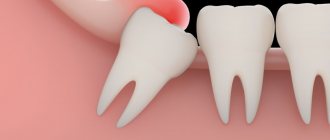
Almost every person experiences discomfort during the eruption of wisdom teeth. The intensity of pain symptoms may vary in each individual case, but usually the eruption of third molars is problematic.
When a wisdom tooth grows and the gums hurt, other signs are often observed - swelling of the soft tissues of the mouth, increased temperature, impaired bowel movements, etc. People often try to cope with pathology at home: using traditional methods or anesthetic drugs. However, it must be remembered that all these measures provide only temporary relief of symptoms. Independent actions lead to a worsening of the pathology. Therefore, it is important to know under what signs you can use alternative medicine, and under what signs you should urgently consult a doctor.
Features of the structure and eruption of wisdom teeth
Unlike other teeth, the rudiments of “eights” are formed not during intrauterine development, but at 3–5 years, when the child’s body is preparing to change the primary dentition to a permanent one. At this age, you can determine the number of future eights (from one to four). However, it is impossible to detect possible developmental pathologies at this stage.
The crown part of third molars is formed at approximately 12 years of age, but the development of the root part takes several more years and can continue even after tooth eruption. Considering that the most common age for the appearance of third molars is 18–25 years, the eruption of wisdom teeth occurs already in adults. However, approximately 10 - 15% have no eights at all, which is why it is considered normal for an adult to have from 28 to 32 teeth.
Causes of the inflammatory process
It is not unusual for a dentist when patients come to him and complain that the gums near the wisdom tooth are swollen. No one is safe from such an incident.
Eights are specially designed, for example, they never have milk teeth predecessors, which causes them to take a long time to form, they have a different root system from the rest and begin to erupt quite late.
All people have the rudiments of molars on the distal part of the jaw, however, not all people develop completely and turn into a full-fledged tooth. In some of the population, they never begin to emerge or do not emerge completely.
Note. Wisdom teeth always grow for a long time and very slowly. This often causes discomfort, and in some cases, serious inflammatory processes, so it is important not to delay your visit to the dentist. The patient will be examined and given instructions on further actions.
Symptoms of wisdom tooth eruption
When the coronal part of a wisdom tooth begins to erupt onto the surface of the soft tissues, this process is rarely asymptomatic. The difficulties are largely due to the fact that wisdom teeth do not have milk analogues, so even if the third molars erupt correctly, a person experiences a number of unpleasant sensations.
Signs of wisdom tooth eruption
- Itching in the eruption area (at the initial stage).
- Inflammation of the gums during the eruption of wisdom teeth.
- Aching or throbbing pain in the jaw.
- Pain when swallowing and difficulty chewing food (especially hard food).
- Temperature increase. The temperature during the eruption of a wisdom tooth in adults increases by an average of 1 - 2 degrees.
- Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the gums near the eighth tooth is accompanied by pain and discomfort. To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the tooth and take a blood test. Based on the results of the studies, the doctor makes a decision:
- Remove the tooth.
- Prescribe therapeutic treatment.
- Or cut the gum.
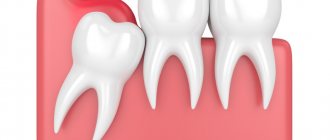
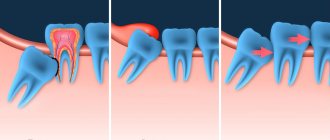
The gums can become inflamed and painful, most often due to the incorrect position of the tooth, which has difficulty erupting and grows in the wrong direction relative to the dental arch. The number eight can take a very long time to erupt, up to several years.
Difficulty erupting wisdom teeth
If there are the beginnings of eights, then there are two options: normal eruption of wisdom teeth or difficult. With the first option everything is very clear. But problems during teething may indicate the presence of pathologies - dystopic and impacted wisdom teeth.
Clinical manifestations
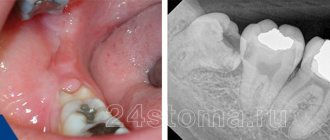
After cutting the gum, a growing molar is visible - the cause of pain and swelling
Symptoms indicate what processes are occurring and how serious the pathology is.
Problems with the germination of wisdom teeth may be the following:
- weak, aching pain indicates that the sharp edge of the tooth is pressing or cutting the gum;
- hot tissue in the area of the third molar is a sign of an inflammatory process, which is possible with a hematoma, pericoronitis or abscess;
- severe pain with sharp spasms or tingling;
- the appearance of bad breath in the presence of the above symptoms may mean the spread of alveolitis;
- swelling can be very pronounced, spreading to the cheek and even the neck, which will create certain difficulties when swallowing; a similar picture is typical for an abscess, which can result in a phlegmatic complication;
- purulent processes can contribute to the formation of a cyst - a small ball with a purulent mass on the gum.
Complications if you consult a doctor in a timely manner are unlikely, however, if you ignore the initial symptoms and go to the dentist for severe pain, then in most cases pathological processes can already develop in this situation.
A high temperature rises, the person has a fever, purulent processes form in the gums, etc. Therefore, it is advisable not to take things to extremes and visit the clinic at the first negative signs.
Complications of wisdom teeth eruption
| Type of pathology | Description |
| Dystopia | Incorrect position of the tooth. When a wisdom tooth comes through, it hurts much more than usual. It can push against neighboring teeth, causing them harm. |
| Retention | The tooth is completely or partially hidden in soft tissue or even bone. When a wisdom tooth erupts, the gums hurt and pericoronoritis may develop (inflammation caused by the activity of bacteria that accumulate in the gum hood). |
| Mixed pathology (retention + dystopia) | Incorrect position is complicated by tooth retention. The most severe pathology that provokes the occurrence of phlegmon, abscesses and osteomyelitis. |
Symptoms of the eruption of wisdom teeth in adults with suspected development of pathology:
- when a wisdom tooth erupts, the cheek becomes swollen;
- blood and pus are released when a wisdom tooth erupts;
- severe pain in the gums and jaw when wisdom teeth erupt;
- injury to the cheeks and tongue.
Causes of periostitis
In addition to advanced caries, swelling of the cheek due to a tooth can be caused by other factors.
Inflammation of the gums
Periodontal disease can serve as a starting point for infection to penetrate the periodontal tissue. This diagnosis requires a thorough examination and often long-term treatment.Reaction to poor-quality canal filling
If depulpation is carried out without modern diagnostic equipment, the doctor may not completely clean the root canals. As a result, the remaining nerve tissue becomes inflamed and leads to such unpleasant complications as periostitis.
Inflammatory reaction to tooth extraction
Any tooth extraction is considered a minor surgical operation. It leaves an open wound that can become infected. In this case, the inflammatory process in the tissues occurs quickly and with complications in the periodontal tissue and periosteum.
Cyst formation in periodontal tissues
A tooth cyst can develop in a person over several years, and then at one point this process can spread to the periosteum tissue. If the spread of infection has gone so far, then the most likely option is to remove the diseased tooth, cleanse the affected tissues, and thoroughly treat all tissues with antiseptic drugs.
Infection due to injury
As a result of an open fracture of the jaw, pathogens can penetrate the tissues near the tooth, both soft and bone.
Infection through lymph nodes
In rare cases, the infection enters the periosteum through blood vessels or through inflamed tissue in the lymph nodes, such as with tonsillitis.
An indirect factor in the occurrence of periostitis may be concomitant diseases, decreased immunity, sore throat, acute respiratory infections, stress, etc. By the time a tooth hurts and a cheek swells, there is probably an accumulation of pus in the periodontal tissues. This process is quite dangerous for the body, as it can be accompanied by symptoms of acute inflammation:
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, body fatigue;
- headaches, local pain in the area of inflamed tissue;
- formation of a purulent fistula with access to the oral cavity or through the soft tissue of the cheek;
- increased pain symptoms at night or when trying to chew.
If caries can be ignored, then with periostitis, patients simply “fly” to the dentist for help. The course of the disease can be so acute that there is no way to tolerate it. The specialists of the LeaderStom network of clinics have extensive experience in treating periostitis. With such a diagnosis, therapy is required not only for the tooth itself, but also for the entire body. Therefore, be prepared to follow all doctor’s orders, take antibacterial medications and regularly rinse your mouth every half hour.
If you have a toothache or a swollen cheek, it is recommended to immediately seek help from a dentist, but if this is temporarily unavailable, the following recommendations will help you cope with the pain.
- If your cheek is swollen and your tooth hurts, you should not apply warm compresses or bandages to your face, as heat promotes even greater inflammation of the dental tissues and can cause complications.
- A cold compress should be applied to the affected side of the face.
- Be sure to take a pain reliever.
- Rinse your mouth several times with infusion of chamomile, sage, and St. John's wort.
- It is strictly prohibited to take anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics without a diagnosis of “periostitis” and a doctor’s prescription.
Causes of swelling of the cheek and gums during wisdom tooth growth
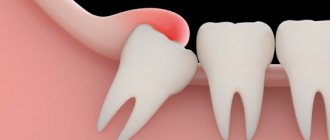
A “hood” appears over the erupting “third molar,” just like over any other tooth that begins to grow. It is a fold of gum, which, if the tooth is positioned correctly, should be cut by it, giving way for further growth. But, if there is a shortage of space, the “hood” remains. Residues of food can get there and, in combination with insufficient cleansing of the space closed by the gums with saliva, the growth of harmful bacteria occurs. As a result, an inflammatory process begins - pericoronitis.
This disease can be provoked by reasons related to external factors, or as a result of delaying the cutting process itself. The first case includes:
- Injury to soft tissues around a growing tooth by hard food particles or a toothbrush.
- The appearance of small ulcers or erosions on the gums.
Prevention
To prevent problems associated with wisdom tooth growth, the following measures should be taken:
- Timely visit to the dentist . Even in the absence of complaints, it is necessary to conduct an oral examination at least twice a year to identify possible diseases.
- High-quality teeth cleaning . Teeth should be brushed thoroughly twice a day for at least three minutes. Once every three months it is necessary to replace your toothbrush.
- Delivery of essential vitamins and minerals to the body . You need to eat foods rich in calcium, phosphorus and vitamin C.
Many experts recommend removing a wisdom tooth when it grows incorrectly. In this way, maximum treatment effectiveness is achieved. But patients are not always ready to take such a step, since there is an opinion that “a person cannot have extra organs.”
Indeed, the “eight” may prove useful in the future, when it is necessary to secure a denture if other teeth are lost.
The “third molar” is cut at a later age, which means it begins to deteriorate much later, which allows it to withstand the load of the prosthesis, which the rest of the teeth are no longer capable of.
Often, when the erupting wisdom tooth is potentially in the correct position, the doctor suggests getting rid of not the tooth, but the “hood”, which can lead to inflammation. This procedure is simpler and safer. For the patient under local anesthesia, the excess part of the gum is simply cut off. In the future, you will need to use antiseptic solutions and ointments prescribed by your doctor for some time. But the tooth will now be able to develop unhindered in the oral cavity.
When swelling is normal
Swelling after wisdom tooth removal is a consequence of:
- allergies to medications used during surgery or to sutures applied after wisdom tooth removal;
- purulent inflammatory focus, usually eliminated before surgery;
- severe traumatic damage due to difficult removal;
- infection of soft tissues during the procedure;
- non-compliance with doctor's instructions.
A swollen cheek after wisdom tooth removal can be caused by chronic diseases: hypertension, neuralgia, psycho-emotional disorders. Along with the cheek, the gums may also swell after wisdom tooth removal.
How long after wisdom tooth removal the swelling disappears depends on the nature and complexity of the operation. As a rule, it gradually goes away within 3-7 days. The pain after wisdom tooth removal is aching in nature and occurs due to a violation of the integrity of tissues, blood vessels, and nerves.
Negative sensations in the jaw after wisdom tooth removal often appear due to prolonged sitting motionless with an open mouth during surgery. If your gums hurt after wisdom tooth removal, it is recommended to take analgesics.
Blood after wisdom tooth removal is the result of damaged blood vessels. Within a few hours after surgery, the bleeding should stop. The temperature after wisdom tooth removal may rise to 37.5°C, but after a few days it should return to normal.
How much it hurts after wisdom tooth removal depends on the complexity of the surgical procedure. Typically, the healing period does not exceed a week.