- Causes of jaw inflammation
- What to do if the lower jaw is inflamed
- Diagnosis and treatment of jaw inflammation at the dentist
- Features of treatment for older patients
Inflammatory diseases are very common and are presented in all their diversity, from clinical manifestations to localization. Differential diagnosis is not always easy, especially if there are no specific signs. Often a dentist finds himself in this situation when a patient comes to him with inflammation under the jaw on the neck. In this case, it is very important to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Causes of jaw inflammation
The lower jaw and the area under it have a rather complex anatomical structure. Muscles, lymphatic and blood vessels, bone structures, etc. are concentrated in this zone. Also, the temporomandibular joint or other anatomical zones may be involved in the inflammatory process, from which the lesion spreads to the neck area. Common causes of inflammation of the jaw are:
- Tooth root cyst.
- Osteitis.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Tumors of blood vessels and soft tissues of the neck.
- Traumatic injuries.
- Inflammation of the middle ear.
- Gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, etc.
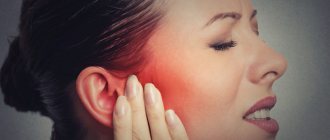
Given such a variety of causes, the approach to diagnosis and treatment must be individualized. Due to his ignorance, the patient may choose the wrong doctor and waste his time. In situations where something is inflamed under the jaw on the right or left and at the same time a tooth or temporomandibular joint hurts, you need to consult a dentist. If the pain is localized in the ear area, then you need to visit an ENT specialist.
Neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis
Neuritis and neuralgia are different diseases, although (as in the case of the trigeminal and facial nerves) some “specialists” combine them or replace one with the other. The main difference lies in the nature of their occurrence. Neuritis is always associated with an inflammatory process, hence its name: the ending -itis - from Lat. -itis always denotes inflammatory diseases. Neuralgia is irritation of the nerve as a result of concomitant diseases or exposure to external factors. Unlike neuritis, neuralgia does not cause changes in the structure of the nerve.
Most doctors consider neuritis to be a much more dangerous disease, since the inflammatory process affects the inner part of the nerve. At an advanced stage, the disease causes nerve damage and spreads to the auditory nerve, and can also lead to ataxia, a motor disorder. In this case, neuritis and neuralgia can occur together and have some similar symptoms. First of all, these are painful sensations, which, however, vary in nature and intensity.
What to do if the lower jaw is inflamed
First of all, it is important to identify the symptoms of the problem. One of the very first and most obvious is an increase in soft tissue volume.
This can be either a slight swelling or a very large tumor-like formation. Other symptoms may include:
- Increased body temperature.
- Redness of the skin.
- Painful sensations.
- Incomplete opening or closing of the jaw.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing.
- Hearing loss.
If the symptoms are confusing and it becomes unclear which doctor you need to see, you can make an appointment with a therapist who will conduct an initial examination, examine the complaints and issue a referral to the right specialist.
Prevention
The main preventive measure to prevent the manifestation of severe pain in the jaw is a timely visit to the doctor. If any minor deviations occur, you should immediately consult a specialist. Early identification of the cause of a pathology that begins to develop is the first step towards solving the problem.
The patient should already be alerted by the appearance of unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the form of:
- deterioration of jaw mobility;
- crunching while yawning or chewing food;
- pain when opening the mouth;
- noise or pain in the ears;
- frequent headaches;
- grinding or creaking of the jaw;
- painful sensations in the neck and back.
Such symptoms are a reason to undergo diagnostic measures and, after diagnosis, receive the necessary treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment of jaw inflammation at the dentist in Odintsovo
If inflammation of the jaw has developed due to diseases such as pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, as well as as a result of injuries and damage to the temporomandibular joint, then the treatment will be carried out by a dentist. First, a specialist must establish an accurate diagnosis. To do this, he collects anamnesis, finds out complaints, and conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity. Additionally, an X-ray examination of the jaws, laboratory tests and other diagnostic tests may be prescribed, with the help of which it will be possible to obtain objective information about the condition of the patient’s dental system.
Treatment of inflammation in our clinic in Odintsovo is usually carried out using combined methods, which include:
- Conservative therapy. Typically, the dentist prescribes antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
- Surgery. It involves the removal of non-viable tissue, drainage of the inflammatory focus and, if necessary, other procedures that are aimed at eliminating the pathological area.
The duration and complexity of treatment largely depends on the degree of neglect of the process. The sooner a patient seeks medical help, the easier it will be to restore lost health.
Pain that comes with a draft - how to treat it?
More often, pain of this kind appears against the background of pre-existing pathologies or diseases of the spine and joints. The body, weakened by existing diseases, becomes vulnerable and is easily susceptible to new diseases. However, even many healthy people are familiar with the concept of “drafty air” - this is the result of a sharp temperature change. Most often, such pain is caused by myositis, an inflammation of the skeletal muscles. Myositis is divided into many types based on various characteristics.
Causes
Cervical myositis is inflammation in the muscles of the neck and shoulder. It occurs suddenly, and the main reasons for its appearance are:
- hypothermia (sharp temperature change from warm to cold);
- uncomfortable sleeping position;
- uncomfortable body position for a long period, for example, during work;
- weakened immunity after/during viral diseases.
What are the symptoms of the disease
The main symptom is localized muscle pain, which may worsen with movement, changes in temperature or weather. As a rule, such pain occurs only on one side of the neck and can spread from the head towards the lower back. At an early stage, it may manifest itself as an increase in temperature.
Without proper treatment, myositis can progress and cause complete or partial atrophy of skeletal muscles. It can also spread, affecting neighboring muscle groups, in particular, cervical myositis can affect the muscles of the larynx, pharynx, esophagus and even the respiratory muscles, resulting in difficulty swallowing food, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Inflammation of the muscles of the cervicobrachial region is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Unilaterally located pain that extends to the arm and/or interscapular area.
- Severe tension in damaged muscles.
- Low mobility of inflamed muscle groups.
- Numbness of the affected muscles.
How will the therapy work?
The general practitioner will give a referral to a neurologist, who in turn will determine the course of treatment, which may include recommendations such as:
- rest for the affected muscle area;
- warming and anti-inflammatory ointments;
- “gentle” course of physiotherapy;
- spine massage
; - magnetotherapy.
Basically, all actions are aimed at relieving inflammation, increasing immunity and getting rid of the symptoms of the disease. In severe cases, in order to avoid muscle spasms, reduce swelling and pain, the doctor may prescribe a novocaine blockade.
Some doctors also recommend manual therapy to relax the muscles and speed up recovery.
Pre-medical treatment
It is not always possible for a sick person to immediately consult a doctor for qualified help. And what to do if this is not possible?
To relieve pain, you can take a painkiller, preferably with an anti-inflammatory effect. It is best to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
You can also warm the area where the pain is felt with “dry heat,” which is also recommended by doctors. To do this, use a frying pan to heat regular table salt on the stove; when it is hot enough, pour it into a towel and, carefully wrap it, apply it to the source of pain.
You can use warming patches - they need to be stuck on the desired area for a long period of time, or use mustard plaster - it will be enough to hold it for about 10-15 minutes.
Alcohol-based rubs are also effective.
Diet to restore the body
Any inflammatory process in the body entails many unpleasant consequences. To minimize damage to the body due to inflammation, it is recommended to follow a diet that will help neutralize the accumulation of harmful substances in the muscles. These are vegetables, fruits and berries that will give the body the necessary vitamins.
Fatty acids contained in sea fish reduce and stop inflammation.
In addition, the cause of spasms may be a lack of magnesium, calcium or zinc, which are found in cereals, cereals, dairy, fermented milk products, liver, and raw meat, respectively.
Easily digestible proteins and salicylates help with myositis. They contain soy, chicken, almonds, beets, carrots, etc.
These foods should be eaten daily. It is also recommended to drink at least two liters of liquid daily: water, green tea, compotes or vitamin decoctions. As with many any diseases, salty, fatty and alcohol-containing foods can negatively affect the patient’s condition.
Prevention
The main preventive measures to protect against this disease coincide with the prevention of spinal diseases.
It is worth paying attention to light warm-up and exercises, especially for people with sedentary work. Try to avoid muscle overstrain when performing heavy physical exercises and physical activity. Doctors also recommend monitoring your posture and engaging in sports such as gymnastics, swimming and cycling.
Avoid contracting viral infections, and in case of infection, do not advance the disease and consult a doctor promptly. Do not tolerate diseases “on your feet” - this can lead to serious complications.
One of the main factors of prevention, as with most diseases, is nutrition.
The risks of contracting a disease are reduced when the body receives all the necessary substances and microelements, so the main recommendation of doctors is always a healthy diet. And the main advice is to avoid, if possible, drafts and muscle hypothermia. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Features of treatment for older patients
Among the common age-related changes in the lower jaw, changes in the content of water, organic and inorganic substances are noted, osteoporosis, atrophy and thinning of bone tissue are often detected. In addition, older patients often have concomitant diseases, such as diabetes. All of these factors can greatly limit treatment options. For example, if dentures are required, then in some situations the dentist may only offer removable dentures. Placing implants will be risky and ineffective.
Nevertheless, modern dental capabilities make it possible to find a way out of any, even the most difficult situation. A wide variety of materials and techniques can eliminate existing problems and significantly improve the patient’s quality of life.
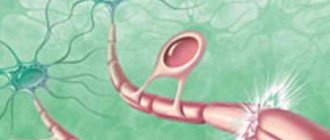
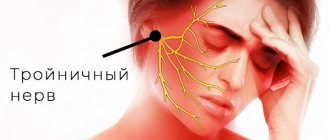
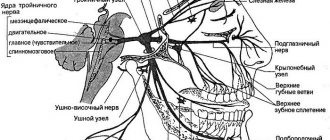
Trigeminal nerve - what is it?
The trigeminal nerve is located on both sides of the face and is one of the cranial nerves, being one of the largest and most important in terms of functionality. It is responsible for the sensitivity of the skin of the face, teeth, oral mucosa and some other areas of the head, and also partly regulates the process of salivation.
Many people often confuse the trigeminal and facial nerves or even believe that they are one and the same thing. The Internet is full of materials that talk about inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve or describe the symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve. These formulations are incorrect and mislead people, since these are two different pairs of nerves with their own structural features and functional purpose. The facial nerve is also one of the cranial nerves: it runs quite close to the surface of the face and is also responsible for the work of facial muscles. Neuritis can also affect the facial nerve, but the disease will progress differently.
It is also incorrect to talk about inflammation of the trigeminal nerve of the tooth, since there is no trigeminal nerve in the teeth, but its processes are in close proximity to them.
Treatment methods
A person who has caught a toothache needs urgent treatment. To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to promptly eliminate the root cause of inflammation. To determine it, the dentist conducts an examination with percussion and radiography. The treatment regimen may include:
- preparation and medicinal treatment of carious cavity,
- tooth depulpation and root canal treatment,
- remineralization of enamel and installation of a crown on a damaged tooth.
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the clinical picture.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Neuritis of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, as a rule, does not affect all three processes. Most often, inflammation is observed in the peripheral areas of one of the branches, most often the maxillary (inflammation of the trigeminal nerve of the jaw). That is why the main manifestation of neuritis (pain) is most clearly observed during food intake and hygiene procedures. Below are the main signs of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
- Pain due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
With neuritis, pain occurs in the place where the nerve process passes. Usually it is quite acute and pronounced, but with an extensive inflammatory process, prolonged attacks of aching pain can be observed, covering large areas (chronic inflammation of the trigeminal nerve). - Impaired functionality of the facial muscles.
Signs of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face are observed due to the fact that the trigeminal nerve contains both motor and sensory fibers. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve branch can be manifested by disruption of the facial muscles (decreased sensitivity and muscle atrophy in the later stages of the disease). - Temperature and other signs.
With neuritis, it is also possible to increase salivation, lacrimation, dullness of auditory and visual reflexes, impaired taste, and so on. These manifestations of neuritis occur individually and are associated with the form and severity of the disease. The temperature during inflammation of the trigeminal nerve often exceeds normal values, but only slightly.