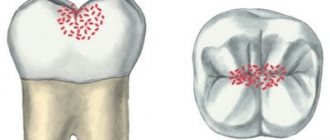
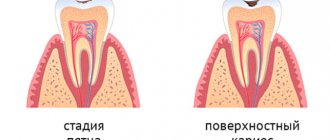
For children's teeth, caries is even more dangerous than for adults. The enamel of baby teeth is thinner and is destroyed very quickly, so carious cavities can develop into pulpitis or periodontitis in a baby in just a matter of weeks. That is why experts recommend that parents carefully monitor the condition of their dear children’s teeth.
Regularly inspect the surface of your teeth for the appearance of carious spots and remember that proper prevention can effectively protect baby teeth from this disease, and you from unnecessary troubles and worries. What is it made of? Let's talk about this in more detail.
Important components of the prevention of dental caries in children
In general, all preventive measures can be divided into three types:
- antenatal – carried out during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, they are aimed at the correct formation and development of tooth buds;
- endogenous - a set of measures to saturate the baby’s teeth with the necessary mineral components from the inside, ensured by consuming properly selected food products or taking medications;
- exogenous – thorough and regular oral hygiene, carried out both at home and in the doctor’s office.
All three types of caries prevention are equally important, so you should not think that only proper nutrition or high-quality teeth cleaning can protect you from tooth diseases. Only an integrated approach brings success, and the use of preventive measures should begin during pregnancy.
Endogenous prevention
It involves strengthening the entire human body. Of primary importance for such caries prevention is: diet, high-quality food composition, sufficient intake of fluoride and calcium into the body.
Features of endogenous prevention of dental caries in pregnant women and school-age children
School period. At school age, baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. Mineralization of the latter ends only by the age of 16. Therefore, a schoolchild’s diet should include vegetables and fruits in significant quantities. Bakery products, pasta, and sweets should be limited. There are three rules to remember.
- Do not eat sweets at night.
- When eating, a sweet dish should not be the last dish.
- Don't eat sweets between meals.
If any of these rules are violated, it is necessary to rinse your mouth or brush your teeth.
Pregnancy period. Calcium and iron deficiency, the growth of opportunistic microflora in the oral cavity and other factors lead to an increase in the incidence of caries in pregnant women. The main measure of endogenous prevention is sufficient intake of calcium, iron and phosphorus into the pregnant woman’s body. For this, in addition to food, special complexes and medications are used, prescribed by the attending physician.
Antenatal prevention of caries in children - take care of your baby in advance
The degree of resistance of the teeth to the development of caries depends on how mineralized the buds of children's teeth are during pregnancy. The following will help ensure proper intake of minerals into the child’s body:
- Correct diet for the expectant mother and strict selection of products
Reduce your consumption of sweets and flour products as much as possible and generally reduce the amount of carbohydrates in your diet, while at the same time introducing mandatory daily consumption of foods containing calcium (this includes all dairy products).
- Timely completion of comprehensive medical examinations both during pregnancy planning and during it
They will prevent the development of a deficiency in the mother’s body of certain elements necessary for the baby.
- Oral hygiene
Do not be lazy to regularly clean the surface of your teeth with brushes, and the spaces between them with dental floss.
- Monitoring the condition of a pregnant woman's teeth
Visit the dentist's office regularly, and also take care to prevent the development of dental diseases and promptly sanitize carious lesions.
- Routine professional teeth cleaning
It should be carried out only on the recommendation of specialists and strictly in a certain trimester of pregnancy.
- Use, if necessary, vitamin-mineral complexes that reduce the deficiency of nutrients
Please note that they can only be taken after consultation with the gynecologist.
You shouldn’t relax in the fight against caries even after the baby is born. First of all, ensure that your baby maintains the necessary oral hygiene.
Prevention of dental diseases
Prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women:
The health of the mother affects the development of the child's teeth, especially during the period of 6-7 weeks, when the period of tooth formation begins. During the pathological course of pregnancy, the mineralization of tooth enamel slows down and often stops at the stage of initial calcification. In the postnatal period, the mineralization of such teeth, although improved, does not reach the normal level of calcification of primary teeth.
There is a group of factors whose action disrupts the full formation of the dental system. These include:
- the presence of extragenital pathology in the mother;
- complications of pregnancy (toxicosis of the first and second half);
- stressful situations during pregnancy;
- diseases of newborns and infants;
- early artificial feeding
Prevention of dental diseases in children under 3 years of age:
- Breastfeeding for at least a year.
- Strict adherence to the pediatrician’s recommendations on diet and sugar levels in nutritional formulas for infants.
- In the case of artificial and mixed feeding, the nipple should be elastic, with a small hole, which promotes active sucking and proper development of the jaws.
- As teeth erupt, accustom the child to hard foods, which promotes the development of the dental system and self-cleaning of the oral cavity.
- Starting from the age of 2, the child must be taught to brush his teeth, and by the age of 3-4 the child should brush his teeth independently 2 times a day.
- Prescription, if necessary, of fluoride preparations for the prevention of dental caries by a dentist.
- A mandatory visit to the dentist when the child turns 6 months old.
It is necessary to contact the dentist when the child is healthy and has not experienced toothache!!!
Prevention of dental diseases in preschool children:
- Compliance with diet and limiting carbohydrate intake.
- Thorough and regular brushing of teeth morning and evening.
- Develop skills in hygienic oral care (parents, educators).
- Elimination of bad habits.
- Prescription of medications by a dentist to prevent caries.
- It is mandatory for the child to visit the dentist immediately after the eruption of his first permanent molars (5-6 years).
- Regular (once a year) visits to the dentist to prescribe and monitor preventive measures, as well as for early detection and treatment of dental diseases in the child/
Prevention of dental diseases in school-age children:
- Limiting intake of carbohydrate foods.
- Instilling in the child a nutritional culture (regime, balance, vitamins, etc.).
- Hygienic oral care.
- Conducting preventive examinations in schools.
- Carrying out special preventive procedures (fluoride varnish, etc.).
- Mandatory visits to the dentist 2 times a year.
Antenatal prevention of caries.
Pregnant women are recommended to carry out a set of general preventive measures, including the correct work and rest schedule, good nutrition, and multivitamin preparations.
The diet should be varied, with the necessary amount of vitamins and microelements. In the first half of pregnancy, women's bodies need a continuous supply of protein. In the second half, the body's need for vitamins, microelements and mineral salts (vegetables, fruits) increases. Multivitamin preparations are prescribed: “Dekamevit”, “Undevit”, “Gendevit”, which leads to the intensification of redox processes in the body of the fetus and mother. To correct homeostasis, it is possible to prescribe a multivitamin preparation with mineral supplements “Pregnavit”.
To replenish minerals and vitamins in case of insufficient intake from food or impaired absorption, you should:
- In the last three months of pregnancy, take 1-2 drops of Vit oil solution daily. D2.
- For toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy, prescribe Ca glycerophosphate in granules, ½ teaspoon per day or 1 tablet 2 times a day.
- In winter and spring, take ascorutin 2 tablets 3 times a day for a month
When carrying out treatment and preventive measures, the activity of dental caries in a pregnant woman’s teeth should be taken into account.
As a means of pathogenetic therapy and prevention of dental caries, drugs are prescribed orally, which are also means of antenatal prevention of dental caries:
- Ca preparations (CA gluconate, Ca glycerophosphate, Ca lactate).
- We can recommend “effervescent tablets” (“Calcium C”, “Calcium C 1000 Sandoz”, “Calcium Sandoz Forte”).
- Ca tablets for chewing (“Calcimax”, “Calcimax + D”, “Calcinova”).
To achieve the maximum preventive effect, clinical examination of women is necessary throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
It is advisable to carry out the following activities in dental offices:
- Training in rational oral hygiene followed by supervised brushing of teeth, assistance in selecting basic and additional hygiene products
- Sanitation of the oral cavity
- Professional hygiene
- Local remineralizing therapy
- Dental education of women on the prevention of dental diseases and motivation to care for children’s teeth immediately after teething.
The drugs used to prevent dental caries are not chemically pure fluorine, but its compounds – fluorides, where the element is contained in the form of a fluoride ion bound to some cation.
Fluorides enter the body with water, food, medicines, pesticides, and a significant part of them is the result of human activity.
When studying the metabolism of fluoride in the human body, it turned out that its compounds have an affinity for the minerals from which bones and teeth are built. The accumulation of such compounds occurs in those areas of tissue that are in contact with circulating fluids (in surface enamel and dentin).
The process of fluoride accumulation in tooth tissues occurs most intensively during the formation of the crown and during the period of mineralization in the first years after tooth eruption. The fluoride content is higher in the superficial layers of enamel and decreases towards the deeper layers. In the area of the cutting edge and chewing surface of the teeth, the fluoride concentration is much higher than in the neck area. Temporary teeth have a lower fluoride concentration than permanent teeth. With age, the concentration of fluoride in permanent teeth decreases, which is probably due to the gradual wear of enamel.
In saliva, the fluoride concentration is 1 µmol/liter or 0.019 ppm, which corresponds to approximately 1/50 of the optimal fluoride value in drinking water (1 ppm).
If optimal doses of fluoride are given before teeth erupt, then:
- The size of hydroxyapatite crystals increases
- In hydroxyapatite, hydroxyl groups (OH) are replaced by fluorine ions with the formation of fluorapatite crystals
- Carbonate content is reduced
- The enamel becomes stronger
- Fissures become less deep and wider
If fluoride is taken after teething, it:
- Reduces enamel solubility
- Promotes remineralization of partially demineralized enamel.
The optimal daily fluoride intake ranges between 0.05 and 0.07 mg per kg of body weight. Total fluoride intake should not exceed 0.1 mg/kg body weight per day to avoid dental and bone fluorosis.
In the structure of caries resistance, a sufficient intake of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins into the body plays an important role.
Phosphorus and calcium preparations are indicated for poor nutrition, lack of breastfeeding for up to 6 months, dyspepsia, rickets, treatment with antibiotics, corticosteroids, intestinal toxicosis, multiple caries. They are prescribed for the prevention of caries or complex treatment of caries. It is better to take calcium and phosphorus supplements with a vitamin. Preventive measures are more effective the earlier they are started. To get results, they need to be carried out for at least 2 years, and in case of expected systemic caries - the entire period of tooth mineralization. Preventive courses are prescribed for 2.5 months, 2 times a year. The dosage is calculated based on the daily requirement depending on age.
Calcium preparations regulate the activity of the central nervous system, the correct structure of bones, and have a general strengthening and desensitizing effect.
Representatives of the group : Ca glycerophosphate (powder, tables 0.2 and 0.5), glycerophosphate (granules 100.0), phytin (powder and table 0.25), gephefitin (phytin + brewer's yeast) - table. 0.25.
Contraindications to the use of drugs_Ca:
Acute liver and kidney diseases, chronic liver failure, hypercalcemia.
For fluoride: hypervitaminosis D and A.
Endogenous drug-free prevention of caries:
The main factor of protection against diseases is provided by the high resistance of the child’s body to damaging factors, therefore endogenous drug-free prevention of caries includes:
- Hardening the body, physical culture
- Providing a balanced diet (dairy products, vegetables, fruits).
Objectives of remineralizing therapy:
- Creating conditions for the full formation and mineralization of hard dental tissues.
- Ensuring the physiological course of the maturation process of hard dental tissues, and, if necessary, stimulating these processes.
- Prevention and elimination of the formation of a cariogenic situation.
Indications for use:
- Prevention of dental caries.
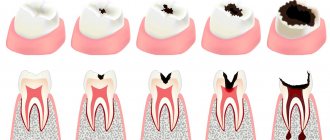
- Conservative treatment: initial caries (in the spot stage), superficial, medium and deep caries, hyperesthesia of enamel and dentin, hypoplasia, fluorosis, dental trauma, periodontal tissue diseases.
Methods of remineralizing therapy:
- At the level of the body (prescription of drugs orally - to regulate mineral metabolism).
- On hard dental tissues (topically - in order to increase their resistance to caries-active components and restore the damaged crystal structure)
The conditions necessary for remineralization are the preservation of the protein matrix of the enamel.
Exogenous drug-free prevention includes:
- Hygienic oral care.
- Balanced diet.
- Nature of food.
- Limit intake of sugar-containing foods.
One of the most common means of local prevention of dental caries are varnishes, which are used to prolong the period of exposure of fluoride to the enamel. They form a film adjacent to the enamel that remains on the teeth for several hours, and in fissures, crevices and microspaces for several days and even weeks.
The remineralizing effect of gels is based on the diffusion of substances from the gel into saliva, and from it into the tooth enamel.
The role of hygiene in the prevention of dental caries in children
Quite often, parents begin to pay attention to oral hygiene issues only after the baby has his first tooth. But you need to start caring for the first teeth long before they appear, literally from the first months of a child’s life.
For this purpose, experts recommend using special sanitary napkins for infants, for example, ASEPTA baby wet wipes. They will help to carefully and efficiently clean the gums, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks, significantly reducing the number of bacteria in the oral cavity.
For children whose first teeth have already erupted, we can recommend using a soft toothbrush and toothpaste from the ASEPTA baby series, designed for children aged 0 to 3 years. It does not contain abrasives or fluoride, the ingestion of which is highly undesirable for a child, and at the same time carefully cares for the surface of baby teeth, providing protection against caries.
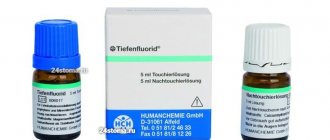
To prevent caries in children, we can also recommend a procedure for remineralization of enamel and its deep fluoridation. It is carried out by specialists and, as a rule, already in cases where caries is detected at the spot stage.
An equally important place in preventive measures is given to the preparation of the child’s correct diet.
Healthy nutrition is the key to successful prevention of dental caries in children
Try to exclude sweets, flour products, as well as sweet juices and carbonated drinks from the menu. Plain water will be much healthier, and for snacks between meals, it is better to use apples, pears and other solid fruits and vegetables.
A child’s daily diet must include various dairy and fermented milk products. They will help avoid calcium deficiency and resist the development of caries.
Give preventive measures enough effort, time and attention, and your baby’s teeth will be beautiful and healthy.
Antenatal prevention
The earliest prevention. In order for the formation of the baby’s teeth to occur correctly, a pregnant woman needs to:
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- eat rationally (balanced nutrition, including a sufficient amount of minerals, vegetable proteins, vitamins);
- carry out timely treatment of infectious diseases, etc.
After the birth of a child, proper nutrition of the baby ensures the further course of antenatal prevention. Breastfeeding is of primary importance. A child under 3 years of age should receive a sufficient amount of milk, cottage cheese, fruits and vegetables (in addition to potatoes). Sweets and carbohydrates, on the contrary, should be limited.