What dentures are installed if there is periodontal disease and periodontitis - review of options and choice of the best
Article navigation
- What kind of pathologies are these – what are their differences and commonalities?
- Is it possible to install dentures?
- What are the features and risk factors
- Solutions for mild tooth mobility, inflammation and atrophy
- — veneers and restorative inlays
- - crowns and bridges
- - removable dentures
- Options for severe looseness, inflammation, bone resorption
- — implantation with immediate prosthetics
- — splinting “clasps”
- Stages of dental restoration
- — diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease
- — preparation and planning of prosthetics, implantation
- — manufacturing and installation of orthopedic structures
- Service life of structures
- What is better to choose
- Proper oral care
Question for a specialist
Prosthetics for periodontal disease and periodontitis is complicated by the fact that an incorrectly selected prosthesis can aggravate the disease. That is, intensify inflammatory and atrophic processes in periodontal tissues (this is everything that surrounds the teeth). As a result, the person will be left without new teeth, without the usual and nutritious diet, and with a negative attitude towards dentistry. But there is a solution for any case, even complex ones. Next, we will tell you which dentures are best to choose for periodontitis and periodontal disease, how they are placed, and how long they will last.
Stages of prosthetics using implants
After preparing the oral cavity, classic one-stage or basal implantation is performed. The first option involves immediate installation of an implant after tooth extraction. Then the abutment is screwed onto it and a crown or prosthesis is put on. The procedure is different in that it does not require an incision in the gum and detachment of the periosteum; a small puncture is sufficient. After six months, instead of a temporary crown, a permanent crown is fixed; during this period, the implant should take root.
If the tooth has been removed a long time ago, tissue volume is increased or the basal implantation method is used. It lies in the fact that the artificial root is not implanted in the place of the previous one, but where there is enough tissue volume, that is, in a deeper layer (basal). Likewise, it requires no incision, just one puncture. This type of prosthetics is used most often when several adjacent teeth are missing. Immediate load on the bone will improve blood supply to the tissues, which will have a beneficial effect on periodontal diseases.
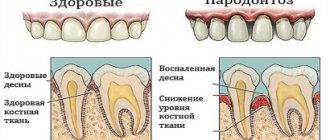
What kind of pathologies are these – what are their differences and commonalities?
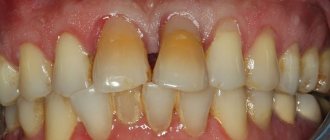
Very often, patients and even some dentists confuse these two diseases. Let's figure out what's what. So, periodontitis is a deep inflammation of the gums, periodontal ligaments of the tooth, and the bone socket (where the roots are located). In this case, the gums turn red, become swollen, and blood or pus is released from under them. The cause of the pathology is untreated gingivitis and poor oral hygiene. After all, food plaque, inhabited by dangerous bacteria, turns into stone and grows along the root. Consequently, microbes penetrate deeper and deeper, and their toxins poison surrounding tissues.
Periodontal disease is NOT an inflammatory, but an atrophic periodontal disease. That is, the tissues lack nutrition, but not due to inflammation. At the same time, the teeth also become loose, the gums and jaw bones also decrease. However, the gums have a whitish tint and are not swollen. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established, but experts are inclined to believe that systemic diseases of the body, hereditary characteristics, and smoking are to blame.
Periodontitis occurs in 95-99% of cases, and periodontal disease is detected in 1-5% of patients - this is actually a very rare disease. Two consonant pathologies are also confused because they have common manifestations. For example, ligaments are destroyed, bone tissue around the roots atrophies, gums recede - so dental crowns appear long, and teeth begin to loosen. In both pathologies, the gums peel off from the roots, which is how periodontal pockets appear. Food debris gets clogged there, microbes penetrate, plaque and tartar form on the roots.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 4 IMPLANTS - from RUR 170,000.
The price includes all procedures for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and fix your prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
What are the dangers of periodontitis and periodontal disease for a patient?
- inflammation of the ligaments of the teeth and nearby bone tissue,
- formation of voluminous gum pockets,
- loss or contraction of the gums, as a result - exposure of the roots of the teeth, which is fraught with increased sensitivity and an increased risk of developing caries,
- accumulation of a large amount of dental plaque,
- bad breath due to rotting food debris and plaque deep in the pockets,
- gum recession and root exposure,
- development of periodontitis - formation of cysts and granulomas on the roots of teeth,
- violation of the aesthetics of the dentition - due to the absence of teeth, changes in their shade and the appearance of gaps in the root area,
- mobility and loss of teeth.
But, unfortunately, inflammation is not limited to just one oral cavity. Periodontitis leads to many problems throughout the body - disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (which is logical, since along with food we swallow pathological microorganisms that are in the oral cavity), pathologies of the cardiovascular system and even kidneys! Read more in the article “The nature and dangers of periodontitis”
Just 10 years ago, periodontitis was an incurable disease. Medicine was unaware of methods for relieving inflammation and restoring periodontal ligaments to reduce the depth of periodontal pockets. All measures were aimed only at improving hygiene to stop the inflammatory process and slow down the progression of periodontitis. At the same time, the depth of the periodontal pocket did not decrease and, with poor hygiene, the disease took hold.
Is it possible to install dentures for these diseases?
Prosthetics for periodontitis and periodontal disease are quite possible - but its method and type will depend on several factors. In case of exacerbation of any of the pathologies, classical prostheses cannot be installed - this will only intensify the symptoms. Dental prosthetics for periodontitis and periodontal disease are recommended only after the patient has undergone treatment (more about it below in the article) and the periodontal condition has stabilized. You also need to first make a diagnosis using computed tomography (CT). It is the most informative, accurately showing the width and height of the bone around the entire root, the condition of the ligaments, the size and shape of the cysts (if any) under the roots.
Important details of prosthetics
Before you begin the dental restoration procedure, you need to properly prepare for it. Let's carefully consider the goals and features.
Goals:
1. Distribute the load evenly across the necessary units to restore chewing function.
2. Secure teeth that move.
3. Protect the affected units from the chewing process.
Before installing the structure, mobile teeth are strengthened and worn-out teeth are removed to stop the loss of bone tissue.
There are many factors to consider before starting the whole process:
- how long has the disease lasted?
- how severe the disease is;
- jaw structure.
What features and risk factors need to be taken into account when using prosthetics?
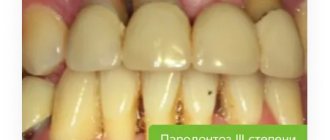
The danger of periodontal disease and periodontitis is that they have a long course - months and years, and at first have mild symptoms. In the initial stages, when conditions for dental treatment and prosthetics are best, patients simply do not go to the dentist. Because they try to cope with folk methods at home or believe that there is no treatment. At stage 2 or moderate, the symptoms are already more pronounced. And at stage 3 (severe), people begin to rapidly lose teeth against the background of acute atrophy and tissue loss.
The choice of prosthesis and method of prosthetics should be based on the stage or degree of damage to periodontal tissue [1], the patient’s condition, the presence of allergies and diseases (for example, diabetes). When looking for options, it is necessary to evaluate whether the supporting teeth will withstand the chewing load - they must not become loose, break or fall out.
Even impressions (casts) before prosthetics are taken after highly mobile teeth have been splinted with a special thread - otherwise they may fall out. As for the need for preliminary treatment of gums, consider the following situation. Impressions were taken when the gums were swollen - such a step would lead to the production of uncomfortable dentures, crowns, veneers, and restorative inlays. After all, if the inflammation then subsides or the gingival contour “sags,” then a gap will form between the prosthesis and the gum - this is unsightly and creates a risk of root infection. If the inflammation intensifies, the edges of the orthopedic structure will literally “dig” into the tissue.
Dentures should not provoke an increase in the inflammatory process during periodontitis, rub the gums or put too much pressure on them at some points. The orthopedic design should not accelerate bone atrophy, incl. with periodontal disease. This is especially true for complete removable dentures that rest on the gums - although they are the most inexpensive, the risk of exacerbation of pathologies when wearing them is the highest.
Complete dentures
If a patient with periodontal disease has lost all his teeth, then the above prosthetic options will not suit him. In case of complete edentia, removable dentures are sometimes used with support on the mucous membrane, which are “sucked” to the jaw. But this is perhaps the worst solution to the problem.
- Such a prosthesis constantly “pleases” its owner by shifting and falling out. This happens due to the fact that the mucous membrane with periodontal disease in different areas has different volume and height, that is, there is no talk of any tight fixation of the prosthesis.
- The entire load goes not to the bone tissue, but to the mucous membrane. Because of this, blood flow in the gums is disrupted - and this is half a step before inflammation.
- Complete removable dentures require careful care to avoid the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria in the mouth.
All this does not help the patient with periodontal disease, but only worsens his mood and the condition of the oral cavity.
Solutions for mild tooth mobility, inflammation and atrophy
Let's begin to consider options for dental prosthetics in the early stages of periodontal disease and periodontitis. When the tissues are not yet very badly affected - inflammation and atrophy have not reached their maximum, the teeth do not loosen or loosen slightly. However, before restoring your smile, it is necessary to undergo gum treatment, relieve acute periodontal inflammation - ideally, stop the pathological process altogether (we will tell you more about treatment below).
Veneers and restoration inlays
- advantages: high aesthetics, long wearing period,
- disadvantages: more complex and time-consuming execution, higher cost - all in comparison with a filling. It is necessary to treat the gums very carefully before using prosthetics. In the absence of careful care, aesthetics are quickly lost.
If the patient has preserved teeth, but for some reason they are not happy with their appearance, and you don’t want to put fillings, then there is a better solution for restoring aesthetics - these are veneers and restorative inlays. Such microprostheses are made from hypoallergenic ceramics and the strongest zirconium dioxide. Restorations last 10 years or more and retain their shape and natural color throughout the entire period of wear.
Crowns and bridges
- advantages: a familiar method practiced by all orthopedists,
- Disadvantages: you cannot restore more than 4-5 teeth in a row; you need to grind down the supporting teeth that are outermost from the defect, which are used to fix the bridge. Expensive materials are used that are safe for gums. Before prosthetics, you need to undergo long-term periodontal treatment.
For people with periodontal disease and periodontitis, it is recommended to use the following types of crowns and bridges - ceramic, zirconium dioxide, metal-ceramic on the shoulder mass (they have ceramic applied along the lower edge so that the metal does not touch the gums). Such orthopedic structures are aesthetic and do not cause irritation. But, for example, from pure ceramics you can make a bridge of a maximum of 3 crowns in length (including support ones) and only in the “smile zone”. That is, if you need to restore four front teeth, then it is better to choose the most durable materials for prosthetics - zirconium dioxide and metal-ceramics.
Removable dentures – acrylic, Acry-free, clasp, Quattro Ti
- advantages: inexpensive method, minimum contraindications,
- Disadvantages: rub gums, injure supporting teeth. Most structures have a short service life and also provoke deterioration of the periodontal condition. In case of exacerbation, inflammation is not established.
When it comes to what type of prosthesis is best to install for periodontitis or periodontal disease, orthopedists often offer removable clasp structures. Due to their rigid metal frame, they distribute chewing pressure well - without overloading individual zones of the row. Less often, metal-free analogues of clasp ones are used for dental prosthetics - these are acetal structures and Quattro Ti (“Quadrotti”). And acrylic and Acry-free (“Acry-free”) are used only for very mild manifestations of periodontal pathologies, or for completely toothless jaws. Although, as already noted, this is not the best solution, because... there is a high risk of inflammation and increased atrophy.
Features of basal implantation
This type of prosthetics is the least reliable. The service life of the basal implant is more than 5 years
Disadvantages: high cost, extended requirements for the qualifications of a doctor.
In Moscow, many dentists successfully cope with implantation tasks. Dentistry AcademyDent guarantees the quality and reliability of implants for patients of all ages in the absence of serious contraindications.
Reasons for refusing implantation may include:
- mental disorders;
— oncology;
- severe heart disease;
- pregnancy.
Basal root implants differ from classic ones in their greater length and integrity of the structure along with the abutment. The angle of inclination of the platform under the prosthesis can be changed, which allows you to select the strongest areas of the bone and increases the area of contact of the implant with its surface. But achieving aesthetics with basal implantation is very difficult.
If all teeth are removed or lost, implantation can be carried out according to several schemes: four, six or twelve units of implants. On their basis, a permanent prosthesis is placed, which allows to reduce the recovery time after the procedure.
In order to get excellent results, implants from trusted manufacturers are installed for periodontitis: Nobel Biocare, Astra tech, INNO.
Options for severe looseness, inflammation, bone resorption
How to make a prosthesis for periodontitis and periodontal disease in difficult clinical conditions? In cases of severe mobility, pronounced bone atrophy in height and width, and half or more of the root being exposed, there are also various methods of prosthetics. As a rule, patients in the later stages of periodontal pathologies experience almost complete adentia, swelling and bleeding of the gums, and a large amount of tartar. Let's consider the optimal solutions - in terms of aesthetics, functionality, safety and long-term preservation of the restored smile. These are implantation with immediate loading and splinting “clasps”.
Veneers, bridges and crowns are not recommended. Because if the root is severely exposed and loose, veneer restorations will look unattractive, and crowns and bridges will quickly fall out. Classic removable ones won’t work either, because... cause complications.
Implantation with immediate prosthetics
- advantages: no need to stop inflammation, because you can immediately remove diseased, damaged, severely loose teeth, clean the sockets of granulations and place implants and dentures. Smile restoration is quick - literally 7-10 days. With the new “jaws” you can immediately chew your favorite foods without pain, wear them comfortably - the products are firmly fixed and do not fall out. Long service life (about 10 years, then the structure needs to be replaced), and implants last indefinitely,
- disadvantages: the need for a surgical stage, the presence of contraindications, higher cost.
Why is implantation with immediate prosthetics recommended in the later stages of periodontal disease and periodontitis? The point here is not only the speed of smile restoration and a more comfortable life (compared to traditional dentures). The result of the treatment will be truly long-lasting, because... implants stop atrophy and promote bone restoration. After all, the patient begins to chew immediately, the load on the bone is also transferred immediately and physiologically (as from natural roots). And the inflammation goes away, because... its source is removed, and it does not develop again if special implants with a smooth antibacterial coating are installed. Of course, with adequate oral care.
Implantation with delayed prosthetics can also be used, but only after complex treatment of periodontal tissues and removal of decayed teeth. This is a longer treatment path - and in late stages of pathologies it is very long (1-2 years). If it is used, it is only for single restorations and in the early stages of periodontal disease.
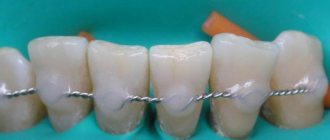
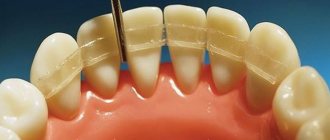
Splinting "clasps"
- advantages: well fix the movable units of the dentition into one fixed segment. Do not create obstacles for cleaning at home and in dentistry, as well as for medical procedures,
- Disadvantages: large mass, difficulty in manufacturing the product, poor aesthetics. The risk of loosening as bone loss continues, the risk of teeth falling out when the structure is removed.
Splinting clasp devices used to be the only option for patients with severe periodontal diseases. Now they are used less frequently, because have more disadvantages than implantation.
“I went to the dentist about periodontitis, my teeth were very loose. I was offered the choice of implantation or splinting clasp. For my own reasons, I chose the last option. And you know, it turned out to be very convenient to use it from the first day. I chew normally, nothing is loose, my diction is intact. The doctor did a great job."
Vladimir Vasilyevich, 68 years old, review from the website of a dental center in Moscow
Installation of implant-supported dentures for periodontal disease
Implantation for periodontal disease usually proceeds as follows:
- the doctor agrees with the patient on the treatment method;
- removes all diseased teeth;
- performs plastic surgery of bone and soft tissues;
- performs one-stage or basal implantation.
The choice of implants for periodontal disease is very important. Dentists use implant systems with maximum survival rates and primary stability. Often these are artificial roots that have a smooth antibacterial coating - it reduces the risk of developing peri-implantitis. Another requirement for implants when working with a patient with periodontal disease is that they must be installed in the basal layer of bone, the likelihood of inflammation of which tends to zero.
But no matter how high-quality an implant the dentist installs, its service life depends on the patient. If he does not regularly undergo periodontal therapy and the disease leads to relapse, the risk of implant failure will increase significantly.
Stages of dental restoration
From the first visit to the clinic to the installation of a removable or fixed denture for periodontitis or periodontal disease, it takes from 1-2 weeks to 1 year - depending on which treatment option the patient has chosen. You can take the fast track and perform implantation with immediate loading. You can also undergo a course of periodontal tissue restoration, which takes up to 12 months, and further prosthetics (traditional or using implantation with delayed loading). Let's look at the stages of smile restoration below.
Diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease
After instrumental and x-ray examination, treatment begins. It is always comprehensive and includes mandatory procedures - splinting or removal of loose teeth, removal of food plaque, tartar above and below the gums (gingival curettage). To restore tissues, they are disinfected and stimulated with a diode laser. Further treatment is carried out if the patient is targeting two-stage implantation or classic prosthetics - in these situations, periodontal health is extremely important.
The patient is given injections of medications into the gums (vitamins, antibiotics, hyaluronic acid, plasma enriched with growth factors - platelets and fibrin). Plasma from the patient's blood can also be used in the form of a membrane (clot). To regenerate ligaments, restorative biogel Emdogain (Straumann) is introduced into periodontal pockets. To replenish the bone volume, Bio-Oss material is implanted, which is covered with a protective absorbable Creos membrane from Nobel Biocare. The course of treatment usually includes about 20 visits to a periodontist over the course of a year. This comprehensive approach allows you to restore up to 80% of tissues.
By the way, these bone materials and membranes are also used for one-stage implantation - directly during surgery for rapid regeneration and reducing the risk of inflammation.
Preparation and planning of prosthetics, implantation
At this stage, impressions are taken from the dentition, dynamic parameters of the bite (position of the jaws, features of joint movement, work of the facial muscles). They are necessary to create the model. It is optimal if the clinic has modern equipment - then parameters and impressions can be taken quickly, carefully and very accurately (all at once in digital form, without physical units and a large volume of viscous impression compounds). After all, when making prosthetics for periodontitis and periodontal disease, it is important not only to restore missing ones, but also to preserve existing teeth, if they are not very loose.
The bite parameters are loaded into the program (if the clinic uses such software), where a classic prosthesis is modeled. Thanks to 3D modeling, it will be immediately comfortable, functional and aesthetic. If implantation is planned, then first, based on the CT scan, the implantologist creates a virtual operation plan, selects implants and their installation sites. Then the orthopedist models the prosthesis. But it will be manufactured only after the implants are installed. 4-7 days are allotted for preparation before implantation, and the implants themselves are implanted in 1-3 hours (depending on the complexity of the case).
Read more about how implants are installed and what are the advantages of implantation over traditional prosthetics.
Manufacturing and installation of orthopedic structures
Manufacturing is carried out in the laboratory based on a previously developed real or virtual model. Then the product is tried on by the patient, if necessary, all defects are eliminated and the product is installed for permanent wear. But there is a nuance here, for example, after implantation, an adaptation structure is often placed first (it is not removable for the patient). They wear it temporarily - 6-12 months, to align the bite and occlusion - after all, with a long absence of teeth, they are damaged. Then re-prosthetics are performed.
With classic dentures, temporary bridges or crowns can also be placed for 1-2 weeks while the permanent structure is being made. But you should treat such products with care, because... they are quite fragile.
Implantation is the only effective way
Implants are screwed into the bone and do not require periodontal ligaments to secure them. The surface of the necks of special implants is resistant to the accumulation of microbes. Thus, dental implantation is the only effective way to restore teeth in conditions of periodontitis , but only if the disease is stopped . The patient gets rid of chronic periodontitis, the periodontal ligaments are restored, and the soft tissues are strengthened, remodeled and, with good hygiene, serve as a natural barrier to the penetration of infection into the bone.
The integrity of the dentition and proper distribution of the chewing load contributes to:
- stimulating blood circulation and normalizing nutrition of bone and gum cells,
- stops uneven distribution of chewing load and overload of teeth,
- prevents changes in bite and tooth mobility.
Implants should not be installed near teeth affected by periodontitis. If the remaining teeth, as the main source of “infection,” are left without complex therapy, then the development of infection will lead to an attack by pathogenic microflora on nearby implants and the soft tissue around them, and this will lead to complications and even rejection. Therefore, first of all, before implantation, you need to undergo a comprehensive course of periodontitis treatment and reduce the risks.
BE CAREFUL! Some unscrupulous and inexperienced doctors convince patients to place implants next to adjacent teeth affected by periodontitis, without informing them of the danger and essentially hoping for a “miracle.” Under no circumstances do this without simultaneous treatment and bringing periodontitis into a state of stable remission. Plus the realization that careful hygiene with this approach is very important in the future.
ON A NOTE! According to the American Association of Periodontists www.perio.org, the average age of a patient with periodontitis is 40+, 70% have implants in the oral cavity with developing complications.
With the development of microbiology and nanomaterials, drugs have been developed that not only stably stop the disease for many years, but also make it possible to restore the consequences of complex forms of periodontitis up to 80% in 1 year. Today, advanced dentistry has effective tools for preserving teeth. Smile recovery periodontal complexes are aimed initially at eliminating the environment for the development of the disease, and then enriching the affected areas with active growth factors to create a favorable environment for the natural regeneration of the patient’s cells and tissues.
Deep cleaning of periodontal pockets and 1-2 procedures will not stop the progression of the disease. Periodontitis is a multifaceted disease with an individual pathogenic flora for each patient and it must be treated accordingly, using a set of antibacterial and restorative measures, selected individually after a thorough study of microflora culture from periodontal pockets, drawing up a periodontogram, analyzing the state of bone tissue using computed tomography and additional blood tests.
Do you want to save your teeth and stop the disease? Smile recovery periodontal complexes that really work.
find your solution
What is better to choose in case of partial or complete absence of teeth?
What dentures are best for periodontal disease and periodontitis? In case of partial edentia, you can choose crowns and bridges - if the symptoms and manifestations of pathologies are mild, and the patient has undergone comprehensive treatment and generally maintains health (in the presence of chronic diseases). Veneers and inlays can also be placed without the risk of complications. If strong mobility is already observed, then you can choose a splinting clasp.
PROSTHETICS WITH 6 OSSTEM IMPLANTS FROM RUB 220,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Call now or request a call
However, do not forget that for fixed bridges and some types of removable ones (clasp bridges with attachments, for example), you will have to grind and depulp the abutment teeth. And with a splinting “clasp” you won’t be able to smile openly, because... the hooks are noticeable from the side.
If the patient has a complete absence of teeth, removable orthopedic structures will strongly rub the gums and provoke accelerated atrophy. And it is very difficult for them to chew their favorite food. Therefore, for partial and complete edentia, the best option is implantation with immediate prosthetics. Moreover, periodontitis will disappear, and periodontal disease will stop progressing, because implants help restore bone and gingival levels. You will be able to chew without pain, smile openly and not worry about the denture falling out of your mouth.
Not all implants can be installed for periodontitis
In addition to therapy against periodontitis, it is important to choose the right implants. They must have high primary stability in the current unfavorable conditions and have a special coating to improve integration, both with the soft tissue of the gums and with various types of bone tissue. The surfaces of these implants at the level of contact with the gums have properties of resistance to the accumulation of microbes.
In the world, there are only 3 implantation systems, Nobel Biocare, Straumann, Oneway Biomed, which have been studied for more than 40 years, the implants of which take root and are not rejected in conditions of periodontitis. Naturally, provided that foci of infection are eliminated, complex treatment and rehabilitation of the affected tissues are completed.
Nobel Biocare® - Xeal® and TiUltra® Surfaces The intimate contact between the soft tissue and the abutment creates a barrier that protects the underlying bone and ensures long-term stability and healthy gum tissue.
It is a smooth, non-porous, nanostructured anodized surface with a chemical composition and topography designed specifically to enhance soft tissue attachment.
When developing these surfaces, scientists relied on 20 years of research into the effectiveness of anodized implants and laboratory results.
The single orthopedic surface of On1 eliminates the need for surgical manipulation of soft tissues during subsequent prosthetics.
The main objectives of these surfaces are to ensure a favorable outcome of implantation in the long term and reduce the incidence of re-implantitis.
More details
Straumann® Roxolid SlActive - Tissue Level Straumann® Tissue Levels have a smooth milled neck, which simplifies the manipulation of soft tissues and eliminates the need for the use of healing abutments during subsequent prosthetics. In the event of a slight recession of the soft tissue, the polished neck of the implant will protect the surface of the implant from the accumulation of microbes.
Nanostructures on the implant surface promote early osseointegration and a larger area of bone penetration.
The SLActive® surface is characterized by an increased anti-inflammatory response during the early healing stage. The results of world studies have confirmed the exceptional survival rate of implants in difficult clinical situations and when using aggressive treatment protocols: in patients with diabetes mellitus, after chemotherapy and radiation therapy, in heavy smokers, in patients with chronic periodontitis.
More details
OneWay Biomed® - antimicrobial coating BCS MU and Zygomatic implants are one-piece structures designed for osteofixation in the deep parts of the maxillofacial bone and cranial buttresses. For example, the bicortical plate, basal bone, zygomatic region, jaw tubercles, hyoid and mental bones, pterygoid process, etc.
Such implants do not require integration with the alveolar bone of the jaw, since they are securely fixed in other, non-resorbable areas. Over time, the newly formed alveolar bone compacts around the implants, providing additional support.
The surface of the implants has an antimicrobial coating, which prevents plaque and bacteria from accumulating.
The implant and abutment are a single whole; after implantation, soft tissues are not subjected to additional surgical interventions at the prosthetic stage.
More details
In addition, it is important to minimize the number of surgical manipulations on soft tissues after implantation, therefore implants with a single orthopedic surface On1 installed at the soft tissue level are preferable. During subsequent prosthetics, the orthopedist does not injure the gums and does not create additional mechanical stress on the implant, essentially working “above the gum.” In addition, all components of the prosthesis must be bioinert, that is, not cause inflammatory reactions from surrounding tissues.
Proper oral care
After installing a denture for periodontitis and periodontal disease, it is necessary to strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations - carry out regular cleaning in the morning and evening, soak removable structures in disinfectant solutions once every 1-2 weeks. For cleaning it is better to use special brushes and pastes. Brushes and flosses (threads) do a good job of cleaning interdental areas - but these devices can only be used with the permission of the dentist. And you should visit an orthopedic dentist, periodontist, implantologist (or all at once) 1-2 times a year for examination and professional hygiene.
[1] Wolf G. Periodontology, 2007.
Basal implantation
Features of this method: rapid insertion of an elongated pin, sometimes at a certain angle, into the basal (deep) layer of bone.
Stages of basal implantation:
- Computer modeling based on survey results and creation of a 3D model.
- A thin deep puncture of the gums with a special instrument, which reduces the degree of trauma of the operation for patients with weakened gums.
- Introduction of a metallic “root”.
- Attaching the permanent prosthesis to the abutment 2-3 days after installing the pin.
After this operation, chewing loads are immediately recommended.
Materials
Dental implants for periodontal disease can be made of titanium alloy - these are the models that are offered to patients in most cases. However, with inflammation or atrophy of the periodontium, the likelihood of allergic reactions increases, and even titanium sometimes causes them.
Today, implants made of zirconium dioxide are increasingly used in dental practice - this is the development of European scientists. They are made in Switzerland, Germany and the USA.
Important!
Zirconium roots are absolutely hypoallergenic.
Titanium implants are not placed in cases of hypersensitivity to certain metals and alloys, multiple allergies, or hay fever. They are used with caution in patients with psoriasis.
Prices
Patients with periodontal problems require additional treatment before implantation: sanitation of the oral cavity, curettage, scaling, removal of loose teeth. Therefore, the total cost of implantation for periodontitis will be determined by the volume of preparatory procedures.
| Service | Price |
| Consultation and treatment planning | for free |
| Orthopantomogram | for free |
| Nobel | 55 000 ₽ 38 500 ₽ |
| Ankylos | 50 000 ₽ |
| Straumann | 60 000 ₽ 38 500 ₽ |
| AnyRidge | 60 000 ₽ 47 000 ₽ |
| Prosthetics of the entire jaw using the All-on-4 method (price includes: implants + surgery, taking impressions, temporary prosthesis) | from 189,000 to 400,000 ₽ (depending on the brand of implants) |
| Service | Price |
| Consultation and treatment planning | for free |
| Orthopantomogram | for free |
| Nobel | 55 000 ₽ 38 500 ₽ |
| Ankylos | 50 000 ₽ |
| Straumann | 60 000 ₽ 38 500 ₽ |
| AnyRidge | 60 000 ₽ 47 000 ₽ |
| Prosthetics of the entire jaw using the All-on-4 method (price includes: implants + surgery, taking impressions, temporary prosthesis) | from 189,000 to 400,000 ₽ (depending on the brand of implants) |
See all prices for orthodontic treatment and implantation.
Expert of the article you are reading: Kuzmenko Viktor Valerievich Orthopedist, surgeon, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
16 years
Clinical experience
Krasnogorsk
Moscow region, Krasnogorsk, Podmoskovny Boulevard, 5
+7
Free consultation with this specialist
Implantation options depending on the severity of the disease
| Partial implantation (remaining teeth are retained ) | Full implantation (all teeth are removed) | |
| Depth of periodontal pockets | up to 8 mm | more than 8 mm |
| Nature of inflammation | localized | generalized (affects the entire jaw) |
| Mobility of dental row units | I-II degrees | III degree remaining units |
| Bone quality | Type II-III (cortical layer thickness 3-5 mm, spongy layer with a developed network of thin trabeculae) | severe atrophy of the jaw bone |
| Condition of remaining teeth | satisfactory | accumulation of dental plaque |
| Tissue healing ability | high or medium | low |