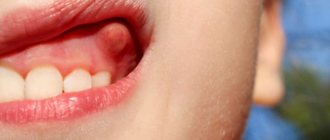
Flux is one of the most unpleasant phenomena in dental practice. It is a growth with purulent contents located on the gum. The tumor is formed due to inflammation of the periosteum. As a rule, it occurs against the background of advanced dental diseases.
Did flux form after installing the filling? Are your gums swollen and painful? In this case, you should contact your doctor or another dentist as soon as possible. Do not delay your visit to a specialist to prevent the development of more serious complications.
Causes of dental periostitis
In dentistry, gumboil is commonly called periostitis of the jaw. According to statistics, this disease is diagnosed in approximately 5% of patients. In most cases, the infectious-inflammatory process affects the lower jaw and occurs in an acute form.
Periostitis can be provoked by:
- chronic periodontitis - prolonged inflammation of the periodontal tissues,
- alveolitis - infection of the socket after tooth extraction,
- jaw cyst is a benign neoplasm with liquid contents,
- complicated wisdom tooth eruption,
- mechanical damage to the jaw,
- sore throat, flu, acute respiratory viral infections,
- dentist mistakes when cleaning tooth canals and filling.
After installing a filling, flux may form due to hidden inflammation. When a toothache occurs, many patients take painkillers rather than see a doctor. Tablets eliminate pain, but not its cause.
The dangers of flux and the dentist's tasks
It is the identification of such foci and their elimination, especially in persons suffering from inflammatory processes of internal organs and in pregnant women, that is one of the essential tasks of a dentist. Untimely sanitation of the oral cavity or its absence in the presence of teeth affected by chronic periodontitis can lead to the development of a number of more severe inflammatory processes, the first of which is acute purulent periostitis.
Purulent periostitis
This disease is an acute purulent inflammation of the periosteum of the alveolar process of the jaw and accounts for up to 40% of complications of odontogenic infection, mainly chronic periodontitis. The cause of the development of this disease is most often large molars, which are primarily affected by the carious process.
The clinical picture of acute purulent periostitis is diverse and depends on the nature of the microflora, localization and extent of the inflammatory process. When the upper jaw is affected, the external manifestations of acute inflammation, in particular hyperemia, infiltration and swelling of soft tissues, are usually more pronounced than when the flux is localized in the lower jaw. However, the phenomena of general intoxication are more pronounced when the alveolar process of the lower jaw is affected, which is due to the difference in the anatomical and topographic relationships of soft tissues and jaw bones.
When examining the oral cavity, smoothness or swelling of the transitional fold of the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the oral cavity, its hyperemia, and sharp pain when touched by the dentist’s hands or instruments are noticeable.
It should be borne in mind that the pain in the “causal” tooth due to the release of exudate (liquid released into the tissue or cavity of the body from small blood vessels during inflammation) beyond the periodontal gap subsides to a certain extent, but slight mobility of the tooth appears. This circumstance sometimes serves as a justification for delaying visiting a doctor and as a cause of aggravated course of the inflammatory process in the future.
The diagnosis of “acute purulent periostitis” is an absolute indication for surgical intervention in the form of opening and drainage of the periosteal purulent focus and removal of the “causal” tooth.
Options for non-drug treatment (physiotherapy) depend on the patient’s general condition, age, and concomitant chronic diseases. In the latter case, the volume and nature of drug treatment is determined by the dentist of the appropriate profile. It is especially important to carry out adequate treatment in patients suffering from rheumomyocarditis, diabetes mellitus, nephritis and some other chronic diseases.
Another complication of chronic granulating periodontitis is the development of acute odontogenic osteomyelitis , accompanied by the formation of phlegmons and abscesses of the cellular spaces of the face and neck.
These complications of flux are the most severe and dangerous result of the progression of odontogenic infection, and depending on the location and nature of the microflora, they can lead to severe complications including the development of sinus thrombosis and mediastinitis.
It is their timely diagnosis in somatic patients that largely determines the outcome of the disease.
The clinical manifestations of phlegmon are different and depend on the location of the flux (deep, superficial), the nature of the pathogen (aerobic, anaerobic flora), body resistance, concomitant diseases, age, etc.
Today, persistent, sluggish chronic necrotic processes in the bone and soft tissues of the face often occur against the background of drug addiction.
Deep phlegmons of the pterygomaxillary, infratemporal, peripharyngeal spaces are manifested by sharp pain of the corresponding localization, severe manifestations of general intoxication up to acute intoxication psychosis, severe inflammatory contracture of the masticatory muscles, pain when swallowing, with an almost complete absence of external manifestations: hyperemia, infiltration, fluctuations, etc. .
Underestimation of certain symptoms of gumboil can lead to a delay in seeking dental care, ineffective therapy and progression of the inflammatory process.
Clinical picture
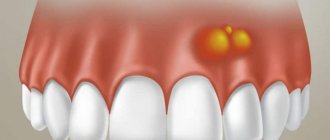
A clear sign of gumboil is a lump on the gum with purulent contents. Before its formation, the disease makes itself felt by throbbing pain in the tooth. Symptoms of the pathology are also:
- swelling and redness of the gums,
- swelling of the cheek or lip,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- pain when opening the mouth and swallowing,
- discomfort when pressing on a tooth,
- increase in body temperature,
- excessive weakness
- decreased appetite.
If you detect at least one of the listed signs of flux, you should contact the dentist. You should not warm the sore spot with a warm compress, take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription, or open an abscess at home.
What can you do before visiting the clinic?
Our dentists' recommendations will help you temporarily reduce discomfort.
- Wet a terry towel with cold water and apply it to the swollen cheek for 10-15 minutes. This compress will reduce pain and swelling.
- Do not heat the sore spot under any circumstances. Do not sleep on this side, do not tie it with a scarf, or apply a heating pad. Is it dangerous!
- Take a small dose of pain reliever. If it doesn't help, drink again after a few hours.
- Regular rinsing with warm infusions of sage, elecampane or valerian helps a lot.
- If your temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic. The medicine didn’t help, but the swelling and fever are increasing? Call an ambulance immediately!
Diagnosis and treatment
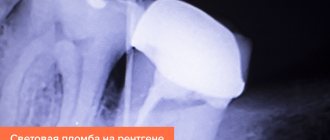
To make a diagnosis, the doctor only needs to examine the oral cavity and study an X-ray of the jaw. The flux treatment regimen is compiled individually for each patient. This may include:
- complex treatment of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis,
- taking antibacterial drugs,
- opening the abscess and draining the contents,
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions,
- physiotherapy - UHF, laser therapy, electrophoresis.
Causes of edema
Swelling of the gums is a consequence of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the soft tissues, causing infection.
Provoking factors:
- tartar formed due to poor oral hygiene;
- advanced form of caries;
- untreated stomatitis;
- infectious diseases of the throat;
- mechanical damage to soft tissues;
- difficult teething;
- immunodeficiency;
- vitamin deficiency (mostly severe lack of vitamin C);
- herpes virus activity;
- allergies to dental drugs or materials;
- development of purulent processes inside the tooth;
- the presence of tumors on the tooth root;
- gum diseases.
Before making a diagnosis, the dentist will definitely prescribe diagnostics to determine the internal state of the tissues, which will more clearly define the clinical picture and identify the main cause of the pathology.
When is tooth canal cleaning performed?
It is necessary to treat and fill root canals in the following cases:
- If caries has progressed to pulpitis (infection has spread to the dental pulp, or colloquially “dental nerve”). The pulp will have to be removed (the tooth depulped), and the root canals in which it was located will have to be thoroughly cleaned of tissue debris and sealed.
- If it is necessary to prepare a dental unit for the installation of a crown and the doctor believes that depulpation is necessary. Previously, when installing single crowns or supporting crowns of a bridge, the teeth were necessarily subject to depulpation; now this procedure is not performed in all situations and only when installing certain types of dentures.
- If there is a need for re-treatment of the tooth after the occurrence of a secondary source of infection or with the development of periodontitis, inflammation of the tissues around the tooth root (develops with poor-quality canal filling).
In all these situations, endodontic treatment is carried out (the name comes from the Latin words “inside” and “tooth”, that is, it can be literally translated as intradental treatment) with mandatory filling of the dental canals.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Why is it important to treat flux
Dentists warn that advanced periostitis is very dangerous. If you ignore its occurrence and do not carry out the necessary treatment, the following consequences may occur:
- accumulation of a large amount of pus, loosening of the tooth;
- destruction of the rudiments of permanent teeth (then after the loss of milk units, the permanent ones will not erupt - the child will face complete or partial adentia);
- abscess (in place of the abscess, the tissues seem to melt, forming a huge cavity filled with pus);
- phlegmon (can lead to blood poisoning and death).
Treatment of post-filling pain
Home treatment for pain that occurs after filling is fraught with serious complications. If a surgical visit to the doctor has to be postponed for several days (when the pain catches you on vacation or on a business trip), you can temporarily suppress it with the help of:
- rinsing with herbs (decoctions of chamomile, calendula, sage have a calming effect);
- disinfection with antiseptics (rinsing, using spray).
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken with caution, always in accordance with the instructions.
You should never put off going to the doctor. But in some cases this needs to be done immediately. Delay is dangerous when:
- the pain has become unbearable;
- the temperature has risen;
- inflammation began (gums, cheeks);
- lymph nodes have enlarged;
- abscesses have formed.
Incomplete treatment can lead to serious complications: the development of pulpitis, tissue necrosis, tooth destruction and loss. Therefore, try not to lose contact with your doctor until the post-filling recovery period has passed.
Number of views 5,643
Why does pain occur after an injection into the gum?
Since the needle is inserted into soft tissues, it injures them and provokes discomfort. The patient may feel pain at the injection site for 1-2 days, or even more. The duration of the recovery period depends on the characteristics of the body and the perception of stimuli at the neuropsychic level.
Overly sensitive patients should be prepared for aching pain. Most often, no action is required. Usually the pain subsides on its own. In the case when it does not go away and only gets worse over time, we can talk about the development of a complication. At the same time, other signs of disturbances may occur.
Sometimes the patient thinks that the injection site hurts, but the localization is in a different place. So, after caries treatment, you may feel aching pain that radiates to the gums. Removal of a wisdom tooth is accompanied by pain in the socket, while the patient thinks that the problem is localized at the injection site.
What to do with flux - treatment features
It is important for parents to remember: if a child’s illness appears, they must be shown to an experienced dentist. Attempts to open an abscess on your own can only aggravate the situation and lead to blood poisoning. The only thing is, if you can’t consult a doctor right away today, you can rinse the affected tooth with water and soda or salt. Also suitable for these purposes are pharmaceutical antiseptics designed specifically for treating the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
The dentist always decides how best to deal with gumboil, taking into account the condition of the gums and the age of the patient. If the affected tooth is about to fall out, it is removed immediately. There is no point in stressing out a child by trying to save a unit that is about to leave the dentition anyway.
If we are talking about a tooth that the patient must live with for several more years, then conservative treatment is most often carried out. It is preferred to avoid crooked teeth in the future. Indeed, often when a tooth is pulled out prematurely, “neighbors” take its place. Because of this, the permanent unit then begins to erupt to the side, and it has to be put in place with the help of complex orthodontic treatment.
Conservative therapy involves opening a purulent neoplasm. The formed cavity is drained and washed with an antiseptic composition. If necessary, a drainage tube is installed in the gum for a while to avoid the re-formation of a purulent “bump”.
After such a procedure, special attention is paid to therapeutic rinses. The baby may even be prescribed antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs.