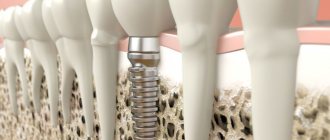
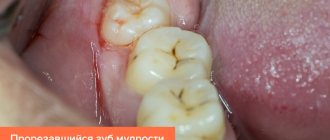
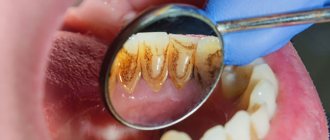
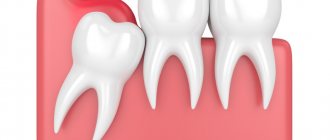
Gum inflammation is one of the most common dental problems. The cause of inflammatory processes is often poor oral care and non-compliance with rules and regulations of hygiene, as well as injuries to the mucous membranes, accompanied by a violation of their integrity. It happens that inflammation begins after treatment at the dentist. If a patient’s gums become inflamed after going to the doctor, they should visit the dental office again, since this symptom almost always indicates the need for repeated medical intervention.
Slight soreness and swelling of the gums may be normal after complex dental treatment (for example, depulpation), but these signs should not be of high intensity or last more than 24 hours. Inflammation following extraction should also resolve within 48-72 hours after surgery. In all other cases, it is necessary to find out the cause of inflammation and take timely measures to prevent complications.
Why is my gum swollen?
There are many factors in the periodontium that can cause the soft tissue in the mouth to swell. Among them are doctor errors during treatment, the presence of dental diseases, and poor quality oral care. In addition, the cause may be a lack of vitamins in the body, a lack of saliva production or its excessive viscosity, general diseases that have affected the human body, or even pathology of the spine. Before taking any measures to eliminate the disease, you must first determine what caused the defeat.
The gums are swollen and painful
Several different factors can cause gum swelling and pain of varying intensity: gumboil, cysts, poorly adjusted dentures, use of toothpaste with aggressive ingredients or brushes with too hard bristles. Flux and cysts are considered the most dangerous, so if you have swollen gums and it hurts, do an examination yourself or immediately consult a doctor to rule out the presence of the above-mentioned gum diseases.
Treatment of gum inflammation at the Eurodent clinic
Self-medication in case of gum disease is only permissible as a temporary measure to relieve pain. To ensure that the disease does not become chronic, you should definitely contact a dental clinic. When you see a doctor, you will be given an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment will be prescribed.
The Eurodent clinic operates 24/7, so you can contact us for qualified help at any time. We remind you that the initial consultation is free.
We are waiting for you at the following addresses: Zheltoksan, 83, ug.
st. Aiteke bi and Zhandosova, 42, corner. st. Aimanov. Based on: 6 votes
The gums are swollen, the tooth does not hurt
Swelling not accompanied by toothache is a common occurrence that can be caused by a variety of reasons. The most common are:
- Inflammation of the tooth root. Occurs after pulpitis, prolonged caries and other diseases in which the dental nerve is removed. The root provokes inflammation of the gums.
- A tumor is a benign or malignant formation. May be caused by prolonged inflammation or gum trauma.
- An abscess is a complication caused by swelling in the mouth. Accompanied by the appearance of pus in the gum cavity. Cellulitis is considered a similar phenomenon, but in this case the lesion is not localized and the pus can easily spread to adjacent soft tissues.
- Mechanical injury to the gum or tooth . A tumor on the gums can occur as a result of a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, skin, or a blow from a cutting or piercing object. Swelling will occur in the damaged area.
Complications
In the absence of timely and high-quality treatment, the disease can cause serious complications. A frequent consequence of suppuration during periodontitis is periodontal disease, a disease characterized by the formation of very deep gum pockets and the spread of foci of infection and suppuration throughout the gums. Over a long period of time, periodontal disease usually leads to loosening of teeth and their loss. In addition, inflammation can lead to the formation of gumboil, a large abscess that causes the gums and cheek to swell and lose their natural shape. Treatment for flux usually requires surgery.
The presence of a constant source of infection in the body negatively affects the functioning of all organs and systems, in particular the functioning of the immune system. Abscesses and other chronic infectious diseases lead to a steady decrease in immune status, which creates favorable conditions for the development of a whole range of diseases.
We should not forget that the muscles and nerves of the face are located in close proximity to the gums. For example, the formation of a large abscess on the gingival part of the upper jaw can lead to damage to the trigeminal nerve, which innervates the nasolabial triangle. Sharp pain of a neurogenic nature, paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles are rare, but still probable consequences of gingival abscesses.
Why do my gums swell and bleed?
These signs may indicate gingivitis - when the gums are swollen, but the tissue is not damaged. Gingivitis is characterized by the presence of swelling, slight bleeding, the patient feels pain when brushing his teeth, which is why he avoids it, as a result of which plaque forms near the gums. There are several different forms of gingivitis, and for some of them the tumor is not a necessary factor. The causes of gingivitis are:
- avitaminosis;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- tooth eruption;
- human hormonal imbalance.
After nerve removal
Nerve removal is a surgical intervention that disrupts the integrity of the structure of dental tissue and blood vessels. Painful sensations are allowed in dentistry, but their duration should not be more than 1-3 weeks, during which the pain decreases and goes away. If the patient experiences swelling of the gums near the tooth, increased pain, or a temperature rise of 38-40 degrees, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor, because the reason for this may be poor cleaning of the canals or the presence of part of the nervous tissue in the canal being treated.
Why gums become inflamed after treatment: possible reasons
Minor inflammation after dental canal filling or other types of treatment is considered normal and does not require special therapy except for maintaining a hygienic regime. But if the inflammation does not go away on the second or third day, and is accompanied by severe pain, hyperemia of the mucous membranes, and swelling, the cause should be found out. It is not recommended to use anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs without consulting a dentist - self-medication can aggravate the problem and lead to progression of the pathology.
Allergic reaction
One of the most common causes of inflammation of the gum tissue is an allergy to medications used for local anesthesia. In this case, inflammation is manifested by severe local swelling at the injection site, redness and soreness of the tissue. An allergic reaction can also occur to the following groups of drugs used during dental procedures:
- hemostatics (hemostatic drugs, used mainly after extraction of a tooth from a bone alveolus);
- antibacterial drugs (placed in the tooth cavity when there are signs of an infectious process);
- antiseptics, which are used to disinfect dental canals;
- disinfectant solutions for sterilization of medical instruments;
- arsenic paste for killing the dental nerve (rarely used in modern dental practice).
In addition to swelling and redness, rashes in the form of small pale pink dots may appear on the mucous membranes of the gums, accompanied by itching and burning.
Allergy treatment involves the use of drugs from the group of histamine receptor blockers. Popular antihistamines, as well as their regimen, are listed in the table below.
| A drug | Image | Reception scheme | Cost (average values are indicated for packaging with a minimum volume) |
| "Claritin" | 10 mg 1 time per day, regardless of meals | 155 rubles | |
| "Loratadine" | 10 mg 1 time per day | 12 rubles | |
| "Erius" | 5 mg once a day at the same time | 224 rubles | |
| "Fenistil" | 20 drops in the morning during breakfast and 40 drops in the evening before bed | 356 rubles | |
| "Zodak" | 10 mg 1 time per day | 122 rubles | |
| "Tavegil" | 1 mg 2 times a day before meals | 145 rubles |
Important! All dosages in the table are indicated for adult patients and adolescents over 12 years of age. The regimen for use in childhood is selected individually.
Poor quality treatment
Errors during dental treatment can also lead to inflammation on the first or second day after the manipulations. The most common cause of such symptoms is infection of soft tissues as a result of pathogenic bacteria, fungi or viruses entering the damaged gum. To avoid this, you must follow all the dentist’s recommendations, especially in the first 72 hours after treatment. To prevent complications, which include inflammatory processes in the gums, the patient is recommended to:
- do not eat or drink for 2-8 hours after treatment (the final time depends on the type of therapy performed, the severity of the underlying diagnosis and the medications used);
- rinse your mouth with antiseptics or anti-inflammatory decoctions of chamomile, calendula or St. John's wort (on the first day it is better to do oral baths);
- take antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs if prescribed by a doctor;
- maintain a gentle hygiene regime so as not to injure your gums.
Important! In especially severe cases, inflammation can be triggered by a foreign body. This situation is possible when the special needles that are used to clean the canals break off. Symptoms of this pathology will be manifested by severe pain, swelling and swelling of the gums, severe hyperemia of the mucous membranes around the filled tooth. If such signs occur, you should immediately consult a doctor (if pain and inflammation appear at night, you can contact the emergency dentist).
Tooth injury during treatment
Damage to soft or hard tissue that may occur during the use of medical instruments can lead to the formation of cysts. Cysts are growths in the form of cavity sacs that have an oblong and elongated shape and are filled with exudative or purulent fluid. If the cyst is not treated in time, it can develop into a granuloma - a benign tumor of the dental root (located mainly at the top of the root system).
Cysts can go undetected for a long time. They are characterized by a slow course with mildly expressed symptoms. During the formation of a cyst, the gums may look inflamed and hyperemic, but after a few days these signs disappear, and the person mistakenly thinks that everything is fine.
Important! If there are frequent inflammatory processes in the gums around the tooth that has been treated, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo an X-ray examination to exclude formations of various etiologies.
The child has
The cause of swelling in a baby under one year of age is most likely teething, which is accompanied by sleepless nights, poor appetite, and crying for no apparent reason. If the temperature rises with a tumor, you should consult a doctor - this may be caused by a cold or a lack of vitamin C in the body. In addition to the above-mentioned reasons, swelling is provoked by various types of inflammatory phenomena, for example, a flux (fistula) or a cyst (a growth that looks like bump).
Treatment
Only a dentist has the right to prescribe specific and appropriate treatment, because everything here depends on the reason why the inflammation occurred: if the swelling is due to pulpitis or caries, the tooth will be filled; if the crown is destroyed, the tooth must be removed. If the wisdom tooth erupts incorrectly, with purulent inflammation, pericoronitis or cysts, surgical intervention will be required. In the process of treating gingivitis or periodontitis, the patient has tartar removed, after which antibacterial drugs and ointments are prescribed.
If you can’t go to the doctor, then anti-inflammatory ointments, rinses and applying ice compresses to the sore spot will help you deal with swollen gums. In addition, follow these rules:
- Use painkillers. It is allowed to crush the tablet into powder or small pieces and pour it onto the swelling.
- Do not apply warm compresses to the tumor, avoid exposure to the inflamed area - such manipulations will aggravate the situation.
- Treat the oral cavity with an antimicrobial drug, which additionally produces an analgesic effect.
- Disinfect your mouth with an antiseptic solution (for example, Chlorhexidine).
Pain at the site of a dead tooth
It happens that the nerve has been removed from the teeth, but they still hurt. If the nerve is not completely removed or the doctor put too much filling material into the canal, then the pain will not leave you for a very long time and will occur when eating hard, cold or hot foods.
Pain in a dead tooth can appear due to the fact that tissue inflammation has gone too far, and not only the nerve and pulp are affected, but also the bone tissue that surrounded the tooth, as well as due to the use of too aggressive drugs in treating the nerve.
Often, to regenerate tissue at the site of the inflamed nerve, a course of special anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. To avoid problems with inflammation when extracting the nerve, it is recommended to first install a temporary filling.
Medicines
When serious inflammation begins, it may not be possible to remove it by rinsing. In this case, it is recommended to resort to antibiotics, but they should be prescribed by a dentist after identifying the cause of the disease. Medicines must be taken in a course and under the supervision of a doctor. It is worth noting that in addition to antibiotics, drugs to restore microflora (Linex, Hilak Forte) are prescribed. The following drugs help remove swelling:
- Amoxiclav (Augmentin) is a semi-synthetic medicine based on clavulanic acid and amoxicillin. The second substance kills microbes, and the acid blocks the action of b-lactamase, an enzyme in bacteria that forms their tolerance to the drug. It is recommended to use Augmentin for purulent-inflammatory processes or to relieve pain after minor operations. The patient can be of any age - the appropriate dosage is selected for each. The advantage of the drug is its easy tolerability and low number of side effects. The disadvantages include the impossibility of using Amoxiclav by people who are allergic to penicillin and those who have liver or kidney disease.
- Tsifran ST is an improved formula of the usual Tsifran. The antibiotic consists of tinidazole and ciprofloxacin hydrochloride: they fight infections that were caused by aerobic or anaerobic bacteria. The drug is indicated when chronic periodontitis worsens, with an existing risk of purulent inflammation, with osteomyelitis and other maxillofacial ailments. The advantages are the effectiveness of the drug, the impossibility of overdose, low cost and absence of side effects. Among the disadvantages are age and other restrictions - from 18 years old, pregnancy and the inability to use for people with weakened bodies.
- Lincomycin is a cheap and effective antibiotic used to treat purulent-inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. The drug is available in the form of ointment, capsules, injection solution, film. The ointment has found wide use in dentistry: it is recommended for use in ulcerative gingivitis, small abscesses and fistulas, various types of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, and ostiomyelitis. The method of application and dosage of Lincomycin should be prescribed by a specialist. The advantages of the product include its effectiveness in the fight against harmful microorganisms and the fact that by accumulating in bone tissue, it minimizes the likelihood of pus formation in the future. The disadvantage is the narrow spectrum of antimicrobial action. Violation of the regimen of use of the drug can lead to recurrent oral disease.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
In case of poor-quality root canal treatment, due to tooth trauma, or in the absence of timely treatment of caries and pulpitis, inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, which dentists call “periodontitis.” Sometimes the terms “granuloma” or “cyst” are used to refer to periodontitis, which you may well have heard. Such names are due to the fact that the focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root in these cases has the appearance of a purulent sac.
Symptoms - usually periodontitis has a chronic asymptomatic course, or there is only slight pain when biting on this tooth. But sometimes periods of exacerbation of inflammation occur, and in this case, acute pain may first occur in the causative tooth (especially when biting on it), and a little later, swelling of the gums usually appears in the projection of the causative tooth. But sometimes pain may be completely absent, and patients complain solely that the gums near the tooth are swollen (Fig. 1-3, 7-9).
Please note that with periodontitis, the source of inflammation is located at the apex of the tooth root, i.e. quite deep in the bone tissue. Therefore, swelling of the gums during periodontitis usually develops not just in the projection of the causative tooth, but most often in the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth. And in multi-rooted chewing teeth - no less often in the projection of the bone interradicular septum. But periodontitis is not characterized by swelling of the interdental papilla or the gingival margin adjacent to the neck of the tooth.
In general, if you have swelling on the gum in one of your teeth, pain occurs when you bite on it, and there is a crown, filling or carious destruction on the tooth, and also if, in addition to swelling on your gums, you also have swelling of soft tissues face (again in the projection of the causative tooth) - you can definitely make a diagnosis of “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.” An X-ray of this tooth will allow you to accurately determine the cause of periodontitis and the required amount of treatment.
What treatment may be required -
As we said above, if the gums are swollen and painful, then in most cases the reasons are poor-quality filling of the canals, or the lack of timely treatment of dental caries and pulpitis. Only according to official statistics, root canal fillings are performed poorly by dentists in at least 60-70% of cases. The main errors during treatment are underfilling of root canals, poor obturation of root canals with filling substances, breakage of instruments, perforation of the tooth root...
As a result of this treatment, a focus of purulent inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root. Moreover, in the absence of timely treatment of the tooth for caries and pulpitis, exactly the same focus of inflammation will appear at the apex of the tooth root, but only against the background of unsealed root canals. In Fig. 10-12 you can see how the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root looks like during periodontitis (on the diagram, x-ray and on the root of the extracted tooth) -
Below we describe several treatment options that may be possible for patients with gum swelling due to dental periodontitis. In any case, the doctor will first be forced to take an x-ray. The image will allow us to determine whether this tooth can be saved at all, the size of the inflammatory focus at the apex of the root, and whether root canals have been filled in this tooth previously. The treatment tactics will depend on the latter, and below we will tell you how to cure a tooth and remove swelling from the gums so that it does not appear again.
1) If the channels are not sealed -
If root canal treatment has not previously been carried out on this tooth, then standard treatment of periodontitis is carried out with mechanical treatment of the root canals and treatment of the source of inflammation behind the root apex. On your first visit, they will open your tooth, expand the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them, and leave the tooth open for several days, prescribing antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If necessary, your dentist may then refer you to an oral surgeon to make a small incision in the gum to allow additional drainage of pus. After about 3-5 days, the doctor makes an appointment for a second appointment and, if the inflammation subsides, completes the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seals them - either first with a temporary medicinal paste, or immediately with gutta-percha (the latter depends on the size of the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root). You can read more about the treatment of periodontitis at the link above.
How the gum incision is made - significant swelling of the gums, or if your gums and cheek are swollen at the same time - indicates the formation of a large purulent abscess, which will require not only opening the root canals of the causative tooth, but also making an incision in the gums to release the pus. The incision is made under local anesthesia, the wound is then washed with antiseptics and a drain is inserted into it (see video below).
2) If the channels are sealed poorly -
If an x-ray shows that canal treatment has already been carried out previously and the cause of inflammation was incomplete filling of the root canals to the apex of the tooth root, then there are 2 treatment options: either standard conservative therapeutic treatment, or an option associated with resection of the root apex.
- Conservative therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the filling/artificial crown is removed from the tooth, poorly filled root canals are unsealed, washed with antiseptics, and antibiotics are prescribed.
If necessary, the patient is referred to a dental surgeon to make an incision along the gum. Thus, to the treatment we described in the previous section, only 1 point was added here (unsealing the root canals). Then everything is the same - after the inflammation subsides, temporary or permanent filling of the root canals is carried out. If the source of inflammation is small, the canals are usually filled immediately and permanently with gutta-percha, and a permanent filling is placed at the next visit. If the inflammation is large, the canals are sealed with temporary medicinal paste for 1-3 months, and a temporary filling is placed. And only after this time the canals are filled with gutta-percha + a permanent filling or crown is placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This surgical method is much simpler and much cheaper than conventional therapeutic treatment, and it allows you to avoid removing the crown from the causative tooth in order to unfill and reseal the root canals.
However, this method is only suitable for those teeth in which the root canal was poorly filled only at the very apex of the root (and throughout the rest of the length the canal should be filled normally). This simple surgical operation is carried out within 25-35 minutes and consists of cutting off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal using a drill. To do this, an incision is made along the gum and a flap of the mucous membrane is moved back to give access to the bone tissue in the projection of the apex of the tooth root. Next, a small hole is made in the bone with a drill, through which the apex of the root is cut off and removed from the wound along with the granuloma/cyst at the apex. The wound is sutured and antibiotics are prescribed. Pros: cheap, simple, no need to remove the crown and re-treat the tooth.→ How is root resection surgery performed?
Gels
For local treatment of inflamed gums, gels are often used that can relieve swelling and have an antimicrobial or analgesic effect:
- Metrogyl Denta is one of the most popular and inexpensive means of fighting inflammation. The main active components of the gel are chlorhexidine (an antiseptic) and metronidazole (an antibiotic that can suppress the growth of anaerobic microorganisms). Indicated for use in gingivitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis, alveolitis and other diseases. It must be applied to the affected area with a cotton swab and left for 30 minutes. You can repeat the procedure up to 2 times a day. The advantage of the drug is that it effectively relieves inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. The disadvantages include the fact that Metrogyl Denta cannot be used by children under 6 years of age, during lactation and in the first trimester of pregnancy. An overdose can cause an allergic reaction, and if the ointment is swallowed, the side effects increase: vomiting, taste disturbance, convulsions, nausea.
- Cholisal-gel is a combined drug used to relieve inflammation in dental treatment, because it quickly eliminates pain, reduces swelling, and prevents infections. The gel is recommended for gingivitis, stomatitis, household injuries to the oral cavity, and after tooth extraction surgery. You need to apply a small amount of the product to the inflamed area and rub it in with your finger. It is recommended to use the gel 2-3 times a day. The positive aspects are the low price of the drug and the minimum of side effects. The negative side is the recommendation not to use Cholisal-gel for persons who are intolerant to the active components contained in the composition.
- Dentol-gel , which reduces pain during inflammation of the oral mucosa, can speed up the patient’s recovery process. It contains a derivative of corn oil, which forms a kind of protective film on the mucous membrane. The product should be distributed over the lining of the mouth, while massaging the gums with stroking movements. The advantage of Dentol-gel is that it can be used even for children who are teething - the effect occurs instantly. However, the product also has a disadvantage - pain relief does not last long.
Pain due to alveolitis
One of the reasons why gums hurt if a tooth has already been removed is alveolitis. This disease manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the tooth wound due to the fact that the blood clot is too loose and gradually disintegrates. Over time, the extraction site begins to hurt and become inflamed due to a number of reasons:
- poor immunity;
- failure to comply with hygienic requirements for oral care;
- inflammatory processes in the tooth and gum tissue due to caries or more serious dental ailments;
- parts of the tooth remaining after improper extraction.
To treat alveolitis, you should make an appointment with a dentist, who will clean the wound and prescribe a course of medication. With alveolitis, the process of flesh regeneration can last about 3 weeks after the start of treatment, but pain in the gums between the teeth will stop within 24 hours.
How to rinse
To relieve inflammation of the oral mucosa and reduce pain, you must definitely consult a dentist, but until this point, you can begin to treat the resulting tumor on your own. Rinsing with inexpensive but very effective ingredients that can have an anti-inflammatory effect will help with this: calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, soda and salt, oak bark, etc. In addition, wiping the gums and lubricating them with vegetable oils will help cope with swelling.