental space.
When infection penetrates into the pulp, pulpitis develops rapidly. A few hours is enough. The disease is accompanied by increasing pain. It needs to be treated immediately.
Potential consequences and complications
The very question of whether caries should be treated is very dangerous. It is important to never doubt that treatment is necessary. Often a person observes the first symptoms of a problem, but begins to put off going to the dentist. The time for treatment is constantly being delayed more and more.
The main danger of this approach is the likelihood of complications. The most common among them is the appearance of periodontitis or pulpitis.
There are several of the most serious consequences of untreated caries:
- Tooth loss. If the tooth is severely damaged or the lesion has gone very deep, there is nothing left except surgical intervention.
- Pathological processes in the gums. They can lead to the need to remove not only the affected tooth, but also its completely healthy neighbors.
- Systemic complications in the functioning of internal organs. The gastrointestinal tract and immune system suffer greatly. It is important to understand that a sluggish inflammatory process has a sharp negative effect on the entire body and weakens it.
The question of how caries is treated in dentistry in children is always considered separately. It is necessary to solve the problem that has arisen with baby teeth, because advanced disease leads to pathologies in the formation of permanent dentition.
Is it possible to treat deep caries of a wisdom tooth?
The patient can make the decision to remove a wisdom tooth if pain occurs on his own. But only a highly qualified dentist can make a verdict on its treatment.
Treatment of a carious "eight" is considered rational if it has a partial covering in the form of a hood of gum, as well as an antagonist - the third molar located on the opposite side.
Removal shown:
- with a horizontal tooth position;
- presence or absence of 1st and 2nd molars;
- impossibility of treatment due to incomplete opening of the mouth;
- displacement of teeth in a row due to wisdom teeth.
Expert opinion
Lyubov Ivanovna Kopylova
dentist-therapist
Experience: more than 10 years
If you have the opportunity to go to a dental clinic equipped with an electron microscope, take advantage of it! Even the most experienced dentist works with canals without a microscope by touch. This means that there is a risk of underfilling or, on the contrary, excessive deepening into the canal, leading to perforation. The use of a microscope, when the working field is clearly visualized and the doctor efficiently cleans and seals even the thinnest and most curved canals, will allow this situation to develop.
Infiltration method
Icon infiltration technology was invented at the Celtic University of Germany. This method of microinvasive treatment of caries refers to chemical-mechanical treatment, which completely eliminates tooth preparation - drilling, and is used only in the treatment of initial caries, initial carious lesions after using braces, as well as caries in the spot stage. The principle of operation of the method is to apply a special gel to the surface of the affected area of the tooth, which splits the enamel, after which the carious lesion is dried with 99% ethyl alcohol in combination with an air stream and impregnated with a polymer resin. The procedure protocol is clearly depicted in the figure below.
The positive aspects of this technology can be considered painless and quick (the procedure takes 15–20 minutes) removal of exclusively the affected part of the tooth. However, the method is applicable only on the smooth surface of the teeth or between them. Also, the shape of the “hole” should be ideal - with smooth edges and a wide entrance. International studies have confirmed the effectiveness of the infiltration method, which has made it possible to stop the development of caries for many years in both adult patients and children.
Preventive actions
Prevention of initial caries is aimed at proper oral hygiene. Try to brush your teeth after every meal. Use an antibacterial mouthwash and remember to brush the insides of your cheeks and tongue. Buy dental floss to easily remove food debris between your teeth. If finances allow, purchase an irrigator. This device thoroughly cleans teeth and removes pathogenic microorganisms from the enamel surface.
Let's consider a few more tips:
- Eat a balanced diet so that your body does not experience a deficiency of vitamins and microelements. Strengthen your immune system in every possible way. And, the most important rule, visit the dentist more often and promptly begin treatment for various oral ailments.
- It is important to maintain normal oral microflora. For this reason, you need to start treating colds in a timely manner and check your stomach condition once a year.
- An excellent preventative measure is to coat the enamel with fluoride varnish. This coating prevents bacteria from multiplying and prevents the development of superficial caries. For the highest efficiency, the procedure is carried out only 2 times a year.
- Dose out sweets, especially for children. Such products provoke the growth of bacteria. You should also limit liquids, which wash calcium from the body and make the enamel more vulnerable to the development of superficial caries.
Advantages of the Novodent clinic
Many patients come to us from Khimki, Kursk, Novogorsk and other cities. The list of advantages of contacting us includes the following:
- Affordable prices for treatment, many special offers and discounts.
- High-quality provision of services for all categories of patients.
- Safe, proven preparations for fillings and anesthesia.
- High speed of completion of all tasks assigned to the doctor.
- Extensive consultations on all issues related to the prevention and improvement of oral health.
- Lots of services and treatment options.
- Advanced equipment and techniques.
Call us or leave a request on the website to make an appointment with a dentist at a convenient time.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of ASEPTA series products has been repeatedly proven clinically. For example, multiple clinical studies have demonstrated that using ASEPTA propolis gum gel for a week can reduce gum inflammation by 31%. And the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Comparative clinical evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa IORDANISHVILI A.K. *,** Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Professor of the Department *Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (rector - Doctor of Medical Sciences Sayganov S.A.); **Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Military Educational Institution of Higher Education “Military Medical Academy named after S.M. Kirov" of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (chief - Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor A.Ya. Fisun).
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry