Causes Symptoms Treatment Possible complications Prevention
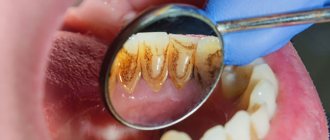
Gum hyperplasia is a condition in which tissue begins to grow excessively. They hang over the teeth, forming false pockets, covering most of them, interfering with hygiene procedures. There are several terms in the literature that describe this condition: gingival overgrowth, hypertrophy, or hypertrophic gingivitis.
The main danger of tissue proliferation is that it promotes the proliferation of bacteria, causing serious diseases such as periodontitis.
Causes of gum hypertrophy
The main reason for tissue hypertrophy in the mouth is poor hygiene. Remains of food and decay products settle on the enamel of the teeth. They accumulate, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane, one of the manifestations of which is hyperplasia.
Other reasons include:
- Taking certain medications
A side effect of some anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, and some heart medications, is gum overgrowth. However, you should not stop taking them or reduce the dosage if your gums have increased in size and began to bleed, without consulting a doctor.
- Genetic predisposition
Most people experience tissue growth during puberty. In most cases, after the end of hormonal changes, spontaneous reduction is observed. But in some patients, the gums do not shrink and may even increase in size. This phenomenon is characteristic of hereditary fibromatosis.
- General diseases
Leukemia almost always provokes tissue hypertrophy because they are saturated with dense masses of immature leukocytes. The gum turns into a hard surface on which wounds appear at the slightest pressure. This problem is also typical for sarcoidosis.
- Hormonal instability
Pregnancy and diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, disrupt metabolic processes in tissues and lead to inadequate growth.
- Crowded teeth
If teeth creep onto each other and overlap surfaces, this interferes with proper cleaning of surfaces and contributes to the formation of microbial plaques. They, in turn, provoke inflammation.
What can happen if you refuse the help of a specialist?
If the tooth root remains under the layer of gum tissue, decay can spread to neighboring units. In this case, treatment will be longer and more expensive. The main symptoms of this problem are a strong odor from the mouth and periodic pain that radiates to the head. Harmful microorganisms will begin to accumulate under the gums, which can lead to the development of caries.
In 99% of cases, the patient has a small sac with purulent filling at the apex of the root. After some time, it inevitably turns into a painful swelling called gumboil. The only correct solution when gums grow on a tooth is to quickly contact an experienced dentist. It will not only eliminate inflammation, but will also be able to save the destroyed unit.
previous post
What happens if you swallow toothpaste?
next entry
Symptoms
The growth of the mucous membrane is a gradual process. There are 3 degrees:
- The gingival papillae increase in volume. The gingival contour is disrupted and hangs over the tooth.
- The growth progresses, the tissue covers up to half of the coronal part. Bleeding and discomfort when brushing teeth and eating food develop.
- The gum covers the tooth by two thirds, sometimes completely. Folds form in which microflora accumulate, causing inflammation.
The process is generalized
when the entire gum on the jaw suffers.
Focal
hyperplasia is located around one or more teeth.
The edematous form is characterized by the presence of plaque, there is a lot of it, it is quite soft, but covers the enamel with a thick layer. Gum pockets form. The papillae turn red and bleed when pressed.
Patients complain of itching, discomfort in the mouth while eating, and an unpleasant odor.
With fibrous gingival hyperplasia, patients are only concerned about the unusual appearance of the mucous membrane. There is usually no pain or bleeding, but there are complaints of an unpleasant odor.
Gingivectomy - what is it?
With advanced periodontal disease, pockets form into which food debris gets trapped.
Over time, they become the cause of infection. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, serious negative consequences are possible, including removal of infected bone tissue and teeth. Gingivectomy can prevent this. The operation can be carried out either locally, when one tooth is affected, or on a large scale - if necessary, treat several units at once. Initially, dentists try to cure periodontal pockets using therapeutic methods. However, this often does not give the desired result, especially if the depth of the pockets reaches 2 mm or more. As a result, there is a need for an operation to excise the gingival margins.
The dentist first measures the depth of the pocket. Based on these and other data, a decision is made on further treatment tactics. The sooner the patient turns to a specialist, the higher the likelihood of solving the problem through simple therapeutic means. If there is no chance of successful treatment with this method, surgery is prescribed.
Advantages
- Getting rid of the source of infection.
- Restoring the aesthetics of the oral cavity.
- Improved overall well-being.
Flaws
- Long recovery time.
- The need to strictly follow the dentist's recommendations.
- Obligatory observation by a specialist over the next two weeks.
- Restrictions on food and lifestyle during the rehabilitation period.
Contraindications
- Low level of immune defense
- Bacterial endocardid
- Congenital heart disease and other cardiovascular diseases
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Bridle or cords in the area of the operation
- Blood diseases
- Inflammation of bone tissue
Indications
- Periodontitis, gingivitis
- Deep pockets between tooth and gum
- “Gummy smile” - achieving an aesthetically pleasing oral cavity
- Epulis
- Large size of interdental papillae, gum grows onto the crown
- Subgingival location of the filling
- The need for root polishing
Treatment of gum hyperplasia
Any medical intervention is preceded by diagnosis. The clinic conducts a visual examination using dental instruments. An X-ray is taken and, in some cases, a tissue biopsy. Collect information about current diseases and what medications the patient is taking.
Gingival hypertrophy is differentiated from papillomas, granulomas, epulis (neoplasms) or swelling of the gums as a result of periodontitis.
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the degree, course and reasons for which the gums have grown.
For concomitant diseases, procedures should be agreed with the attending physician. Sometimes, simply changing the drug leads to a reduction in overgrown tissue.
Therapeutic methods
They are used mainly after replacing the drugs that caused hyperplasia.
- Decoctions and applications
from oak bark, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula. Tannins in these plants narrow and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability. As a result of combining with proteins, tannins form an insoluble film on the mucous membrane. This protects nerve endings from breakdown products and reduces pain.
- Installations in gum pockets.
Plant-based preparations are placed in pockets for 15-20 minutes, for up to 3 weeks.
- Dorsenval therapy.
After the elimination of the inflammatory process, physiotherapy is carried out to strengthen blood vessels.
The main treatment measure is professional teeth cleaning.
If the effect of the procedures is insignificant, as well as with fibrous hyperplasia, gingivectomy
.
Surgery
In cases where the gum has grown on the tooth so much that it covers half of the surface or more, the excess tissue is removed. For fibrosis, therapeutic treatment is not used at all; in other cases, the decision depends on the clinical picture.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Apply:
- Classic way
. The tissue is excised with a scalpel. The surface of the roots is polished with instruments, and the wound is treated with an antiseptic. Finally, a special bandage is applied (septopak, vokopak). - Laser
removal of overgrown gums . This is a minimally invasive operation, after which healing occurs much faster. During surgery, the vessels are sealed with a laser beam, which eliminates bleeding. At the same time, pathogenic flora is destroyed. Complications after such operations are extremely rare.
How is the procedure performed?
Before starting the procedure, the dental surgeon takes into account all the individual characteristics of the patient: age, allergic reactions, chronic diseases, etc. After making sure that the procedure can be carried out, the doctor begins excision.
Stages of excision of the hood:
- X-ray diagnostics.
- Local anesthesia.
- Gum incision.
- Washing the wound.
- Applying a therapeutic bandage.
After surgery, the doctor schedules a follow-up appointment to examine the wound. As a rule, the gums heal in about ten days. If the process is delayed, this may be a symptom of complications.
Complications
Hyperplasia is dangerous because without treatment it provokes inflammatory processes in the periodontium: gingivitis and periodontitis. This leads to loosening of teeth and their loss.
Due to the fact that it is impossible to clean teeth well, caries often develops. Enamel demineralization occurs. Metabolic processes are disrupted.
Due to increased sensitivity, patients try not to chew on the side where the gum has grown. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, and the risk of losing teeth increases.
When to carry out the procedure and when to refrain from it
Indications for the procedure:
- strong pain;
- the appearance of putrid odor from the mouth;
- discharge of pus from the gums;
- swelling, bleeding and soreness of the gums;
- general weakness, elevated body temperature, dizziness and nausea (such symptoms are a sign of intoxication of the body).
Contraindications:
- mucosal infections (stomatitis, herpes, gingivitis, periodontitis);
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Prevention
Simple measures will help prevent gum overgrowth. Dentists recommend brushing your teeth with a soft brush, using dental floss or interdental brushes. Using a rinse aid reduces the number of bacteria settling on the enamel. But all these measures will not help if there is plaque on the teeth. Therefore, professional teeth cleaning in dentistry is where the prevention of hyperplasia begins.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
Lack of flush hole: consequences
In the absence of a flushing space, the consequences may be as follows:
- inflammatory processes caused by constant contact of mucous membranes with the prosthesis;
- tissue damage with subsequent exposure to pathogens;
- tissue hypertrophy in the affected areas of soft tissue.
If you look at it from a different angle, the rinsing space provokes the penetration of food into the area between the prosthesis and the mucous membrane. But without this gap, the patient will not be able to provide proper oral care. Plaque can accumulate under the bridge, so this area needs more thorough cleaning.
If the patient notes that food debris has entered the resulting space, this may be caused by incorrect installation of the prosthesis, poor quality of construction, or the development of pathologies of the oral cavity. Normally, this situation should not exist.
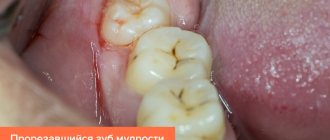
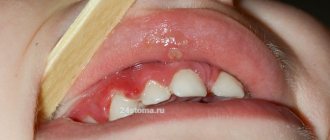
Eruption of wisdom teeth: inflammation and consequences
The figure eight on the lower jaw begins to create problems from the moment of eruption, when the crown rests closely on the adjacent tooth or is tightly covered with a hood. When the hood becomes inflamed, favorable conditions are created under it for the proliferation of pathological microorganisms, and the gums are involved in the process. This manifests itself as pain during chewing or when accidentally biting the mucous membrane. It happens that a wisdom tooth partially erupts, and one or more tubercles rest against the hood, injuring it. In this case, the inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth will have to be treated by removing the hood or the tooth itself. If the figure eight is healthy and does not interfere with the adjacent tooth during eruption, then the dentist makes an incision in the hood so that the tooth can erupt calmly.
How to treat inflammation of the hood and gums near the wisdom tooth at home? To do this, you will need to regularly rinse, rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions and take analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief: Nimesil, Ketanov, Ibuprofen. If the hood is inflamed, you can rinse your mouth with weak solutions of the antiseptic Chlorhexidine, soda and saline solutions.
How to identify the problem?
If the flushing space corresponds to the norm, then:
- the prosthesis is fixed correctly;
- the gap between the bridge and the crown allows hygiene procedures to be carried out without any difficulties;
- the risk of developing periodontal pathologies is minimal;
- The device works normally for a long time.
You should consult a doctor as soon as possible if:
- after installation of the prosthesis there is noticeable discomfort or pain;
- there is a change in the location of the apparatus in the oral cavity;
- increased sensitivity to cold/hot;
- there is a burning sensation and other obvious signs of deterioration in the condition of the oral cavity.
Solution
If the gums rise or fall above the coronal part, you must consult a dentist. The doctor must take measures to restore the normal fit of the prosthesis, taking into account the distance between the structure and the surface of the oral cavity.
It is important to understand that the presence of any foreign object in the mouth is initially accompanied by discomfort, which goes away within a few days. If negative symptoms do not go away longer, you should immediately inform your doctor about this so that appropriate correction can be made.
Correction methods
- Local treatment with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs (performed after removal of the orthopedic device).
- Correction of an existing prosthesis or production of a new one (the decision is made based on the results of an orthopantomogram).
- Fitting the prosthesis using the grinding method.
- Measures to strengthen supporting teeth with repeated prosthetics.
- In rare cases of the bridge coming off, which increases the risk of displacement of the supporting units, the prosthesis is reinstalled. To prevent this, it is important to consult a doctor immediately after identifying the problem.
How to treat gum recession?
To cover the exposed root, a small operation is performed in the gum area.
There are many methods of gum plastic surgery, but they are fundamentally divided into 2 types:
- gum plastic surgery with local tissues (when the existing gum is “stretched” or moved to the root in a certain way so that the exposed area is closed, and fixed with small sutures, which are removed after healing).
- gum plastic surgery using a “patch” (the patch can be a special collagen-based material or the patient’s own tissue from the hard palate or the area of the far upper tooth - gum transplantation).
The choice of method is at the discretion of the doctor, according to each specific situation.
Contraindications for surgery
Gum grafting is considered a minor surgical procedure, however, it has a number of contraindications. In particular, gingivoplasty is not performed if the patient:
- blood diseases, especially bleeding disorders;
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus;
- immune diseases in which such operations are prohibited;
- acute respiratory, inflammatory, infectious, etc. disease (temporary contraindication).
Also, before surgery, as a rule, it is recommended to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity, if necessary, to clean the gum pockets and get rid of tartar. This is necessary so that there are no pockets of infection left in the mouth, which can cause postoperative complications.
Recovery period after gum resection
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the volume of excised tissue. Maximum recovery takes up to 1 month. Compliance with the doctor’s prescriptions allows you to speed up healing time and prevent the development of complications.
During this period, you need to give up smoking and alcohol, and exclude foods that irritate the mucous membrane (hard, spicy, salty, sour) from your diet. Food and drinks should be warm (neither hot nor cold). It is mandatory to take prescribed medications.
Then, once every 3-6 months you need to visit a periodontist to monitor the situation.
What are the features and complications after gum recession surgery?
With a mild course of the rehabilitation period, patients do not note any peculiarities . But sometimes it is possible:
- the appearance of white plaque on the gums (this is normal, one of the healing options after gum surgery).
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face (from minor swelling to significant) depending on the extent of the surgical intervention (number of teeth involved), the size of the recession, the method of its closure, anatomical features and the patient’s body.
- hematomas on the facial skin (rarely encountered with gum surgery).
- increase in body temperature.
- pain (relieved by painkillers).
Tissue augmentation – during recession and implantation
Gum grafting with root exposure (recession)
solves not only aesthetic, but also medical issues, protecting this part of the tooth from increased sensitivity, caries formation and other problems. One of the common causes of recession is periodontitis and gingivitis. A similar disorder also occurs with periodontal disease; if the gum tissue is too thin; due to improper oral hygiene and a number of other reasons.
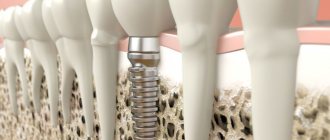
Build-up may also be required when installing an implant - when a tooth is removed, the volume of bone and gum tissue decreases over time. Accordingly, if it becomes insufficient for implantation, the tissue is built up. Sometimes it is necessary to work only on the gingival contour - so that the implant looks as aesthetically pleasing and natural as possible.
To cover exposed areas, so-called patchwork plastic surgery is often used. The doctor cuts the tissue in the treated area and replaces/extends the resulting flaps using flaps taken from the palate, cheek, and other areas of the periodontium. Then stitches are applied.
How is the operation performed?
- Anesthesia Local anesthesia is used, which eliminates any discomfort. At the request of patients, the procedure can be performed under sedation.
- Operation Excision of excess gum according to the selected protocol, cleansing periodontal pockets of hard deposits and dental plaques.
- Antiseptic treatment Disinfection of the surgical area by repeated rinsing with antiseptics, applying a periodontal bandage.
The use of sedation ensures complete physical and emotional comfort for the patient during the procedure.
After surgery, the gums heal quickly. But in order to avoid complications, we ask you to strictly follow the doctor’s home care instructions.
Methods of conducting
The choice of technique depends on the severity of the disease
- Partial The least traumatic option involves excision of only the affected part of the periodontal tissue.
- Simple The entire volume of overgrown mucous membrane is removed, leaving only a 1 mm margin from the gum pocket.
- Radical Performed in severe cases, not only necrotic soft tissue is removed, but also the affected part of the bone.
Any surgical intervention on the gums should be carried out extremely carefully, with minimal tissue trauma. For this purpose, our Center uses a dental microscope, which increases visibility, increases the accuracy of manipulations, allows you to make neat cuts with special micro-instruments, and use the finest threads to apply sutures that do not injure the mucous membranes. All this ensures quick recovery, shortens rehabilitation time, and prevents possible complications.
Gingivoplasty at NovaDent
If you need gum grafting, contact the NovaDent network of clinics. We employ only highly professional doctors with extensive experience in this field (the average experience of a doctor in the clinic is 12 years, the experience of some specialists exceeds 20 years), and in treatment we use the most advanced and current technologies and materials. In addition, we are distinguished by the very favorable cost of gum recession plastic surgery in Moscow, as well as affordable prices for other types of gingivoplasty. Sign up for a free consultation and our specialist will create the optimal treatment program for you.
Why is the tooth root exposed?
The reasons for the development of gum recession can be different, and in some cases there is a combination of several factors at the same time.
- aggressive brushing with a toothbrush - there is such a thing as brush gum recession. They occur when there is excessive pressure on the toothbrush when brushing, or when using a brush of unsuitable stiffness (hard). If you have increased tooth sensitivity when brushing, if your toothbrush becomes deformed over time (the villi move in different directions), you should consult a dentist about proper self-hygiene.
An example of brush gum recession on the upper jaw.
- incorrect position of the tooth in the dentition. Sometimes even a small bite problem can lead to gum pathology. This occurs because the tooth bears excess load when chewing or when teeth are closed, which over time leads to atrophy of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, including the gums. In addition, excessive protrusion of the tooth root from the dentition also leads to gum atrophy.
Multiple gum recessions caused by malocclusion.
- caries - in cases of gingival caries, gum loss often occurs due to the presence of an infectious focus in the immediate vicinity of the gingival margin.
Gum recession caused by tooth decay in the immediate vicinity of the gum margin.
- Tartar can also cause root exposure.
- anatomical features - for example, a thin biotype of gingival tissue in combination with other factors can lead to recession. Shallow vestibule of the oral cavity (in which the muscles of the lips attach very close to the gingival margin and gradually “pull back” it, exposing the roots of the teeth). In addition, improper attachment of the lip and tongue frenulum can contribute to gum recession.
The frenulum of the lower lip, a thin tissue biotype, caused the exposure of the lower incisor root
- bad or professional habits - for example, chewing a pen/pencil, biting threads (for a seamstress), pinching metal objects with teeth, etc.
- lip or tongue piercing - constantly touching the gums and regularly injuring it, metal jewelry can lead to exposure of the roots of the teeth.
- periodontitis - with inflammatory diseases of the gums, the roots are often exposed due to the resorption of the tissues surrounding the tooth, including gum tissue. Unlike “normal” gum recession, periodontitis is treated differently and the prognosis for such recessions is somewhat worse (as a rule, it is impossible to restore the volume of lost gum by completely covering the exposed root).