Treatment of caries for children Caries is a very common dental lesion, which is important to pay attention to. Baby teeth are no exception; they need to be treated, despite the fact that even at a young age they are completely replaced with permanent ones. The health of permanent teeth, the oral cavity as a whole, and the child’s quality of life depend on the condition of baby teeth. One of the main principles in this case is high-quality prevention, professional treatment tactics and minimal intervention.
How to identify milk caries
It is quite simple to identify caries in young and older children. White or brown spots appear on the teeth, a painful reaction to hot and cold is observed, and the child may develop bad breath. When these first symptoms of caries appear, it is already worth sounding the alarm, since the carious process is developing very rapidly. It is characterized by almost instantaneous damage to several teeth, and if measures are not taken, the entire dentition may be affected. Of course, it is often difficult for a child to articulate that his baby tooth hurts. He may refuse to eat or chew on only one side. This should also alert parents and encourage them to take their child to pediatric dentistry.
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
Caries of primary teeth must be treated at any stage. The sooner you start this process, the less effort it will take. If treatment is not carried out, this will certainly affect:
- growth and development of permanent teeth - infection, abnormal growth, and disruption of eruption may occur;
- the general condition of the child - the source of infection increases the risk of developing chronic diseases, promotes sensitization of the body, reduces immunity, and inhibits the growth and development of the child.
Where does childhood caries begin?
There are more reasons for this than meets the eye. This includes improper oral hygiene, sharing cutlery with adults who have caries, and much more. However, the main causes of occurrence are the influence of consumed carbohydrates that destroy the tooth, accidental infection from a carrier of a carious infection, a genetic factor, the immaturity of the children's skeletal system, and improper use of pacifiers and nipples.
- Of course, the main and most common reason why childhood caries occurs is poor oral hygiene and the influence of sweets. According to statistics, caries develops in young children in 73% of cases. Sucrose, glucose and fructose are the acids that are formed during the fermentation of carbohydrates and lead to the destruction of enamel. Immediately after ingesting carbohydrates, the pH of saliva decreases from 6 to 4 and pathogenic bacteria settle in food debris that is not cleaned from the teeth.
- Remember the children's saying “from mouth to mouth you get a germ”? It turns out that she is not so far from the truth. The fact is that caries is an infection, an infection. That is, a loving parent, being a potential carrier of carious microbes, does not even suspect that by kissing his baby or sharing dinner with him, he can personally infect his child!
- Another reason why caries may occur on baby teeth is genetic. Teeth begin to form during the prenatal period, in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, smoking by a negligent parent, her illnesses suffered during this period, or taking medications can lead to disruption of the proper development of the child’s teeth.
- Caries in children 2 years old, that is, early caries in children, may be associated with the following factor: baby teeth have a low degree of mineralization and erupt “immature”, and only then “mature” in the oral cavity. Final mineralization lasts for one and a half to two years for baby teeth and about three years for permanent ones. Pediatric dentists call such periods of “maturation” the most susceptible to caries. Therefore, the reasons why caries occurs in a child of 2 years and at an earlier age may also be chronic diseases, the effects of medications, the composition of saliva and the fluoride content in water and food.
- Another reason for the development of caries in very tiny children is the incorrect use of pacifiers. A baby who falls asleep with a bottle in his mouth runs the risk of getting caries on his front teeth, so-called bottle caries. In this case, prolonged contact of the sweet liquid with the teeth leads to caries of all front teeth. In this case, the disease spreads around the entire visible part of the tooth along the perimeter.
As you can see, there are more than enough reasons for the appearance of caries. But they all boil down, as a rule, to demineralization of teeth and destruction of hard tissues. Characteristic changes occurring in teeth can only be diagnosed by a dentist. Further treatment will depend on how severe the caries has developed. What are the stages of development of caries in primary teeth?
Stages of the carious process
The carious process on baby teeth is more intense, this is due to the structural features of the enamel and dentin of children's teeth. The hard tissues of the tooth are poorly mineralized, the surface of the tooth is more porous, and the dental pulp is immature.
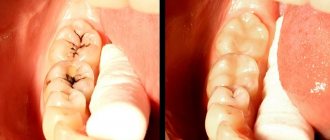
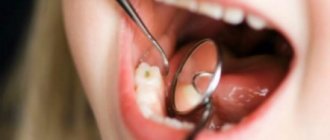
The first stage is a carious spot. If the plaque that has formed on the surface of the tooth is not removed within 24 hours, then the bacteria inhabiting it begin to actively reproduce. acids are formed that wash away fluoride and calcium from tooth enamel. As a result, cariogenic bacteria penetrate deeper into the tooth and damage it. This is the first stage of caries - a carious spot. At this stage, the process is quite easily reversible; it can be cured even without a drill. There is a modern and safe method of chemical-mechanical treatment of tooth enamel with a special gel - ICON. At this stage, it is almost impossible to determine tooth decay on your own, which is why it is recommended to visit the dentist regularly.
In the second stage - initial caries , bacteria damage dentin, thereby forming visible tooth decay. The tooth begins to react briefly to cold and sweet stimuli. If there is a cavity (even the smallest one), ICON will not help - invasive treatment with removal of carious tissue and filling is required.
The third stage is middle caries . Here, bacteria cross the enamel-dentin boundary, and dentin destruction occurs faster than enamel. In an adult, the process will be slow. Since protective dentin begins to be produced, the tooth “fights” the disease, but in baby teeth such protection is significantly lower. At this stage there is already a carious cavity, which is probed. And the reaction to irritants is more pronounced, food begins to get stuck in the cavity.
The fourth stage is deep caries. Bacteria penetrate closer and closer to the center of the tooth, to the pulp. By this time, most of the dentin has already been destroyed, there is a large carious cavity, the tooth reacts strongly to irritants: cold. hot, sweet, the pain goes away only with time, but at this stage the tooth itself does not hurt yet. In all three cases: from initial to deep caries, the tooth can be cured by placing a regular filling. inlay or crown, leaving the tooth “alive”.
The fifth stage is pulpitis. This is already inflammation of the neurovascular bundle located in the pulp chamber. These tissues are destroyed. Accompanied by severe throbbing pain, both in response to irritants and spontaneously. Very often, parents pay attention to tooth decay in their child only at this moment, the toothache is very acute and a visit to the dentist is urgent.
The sixth stage is periodontitis. This is an inflammatory process outside the tooth. It can be asymptomatic in an already pulpless tooth and lead to complex consequences. such as bone loss. At this stage, the tooth hurts when eating hot food or biting.
Stages of development of childhood caries
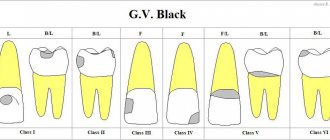
Dentists divide caries of primary teeth into several types according to the depth of damage:
- elementary;
- surface;
- average;
- deep.
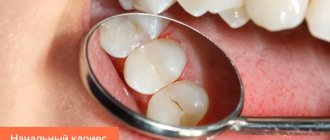
Initial caries
Initial caries can be recognized as follows: white spots of various shapes and sizes appear on the enamel, but there is no pain. In advanced cases, initial caries progresses - the spots darken, becoming brown and then black.
Superficial caries
With superficial caries, the defect in the dental tissue is located within the enamel, and the carious cavity can be either light or dark. However, in this case, pain occurs when the tooth comes into contact with sweet, sour or salty foods. In this case, treatment of the baby tooth and filling of the cavity is already required.
Average caries
Medium caries affects the enamel and inner tissue of the tooth (dentin). In addition to the unpleasant sensations from sweet, sour and salty, pain from hot and cold is added. In this case, as with superficial caries, filling is necessary.
Deep caries
With deep caries, the enamel and a significant part of the dentin are affected. If treatment is not carried out at this stage, then caries can affect the pulp of the tooth and then reach the root, often resulting in a cyst of milk teeth. Here you just need to see a doctor before the infection goes further. In this case, caries of primary teeth and its treatment will depend on how far the caries has spread.
Initial caries
First, a white or yellow spot appears under the plaque - initial caries or caries in the spot stage. Caries in the spot stage is usually asymptomatic; sometimes hypersensitivity to chemical irritants (sour, sweet, salty) may occur. With timely and correct treatment, further development of caries can be stopped.
Treatment of caries in children
Childhood caries and its treatment still remain an open question for some parents. Even knowing that the child has caries, they are in no hurry to see a doctor, thinking as follows: “Dairy teeth will fall out anyway.” Such judgments are absurd, because infected baby teeth will lead to complications in the growth of permanent teeth or provoke an exacerbation of other diseases in the baby’s body. One way or another, you will have to remove the baby tooth ahead of time. Caries in pediatric dentistry is considered one of the most common diseases, so both parents and specialists should ask questions about how and why to treat caries in children. Dentists believe that treating caries in a baby tooth will preserve it until the molars appear.
If the doctor finds that a child has incipient caries, then most likely, treatment of baby teeth will not be required. The specialist will protect the enamel from further destruction using a painless and effective procedure - applying fluoride varnish or a silver fluoride compound. Then, when the baby gets permanent teeth, the dentist can seal the fissures - the depressions between the elevations of the tooth, which will prevent the occurrence of bacterial plaque that destroys the enamel. If caries progresses, you can no longer do without filling. The doctor will quickly and almost painlessly remove the affected tissue and hermetically seal the tooth. Otherwise, caries can turn into pulpitis in a child, and then into periodontitis.
How is chronic periodontitis treated?
Treatment of periodontitis is long and complex and does not always result in a cure. In temporary teeth, most often the tooth affected by periodontitis has to be removed.
Treatment of this disease in permanent teeth consists of eliminating the pathological process. With subsequent sanitation of the inflammatory focus and filling of the destroyed canal. Lack of treatment leads to damage to the root and cortical area. With treatment performed by a specialist and the use of high-quality materials, the symptoms, as well as the disease itself, in the affected area can be eliminated for a long time.
Features of caries treatment in children
- Before administering anesthesia, the doctor must numb the injection site using special gels or spray. Moreover, the content of the anesthetic component should be minimal. Anesthesia is, as a rule, carried out only in cases where pulp removal is required - that is, with medium and deep caries.
- It is advisable to remove affected tissue using hand tools or a drill, taking frequent breaks.
- As fillings, materials that can be applied “one time” should be used in order to reduce the operation time.
- If caries is complicated and its treatment requires the necessary filling of the roots, then the canals are disinfected without special mechanical treatment and filled with a special paste.
- Treatment of baby teeth in children should take no more than half an hour, otherwise the child will get tired.
- Treatment of multiple, or bottle, caries, as a rule, takes place in several stages and requires the use of sedation.
- Dental treatment under general anesthesia in children is carried out strictly according to indications.
You can get rid of carious lesions at the initial stage using modern methods of caries treatment without a drill. Comfortable, painless treatment is suitable for those children who are afraid of manipulation with a dental bur. The cost of treating caries in baby teeth without a drill is slightly higher than the price of traditional dental treatment for children, but it is worth it. If simple caries gives complications, then you will have to resort to classic drilling. The cost of treatment of complicated caries of primary teeth will depend on the degree of neglect of the disease.
General information
According to medical statistics, 70-80% of children under the age of 10 suffer from caries.
Even children aged 1-2 years are susceptible to the disease, in which areas near the neck of the incisors and canines are affected. Caries quickly spreads throughout the mouth of children. This is due to the characteristics of children's saliva, which does not have antiseptic properties. Bacteria multiply quickly, attacking tooth enamel. Depending on the depth of the cavity defect, uncomplicated and complicated caries are distinguished. The latter is characterized by the development of pulpitis (inflammation of the pulp), periodontitis (inflammation of the tissue between the root and the tooth socket). Depending on the course, dental caries in children can be acute or chronic. The first option is also common in childhood and requires the intervention of a dentist.
Prevention of caries in children
Prevention of childhood caries includes several areas, which boil down to proper nutrition, as well as home and professional hygiene.
Individual oral hygiene
Home hygiene means that as soon as the first tooth hatches, a brush for the baby should appear in a glass next to the parents’ brushes. The same applies to toothpaste. At first, the paste can be applied to gauze or a fingertip to clean your teeth so as not to injure your delicate gums. You need to clean your teeth from all surfaces vertically, then wipe them with a brush soaked in water. Thus, firstly, plaque will be removed, and, secondly, parents will teach the baby to take care of the oral cavity.
Preventing caries with a well-chosen diet
As for nutrition, parental duty is to breastfeed the baby from the very beginning. There is no need to talk about the beneficial properties of breast milk, and the sucking process greatly affects the developing jaw system. Then the baby should be accustomed to fermented milk products. By six months, the child should be fed kefir, and later - cottage cheese and cheese. Parents should remember that the main formation and formation of permanent teeth occurs up to 3 years of age. This means that calcium must always be present in the daily diet.
Professional oral hygiene
This type of prevention involves periodic visits to the dentist and hygienist. The first visit should occur on your first birthday. The specialist will not only give recommendations for care, but also create a diet regimen and examine the mouth. When the first teeth emerge, you and your child will be shown how to brush their teeth properly at an appointment with a hygienist. If there is a problem such as tartar in children, you cannot do without professional hygienic cleaning. It is important for parents to make it a rule to visit the doctor twice a year. And if there are problems with teeth, then more often - once every three months. This is largely due to the fact that various pathologies develop too quickly in childhood. Meanwhile, early diagnosis will lead to quick, painless and relatively inexpensive treatment of caries.
As you can see, in most cases, when caries can attack children's teeth, parents are able to resolutely rebuff it. Of course, there is no escape from genetic predisposition. But it’s not without reason that dental experts say that sweets are the main cause of the development of the disease! So isn’t it better to eliminate the constant source of bacteria and, instead of harmful carbohydrates, offer the child fruits, which are much healthier, after the main meal? Ultimately, your child will thank you in the future for being vigilant and maintaining healthy teeth!
Detailed information and registration by phone: +7 (391) 200-1000.
Make an appointment
Request a call
Therapy methods
Treatment of caries detected at the initial stage of development is carried out conservatively using methods of silvering or deep fluoridation of enamel. When carious cavities are detected, they are cleaned (using a drill or chemical preparation) and filled with quickly hardening composite materials.
All therapeutic procedures are performed only after the anesthesia procedure. In this case, preference is given to local anesthetics, but if necessary, treatment can be carried out under general anesthesia.
Diagnostics
To establish the correct diagnosis, the dentist first collects anamnesis - carefully asks parents about complaints, the course of the disease, and the hereditary characteristics of the child’s body. After this, he examines the oral cavity. If there is a suspicion of a carious cavity, then the examination is carried out using a special probe, which allows identifying carious cavities in different parts of the dental crown. If this is not enough to establish a diagnosis, then additional examination is prescribed:
- staining with a special harmless dye in blue or pink; where there are externally invisible carious areas, the most saturated color is obtained;
- examination of the interdental space using floss - flossing of the thread indicates the presence of altered enamel;
- transillumination - illumination with a special lamp; at the same time, the carious cavity becomes visible;
- EDI (electroodontometry) – the action of electric power is used. current on dental tissues; tissues altered by caries respond to EDI exposure differently than unaltered tissues;
- orthopantomogram (OPTG) - this type of x-ray diagnostics is allowed to be performed from 5 years of age; children undergo OPTG with reduced radiation exposure;
- laser diagnostics using the Diagnodent device - instant detection of pathology and the stage of its development; The study can be carried out on children of any age.