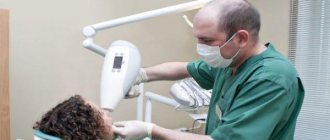
Inflammation of the oral mucosa is observed in 70% of pregnant women. This disease is diagnosed as gingivitis and occurs for several reasons, one of which is hormonal changes in the body. During pregnancy, there is an active production of hormones such as gonadotropin, progesterone, and somatomammotropin. These hormones cause significant changes in the systems of the female body, in particular in the gums.
During the period of fetal formation, the expectant mother experiences a disturbance in the blood supply to the tissues. For the skin, this is fraught with the appearance of acne and stretch marks in certain areas of the skin, and the mucous tissue of the gums can be subject to chronic inflammatory processes to varying degrees during pregnancy. At the same time, the gum tissue becomes vulnerable and is easily subject to mechanical and chemical irritation.
The second factor that provokes gingivitis is considered to be insufficiently thorough hygiene of the gum tissue. Bacteria living in dental plaque begin to actively multiply. They settle in periodontal pockets and cause pathological processes in soft tissues. It must be taken into account that pregnant women tend not to deny themselves nutrition and all kinds of delicacies. A large amount of sweet and carbohydrate foods is also a factor in the growth of pathogenic microflora and the occurrence of gum gingivitis. An imbalance in the acid balance in the tissues of the oral cavity promotes the active growth of pathogenic bacteria: they form more and more plaque in the gums.
When carrying a child, the expectant mother should pay special attention to the condition of the gum tissue. And if there is a need to visit a doctor, if there is a suspicion of gingivitis, then we hasten to inform you that the safest and most favorable period for visiting a dentist is 13-24 weeks of pregnancy.
It is important for women in an interesting position to remember that their body and the body of the unborn baby are a single whole, and therefore, with gingivitis, bacteria from the mother’s mouth can easily penetrate into the child’s body, and therefore the work of the baby’s immune system may receive additional stress.
The first symptoms of incipient gingivitis may be:
- painful sensations in the gums when chewing rough food;
- reaction of soft tissues to cold and hot;
- bleeding in the area of the gingival papillae;
- swelling of tissues in the area of periodontal pockets;
- increased plaque with an intense yellowish tint;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the mouth.
Why do teeth and gums hurt during pregnancy?
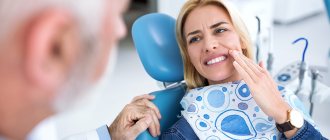
During pregnancy, gum disease worsens, so when brushing you may see blood on your toothbrush. This occurs due to inflammation of the tissues in the oral cavity. To save your teeth, you need to identify the problem and begin treatment.
Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone in the body contribute to inflammation of the gums and increase their sensitivity. This condition is called pregnancy gingivitis, and it develops in 50% of all pregnant women.
Another problem associated with pregnancy is that some women develop tumors on the gums known as pyogenic granulomas. This is an immune response to an irritant, in this case plaque. Granulomas usually disappear after childbirth.
Why does gingivitis occur during pregnancy?
Tens of millions of microorganisms live in the oral cavity. Slight swelling of the gums leads to an increase in periodontal pockets, which become an excellent reservoir for the life and reproduction of bacterial microflora. In addition, microorganisms do not lack nutrition, since pregnant women like to pamper themselves with sweets, and carbohydrate foods are the best substrate for the development of bacteria.
Swelling of the gums, leading to an increase in periodontal pockets, excessive salivation, an acidic environment in the mouth, an increased feeling of hunger - these features that accompany pregnancy are the main factors contributing to the rapid growth of oral microflora. And this, in turn, provokes inflammation of the gum tissue - gingivitis.
How can oral health affect a child?
Recent research shows that severe gum disease, accompanied by red, swollen or bleeding gums, can harm the health of an unborn baby.
Scientists have found that women with severe gum disease are 7 times more likely to have preterm birth before 32 weeks than women with healthy gums. Another study looked at women with gingivitis and more severe gum disease and found a threefold increase in the risk of giving birth before 37 weeks.
Current research into gum disease during pregnancy shows a risk of prematurity comparable to that of alcohol consumption and slightly higher than that of smoking. Premature babies may have a wider range of health problems immediately after birth than full-term babies.
Women with gingivitis may also have low birth weight babies during pregnancy. Studies have shown that if you have gingivitis during pregnancy, you are 3 times more likely to have a low birth weight baby. This estimate is comparable to the risk associated with smoking during this period.
Features of treatment
Treatment of gingivitis consists of three stages:
- cleaning the oral cavity;
- anti-inflammatory measures;
- prevention of re-development of the disease.
The duration of therapy depends on many factors, among which the stage of pregnancy at which the patient is and her individual characteristics are especially important. The specialist also takes into account the nature of the disease and the degree of its progress. We recommend that you carefully monitor your oral hygiene and diet before and during pregnancy, and if you notice signs of gingivitis, immediately seek qualified medical help. Experienced doctors will examine you and determine the most effective treatment strategy.
What to do if you are diagnosed with gum disease?
During pregnancy, professional teeth cleaning is required once.
If there are serious gum problems, then root scaling is a form of deep cleaning that is recommended when pocket plaque around the teeth exceeds 3mm. By scraping or removing plaque at and below the gum line, the base of the tooth is aligned or smoothed, and less plaque builds up.
Women with gum disease whose teeth were cleaned with this method had six times lower rates of preterm birth (in this case before 35 weeks) than women who received only professional cleanings.
The second trimester is a good time to schedule a routine dental visit. But if a woman is at risk of miscarriage or other problems, then it is better to postpone the dental examination.
During dental treatment, X-rays are often prescribed in order to analyze the condition of the tooth, but during pregnancy, X-rays are contraindicated because they affect the development of the fetus and can lead to irreversible consequences.
To avoid such an examination, you need to go to the dentist in preparation for pregnancy. The doctor will identify existing pathologies and treat them before conception.
Experts' opinion
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-lechebno-profilakticheskie-sredstva-dlya-individualnoy-gigieny-polosti-rta Silantieva E.N., Berezina N.V., Krivonos S.M. Complex treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis using drugs from the Asept line, Practical Medicine journal
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
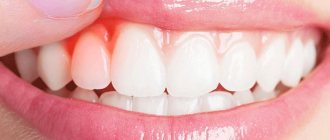
Symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women
The most common symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women:
- swelling and redness of the gums, they can increase and partially or completely cover the tooth;
- bleeding gums (especially when brushing teeth);
- the occurrence of dental plaque;
- painful sensations in the gums (especially when pressing on the gums or brushing teeth);
- pain in the gums while eating;
- bad breath.
Call us now! Phone number to make an appointment: +7(812)309-88-26 St. Petersburg, metro station Pionerskaya, st. Baikonurskaya, 26 Find out the details of our promotions and discounts on dental treatment.
How to treat?
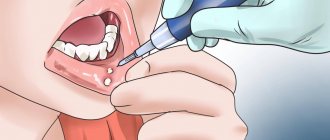
Gum treatment should be done in dentistry. First of all, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis, with a 90% probability that it will be gingivitis. This pathology is typical for pregnant women. First, you need to professionally clean the enamel from plaque and remove hard deposits using ultrasound. Don't worry, it's completely painless and not contraindicated when carrying a child.
In most cases, to eliminate the pathological process, you have to resort to drug therapy. The doctor prescribes only those drugs that are approved for use during pregnancy. Oral rinses with antiseptic solutions such as Miramistin are usually prescribed. Applications with anti-inflammatory plates are also indicated, and sometimes wound-healing ointments for topical use are indicated. In more serious cases, antibiotics may be needed.
Additionally, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs. Chamomile, sage or St. John's wort will do.
When should you see a doctor?
Preventative examination of the oral cavity in the early stages of pregnancy is mandatory even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms. If you suspect tooth decay or inflammation, make an appointment with the clinic as soon as possible.
The changes that occur in the body due to pregnancy can also trigger the development of dental diseases.
Most often pregnant women experience:
- Pain – even if it is mild and one-time, you need to visit a dentist. Usually this symptom indicates the presence of caries, which is easier and faster to cure at the initial stage. Then the doctor will be able to do without potent drugs that are contraindicated for pregnant women.
- An unpleasant reaction to too hot or cold food - increased tooth sensitivity signals damage to the enamel. If you consult a dentist in a timely manner, he will restore the tooth’s coating and protect it from destruction.
- The appearance of inflammation on the oral mucosa is an alarming symptom of the onset of an infectious disease, which can be dangerous for the woman and the fetus. Urgent diagnosis and treatment is required.
- Bleeding gums - this sign may indicate various diseases (periodontal disease, gingivitis, exacerbation of chronic problems) and requires urgent diagnosis.
If you suspect any dental problems, contact your dental clinic. It is imperative to inform your doctor about your pregnancy so that he can draw up a treatment plan and select safe medications.
Make an appointment
Prices for gingivitis treatment and periodontal treatment
| Treatment in the area of the upper and lower dentition using the Vector device | 19900 16900₽ |
| Removal of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque in the area of 1 tooth manually | 900 ₽ |
| Manual removal of subgingival dental plaque in the area of 1 tooth | 600 ₽ |
| Flap surgery | from 6500 ₽ |
| Splinting of teeth and restoration in the area of 2 teeth with fiber material "GlasSpan" | 4700 ₽ |
| Treatment of gums in the area of 1 tooth using the “Vector” device | 1100 ₽ |
| Treatment of gums, periodontal pockets of the 1st jaw with the “Vector” device | 9900 ₽ |
| Lip frenulum correction surgery | 4660 ₽ |
| Vestibuloplasty | from 4950 ₽ |
| Tongue frenulum correction | 1500 ₽ |
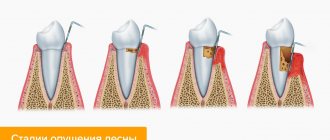
How does inflammation manifest?
How to recognize the presence of an inflammatory process? It’s simple, the following factors begin to cause discomfort to a woman:
- The gums become swollen and acquire a bright red tint.
- Pain occurs on palpation or when eating.
- Acute reaction to cold and hot.
- Possible increase in body temperature.
- If left untreated, pus may appear in the space between the tooth and gum.
In order not to trigger the pathology and provoke more serious complications, we strongly recommend solving the problem in a timely manner.
The danger of toothache
Expectant mothers, fearing the negative effects of medications on the baby’s body, endure toothache. They do not take medications to relieve it and do not go to see a doctor because they are afraid of the dentist using anesthesia. There is also an opinion that dental treatment is dangerous for pregnant women; it is better to wait and treat teeth after childbirth.
These judgments are erroneous; if a woman suffers toothache, she can cause enormous harm not only to her body, but also to her unborn baby. What are the dangers of toothache?
- Acute toothache due to pulpitis or periodontitis indicates the presence of purulent inflammation, which can spread to the periodontal tissues or enter other organs through the bloodstream. Odontogenic periostitis, peri-maxillary phlegmon, sepsis are conditions that can threaten the life of mother and child.
- The addition of even a minor purulent infection requires the prescription of antibacterial drugs, which also harm the unborn baby.
- After childbirth, postpartum sepsis may develop, the cause of which is a sore tooth.
- Teeth deteriorate quickly during pregnancy, so if you endure the pain and do not see a doctor in time, the question of tooth extraction may arise. Carrying out this operation increases the risk of infection entering the body through the hole; Also, removal is unnecessary stress for the patient.
- Constant pain weakens the nervous system of a pregnant woman and affects the intrauterine development of the child: the likelihood that the baby will develop abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular, nervous, and endocrine systems increases. Painful stress can cause premature birth.
- If the cause of toothache is non-dental diseases, failure to see a doctor can lead to unpredictable consequences for the body.
What procedures are allowed during this period, and which are strictly prohibited?
Pregnancy imposes a number of restrictions on treatment, including dental treatment.
Acceptable:
- Treatment of caries, especially in the very initial stages. If the tooth is barely touched, you can even do without anesthesia. In case of increased sensitivity, use a spray with a minimal content of adrenaline.
- Fluoridation, enamel whitening. These manipulations are classified as absolutely safe procedures.
- Gum treatment. It can be carried out in any trimester using anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Installation of crowns and removable dentures. It will not harm either the expectant mother or the child.
- Removal of a tooth. At the level of modern medicine, it is considered a relatively safe manipulation for pregnant women, but it is performed in extreme cases
Forbidden:
- Dental implantation due to the need to take strong medications.
- Removing "eights". Severe trauma to the jaw occurs: a large wound surface can become a source of infection.
- Bite correction. During pregnancy, a woman's body loses a lot of calcium, so braces are likely to cause tooth decay. If pregnancy occurs already during treatment, it is interrupted until the birth of the child.
- Use of general anesthesia for pain relief.
Carrying out local anesthesia with special preparations containing a minimum percentage of adrenaline and calculating the correct dosages is not considered dangerous to the fetus.
Is it possible for pregnant women to have dental x-rays?
Pregnancy is not considered a contraindication for dental radiography. Images are taken using computer radiovisiographs, which deliver a very small dose of radiation. The woman’s body is covered with a special protective apron, and the radiation beam is directed towards the jaw area.
However, such a procedure should be performed only when absolutely necessary and should be limited to taking pictures of one or two teeth. Long-term planned treatment, which periodically requires radiography, is best postponed until the birth of the child and completion of breastfeeding.