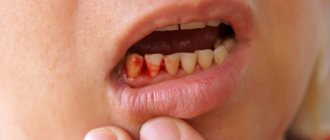
Dental health is closely related to the health of your gums. If everything is fine with some, then the safest conditions in the oral cavity are created for others. However, with weakened, painful, often inflamed gums that are prone to bleeding and pain, serious dental problems can occur.
We often go to the dentist, get new fillings and treat dental caries, but we often forget about the health of our gums. They also need various preventive measures. First of all, care should be taken to strengthen them. We will tell you what safe methods can be used for this.
Don't forget to rinse after meals
Rinsing your teeth only during and after brushing is a big mistake. Any dentist will advise you to carry out this procedure more often, preferably after every meal.
Leftover food in the mouth can cause gum inflammation. Use plain water or special solutions.
Advice! It is especially important to rinse your mouth after eating sweets. Sugar can be the enemy of your teeth and gums. In just a few hours it creates a breeding ground for bacteria.
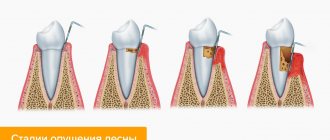
Gums moving away from teeth: reasons
Periodontitis is a continuation of gingivitis, but can occur in parallel with it. A large number of studies have been devoted to the causes of the development of the disease, during which it was found that a chain of pathological reactions is triggered by inflammatory phenomena of the mucous membrane, which can be caused by the following factors:
- Microorganisms. In this case, it is not the microbes themselves that have a damaging effect, but the toxins they produce. If the patient does not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, then a large number of microorganisms accumulate on the teeth, forming a plaque. The abundant release of toxins leads to the destruction of mucosal cells and its inflammation.
- Traumatic factors. In this case, the overhanging edges of the filling or dentures have a damaging effect on the gum mucosa. If the patient neglects the rules of personal hygiene, then inflammation begins to develop very quickly due to the additional exposure to microorganisms. In this case, the problem is local in nature and limited only to the area of injury.
- Excessive load on the periodontium. We are talking about a variety of malocclusions, dental defects, improper installation of dentures, bruxism and some other conditions. As a result, a certain part of the teeth experiences regular overload, which leads to disruption of the blood supply to the periodontium, bone destruction and the appearance of tooth mobility.
These reasons make the greatest contribution to the development of inflammation and subsequent periodontitis. According to research, this process can also be influenced to some extent by other conditions:
- Imbalance of vitamins.
- Atherosclerosis of periodontal vessels.
- Neurodystrophic diseases.
- Decrease in the body's defenses.
- Hypoxia.
- Endocrine pathology.
- Diseases of the blood and gastrointestinal tract.
- Immunological and psychosomatic disorders.
Before you begin to treat periodontitis, it is necessary to establish the reasons that led to the gums moving away from the teeth and eliminate them. For this, various diagnostic methods are used.
Use antiseptics for prevention
Antiseptic solutions are not suitable for continuous use. They are usually prescribed for the treatment of dental diseases, after tooth extraction or other complex operations in the oral cavity.
In addition, antiseptics are recommended for inflammation and bleeding gums to prevent the proliferation and increased activity of bacteria.
What antiseptics can be used to rinse your mouth?
- Furacilin. It is usually sold in the form of yellow tablets that need to be dissolved in a glass of water. The solution has a slight salty taste, usually does not cause irritation and does not increase gum inflammation.
- Miramistin. At the pharmacy, this product can most often be found in the form of a bottle of liquid. The box may contain special attachments. Miramistin solution has virtually no pronounced taste and does not cause discomfort.
- Iodinol. Sold in glass bottles, dark in color. A few drops of the product are mixed with water to obtain a solution. This drug has a pronounced antiseptic effect and a slight unusual taste. May slightly increase gum irritation if inflammation is present.
- Chlorhexidine. Sold in plastic bottles. The solution based on this drug has a mild medicinal aftertaste. Inflammation usually does not increase after use.
Treatment of gums at home
If the disease is in its early stages, folk remedies can be used for treatment.
There are a number of medicinal herbs that help strengthen the periodontal tissues and relieve inflammation.
How to prepare herbal infusions for gums:
- Take black elderberry, St. John's wort and strawberry leaves - one tbsp of each herb. spoon. Boil a glass of water in a small saucepan, add herbs, boil for about 10 minutes. over low heat. Let the broth sit for half an hour, then strain.
- Oak bark is used to eliminate bleeding gums. Two tbsp. Boil tablespoons of bark for 10 minutes, leave for another 10 minutes. After straining, cool and use for rinsing.
- Mix according to Art. spoon of calendula and chamomile, pour boiling water (250 ml), steam for half an hour. Strain through a fine sieve and use for rinsing.
You can cure your gums with folk remedies such as carrot or cabbage juice. Mix the fresh juice of these vegetables with boiled water (1:1) and rinse your mouth.
Rinses are also made from aloe juice, mixing it with water (1:0.5).
Sea salt will help with gingivitis. Pour 250 ml of warm boiled water into a cup, add tbsp. spoon of salt, stir until the salt dissolves.
These compounds should be rinsed on the gums several times a day.
Fight bleeding gums
If the slightest mechanical impact causes pain and easily injures the gums, causing bleeding, then this cannot be considered a normal phenomenon.
First, you need to contact your dentist and find out the cause of bleeding and weak gums. Secondly, you need to use comprehensive methods to treat them and eliminate the problem.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Traditionally, diagnosis begins with a history taking. During a conversation with the patient, the doctor establishes the duration of the disease, studies working conditions and lifestyle, bad habits, and dietary habits. Next, they move on to examining the oral cavity. In addition to receding gums, bleeding gums, bad breath, ulcerative and necrotic lesions and other characteristic symptoms may occur. In order to establish the severity of the disease and assess the extent of damage to all tissues, clinical diagnostic methods are used, which include:
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
- Panoramic or targeted x-rays of teeth.
- Assessment of the resistance of gum capillaries.
- Determination of tooth mobility.
- Measuring the depth of the periodontal pocket.
- Microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen.
- Bacteriological research.
It is not always necessary for a doctor to use all of these methods. Based on the patient’s complaints, clinical picture and general condition of the body, a specific examination regimen is prescribed, which helps confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Massage your gums to improve blood circulation
Strengthening your gums is not just about using toothpastes and rinses. Gums need normalization of blood circulation. This requires a massage. It can be done using circular movements with your fingers or a soft toothbrush.
You can also find special brushes for gum massage on sale. By improving blood circulation, you can strengthen them over time and prevent many complications.
Propolis in the treatment of gums
Propolis has antiseptic properties and has long been used as a remedy for gum disease.
Here are a few recipes with propolis for gingivitis and periodontitis:
- Take Art. spoon of propolis extract (10%) and mix it with 2 tablespoons of sunflower oil. This mixture should be lubricated on painful areas of the gums.
- Soak a piece of cotton wool with an alcohol solution of propolis (30%). Apply cotton wool to the gums in areas of inflammation.
- Grind 25 gr. propolis, add 100 ml. alcohol Pour the composition into a dark glass vessel, add 50 g of dried St. John's wort there. Leave for about three weeks, shaking occasionally. To rinse, dissolve 20-25 drops of tincture in 100-150 ml. warm water.
Types of inflammatory diseases
There are two categories of diseases that provoke the development of such a process. These include:
- Diseases affecting soft tissues. They are caused by injury to the gums. It occurs due to mechanical pressure and chemical burns.
- Diseases of the mucous membrane. Most often they are provoked by infection or fungi. These include diseases such as stomatitis, gingivitis, periostitis, and periodontitis.
Only a doctor can tell you the exact reason. A visual examination of the oral cavity is carried out, and tests for various pathogens will also be required.
Classification of gum inflammation
There are several classifications of the disease:
According to the current, the following types of gingivitis are distinguished:
- acute – severe inflammation of the gums occurs, which is accompanied by bleeding and pain;
- chronic - the disease occurs cyclically, periods of relative calm are replaced by exacerbation of gingivitis, which most often occurs in winter and spring, when the body is most weakened.
Based on the nature of the lesion, the following types of gingivitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- ulcerative;
- ulcerative-necrotic.
Severity of gum inflammation:
- mild – the interdental papillae are mainly affected, the disease is mild and usually ends with complete recovery;
- medium - in addition to the interdental papillae, the pathological process involves the marginal parts of the gums;
- severe - inflammation covers the entire gum, including its alveolar part.
Based on localization, the following types of gingivitis are distinguished:
- localized – one or more areas of the gum are inflamed;
- generalized – the entire gingival space of one or both jaws is affected.
Bee products
Propolis and honey perfectly eliminate lesions, kill microbes and prevent their further development:
- mix 15 g of honey and 3 g of salt. Rub in carefully so as not to injure the mucous membrane. Can be used as applications;
- Stir 20 drops of propolis in 150 g of boiled water. Rinse as needed until symptoms improve;
- Take a small ball of propolis and dissolve it in your mouth until completely dissolved. Try to retain saliva for as long as possible. Repeat daily, before bedtime;
- Pour 100 g of propolis into a bottle of vodka, add calamus root (1 tablespoon). Leave for 3 weeks. Rinse 3 times a day;
- Take a piece of thick honey and massage it into the tissue. It improves blood flow and treats inflammation.
Where can I buy
Traditional herbal medicine puts forward high quality medicinal raw materials as the main requirement for independent production of medicines. High-quality folk remedies in finished form, as well as ingredients for their preparation, are offered by the Russian Roots online store. Delivery of ordered goods in Moscow and the Moscow region is carried out by couriers, and in other regions by mail. You can also purchase the required product in our herbal pharmacies in Moscow.
Attention! All materials published on our website are protected by copyright. When re-publishing, attribution and a link to the original source are required.