Publication date: 01/25/2019 Update date: 08/13/2021
Author of the article: Shamray Olesya Vladimirovna Dentist
Sometimes expectant mothers refuse to visit the dentist because they are afraid of harming the baby. But modern technologies and medications make it possible to make treatment and tooth extraction absolutely safe. Let's dispel some popular myths and decide when you should see a doctor.
Nuances of dental treatment for pregnant women
The period of gestation in itself is not a contraindication to dental treatment. But when visiting a doctor, he must be warned about pregnancy, and also tell the due date. In this case, the following features arise during dental treatment:
- Bleaching is not allowed.
- Local anesthesia is required.
- It is possible to treat caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and gum inflammation.
- Under no circumstances should general anesthesia be used.
- Chemical and photo-curing materials can be used for filling. Polymer lamps do not harm the child.
Advice to expectant mothers - try to treat your teeth and gums before pregnancy or between the 3rd and 6th months of pregnancy, and also review your diet. If you have carious cavities, you will pass on a bouquet of microbes to your unborn child, and the destruction of your own teeth will accelerate several times.
Medvedeva Tatyana Dmitrievna, Pediatric dentist, dental therapist, work experience 19 years
Effect of X-ray
X-rays are another factor that frightens not only pregnant women, but also ordinary people. There are a lot of myths about the negative impact of x-rays on the human body, and since a woman during pregnancy must take care not only of herself, but also of the new life within herself, it is often because of these myths that she refuses dental treatment, for fear of harming the baby.
Of course, the X-ray procedure must be approached with all seriousness, but in this case you should not be afraid of it. After all, we are talking about a targeted effect, which is strictly aimed at a small area in the oral cavity, while the woman’s chest, neck and stomach are reliably protected by a lead apron. Therefore, we can say that exposure to X-rays is minimized and cannot in any way harm either the baby or the expectant mother.
Features of dental treatment at different stages
0-12 weeks. The 1st trimester of pregnancy is very important for the fetus. It is during this period that the baby’s vital organs and placenta are formed. Therefore, the fetus is essentially not protected yet. Serious treatment cannot be carried out at this stage. But the doctor may prescribe topical medications to relieve the inflammatory process. These may be Cholisal, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
13-24 weeks. At this time, the placenta has already formed and protects the baby. Therefore, dental treatment and other procedures can be performed.
From the 25th week until birth. At this time, the female body is weakened, and the uterus is very sensitive to the effects of drugs. In addition, a visit to the dentist is often stressful for an expectant mother. Therefore, it is better to wait for treatment procedures until the feeding period. However, this does not apply to cases of acute toothache.
The effect of caries on pregnancy -
Why is caries dangerous during pregnancy? Is it even worth having dental treatment during pregnancy or is it better not to risk it? The answers to these questions are quite simple. For example, with ordinary average caries, the carious cavities contain a large amount of infection, which, against the background of hormonal changes in a woman (excess progesterone and estrogens), creates an increased risk of developing gum inflammation. The second thing to consider is that toothache leads to the release of a number of hormones and changes in hormonal status, which will certainly affect the fetus.
The influence of dental and gum diseases on the fetus -
Untreated caries in a timely manner leads to the development of a complication such as pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve in the tooth). The fact is that when a carious cavity in a tooth becomes too deep, pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the tooth cavity, where the neurovascular bundle (pulp) is located. However, if pulpitis is not treated in a timely manner, the inflamed pulp dies, i.e. necrosis occurs. As a result, pathogenic bacteria penetrate beyond the teeth through root canals and holes at the tops of the roots of the teeth, causing inflammation there. This inflammation is called periodontitis.
In the presence of an acute or chronic source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (i.e., periodontitis), bacteria in the site of inflammation produce toxins that are absorbed into the blood. The same thing happens when a pregnant woman has gum inflammation, i.e. for gingivitis and periodontitis. The presence of any of the above inflammatory diseases triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins (PGE-2) and interleukins (IL-6, IL-8), each of which can negatively affect pregnancy.
For example, in periodontitis, elevated levels of these inflammatory markers and small amounts of bacteria are even found in the amniotic fluid that contains the fetus. In addition, studies have revealed a clear correlation between the presence of dental inflammatory diseases and premature birth (compared to healthy controls). Premature birth, according to researchers, is associated with two factors.
Firstly, it is the release of PGE-2, which limits placental blood flow, causes necrosis of the placenta and, as a result, restricts intrauterine growth. Secondly, with cytokines that promote contraction of the uterus and dilation of the cervical canal. All this data is taken from clinical studies - 1) Dyortbudak O., Eberhardt R. et al. “Periodontitis - a marker of the risk of premature birth during pregnancy”, 2) Goepfert A.R., Jeffko M.K. et al. “The relationship of periodontal diseases with inflammation of the upper genital tract and early premature birth.”
Dental diagnostics during pregnancy
If there is a need to remove a tooth or the patient has been diagnosed with pulpitis, an image cannot be avoided. However, traditional X-rays are contraindicated for pregnant women. After all, the fetus is sensitive to radiation. If an x-ray is necessary, it is best to postpone such a diagnosis to the 2nd trimester. In this case, it is necessary to cover the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area with a lead belt. It minimizes exposure to radiation.
The safest method of dental diagnosis for pregnant women is digital radiovisiography. This technique allows you to reduce the radiation load by 90% compared to conventional x-rays.
Prices for aesthetic dentistry services
Consultation with a dentist - therapist Free Treatment of caries with placement of a light polymerization filling from 3,000 rubles. up to 4200 rubles. Treatment of pulpitis of the 1st tooth from 3500 rubles. up to 4000 rubles. Treatment of pulpitis of 2 teeth from 4750 rubles. up to 6,000 rubles. Treatment of pulpitis of the 3rd tooth from 6,400 rubles. up to 8200 rubles. Light polymerization filling from 2800 rubles. up to 3500 rubles. Artistic restoration from 4950 rubles. up to 6900 rub. Professional hygiene (removal of dental plaque, Air-flow, polishing). Price for one jaw RUB 2,500. ZOOM whitening RUB 15,000.Features of anesthesia for pregnant women
During pregnancy, drugs that have minimal effects on blood vessels are used for pain relief. They also cannot cross the placenta and affect the baby.
Lidocaine is contraindicated during pregnancy. It can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure, cramps and weakness.
Today, the best anesthesia option for pregnant women remains drugs based on anticain:
- Ultracaine.
- Altrifryn.
- Ubistezin.
- Alfacaine.
The listed drugs do not constrict blood vessels, which would be harmful for the expectant mother. They also have a local effect, so they do not affect the baby.
How to choose the optimal anesthetic?
1. First, you need to decide whether pain relief is really necessary. Many dental procedures are painless or slightly painful. Professional teeth cleaning, treatment and prosthetics of pulpless teeth, in some cases, treatment of caries or wedge-shaped defects in living teeth are unpleasant, but often it is quite possible to endure them without experiencing unbearable suffering. Therefore, it is recommended to try this safest approach. If serious pain occurs, there is no need to torture yourself - it is wiser to agree to local anesthesia.
Cosmetic procedures (teeth whitening, installation of veneers) are completely inappropriate during pregnancy - they can and should be postponed.
2. From the entire range of anesthetics, in the absence of contraindications, it is preferable to choose 4% articaine with adrenaline 1:200,000. Articaine, although it has category C according to the FDA classification, is safer than other anesthetics. Its teratogenic effect was discovered when laboratory rabbits and rats were given loading doses of 4% articaine in combination with 1:100,000 adrenaline (2-4 times the maximum permissible concentration for humans). When using drugs at the level of the maximum permissible concentration for humans, no teratogenic effect was detected in experimental animals.20 Moreover, the concentration of 1:200,000 is half as low, and no one will use 7 carpules at a time (the maximum permissible volume) in pregnant women.
3. If such anesthesia turns out to be ineffective, then it is better to use the second carpule with a ratio of 1:100,000 articaine and adrenaline. The chances of achieving deep pain relief are significantly increased.
4. If adrenaline is completely contraindicated or significantly increases the risk of complications (arterial hypertension, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, bronchial asthma, hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma, etc.), then you need to use 3% mepivacaine without adrenaline.
5. It is acceptable to use lidocaine with an adrenaline concentration of 1:200,000 or 1:100,000 for pregnant women. Lidocaine has category B. However, the effectiveness of its anesthesia is 1.5 times less than that of articaine.21 And the risk of allergic reactions is higher (up to to anaphylactic shock).
Tooth extraction during pregnancy
Tooth extraction is a good reason for stress. During pregnancy it is strictly contraindicated. Therefore, the decision to remove a tooth is made only in extreme cases:
- The presence of a cyst more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
- Fracture of the root or crown.
- Acute pain that cannot be relieved in any other way.
- A deep focus of caries, which is a source of suppuration.
Wisdom teeth should never be removed in pregnant women. After all, after such an operation the socket often becomes inflamed. Stopping this process requires taking antibiotics. This, in turn, is extremely undesirable for the mother and fetus.
When should you see a doctor?
Preventative examination of the oral cavity in the early stages of pregnancy is mandatory even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms. If you suspect tooth decay or inflammation, make an appointment with the clinic as soon as possible.
The changes that occur in the body due to pregnancy can also trigger the development of dental diseases.
Most often pregnant women experience:
- Pain – even if it is mild and one-time, you need to visit a dentist. Usually this symptom indicates the presence of caries, which is easier and faster to cure at the initial stage. Then the doctor will be able to do without potent drugs that are contraindicated for pregnant women.
- An unpleasant reaction to too hot or cold food - increased tooth sensitivity signals damage to the enamel. If you consult a dentist in a timely manner, he will restore the tooth’s coating and protect it from destruction.
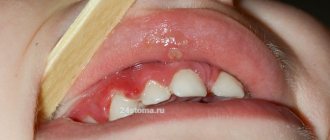
- The appearance of inflammation on the oral mucosa is an alarming symptom of the onset of an infectious disease, which can be dangerous for the woman and the fetus. Urgent diagnosis and treatment is required.
- Bleeding gums - this sign may indicate various diseases (periodontal disease, gingivitis, exacerbation of chronic problems) and requires urgent diagnosis.
If you suspect any dental problems, contact your dental clinic. It is imperative to inform your doctor about your pregnancy so that he can draw up a treatment plan and select safe medications.
Make an appointment
conclusions
- Anesthesia can be given to pregnant women. And it is necessary (if required).
- There is no special anesthetic for pregnant women.
- Some stories about the dangers of anesthesia refer to general anesthesia, not local anesthesia (and there is still a lot of uncertainty there).
- Modern anesthetics are better than the old ones, but they are not completely harmless.
- Anesthesia with adrenaline can be done, and in most cases it is even desirable.
- Adrenaline reduces the tone of the uterus; there have been no miscarriages caused by local anesthesia.
- Local anesthesia in dentistry is not completely safe. It is necessary to balance between the expected benefits and possible risks.
- Of the drugs, 4% articaine with an adrenaline concentration of 1:200,000 is preferable.
- You can also use articaine with an adrenaline concentration of 1:100,000, mepivacaine without adrenaline, lidocaine with adrenaline.
What is the best thing to do before pregnancy?
Even one pregnancy and breastfeeding of one child can trigger the occurrence of caries or periodontal disease. The risk is much higher if you have twins or two children with a small age difference. Carrying a child requires a lot of the body's resources, and although the doctor may recommend mineral supplements, they are not able to compensate 100% of the losses. Therefore, the strength of the enamel of teeth and their roots is reduced. If there has been no caries, there is a risk that it will appear; if it has already happened, it can quickly develop to the 3-4th stage, and the installed fillings will begin to fall out due to weakening of the tooth tissues.
Therefore, ideally, before planning a pregnancy, it is worth treating all teeth, replacing old fillings, and strengthening the enamel - remineralization. If you have inflammation of the gums, then be sure to undergo treatment to prevent the development of periodontal disease.
Diet
First, as already mentioned, you should limit your intake of foods rich in carbohydrates, and first of all, your intake of sugar. It is necessary that food contains in sufficient quantities all the macro- and microelements and vitamins necessary for the human body. Calcium, phosphorus and fluorine1, as well as vitamin D are especially important (cod liver oil, cod liver and Atlantic herring, chicken eggs and some other foods are rich in vitamin D).
Dear expectant mothers, this may sound like a pun, but remember: your teeth are in your hands!
1 About the role of calcium in the body, food and other sources of calcium, see this issue of the journal: L. Belinskaya “Macroelements”. A continuation of this article will be published in the next issue, where you will find information about microelements, incl. phosphorus and fluorine.
Absolute contraindications
At any stage of pregnancy, diagnostics with x-ray radiation are excluded: radiography, computed tomography and similar examination techniques. In case of emergency, the woman is put on a protective apron, even if the procedure is carried out using a modern visiograph with minimal radiation exposure.
The following dental services are contraindicated for pregnant women:
- anesthesia, sedation;
- anesthesia with lidocaine and adrenoline anesthetics;
- bleaching due to increased fragility of enamel;
- installation of implants.
Treatment of deep caries with purulent foci, removal of cysts, granulomas is performed if conservative treatment does not help.
Symptoms
Hyperesthesia is an instant, painful reaction of teeth to external stimuli:
- cold or hot food;
- air temperature changes;
- sour or sweet drinks;
- spicy or salty foods.
Cold or hot food is an irritant for the teeth.
The reaction begins quickly and is accompanied by acute, unbearable pain, but as soon as the irritant is eliminated, the pain immediately subsides.
Let's figure out what can happen if this disease is not treated in a timely manner:
- Increased pain that will continue regardless of the presence of an irritating factor.
- The list of irritants can grow greatly.
- The spread of hyperesthesia to a large number of teeth, it can develop into a systemic stage.
- The appearance of frequent headaches.
Literature
- Pistorius J, Kraft J, Willershausen B. Dental treatment concepts for pregnant patients – results of a survey. Eur J Med Res. 2003 Jun 30; 8(6):241-6.
- Pina PM, Douglass J. Practices and opinions of Connecticut general dentists regarding dental treatment during pregnancy. Gen Dent. 2011 Jan-Feb; 59(1):e25-31.
- Wilder R, Robinson C, Jared HL, Lieff S, Boggess K. Obstetricians' knowledge and practice behaviors concerning periodontal health and preterm delivery and low birth weight. J Dent Hyg. 2007 Fall; 81(4):81.
- George A, Shamim S, Johnson M, Dahlen H, Ajwani S, Bhole S, Yeo AE. How do dental and prenatal care practitioners perceive dental care during pregnancy? Current evidence and implications. Birth. 2012 Sep;39(3):238-47
- Kidd E, Fejerskov O. Essentials of dental caries. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2005. pp. 88–108.
- Amini H, Casimassimo PS. Prenatal dental care: A review. Gen Dent. 2010; 58:176–18
- Vergnes JN, Sixou M. Preterm low birth weight and maternal periodontal status: A meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007; 196:135.e1–135.e7.
- Xiong X, Buekens P, Fraser WD, Beck J, Offenbacher S. Periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review. BJOG. Feb 2006; 113(2):135-43.
- López NJ, Da Silva I, Ipinza J, Gutiérrez J. Periodontal therapy reduces the rate of preterm low birth weight in women with pregnancy-associated gingivitis. J Periodontol. 2005;76(11 Suppl):2144–53.
- Lee JM, Shin TJ. Use of local anesthetics for dental treatment during pregnancy; safety for parturient. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2017 Jun; 17(2):81-90. Translation of this article into Russian: Use of local anesthetics for dental treatment during pregnancy; safety for women in labor.
- Yu CK, Yuen VM, Wong GT, Irwin MG. The effects of anesthesia on the developing brain: a summary of the clinical evidence. F1000Res. 2013 Aug 2;2:166.
- Strasser K, Huch A, Huch R, Uihein M. Placental transfer of carticaine (Ultracain) a new local anesthetic agent. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol. 1977 Apr; 181(2):118-20.
- Morgan CD, Sandler M, Panigel M. Placental transfer of catecholamines in vitro and in vivo. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1972; 112:1068–75.
- Haas A. An update on local anesthetics in dentistry. J Can Dent Assoc. 2002 Oct; 68(9):546-51.
- Hirsch KS, Fritz HI. Teratogenic effects of mescaline, epinephrine, and norepinephrine in the hamster. Teratology. 1981 Jun; 23(3):287-91.
- Hood DD, Dewan DM, James FM., 3rd Maternal and fetal effects of epinephrine in gravid ewes. Anesthesiology. 1986; 64:610–613.
- Mike Samuels, Nancy Samuels. New Well Pregnancy Book: Completely Revised and Updated. 1996
- Hagai A, Diav-Citrin O, Shechtman S, Ornoy A. Pregnancy outcome after in utero exposure to local anesthetics as part of dental treatment: A prospective comparative cohort study. J Am Dent Assoc. 2015 Aug; 146(8):572-580.
- Best AM. More on local anesthetics in pregnancy. J Am Dent Assoc. Dec 2015; 146(12):868-9.
- https://www.drugs.com/pro/articaine-and-epinephrine-injection.html
- Malamed SF. Handbook of local anesthesia. 4th ed. St. Louis, Mosby; 1997.
Dental hygiene during pregnancy
And yet, the main way to fight bacteria is regular (at least 2 times a day!) brushing your teeth and sanitizing the oral cavity. When brushing your teeth, you must follow a number of simple but very important rules:
- The toothbrush should have stiff bristles of different lengths, the head should be elastic and movable (different bristle lengths and the elasticity of the head will ensure better “passability” of the brush). The brush should be changed 2-3 times a month. Fluoridated paste is preferable (see above).
- It is necessary to brush all surfaces of the teeth - the front, palatal ("backside") and chewing ("horizontal"), brush movements - vertical and following the contours of the gums. You need to brush your teeth in the morning and evening (at least) for 3-5 minutes.
- The most vulnerable area to the harmful activity of bacteria is the border between the gums and teeth. These areas need to be cleaned especially carefully and at the same time with great care so as not to injure the gums.
- It is useful to know that caries most often begins with the last - seventh or eighth - teeth. These teeth should be given special attention when brushing.
- No matter how masterfully you use a toothbrush, at least a third of the surface of your teeth will still remain inaccessible to you. Therefore, it is recommended to use floss every day after meals - a special silk thread for cleaning interdental spaces (even fluoridated flosses have appeared recently). In the absence of floss, you can also use a toothpick, but with its help it is more difficult to “get” to hard-to-reach places, in addition, the toothpick should be used carefully so as not to injure the gums.
- As an additional remedy, you can use dental elixirs that have both a cleansing and protective effect. There are special devices that supply dental elixir under pressure, which allows you to “get” to the most inaccessible places.
If you brush your teeth after every meal, it is easier to deal with harmful bacteria, but this, as you understand, is not always available to everyone. Try to at least rinse your mouth after eating, and if you enjoy something sweet, it is useful to eat a piece of cheese. The fact is that there is such a thing as the buffer capacity of saliva. Without going into details, let's say that this indicator characterizes the ability of saliva to neutralize acids and bases. It has been proven that when eating carbohydrate foods, the buffer capacity of saliva decreases, while protein foods (including cheese) increase it, and therefore resistance to caries.
How does the extraction take place?
To begin with, the doctor and the patient choose the appropriate time for treatment. It is also very important to choose a mild anesthetic so that it works well, but is also allowed for use by pregnant women (the medicine should not cross the placenta).
It is imperative to carry out preventive procedures at home - rinsing with herbal decoctions and a solution with soda. If there is severe pain, it is allowed to take Paracetamol or Tempalgin, but in a strict dosage.
When a third molar needs to be removed, the dentist will cut through the gum, drill into the bone, and then use forceps to pull it out. After this, the doctor applies stitches to speed up the healing of the wound.
What kind of water should a pregnant woman drink?
It has been proven that fluoridation of drinking water significantly reduces the likelihood of developing caries. In our country, fluoridation is carried out (the standard concentration of fluoride in drinking water is 1.5 mg/l), however, unfortunately, there are frequent cases of both a lack and an excess of fluoride in drinking water. Don't think that low fluoride levels are the only cause for concern. An excess of this element is fraught with fluorosis (a specific lesion of tooth enamel, manifested externally in the form of yellow spots), which threatens not only the mother, but also the unborn baby (after all, baby teeth are formed at 3-5 weeks of intrauterine development). You can find out what the concentration of fluoride is in your drinking water at your local SES (but do not expect that SES employees will, on their own initiative, inform you about the level of fluoridation in your drinking water!). To regulate the level of fluoride in water, you can use special filters that are now commercially available.