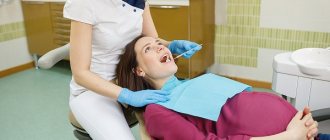
During pregnancy, the processes of destruction of her teeth are activated in a woman’s body, and problems with their treatment often arise. Why does this all happen and how to deal with this problem?
During pregnancy, hormonal changes begin in a woman's body, which are aimed at the full development of the fetus. However, such adjustments do not always go unnoticed for a woman and she develops some problems, for example with her teeth.
Naturally, not all women’s teeth begin to decay. This applies to those pregnant women who have previously completely and efficiently treated all their problem teeth and other diseases that appear in the oral cavity. But life makes its own adjustments to pregnancy: very often women do not treat their teeth enough, which, of course, will then have a very negative impact on the integrity of the teeth.
Causes of dental problems in young mothers
To understand why teeth hurt, decay or fall out after childbirth, you first need to understand the processes occurring in the female body during pregnancy and lactation. Let's consider the reasons that provoke weakening of the dental system:
- hormonal changes: lead to a decrease in bone density, at the same time, less nutrients are delivered through the blood to tooth enamel and gums. Therefore, they become more fragile and provide less protection against microbial attack and tooth decay/weakening gums during pregnancy and after childbirth,
- changes in the composition of saliva: it also contains less calcium, phosphorus and fluoride than usual - i.e. again the enamel receives less nutrients,
- lack of minerals and vitamins: primarily due to the fact that they “go” into breast milk, which is necessary for the baby. But it could also be that after giving birth, a woman simply does not know what food she should eat so that there are enough “benefits” for both the baby’s milk and her own health. The roots of the problem may also lie in poor nutrition during pregnancy, when the woman suffered from nausea due to so-called toxicosis,
- deterioration of oral hygiene: not always a young mother can find time to comb her hair or drink tea, not to mention high-quality brushing of her teeth. Meanwhile, a bacterial film and soft plaque forms on them, which subsequently transforms into hard deposits (inhabited by harmful bacteria) - and not a single toothbrush can handle it,
- stressful situations and weakened immunity: despite the fact that the birth of a child becomes a very happy event, the daily hassle of care and feeding can undermine moral and physical health. As a result, the body will become less resistant to various infections.
Fetal development destroys mother's teeth
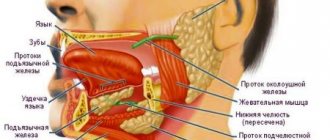
What is the mechanism of tooth decay during fetal development during pregnancy? First of all, a developing baby, of course, eats. To build a full-fledged skeleton, the developing fetus has to take a lot of “building material,” in particular calcium, from the blood plasma of its mother. If the calcium content in the plasma becomes insufficient for the development of the child, this substance begins to be actively washed out of the bone tissue of the pregnant woman, and then is sent to the fetus.
In a normal situation, minerals are constantly washed out of the teeth, but at the same time, through saliva, these same elements re-enter the hard tissues of the teeth. However, during pregnancy the composition and amount of saliva also changes, which is no longer able to replenish the loss of calcium and other important elements. In addition, due to changes in the quality of saliva, its antibacterial and protective functions are disrupted, which are excellent for fighting germs in the mouth, and during pregnancy, bacteria begin to actively develop on the surface of the teeth and gums. These microorganisms, as a result of their vital activity, lead to the appearance and development of carious diseases.
What do women complain about to the dentist after childbirth?
Women often notice a feeling of soreness in their mouth, that their teeth seem to ache, or they have begun to crumble and hurt, old fillings fall out, etc. The main problems that plague a young mother after childbirth are increased sensitivity of teeth, caries, pulpitis, rapid abrasion or destruction of crowns. Problems with the gums manifest themselves in pathologies such as gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease.
On a note! By the way, some mothers’ teeth begin to deteriorate not only after childbirth, but also during pregnancy. But many people don’t do them, putting them off “for later.” As a result, you have to install dentures or completely remove teeth that have crumbled to the roots.
Diagnosis of tooth loss
If the first signs of disease are detected, and even more so of loose teeth. If the problem is ignored, the tooth will be lost forever. The doctor will ask you to take the necessary tests, take pictures, make a diagnosis, taking into account information about previous or existing diseases, and prescribe treatment. The main diagnostic methods are x-rays and, in some cases, dental computed tomography.
In the case when a patient suffers from a chronic disease, tooth loss is a consequence, the elimination of which will be an insufficient measure. The solution is comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease together with a specialized specialist.
Nuances of dental treatment after childbirth - is it possible or not?
Answering the question whether it is possible to treat teeth after childbirth, it is worth saying that during this period all bans on anesthetic injections (which were not recommended during the 3rd trimester of pregnancy) are lifted. However, if the child is breastfed, you will need to express milk in advance for feeding or switch the baby to artificial formula for one day. Also, within 24 hours after the painkiller injection, you will need to express and pour out the milk - and then you can feed the baby as before.
If, after treatment, the dentist prescribed antibiotics - for example, after tooth extraction, treatment of periodontitis or periodontitis, then you should also remember that many drugs pass into breast milk. In this case, you will also need to express and freeze the milk in advance or switch the baby to formula. And in order for lactation to be maintained at the proper level for 5-10 days (while the mother is taking antibiotics), you need to express milk 6-7 times a day, but you cannot give it to the baby.
On a note! It is not recommended to place implants after childbirth for 6-8 months, and implantation should be postponed for another six months after completion of lactation. Since the bone tissue is still quite soft (after pregnancy), the implants may not take root well. The installation of traditional prostheses - crowns or bridges - is discussed individually, because... it all depends on the initial condition of the gums and remaining teeth that may need treatment.
Principles of dental treatment while breastfeeding
In order for dental treatment during breastfeeding to be as safe as possible for lactation and the newborn, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations:
- Before going to the dentist, feed your baby;
- The anesthesia wears off within 3-6 hours, so you cannot feed the baby after the procedures. Express the milk and discard.
- Lidocaine and Ultracaine are administered in small doses and act for a short time, so within two to four hours after the procedures you can feed the baby without any problems;
- If you need serious dental treatment while breastfeeding, be sure to consult your pediatrician. You may need to temporarily stop breastfeeding. But do not decide to stop feeding without consulting a specialist!;
- If you need to temporarily stop breastfeeding, do not use a pacifier for supplemental feeding! Otherwise, the baby will get used to light sucking and will no longer take the breast. Do not forget to express milk to maintain lactation so that you can easily return to full breastfeeding. This should be done at least six times a day.
Remember that sick teeth and oral diseases must be treated. Inaction will lead to even worse consequences. A diseased tooth spreads infection, which easily reaches the baby. In addition, the disease causes great damage to a woman’s immunity and can negatively affect lactation.
Professional hygiene – to brighten enamel and protect against bacteria
If a woman during pregnancy or after childbirth notices that her teeth have begun to look darker or yellowed, she begins to think about whitening. But most bleaching compounds containing hydrogen and urea peroxides have a rather aggressive effect on fragile enamel. Therefore, dentists recommend professional oral hygiene, which includes:
- ultrasonic removal of tartar: hard mineral deposits that accumulate near the cervical part cannot be removed even with the most modern brush. But the ultrasonic waves of a special device (scaler) cope perfectly with the problem without damaging natural tissues,
- Air-Flow water-abrasive cleaning: designed primarily to remove soft bacterial plaque, a thin pigmented film that reduces the aesthetics of a smile. Hypoallergenic preparations are used for Air-Flo, so this treatment can be done for children, pregnant women, and women after childbirth,
- polishing the enamel surface with special rollers and pastes: to make the teeth smooth and gain a natural shine. Also, smoothness prevents microbes from “attaching” to the smallest protrusions - this reduces the likelihood of plaque.
Read on the topic: what is professional oral hygiene – and why every person needs it.
By the way, it is recommended to carry out professional cleaning 1-2 times a year, even if the patient is not bothered by any problems in the oral cavity - because this greatly reduces the likelihood of caries. And after professional hygiene, dentists suggest the next step – remineralization. We will tell you why it is needed further.
How to strengthen teeth during pregnancy
• Visit your dentist regularly. It is best to sanitize the oral cavity before conceiving a child. During pregnancy, you should consult a dentist at least 4 times: at 6-8, 16-18, 26-28 and 36-38 weeks. In the presence of risk factors (aggressive microflora of the oral cavity, a significant decrease in the remineralizing properties of saliva, etc.), the number of examinations is doubled. In the early stages, do not forget to inform the doctor about pregnancy before the examination, since the examination methods and drugs used for treatment should in no case harm the baby. In order to prevent caries and periodontal disease, the dentist can impregnate the enamel of teeth and gums with special medicinal agents. Already in the first weeks of pregnancy, visit the dentist to remove tartar and outline a plan for further monitoring to prevent periodontitis.
• Keep your mouth clean. Teeth should be brushed at least 2 times a day, using a brush with normal or soft bristles and therapeutic and prophylactic pastes that strengthen the enamel and eliminate gum inflammation. Alternate fluoride-containing and calcium-containing pastes, and also use anti-gingivitis pastes that reduce gum inflammation. There are special pastes for pregnant women (for example, Organic). But you cannot use whitening pastes during pregnancy, since they destroy the top layer of enamel, and the body does not have enough resources to quickly restore it. Don't forget to rinse your mouth after every meal. It is recommended to clean the spaces between the teeth with a special silk thread - floss, to remove all food particles, because they lead to the development of infection and gum disease (gingivitis, pulpitis, periodontitis).
• Massage your gums. Massage improves blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the tooth. It is performed as follows: apply a little anti-inflammatory paste to the gums, cover each tooth in turn with your thumb and forefinger and make light movements towards the gum. The duration of the massage is 7-8 minutes. Remember that it is easier to prevent a problem than to fight it.
Teeth during pregnancy and fetal formation
Increased gum bleeding is common during pregnancy. As with other dental diseases, during pregnancy this condition is determined by a number of factors, one of which is a lack of calcium. Especially in the second half of pregnancy, when mineralization (deposition of mineral salts of calcium, phosphorus, etc.) of the child’s skeleton and teeth occurs. During pregnancy, mineralization of the crowns of all 20 baby teeth of the unborn child occurs, which form the basis of the hard tissues of the tooth and, first of all, the enamel. In addition, at the end of pregnancy, the crowns of the first permanent molars begin to mineralize. The period of mineralization is very important for teeth, so various disorders during pregnancy (early and late toxicosis, etc.) can affect the baby’s developing teeth. Oddly enough, the choice of vitamins and microelements that the expectant mother should receive largely depends on the dentist’s prescription.
Formation of a child's teeth
In general, all of a child’s temporary (baby) teeth and ten permanent teeth are formed in the mother’s womb from 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. From this period until the first six months of a baby’s life, the quality of the structure of the enamel of his teeth is determined. Therefore, you need to take care of your baby’s teeth even before he is born.
• Clean your tongue. You should also pay attention to the surface of the tongue, since it contains a large number of papillae (sensitive, gustatory, etc.). Plaque accumulates between them after eating, which is a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic flora. Therefore, the surface of the tongue must be cleaned at least 2 times a day after brushing your teeth. To do this, you need to purchase either a special tongue brush, a tongue scraper, or a special rinse from pharmacies.
• Eat right. By following the recommendations of your obstetrician-gynecologist, you will simultaneously take care of your own teeth, as well as the teeth of your unborn child. After all, the formation of a child’s teeth also depends on the level of calcium in the mother’s blood. If there is a lack of calcium and vitamin D in a pregnant woman’s daily diet, it will immediately affect the condition of her teeth: yellow spots on the enamel, progressive caries, loose teeth, etc. This prevents the consumption of large amounts of dairy products. They contain easily digestible calcium and a lot of proteins, the level of which in saliva regulates the acid-base balance in the mouth. Expectant mothers often ignore dentists' advice to abstain from sweets and foods rich in carbohydrates. But they are the perfect habitat for microbes that affect both teeth and gums.
• Receive ultraviolet light. There is no need to deliberately sunbathe or visit a solarium, but you should definitely be outside regularly and breathe fresh air.
Remineralization – for strengthening and protection against caries
How to strengthen teeth after childbirth? Of course, you need to eat right - but you don’t have to visit the dentist for this (you can consult a pediatrician, obstetrician-gynecologist, or nutritionist). We will talk about the proper diet after childbirth a little later. As for dental or in-office strengthening, the best option here would be deep fluoridation of teeth, which saturates hard dental tissues with useful substances, making them less sensitive and much more resistant to microbial attack, as well as reducing the risk of caries.
On a note! Remineralization not only makes teeth stronger and more resilient, but also reduces their sensitivity to various irritants - sour or spicy foods, hot and cold. Many patients also note that the remineralization course makes the enamel a little lighter.
Also in dentistry, fluoride varnish is used as a remineralizing therapy - but it wears off quickly, and beneficial substances do not penetrate the enamel. For home use, pharmacy gels for remineralization are prescribed - for example, brands ROCS or Biorepair.
“After giving birth, my teeth began to ache very much from various things - from brushing, rinsing my mouth, hot tea, apples when I ate, and a lot of other things - I don’t remember everything now. I went to the dentist, there was no caries (although I was already worried). The doctor said that you need to use a gel for a month or two to strengthen the enamel; they are sold in any pharmacy. And you know, it helped a lot! Now, even when the child has grown up, I still arrange a course of such strengthening for myself a couple of times a year. And by the way, there are such gels for children, too, but we haven’t tried them yet, first I want to consult a doctor.”
Nastya P., Ryazan, review from baby.ru
Proper Teeth Brushing Technique
Increased sensitivity, as well as excessive abrasion of the enamel, a wedge-shaped defect can appear due to improper brushing of the teeth. The technology of proper oral hygiene includes the following steps and nuances:
- The movements of the toothbrush bristles should be vertical – i.e. You need to move the brush from the gum to the cutting edge: this way food particles and soft plaque will be swept away. Horizontal movements do not sweep away excess from the vestibular and oral surfaces of the dentition, but injure the enamel,
- thorough cleaning of the chewing surface of the lateral areas of the mouth: here you need to move the brush horizontally to clean out food debris from the fissures,
- each segment of the row should be given equal time for cleaning: many clean only the “smile zone”, but at the same time the lateral areas become covered with plaque and tartar, which lead to fissure caries or pulpitis,
- The brush and paste should not injure the enamel and gums: therefore, you need to choose a brush from a trusted manufacturer. Otherwise, you can purchase a tool with sharp fibers cut at different angles and scratch the enamel. The same thing can happen if you use a highly abrasive paste.
Don't forget to change your brush regularly (every 2-3 months) and use medicated toothpastes that are prescribed for gum disease, as recommended by your dentist.
My child’s teeth are crumbling, what should I do?
Some parents believe that since baby teeth will eventually fall out anyway, it is not necessary to treat them. This opinion is completely wrong, because the health of the permanent teeth that will replace them largely depends on the condition of temporary teeth.
Diseases of baby teeth lead to their premature loss, which can cause the child to develop an incorrect bite and cause even greater troubles in the future. Therefore, it is very important to show the baby to a specialist in a timely manner, who will help to accurately determine the cause of the problem and prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment of gum disease in a nursing mother
Pathology such as gingivitis often occurs during pregnancy and after childbirth. Moreover, bleeding gums must be neutralized so that dangerous bacteria do not penetrate into the general bloodstream. This can negatively affect not only women’s bodies, but also children’s bodies – if the child is breastfed.
If gingivitis is not treated, the inflammation penetrates deep along the tooth root, leading to periodontal inflammation – periodontitis. Which is more difficult to treat and never goes away completely. Another periodontal disease, periodontal disease, begins due to poor nutrition of the tissues around the teeth (gums and bones). If periodontitis and periodontal disease are not treated, the level of the gums decreases, the teeth look longer and begin to become loose, and may even begin to fall out.
Treatment of gum disease is always complex and consists of the following:
- professional oral hygiene: necessary to remove all dangerous microbes,
- removal of subgingival mineral deposits using “Varius” or “Vector” ultrasonic devices: when using these devices, you can do without gum peeling surgery,
- splinting mobile teeth with a special splint,
- curettage of the gums: often accompanied by a surgical operation to peel off the gums, so subsequently you will have to take antibiotics and resolve the issue of feeding the baby,
- applications and injections with medications (for gums): it is necessary to warn the dentist that the patient has an infant - so that the doctor selects a safe medicine,
- plasmolifting of gums: a very effective technique for gum regeneration, the treatment is based on the ability of platelets to restore living tissue,
- selection and use of toothpaste for inflammation and gum restoration: these can be pastes based on plants or medicinal substances, for example, Parodontax,
- using a toothbrush of medium hardness: “medium” is the optimal solution for high-quality cleaning and massage of the gums, because “soft” does not tone the gums at all, while “hard” injures them,
- taking vitamin complexes to improve the condition of the gums: all medications must be agreed with the dentist so as not to harm the baby. Vitamins C and PP are very useful for gums.
Not calcium alone. Revealing the complete formula for a beautiful smile
No matter how important calcium is for teeth, its content in enamel, dentin and cement does not exceed 36%. However, it is a very soft metal. Let's remember how easily the same chalk crumbles! This means that the retention of this element in the teeth depends on the presence of some other substances. The mineral is embedded in an organic framework - a collagen matrix. Accordingly, it is important to provide teeth with building materials for the construction of this protein frame.
For the formation of collagen, the amino acids glycine, proline, arginine, alanine, lysine, etc. play a primary role. Therefore, adding a set of necessary amino acids to calcium citrate will strengthen teeth both at the mineral and organic level. Taking both these factors into account, the Russian vitamin and mineral complex Osteomed was created.
The source of free, easily digestible amino acids in this product is a unique component - HDBA organic complex. This is a drone homogenate preserved using a special patented technology. It contains more than 20 amino acids, including all essential ones, and serves as an excellent base of building materials for the production of collagen by the body.
This component will also complement the mineral menu for teeth with natural phosphorus, magnesium, sodium and potassium. And the vitamins A, C, D, E, B2, B3, B4 and β-carotene found in it make this natural product a real elixir of beauty.
Caries after childbirth - installation of a filling
If after giving birth a woman notices that her tooth hurts, then most likely the cause is caries or pulpitis. What to do in this case? There is no point in postponing treatment, because... Complications may begin. But there are still restrictions, and they are again based on anesthesia, or rather, on the penetration of the drug into breast milk. Therefore, for now, the baby is fed with formula or pre-expressed “frozen”.
On a note! Not all types of tooth decay require anesthesia before treatment. For example, therapy for caries in the “white spot” stage, medium caries, and sometimes the deep stage, is painless and well tolerated without anesthesia.
After childbirth, the patient can have any modern fillings1 - photopolymer, chemical curing, glass ionomer cements. The dentist decides which material is best placed and where – what is more convenient for the doctor to work with, and which material will better demonstrate its qualities in a particular case.
Read on the topic: what kind of fillings are there - TOP 7 materials for filling.
Proper nutrition for nursing mothers
How to preserve a young mother's teeth after childbirth? To do this, you need to eat right - food should be rich in vitamins, minerals and, at the same time, not cause allergies in the baby. Therefore, your daily diet should include fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, hard cheeses), nuts and seeds (for example, sesame, which contains a lot of calcium), lean meat and fish, cereals, fresh seasonal vegetables and fruits, and herbs.