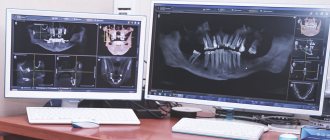
Methods of modern dentistry are aimed at preserving the dental unit. Removal is resorted to as a last resort if gentle treatment techniques are ineffective. Resection of the apex of the tooth root (apicoectomy) is a microsurgical intervention for excision of tissue affected by infection with part of the injured tooth root. The operation is performed if the inflammation has taken the form of a cyst or granuloma. The main condition for the success of such a surgical intervention is the timeliness of the patient’s visit to the dentist. If the pathological process spreads to most of the root, the tooth will have to be removed.
Indications for surgery
- Poor endodontic treatment leading to inflammation of the root apex;
- the presence of a cyst, granuloma or other neoplasm, no more than 1 cm in diameter;
- perforation of the root walls during filling;
- pin or stump inlay in the dental canal;
- obstruction of the dental canal due to a congenital developmental defect;
- a crown or bridge placed on a tooth.
When surgery is not performed
Like any other surgical intervention, apicoectomy has limitations and contraindications. These include:
- Mobility of teeth II-IV degrees;
- destruction of the crown part of the tooth (more than 50%);
- the presence of cracks in the affected root;
- severe curvature of the root canal (impossible to fill);
- crowding of teeth, which does not allow identifying the affected root;
- acute infectious, viral disease;
- severe bleeding disorders;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- severe immunodeficiency;
- oncology in the active stage.
Some of the limitations to root resection are the indication for removal of the affected unit. The second part refers to general contraindications to any surgical intervention. The risk of surgery for the patient is assessed individually.
The specialists at the Ilatan Clinic make every effort to save the dental unit, if possible. But if there are direct indications for removal, for example, extensive damage to dental tissue, the doctor will not suggest apicoectomy.
Features of the technique
Surgical treatment of this disease is carried out using several methods:
- Vagotomy. This is the intersection of the branches of the nerve that stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. After such an operation, the acidity in the stomach decreases, and the tissues heal on their own.
- Removal of part of the stomach using the Blroth I and II methods, as well as their modifications. During the operation, part of the mucous membrane is removed, which intensively produces enzymes and hydrochloric acid. It can be performed in case of perforation of an ulcer and other complications, provided that the patient’s condition allows it.
- Pyloroplasty. This is a method of treating peptic ulcers of both the stomach and duodenum with narrowing of the duodenal bulb and pylorus.
In some cases, laparoscopic excision of the stomach is performed without large external incisions. This operation is performed in case of complications. If the patient is in serious condition, then the perforated ulcer is simply sutured and the abdominal cavity is drained.
Operations can be carried out planned or urgently. Emergency intervention is indicated for bleeding that is not controlled by medications and perforation of the ulcer. In these cases, the ulcer is sutured, the narrowed digestive tube is expanded, and the bleeding stops.
Surgical treatment is also carried out for malignancy of the ulcer. Its success depends on how early the tumor is detected, whether it has affected only the mucous and submucosal layers or has grown into all layers of the stomach, whether nearby organs and lymph nodes are affected, and whether there are distant metastases.
Resection stages
- Formation of access
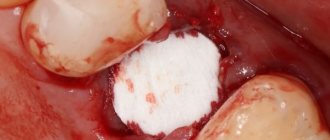
- the dentist cuts through the gum, exposing the jaw bone. Forms a small hole in the bone tissue (in the projection of the root apex), gaining access to the pathological focus. Often, the bone tissue has dissolved in the projection of the cyst; there is no need to cut out a hole. - Excision of tissues and correction of the apex
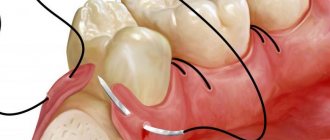
- the doctor removes the source of inflammation along with the dead apex of the root, cutting it off perpendicular to the upper dental axis (to the level filled with the filling mass). The empty space is filled with osteoplastic material (bone volume is restored faster). - Suturing
- suturing the wound area is sometimes performed with the installation of drainage for the outflow of ichor. Drainage is installed between the seams and is removed after 1-2 days.
Root resection takes 40-60 minutes, depending on the location of the tooth. It is easier to intervene on canines and incisors than on multi-rooted units.
Briefly about the treatment method
Bowel resection is an operation to remove part of the small or large intestine. This is a fairly traumatic procedure, so it is not performed without very compelling reasons.
Types of bowel resection
Different types of resections are performed to remove different parts of the intestine. Each type of bowel resection is named based on what it removes: Segmental small bowel resection: A portion of the small bowel is removed. The surgeon may also remove part of the mesentery (the fold of tissue that supports the small intestine) and lymph nodes in the area. This type is used to remove tumors in the lower duodenum (upper part of the small intestine), jejunum (middle part of the small intestine), or ileum (lower part of the small intestine). Right hemicolectomy: removes part of the ileum, cecum (part of the large intestine), ascending colon (part of the large intestine), hepatic flexure (flexure of the colon), first part of the transverse colon (middle of the large intestine), appendix. Transverse colectomy: the transverse colon, hepatic and splenic flexures are removed. This surgery may be used to remove a tumor in the middle of the colon when the cancer has not spread to other parts of the colon. Left hemicolectomy: Part of the transverse and descending colon, the splenic flexure (the curve in the colon near the spleen), and part or all of the sigmoid colon are removed. Sigmoid colectomy: The sigmoid colon is removed. Low anterior resection: the sigmoid colon and part of the rectum are removed. Proctocomectomy with ileoanal anastomosis: the entire rectum and part of the sigmoid colon are removed. An ileoanal anastomosis is a procedure that a surgeon does to attach the lower portion of the small intestine to the anus. Abdominoperineal resection: The rectum, anus, anal sphincter and muscles around the anus are removed. The surgeon makes one cut or incision in the abdomen and another in the perineum (the area between the anus and vulva in women or between the anus and scrotum in men). This procedure requires a permanent colostomy (taking a section of the colon out) because the anal sphincter is removed. Partial and total colectomy: Surgery to remove part or all of the colon (including the cecum).
Recovery period
The entire operation lasts about an hour, the recovery period takes up to six months or more, depending on how quickly the bone tissue regenerates. In the first 1-2 days after the surgical procedure, the patient is bothered by moderate pain, swelling, and redness of the gums. After 3-4 days, the unpleasant symptoms decrease and the condition improves. To ensure that the postoperative period passes quickly and without problems, the doctor will give the necessary recommendations for care, prescribe painkillers, as well as a short course of antibiotic therapy.
Reviews
- Review by Anton Nikolaevich Logvin
The operation was performed 6 years ago. Weight was 175. My knees started to hurt. It was impossible to find clothes. Constant feeling of hunger. Now I weigh 110. The weight suits me. I don't want to lose weight anymore. Boris Yurievich Tsvetkov is a surgeon from God, a very decent person and a wizard, an architect of human bodies. I'll say this.
Photos and interviews
- Review by Olga Vladimirovna Ryabokon
Before the operation, the weight was 154 kg and there were a million concomitant diseases. Now 87-88. I’m no longer treating diabetes, it doesn’t bother me, my blood pressure is very rare. At 64 years old, I don’t walk, I run. Before, I couldn’t walk through the kitchen; I was out of breath.
And after me, my daughter also had the same operation. All the best that I can, I know, all the good words, I dedicate everything...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Irina Sergeevna
Thank you very much to Boris Yuryevich for the gift of a new happy life, with all my heart. I say that I celebrate the day of the operation as my second birthday. My life has changed, my mind has brightened, my soul has brightened, I don’t know, it’s as if I’ve actually become younger. I was 44, now I’m 45, a new life has begun. Thanks to him for his golden hands, thanks to the whole team...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Marina Konstantinovna and Nate Donelson
I would like to express my deep gratitude to Boris Yuryevich and his entire team. The man who changed my life, who changed my husband's life, who saved my husband's life. I am very grateful to him. We are now planning a second child. He may have saved another life. We will have a second child, and at my former weight I could not give birth.
This is a surgeon...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Alexander Semchev
Friends! Previously, some time ago, it was difficult for me to live because the moment of my “promiscuity” played a bad joke on me. But, thank God, Dr. Tsvetkov and his clinic appeared in my life. Thanks to his efforts, his attention, I began to live differently. Of course, with a plus sign.
Photos and interviews
- Anna's review
I would like to say a huge thank you to Boris Yuryevich. He told me everything about the operations competently and in a language that I could understand, where there were any pros and cons. He gave me comprehensive answers to all my questions. He is a professional with extensive experience whom I trusted. I can say one thing. That this is a person who tells patients it like it is, in simple language accessible to...
Photos and interviews
- Review by Tatiana
Boris Yuryevich is a great guy, of course. Attentive, he told me everything that interested me. I walked differently from Marina, for example. Marina probably teased him for a very long time; he probably told a lot of things for a long time. I flew on wings. Everything would have been done faster for me. But what interested me, for example, the same operation, what to do...
Photos and interviews
- Alina's review
Boris Yurievich Tsvetkov is truly a doctor of the highest category, who is adapted for people. All people are different. Some work for their own personal gain. And Boris Yuryevich works for the people. It is available 24/7, which was very important to me. That I could call him at night and say: “Boris Yuryevich, I’m not feeling very well.” He always…
Photos and interviews
- Olga's review
Thanks to Boris Yuryevich for making people beautiful and happy. I already told him that I really have become more beautiful, younger, and much happier. I would like to wish him long life, even more career growth, newer modern technologies.
It's too bad he doesn't do breasts. It does the stomach, but he says I don’t do the chest now. And that’s what I would do...
Photos and interviews
- Valeria's review
I had gastric resection surgery and I am very pleased. What happened before and what happened after is noticeable in life, in health, in everything. A person changes - this is a new life. There is no need to be afraid of this operation, you need to go and do it. Boris Tsvetkov is a worthy, high-quality surgeon who will care for and guide his patient from beginning to end. In the hospital…
Photos and interviews
- Feedback from Natalya Anatolyevna Kukshina
I am a person who, at the age of 26 (at the time of the operation), has experienced a lot - various cleansing programs, nutritionists, fitness programs for losing weight, buying and consuming tons of products, as advertising aimed at weight loss instills in us, I can only say one thing. If you have problems with excess weight, diseases caused by excess...
Photos and interviews
- Alexey's review
What Boris Yuryevich Tsvetkov did... I want to say frankly. Without praising him, nothing, simply, what Tsvetkov did - he simply did what is impossible to do, you know? Tell someone else. I talked with other doctors, with endocrinologists, with therapists, there are a lot of people we know in medicine. Even people who are in this profession…
Photos and interviews
Care after tooth resection
- Do not chew on the operated side.
- Until the wound heals, avoid irritating, solid foods (food should be warm and soft).
- Do not use a hard toothbrush, aggressive pastes, or mouthwash.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to prevent infection.
- Rinse your mouth after eating with an antiseptic solution.
- For the first week after surgery, limit physical activity to moderate, and exclude extreme, contact sports.
- Do not visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna until the wound is completely healed.
- Avoid eating too hard foods until the bone is completely restored (at least 3 months).
- Visit your surgeon regularly to evaluate the results of the operation.
Prevention of recurrence of the disease
First of all, you need to exclude factors that cause peptic ulcer:
- alcohol consumption;
- stress;
- smoking;
- heavy physical activity;
- improper diet, eating fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, fast food;
- non-compliance with diet.
To prevent ulcers you need:
- sleep at least 6-8 hours a day;
- minimize the consumption of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa - fatty, smoked, fried;
- chew food well;
- eat up to 6 times a day;
- eat chopped food, cereals, jelly, omelettes, vegetables, steamed meat;
- See a doctor immediately if you have stomach pain;
- eliminate alcohol and smoking;
- protect yourself from stress;
- reduce coffee consumption to a minimum;
- eat boiled, baked, steamed food with a minimum of spices.
You need to visit a doctor for preventive examinations once a year. Also, for prevention, all patients are prescribed courses of antiulcer medications in the summer and spring.
Possible complications
Root resection is a micro-operation, the purpose of which is to preserve the full functionality of the affected tooth. Usually, the risk of complications is minimal, but they cannot be completely excluded. Sometimes the following complications are possible:
- Bleeding due to injury to nearby vessels;
- infection of a postoperative wound;
- recurrence of cysts, granulomas (if all affected tissues were not removed);
- perforation of the maxillary sinus, nasal passage;
- damage to the nerve passing along the alveolar ridge;
Sometimes complications are caused by structural features of the jaw, for example, the proximity of the roots to the maxillary sinus. Complications caused by non-compliance with medical recommendations include swelling and tissue inflammation. Ignoring advice on limiting physical activity is fraught with the development of bleeding, and failure to maintain hygiene can lead to wound infection.
Cost of tooth root resection
The price of root resection is determined depending on the volume of surgical intervention, the cost of consumables, and anesthesia. The result of the procedure fully justifies the money spent. After all, it is cheaper than removal with further implantation and prosthetics. The doctor will tell you exactly how much tooth resection costs after examination and diagnosis.
Preparation
Breast resection, despite being minimally invasive, is considered a full-fledged surgical intervention, so the woman must undergo examination and prepare for surgery. The list of studies includes:
- Taking a general and detailed blood and urine test.
- Ultrasound, mammography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the breast.
- Fluorography.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Blood test for sex hormones.
- Testing for HIV and hepatitis.
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological examination.
Other diagnostic methods may be prescribed - the list of studies is determined by the attending physician.
Also, before the operation, a woman must follow some rules:
- The operation is carried out strictly on an empty stomach: before the operation you will need to go without food for at least 8-10 hours.
- Tell your doctor about all the drugs you take, including oral contraceptives. The doctor may cancel some of them.
- You must abstain from alcoholic beverages at least 10 days before surgery.
- 2 days before resection, it is necessary to exclude heavy foods, including fatty and fried foods.