Why is temporary filling needed?
The need to use filling material is determined by the dentist. The installation of a temporary filling is prescribed by a doctor in the following cases:
- Carrying out diagnostics. When treating a patient with deep caries, a specialist is not always able to determine the extent of tissue damage. The doctor cleans the tooth cavity and places filling material. If the neurovascular bundle is not inflamed, then after the procedure the person will not experience pain. If the dental nerve and surrounding tissues are damaged, preliminary treatment will be required.
- Removal of the neurovascular bundle. In some cases, nerve sacrifice is required before removal. To do this, the dentist puts a specialized paste into the tooth cavity. After a certain period of time, the specialist removes the pulp and fills the tooth cavity with permanent filling material.
- Dental prosthetics. The dentist prepares teeth for prosthetics. To ensure that the root canals are protected from food and pathogenic bacteria during manufacturing, the specialist places a temporary filling material into the tooth cavity.
- Treatment of diseases. After treatment, the dentist places medications into the tooth cavity. After a certain period of time, the specialist removes the temporary filling and installs a permanent filling.
Causes of bitterness in the mouth
Reasons that cause bitterness in the mouth include:
- poor oral hygiene;
- medications (antibacterial drugs, antidepressants, gout drugs, drugs for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, migraine drugs, anti-parkinsonian drugs, antihistamines);
- pregnancy (bitterness in the mouth can occur in the first trimester of pregnancy due to hormonal changes);
- multivitamins and dietary supplements containing zinc, copper, iron, chromium;
- bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract;
- oral candidiasis (thrush);
- burning mouth syndrome (associated with menopause and postmenopause, diabetes, may be accompanied by dry mouth and a bitter taste);
- xerostomia (dry mouth associated with age-related changes, taking medications, smoking, Sjogren's syndrome);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- liver diseases;
- diseases of the biliary system (cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis);
- neurological diseases (epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, dementia);
- chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
Material requirements
To install a temporary filling, a specialized material is used that can be easily removed by the dentist if necessary. The composition for temporary filling must meet the following requirements:
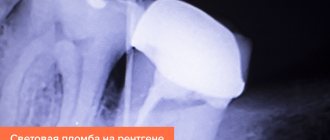
- X-ray resistant. To check the correctness of the filling, the dentist prescribes an x-ray examination. The image allows you to timely identify the presence of cracks in the filling material and eliminate them.
- Good grip on the surface. It is necessary to exclude the formation of microcracks or incomplete adhesion of the material to the tooth tissue. Violation of this rule may result in medication entering the oral cavity.
- Elasticity. The material should easily fill the pores formed in the tooth tissue.
- Strength. The material is installed by the dentist for a certain period of time. When eating, the filling is subjected to high stress. In this regard, the seal must be resistant to mechanical damage.
- Harmlessness. The filling should not cause allergic reactions or negatively affect human health.
- Easy to remove. At your follow-up appointment, the doctor quickly removes the temporary filling.
A mandatory requirement for temporary material is a high curing speed. The filling completely hardens in 2 – 3 hours.
Causes of alveolitis
Normally, after a tooth is removed, a clot of blood cells and fibrin, the protein from which a blood clot is built, forms in the socket. It almost completely covers the bottom and walls of the alveoli. The clot serves as a mechanical barrier, biological protection against infection and additional injury to the wound surface. In this case, healing occurs by primary intention. The wound is slowly filled first with loose tissue, then with denser connective tissue, and later with young bone.
But there are situations when the healing process is disrupted.
Inflammation of the socket occurs if:
- The operation was highly traumatic, which reduced the protective capabilities of one’s own tissues;
- The blood clot, as the main defense, is broken or completely absent (“dry socket”):
- prolonged bleeding;
- early destruction of the clot;
- non-compliance with the rules of care (for example, increased rinsing, eating hard or too hot food soon after surgery);
- Tooth extraction was carried out for emergency reasons due to an acute infectious process: periodontitis or periodontitis with complications;
- There are common reasons:
- reduced immunity;
- blood clotting disorder;
- elderly age;
- lack of proper dental hygiene.
What can happen after installing a temporary filling?
In some cases, patients experience pain after placing temporary filling material into the tooth cavity. Mild pain during the first 5 days after the intervention is considered normal. If pain intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor. Violation of this rule can lead to the development of various diseases and tooth loss.
It is normal to have a smell or taste of medication in the mouth after the procedure. The sudden appearance of a strong smell or taste of medicines indicates depressurization of the filling and leaching of medicines with saliva from the tooth cavity. Some drugs, if they enter the oral cavity, can have a negative effect on the human body. If such signs appear, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Swelling of the gums, darkening of tooth enamel, and the appearance of bad breath indicate the development of diseases. If symptoms appear, you should contact your dentist immediately. The doctor will remove the filling material and carry out diagnostic measures. You may need to contact your dentist if the filling breaks. Failure to visit a specialist in a timely manner will result in food particles and bacteria entering the tooth cavity.
Complications after prosthetics
- The development of inflammation of the gingival tissue - as a result, leads to gingivitis, stomatitis in acute and chronic forms. As a rule, such a complication in the oral cavity occurs due to poor fit of the tooth replacement structure. The process goes like this: the structure puts pressure on the tissue, blood vessels die, there is no blood supply to the tissue, and inflammation develops.
- Carious formations - as a result, the supporting teeth are affected by pulpitis or periodontitis. This usually occurs due to the accumulation of food debris between the prosthetic structure and living tissues. The problem leads to the fact that the teeth are gradually destroyed, cease to perform their supporting functions, and the fixation of the prosthesis is disrupted.
- Infectious lesions of soft and bone tissues – periodontitis. Often obvious destructive changes are noticeable around the product: the gums acquire a bluish tint, swelling and bleeding of the tissue develops. As a result, this leads to tooth loss and disruption of the fixation of the replacement structure.
- Rejection of the structure due to an allergic reaction. It can manifest itself as swelling of the gums, itching, rash and redness in the mouth. In some cases, difficulty breathing and a constant feeling of dry mouth and fever may occur. Allergies may appear in the first few hours after installation of the structure or after several weeks.
- The development of galvanism leads to the generation of galvanic current. What usually happens when using structures with a metal frame is that saliva gets on the material, the patient feels a taste of iron in the mouth, a constant feeling of an acidic environment in the oral cavity, and discomfort. As a result, the crowns darken, aesthetics are impaired, and sometimes the problem is accompanied by a headache.
- Poor quality fixation of the product. As a rule, the product “sits” on a special dental cement, which does not always hold the product in the oral cavity. The prosthesis may come off due to overload, incorrectly selected shape or size of the prosthesis. It is also possible that the dentist did not use enough dental cement for bonding. Sometimes fillings on the teeth prevent the prosthesis from “adhering” to living tissue.
- Product deformation. These can be chips, cracks, breaks, breaks into halves or small parts. The denture can become deformed due to impacts to the jaw projection, accidents, falls, or eating too hard foods. Sometimes the product is deformed due to errors in prosthetic planning.
- Problems with the occlusal plane. We are mainly talking about the surface that passes through the cutting edges of the first incisors of the lower jaw and the tubercles of wisdom teeth or second molars. The plane may shift, causing the temporomandibular joint to suffer.
- Change in bite. The height of dental crowns plays a big role. For example, with a lack of height, the quality of chewing decreases - a low-quality food bolus is formed. When the height of the crowns is high, the jaw is overloaded, which provokes dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
How to solve a problem?
The dentist recommends treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, as well as special gels to activate tissue regeneration processes. With regular treatment and oral care, the gums are soothed.
How to solve a problem?
At least twice a year (or even more often) undergo a full examination by a dentist. Not a single prosthesis, even a well-made one, will stand in such a way that bacteria will not accumulate under it. Care for the cavity with such products should be twice as thorough as usual!
How to solve a problem?
First, the dentist must prepare the teeth without creating so-called ledges. Secondly, the design must be selected strictly; several fittings and adjustments of the product may be required. Thirdly, before installing a prosthetic product, it is necessary to treat the gums. Regular therapy may be needed to maintain the health of the oral soft tissues.
How to solve a problem?
It is necessary to establish which component of the prosthetic structure the patient is allergic to. Most likely, the prosthesis will have to be replaced. That is why, at the stage of planning prosthetics, it is important to study the medical history and make sure that the patient does not have an allergy to metal.
How to solve a problem?
Replace the prosthesis with a product made of ceramic material. When installing ceramic structures, galvanism does not occur.
How to solve a problem?
Determine exactly why the prosthesis is poorly fixed and perform re-fixation with correction of inaccuracies.
How to solve a problem?
If the deformation is minor, the structure can be repaired directly in the oral cavity. Sometimes removal and re-fixation may be necessary. If the damage is serious, the prosthesis will have to be removed and a new one put in its place.
How to solve?
Since the problem is global, most likely, it is necessary to re-plan the prosthetics with a thorough diagnosis of the bite and the production of a new prosthetic structure.
How to solve a problem?
Determine the main cause of the development of malocclusion, re-plan prosthetics with replacement of the structure.
How long can you walk with a temporary filling?
The material used for temporary filling is highly durable. The filling does not break down for a long time. The specialist determines the period of wearing temporary filling material based on the nature and degree of neglect of the disease. The duration of wearing the filling is individual for each patient.
At the end of the established period, the person must immediately contact a specialist. An increase in the time period can lead to the development of diseases. In some cases, the filling may crumble at the end of its period, and the drug will negatively affect the patient’s body.