October 27, 2019
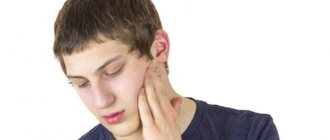
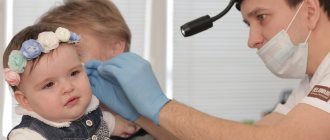
Many people are interested in whether a tooth can hurt their ear. Indeed, such a situation can easily happen, because everything in the body is interconnected. And we should not forget the fact that almost the entire maxillofacial apparatus is covered by branches of the trigeminal nerve, which can react to any disturbance with inflammation or pain. And because the tooth hurts the ear, the clinical picture may be unclear, so some patients are in no hurry to visit the dentist, which only aggravates the course of the disease, believing that the cause lies elsewhere. The editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal offer for consideration the most common situations when these two phenomena - ear and tooth pain at the same time - are interconnected.
Often pain in the tooth and ear are interrelated
Comments
I can’t understand, my tooth hurts and that’s why it radiates into my ear. Or, on the contrary, the ear hurts and it hurts the tooth. Which doctor is better to go to?
Nathan (02.11.2019 at 16:37) Reply to comment
- Dear Nathan! After reading our article, you should have realized that pathology can be caused by completely different reasons. Only a doctor after examination can determine the true one. In your case, it is recommended to first visit two specialists: a dentist and an otolaryngologist. If these doctors do not find anything, then further examination by an orthopedist or neurologist may be required.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (09.11.2019 at 09:14) Reply to comment
Ear and tooth hurt. I did an independent examination in front of the mirror, all the teeth in my mouth were intact, there were no holes. I haven’t gotten my ticket to the ENT specialist yet; in our city it’s a big problem to get to see this specialist for free. To avoid pain, I take pills, my grandmother also advises warming my cheek, supposedly this helps. Is it possible to do this?
AlisaV. (11/26/2019 at 12:19 pm) Reply to comment
- Dear Alisa! If you have not noticed any pathologies externally, this does not mean that you do not have dental problems. For example, it is almost impossible for the patient to notice a cyst in the early stages on his own. Therefore, it is still recommended that you go to the dentist. As for warming up the cheek, this is strictly forbidden, because... if the inflammatory process is to blame, then the infection, when warmed up, can spread through the bloodstream to the surrounding tissues, and your condition will only worsen.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (01.12.2019 at 09:21) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Why does toothache radiate to the ear?
Pain in the ear is observed with disease of the lower molars, and anterior to the tragus - with the upper molars. More often it appears as a result of deep caries and its complications. Diagnosed with the eruption of wisdom teeth, alveolitis, amphodontosis.
Advanced form of caries of extreme teeth
Caring for molars, or molars, is more difficult. In this regard, carious processes often start. The development of caries leads to the fact that not only the tooth, but also the ear begins to hurt. Ear pain worsens while eating, closer to evening.
Pulpitis
Pathology appears as caries progresses. An inflamed pulp causes severe spontaneous pain. Not only the tooth can cause concern, but also the ear close to it, the back of the head and the cheek. Irradiation is observed along the corresponding branch of the trigeminal nerve. Painful sensations are both short-term and long-term.
Alveolitis
Develops as a result of infection, extraction trauma. It is characterized by an inflammatory process of the walls of the socket of the extracted tooth. Pain syndrome appears 1-3 days after removal, accompanied by an increase in temperature. At first the pain is aching and intermittent. Later it intensifies and becomes permanent. It often radiates to the temple or ear.
Endodontic dental treatment
When sanitation of molars, filling material can get into the mandibular canal. This leads to post-filling pain, which is considered a response to tissue irritation by the injected substances. The intensity of the inflammatory process depends on the chemical composition of the drug.
Removal of the third molar or wisdom tooth
Ear pain after wisdom tooth removal is explained by its close location to the trigeminal nerve. Damage may occur during the procedure. There is also a high risk of developing a dry socket within 5 days. This means that the blood clot, which forms after a tooth extraction and helps the wound heal, has been washed out or has disintegrated. Dry socket is dangerous because it exposes bone and nerves and causes intense pain.
Wisdom tooth
Not only children, but also adults, face the problem of teething. Wisdom teeth bring a lot of suffering to many of us. Since they are located in the very corner of the jaw, and the gums are no longer able to loosen as in childhood, the tooth can be cut for several months, causing a lot of inconvenience. There is discomfort when chewing, and some even experience a fever.
In severe cases, there is a feeling that the throat or ear hurts. The mechanism of formation of this phenomenon is the same as in children. But sometimes, when food or infection gets in, pus can form in the gum. Then an inflamed tooth can cause pharyngitis, otitis and rhinitis.
Reasons why the left side of the head hurts
Headache on the left side can be caused by various reasons. It does not necessarily occur in diseases - painful sensations can also appear in healthy people due to stress or fatigue. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain advise you to go for an examination if the pain continues for more than 2-3 days in a row or bothers you too often. It is impossible to determine the exact cause at home or during a simple examination, but the doctor will need information about how the pain began, how long it lasts, in what area it occurs and with what intensity.
Physiological reasons
Even a healthy person, without any disorders or chronic diseases, can have a headache in the left area. If this symptom occurs once, is not very intense and goes away quickly, including after taking painkillers, there is no reason for concern. However, it is important to understand what can trigger a headache attack on the left side of the head in order to avoid such manifestations.
- Intense physical activity is the reason for accelerating blood circulation and activating the central nervous system. As a result, symptoms such as headache, dizziness and dark circles before the eyes, shortness of breath and tingling in the heart area may appear. To relieve them, a good rest is often enough; if the left side of your head hurts badly, you should take a painkiller tablet.
- Stress is one of the most common headaches. They arise as a result of increased concentrations of the hormones adrenaline, cortisol, angiotensin and others. They provoke vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. To relieve pain, it is recommended to rest and resolve stressful situations, otherwise dangerous consequences are possible: chronic headaches, increased risks of stroke.
- Prolonged mental stress, including working at a monitor without breaks, can cause severe pain in the left area of the head. Constant concentration and tension, especially in a sitting position, is dangerous to health. Doctors recommend taking breaks of at least 5-10 minutes every hour and doing a light warm-up.
- Abuse of tonic drinks, which include tea and coffee, is one of the reasons why a healthy person may have a headache. They contain substances such as caffeine and tannin. These are plant components that cause a constriction of the blood vessels that supply the brain. This effect is often accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
- Alcoholic drinks in large quantities are not a cure for headaches, but the cause that causes them. Ethyl alcohol first dilates blood vessels, and then provokes their sharp narrowing. Jumps in blood pressure are accompanied by pain, weakness and impaired heart function.
- Smoking is a source of nicotine, as well as hot vapors of other harmful compounds. This habit provokes the development of atherosclerosis, in which the lumen of the arteries narrows and they cannot supply enough oxygen to the brain. In addition, smokers often suffer from high blood pressure.
Most of the factors that cause pain in the left hemisphere of the head in a healthy person are related to habits and lifestyle. Doctors recommend completely giving up bad habits and spending time relaxing and walking in the fresh air. As a result, you can notice a significant improvement in your well-being and get rid of headaches.
Pathological conditions in which the left side of the head hurts
Pain on the left side of the head requires examination if it occurs frequently and is of high intensity. There are a number of reasons that can cause this symptom. These diseases can progress, so at the initial stage it is important to determine their cause and select an effective treatment regimen.
Migraine
An acute headache that occurs for no apparent reason and is highly intense is a migraine. During the examination, no functional impairment is observed, but it is known that this type of pain on the left side of the head is vascular in nature. Symptoms last from 4 hours to 3 days, and a migraine aura appears before the attack begins. It includes typical symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased sensitivity to light, smells, auditory and tactile stimuli;
- numbness or tingling sensation on the skin of the face and hands;
- decreased visual acuity.
Statistically, women are more likely to suffer from migraines. Despite the fact that its primary cause has not been discovered, each patient has his own factors that can trigger another attack. This could be certain smells, foods, alcoholic drinks, extreme fatigue or stressful situations. You can relieve symptoms with painkillers, but they are not effective enough for migraines.
Tension headaches
Tension headaches are often symmetrical, but can also occur only on the left side. This is a complex of symptoms that develops due to stress, chronic fatigue, and muscle tension in the neck. One of the reasons why pain in the left head can occur on an ongoing basis is injuries in the cervical spine. The patient is concerned about characteristic manifestations:
- compressive pain that covers the temple and back of the head, spreading to the area behind the eyes;
- muscle tension in the neck and shoulder girdle;
- Symptoms increase towards the end of the day.
To get rid of pain in the head on the left, it is recommended to monitor your posture. Massage therapy can also help, but should be performed by an experienced professional, especially if there has been previous injury in the area.
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are considered the most intense and can significantly affect the patient's daily life. They arise in one part of the head or spread over its entire surface, often affecting the area behind the eyes, forehead and temple. Additional signs also appear:
- nasal congestion, difficulty breathing;
- ptosis - drooping of the eyelid;
- increased sensitivity to light in one eye, watery eyes;
- redness of the facial skin, increased sweating.
Cluster headaches are one of the rarest types. Their exact cause is unknown, but they often occur at regular intervals, in spring or autumn. The attack lasts for 5-10 minutes, and then the pain becomes less acute and persists for up to 3 hours. A characteristic sign of cluster pain is that it begins every day, at a certain time, for 1–3 months.
Diseases of the cervical spine
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can be caused by diseases of the cervical spine. Here pass important vessels and nerves that carry blood and impulses to the brain. Their compression or inflammation leads to acute headaches, including unilateral ones.
- Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the cartilage layer between the vertebrae. They become less durable and elastic, and therefore lose their ability to absorb shock during movement. The space between adjacent vertebrae narrows, which leads to compression of blood vessels and nerves. Soreness manifests itself after a long stay in a sitting position or after exercise.
- Displacement of the vertebrae is a dangerous condition that leads to acute pain, inflammation of the nerves and compression of blood vessels. Most often this condition is associated with injuries, falls, or increased stress on the neck area, but in some patients the displacement can also occur in a calm state. In this case, congenital instability of the vertebrae and weakness of the neck muscles are important.
- Protrusion - protrusion of the intervertebral disc, the initial stage of a hernia. The process is accompanied by acute pain in the neck and one part of the head; any movement is difficult. The diagnosis can be made based on analysis of x-rays. The pain in the left hemisphere of the head goes away if the integrity of the spinal column is restored and the compression of blood vessels and nerves is relieved.
Chronic neck diseases require timely treatment as they can progress. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions for a full diagnosis, as well as treatment and recovery from injuries, osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement and intervertebral hernias.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic vascular disease that occurs when fat metabolism is impaired. Some products, including cholesterol, are not excreted, but accumulate in the blood and settle on the walls of the arteries. The vessels become fragile, insufficiently elastic, and cannot fully narrow or expand in response to increases and decreases in pressure. There are a large number of factors that can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, including:
- frequent consumption of fatty foods of animal origin (the main source of cholesterol);
- disruption of the secretion of enzymes that are involved in fat metabolism;
- liver diseases;
- overweight and sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
With atherosclerosis, a headache may occur on the left or right due to impaired blood supply to the brain. Painful sensations are often associated with increased blood pressure. The inability of the blood vessels to dilate and compensate for this condition leads to acute pain, dizziness, nausea and other alarming symptoms.
Traumatic brain injuries
Pain in the left hemisphere of the head can appear even long after injury. Concussions, bruises, open and closed craniocerebral injuries cause disruption of the blood supply to certain areas of the brain. Even in patients whose nervous activity is completely restored, pain may be felt after exercise and due to changes in weather. Injuries often trigger chronic migraines. The pain can be relieved with painkillers, and the doctor will help you choose the most suitable option.
Stroke
An acute headache on the left side of the head is one of the first signs of a stroke. In this condition, a sudden disruption of cerebral circulation occurs, resulting in areas of ischemia. The process can be determined at home, but it is important not to miss its first manifestations:
- acute headache, often one-sided;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- pain in the heart area;
- asymmetry of movements of facial muscles and limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
The most common type is ischemic stroke. It occurs when there is an acute disturbance of cerebral circulation due to vascular disease or blockage. Atherosclerosis, stress and other factors can lead to an attack. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but is more life-threatening. It is accompanied by rupture of the vessel and the release of blood into the brain. It can accumulate in the brain ventricles or meninges, thereby provoking the appearance of areas of necrosis. Help for a stroke can only be obtained in a hospital, in an inpatient setting. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain emphasize that the highest probability of a favorable outcome remains if you seek help in the first 2 hours.
Neoplasms in the brain
Tumors and cysts can cause acute headaches, including unilateral ones. Neoplasms disrupt the processes of cerebral circulation, compress blood vessels and nerve tissue. The pain is chronic and always appears in the same area, but can spread to the entire surface of the head. The diagnosis is made based on CT or MRI data, and treatment tactics are selected individually. Early diagnosis of lumps is important because over time they can grow in size and cause more dangerous symptoms.
Colds
Colds and flu are common infectious diseases that appear more often during the cold season and in the off-season. The virus infects the upper respiratory tract and causes a persistent increase in temperature. Headache is also considered one of the characteristic symptoms. It is associated with pressure changes, high temperature, and also with the accumulation of exudate in the nasal sinuses. It decreases after rest and taking antipyretic drugs.
Arterial hypertension
Increased blood pressure is one of the main causes of headaches in the left area of the head. With hypertension, it is one-sided, pulsating, and can spread to the temple area or the back of the head. At home, you can measure your blood pressure using a tonometer. Normally, the result is about 120/80 mmHg; hypertension can be considered when the result is 140/90 mmHg. and more. An attack of hypertension may also be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- tinnitus, temporary deterioration in hearing and vision;
- rapid heartbeat;
- redness of the facial skin;
- painful sensations and discomfort behind the sternum.
Attacks of hypertension are often triggered by intense physical activity, stress and nervous tension. They appear more often in hot weather and in poorly ventilated areas. The pressure increases due to the need to increase the supply of oxygen to the cells. To normalize blood pressure, it is recommended to ventilate the room and take medicine.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
An accurate diagnosis is made by a dentist based on the results of the examination and additional examinations. You may need X-rays of the jaw, computed tomography, as well as orthopantomography - a common technique for visualizing the stage of carious lesions and assessing the condition of fillings and crowns. The following methods are used for treatment:
- correction of bite using orthodontic structures (plates, braces, mouth guards);
- surgery to remove tumors, damaged teeth and nerves, and to treat caries;
- prosthetics, installation of implants.
If the doctor prescribes surgical treatment, conservative methods and medications are ineffective. They will help temporarily reduce the pain, but then the disease will progress. It is important to remove the main focus of the disease, cleanse the pathological area of microorganisms, pus and other substances, and then pay attention to proper recovery. If necessary, the dentist may prescribe additional routine examinations some time after successful treatment.
Treatment of left-sided headaches
Treatment is prescribed only based on the results of the examination. There are various techniques that can be used in the hospital and at home. So, in case of a sudden headache, doctors recommend ventilating the room, doing a neck and head massage, drinking water and taking a short rest. If the discomfort persists, you can take medicine. The most common recommendations from doctors against headaches include:
- painkillers that relieve acute pain - they can be taken at home, but should not be abused unnecessarily;
- antispasmodics - relieve vascular spasm and restore normal blood circulation;
- massage - it’s worth making an appointment with a specialist who will also show you how to reduce pain at home;
- physiotherapy is effective for osteochondrosis, neck diseases and during the rehabilitation period after injuries;
- specific treatment - you may need a course of drugs to strengthen intervertebral discs (chondrol protectors), drugs to normalize metabolism in atherosclerosis and other drugs to treat the underlying disease;
- surgical treatment is rarely used; it may be recommended in the presence of tumors, cysts and foci of sclerosis that interfere with the normal functioning of the brain and tend to increase in size.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as headaches. Qualified specialists of a wide and narrow profile work here, and there is also the opportunity to undergo a full examination, including specific techniques. There are different ways to get rid of a headache, but only a doctor can suggest the most effective and safe one.
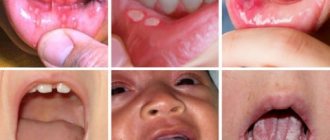
Diagnosis of pericoronitis
Manifestations of acute pericoronitis may resemble pulpitis and periodontitis. But even an untrained person can distinguish these diseases from each other. Thus, with acute pulpitis, throbbing pain does not interfere with opening the mouth, and the gums often remain calm, without swelling and redness.
With periodontitis, swelling and redness of the gums are common symptoms. But periodontitis develops under a fully erupted tooth and is most often a consequence of advanced caries. With pericoronaritis, the tooth has not fully erupted.
A dentist can make an accurate diagnosis. Radiography is mandatory - a targeted image will help to accurately assess the condition of the tissues, the position of the erupting tooth in the jaw, the extent of the spread of the inflammatory process, and also exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms
The choice of method for eliminating pain depends on the cause that caused it. Do not self-medicate: warm, rinse or take pills without consulting a doctor. The insidiousness of pain syndrome is that it is characteristic of different diseases. In some cases, you can alleviate the condition before visiting a specialist.
Ear pain due to caries
You can relieve the pain a little with the help of anti-inflammatory tablets. In such cases, nimide or ibubrofen are recommended. The drugs should be taken after meals in the indicated dosages for no more than 5 days. Fans of traditional medicine use a natural antiseptic – garlic. It is crushed and applied to the diseased tooth.
What to do with pulpitis
The pain with this pathology is often unbearable. Therefore, patients with this disease usually strive to see a doctor as quickly as possible. Treatment can be carried out using biological and surgical methods. In the first case, the tooth is treated conservatively, in the second, the pulp is completely or partially removed. Once the cause is eliminated, the ear pain stops.
How to treat alveolitis
All treatment methods are aimed at eliminating inflammation in the socket. The process is stopped by taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and desensitizing agents. The treatment method is determined by the dentist after an x-ray.
Elimination of post-filling pain
The appearance of ear pain after installing a filling is a reason to remove it. The tooth is treated and filled again. In case of an allergy to the substance from which the filling is made, the doctor selects another material.
Pain after wisdom tooth removal
Damaged tissues and nerves need time to recover. Therefore, pain is a common reaction to intervention. To reduce it, dentists recommend taking painkillers. If the pain not only does not go away, but also intensifies, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics and recommend a special rinse.
What happens if pericoronitis is not treated?
It is important to understand that pericoronitis will not go away on its own. Even if after 4-5 days the symptoms subside, this does not mean that the inflammatory process is over. From time to time the disease will go into the acute stage and cause a lot of inconvenience. In addition, pericoronitis can cause serious complications.
- Periostitis, or flux, as well as osteomyelitis. The spread of the inflammatory process to the periosteum and bone tissue can be explained by a decrease in local and general protective forces and other factors. Such complications will require serious medical intervention.
- Mobility of adjacent teeth.
- Cellulitis, abscess, lymphadenitis.
- Formation of fistula tract, cysts. The appearance of ulcerative stomatitis.
- Damage to nearby tissues, otitis, pharyngitis and other inflammatory complications in the area of ENT organs.
- Sepsis.
Therefore, treatment of pericoronitis is mandatory, regardless of the area in which the inflammation has spread. Lack of timely medical care can lead to inflammatory consequences and even loss of healthy adjacent teeth.
Does your tooth or ear hurt? How to identify the source of discomfort and alleviate your condition
The roots of the chewing teeth of the upper jaw are located next to the ear canals, so discomfort caused by diseases of the hearing organs is often mistaken for pain in the molars. If you have tooth and ear pain at the same time, you need to undergo appropriate diagnostics from a specialist. Only with the help of a professional examination can one differentiate the pathology and choose the appropriate treatment vector. Read further in this article about how to understand whether your ear or tooth hurts, and what to do in such a situation.
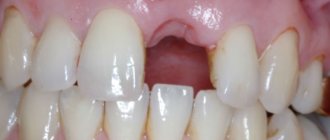
What is post-filling pain?
Post-filling pain is, as a rule, minor pain that occurs immediately after filling teeth in dentistry or a few hours after treatment. If the pain is minor and does not cause obvious discomfort, it is considered normal. This is a natural response of living tissues to external intervention: instrumental damage to the integrity of the tooth, the work of a drill, the introduction of filling material, which the body first “recognizes” and then adapts to life with it. If after treatment the pain is strong, throbbing, intensifies when chewing and pressing on the filling, and does not allow you to sleep, then such post-filling discomfort is already a pathology and a clear signal of mistakes made during treatment.
TOP causes of post-filling pain in patients
- A filling that is too high for the bite
. A situation where the filling material protrudes beyond the boundaries of the crown. Sometimes the problem resolves itself, i.e. After some time, the patient gets used to it and the filling “grinds in.” For this reason, a person turns to the doctor who performed the filling, and the filling is “adjusted” to the bite. - The effect of light curing agents on the pulp during treatment
. The reason is when the powerful light flux emanating from the lamp leads to certain morphological changes in the tooth pulp and it can become very painful. Among them are swelling of the stroma, microhemorrhages and other biological processes that provoke periodic tooth pain. - Incorrect channel processing
. They were poorly processed, imperfectly sealed, and areas of tissue inflammation remained. There is also a risk of existing voids in the canals, where pathogenic bacteria can penetrate over time and provoke a more global inflammatory process already in the canals. - Feeling of a filling being pressed inside
. A common reason is when the patient, due to the effect of the anesthetic, did not indicate this point at the filling stage. - Shrinkage of the filling after treatment or polymerization stress
. A phenomenon in which, after being installed in a patient, the filling shrinks and begins to put pressure on the walls of the teeth - they begin to hurt. Tension is created inside the tooth, which causes pain. Sometimes polymerization stress is caused by mistakes made during the “glowing” of the composite material. In these cases, it is also necessary to consult a doctor - often replacing the filling is required to correct the error. - Complex treatment of tooth canals
. In these cases, post-filling pain is quite understandable, since the doctor performed extensive work on cleaning, processing and filling the tooth canals. They were expanded, “disturbed” by the instrument - therefore, the body’s natural reaction to outside interference manifests itself. If pain continues for about two to three weeks after treatment, it is no longer normal.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Acute, throbbing pain after dental treatment, deterioration in general health and an increase in body temperature are a signal for immediate medical attention. The appearance of purulent discharge, severe swelling of the gum mucosa, or various sensitivity disorders in the oral cavity require a thorough examination by a dentist. You should also consult with a specialist if mild, aching pain bothers you for a long time after treatment or occurs when exposed to any provoking factor.
Preventive measures
We found out why an alarming symptom may appear and what to do about it. Now let's move on to the question of how to prevent an unpleasant situation.
The main preventive measure is regular visits to the dentist for prevention, as well as taking care of your health. It is advisable to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body every year and take all necessary tests. Such a responsible approach will allow timely recognition of the pathological process and initiation of treatment.
Preventative dental examinations will help avoid problems.
Neuralgic diseases usually develop against the background of serious injuries, viral infections, tumors and other systemic disorders. To reduce the risk of developing inflammation, you need to try to eliminate all traumatic factors and strengthen the immune system. Proper nutrition, physical activity and giving up bad habits are the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle.
If a symptom has already appeared, do not delay visiting a doctor. Painkillers only mask the discomfort, while the pathological process continues to progress. If the problem is an infection, it can easily spread through the bloodstream throughout the body, and then there is a serious risk of developing life-threatening conditions.
1Zhuravlev V.P. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment of true trigeminal neuralgia, 2001.
Types and forms of the disease
There are acute and chronic pericoronitis. Acute, in turn, is classified into the following types:
- Catarrhal. The disease begins with swelling and redness of the gums, pain, and itching. This is the simplest form of the disease.
- Ulcerative. It is characterized by the formation of ulcerations covered with a white coating on the mucous membrane of the gums, necrotization of tissue along the edges of the ulcer.
- Purulent. In the area of inflammation, serous and subsequently purulent contents are released. It is characterized by throbbing pain, general intoxication of the body, and bad breath.
Chronic pericoronitis is a consequence of an untreated acute period. With it, the symptoms become less pronounced, but serous or purulent contents continue to form. It can lead to the formation of a pathological passage through which the contents are discharged into the oral cavity. Chronic pericoronitis is characterized by periodic exacerbations; they can be provoked by tooth movement and other unfavorable factors, a general decrease in the body's defenses.
In the chronic form, lymphadenitis is often observed. The mucous membrane, even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms, is swollen and has a reddish tint. Despite the absence of serious difficulties when speaking, chewing, or opening the mouth, it is important to get help from a dentist, since the risk of complications is quite high, and the disease may not go away on its own.