Healthy gums are the key to strong teeth and a beautiful smile. Normally, they are pink, cover the alveolar processes and necks of dental units, and are not damaged. Based on their condition, the dentist can judge the health of the oral cavity.
Soft tissues are the first to react to negative changes occurring in the body. Redness of the gums is one of the main signs of inflammation. It can be associated with various factors - from drinking too hot drinks to the development of periodontitis. Find out if it is dangerous and in what cases you need medical help.
What is epulis
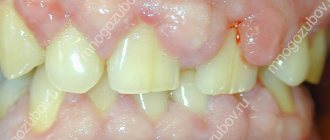
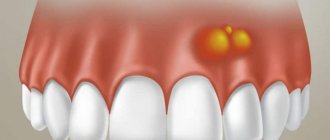
A tumor on the gum is characterized by a benign nature. It is classified as a group of periodontal diseases. Epulis is also called “giant cell granuloma” or “supragingival”. Epulis looks like a lump that is attached to the gum in the area of the interdental space on a stalk. A formation is formed from the epithelium of the alveolar process.
In diameter, an epithelial tumor of the gums can reach a size of more than 3 cm. The shade of a giant cell granuloma can be different: bluish, brown, red-brown, or the color of the gums. Ulcers may appear in the affected area.
If the epulis on the gum has a diameter of up to 2 cm, does not cause pronounced symptoms and progresses slowly, then the pathology is classified as a benign form. With rapid growth of the supragingival tissue, severe pain, inflammation and swelling of the gums, there is a risk of developing a malignant tumor.
According to statistics, the pathology is most often diagnosed in pregnant women, but supragingival formation also occurs in women who are not pregnant. Less commonly, the disease occurs in men and young children when replacing milk teeth with permanent ones.
What reasons can lead to its appearance?
The main cause of epulis on the gums is considered to be constant mechanical impact (rubbing) of soft tissues.
Injury to one area can cause gum swelling:
- poorly installed seal;
- uneven edges of the opposite tooth, which is destroyed or chipped;
- tartar;
- poor quality or incorrectly installed prosthesis;
- agonist tooth for malocclusion;
- adjacent teeth when teeth “pile up.”
Supragingival tissue occurs and, as a consequence, injury to epithelial tissue as a result of a burn, bruise or constant ingestion of irritating foods. In pregnant women, tumors occur due to hormonal imbalances. Epulis on a child’s gums can form due to general causes or disturbances in the eruption of permanent teeth.
Symptoms of the problem
You should consider the main diseases that cause redness of the gums and their distinctive signs:
Causes of gum inflammation
- Gingivitis. The disease is associated with damage to the tissue near the tooth by harmful agents. The main cause of the problem is improper oral care. Untreated gingivitis is complicated by periodontitis or periodontal disease, and tooth loss. The main signs are pain when eating and brushing teeth, bad breath, and fever.
- Periodontitis. In pathology, the soft tissues around the tooth are affected. The disease is acute with pronounced symptoms, as well as changes in pain intensity. The pathological process develops within 7-14 days. If not treated in a timely manner, periodontitis can lead to heart attack, stroke, loss of dentition, and intoxication of the body.
- Periodontal disease. During the disease, the tissues surrounding the teeth also become inflamed. A distinctive feature of the pathology is sluggish development. The problem occurs with hidden symptoms for several years, but ultimately leads to the loss of units. The main signs of periodontal disease: unsteadiness of elements, red growths on the gums, divergence of teeth in different directions. Untimely treatment of periodontal disease can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to inadequate chewing of food.
Types of epulis
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, epulis on the gums is divided into three main types.
- Fibrous. The gum tumor differs in density. Its base is coarse fiber fabric. The tumor grows slowly and asymptomatically.
- Angiomatous. Epulis angiomatous consist of epithelial cells and a large number of blood vessels. The tumor is localized mainly in the molar area. Due to the many blood vessels, even with a slight impact on the tumor, bleeding occurs. On palpation, the lump is soft and painful.
- Giant cell. The tumor formation can be large. Giant cell epulis affects the position of teeth, displacing them. Pain is not typical for this species, but bleeding is possible due to mechanical damage.
The development of giant cell epulis on the gum poses the greatest risk, since the likelihood of the tumor becoming malignant is much higher than with other forms of the disease.
Treatment options
You won’t be able to deal with the problem on your own using emergency methods alone. To prevent dangerous complications, a person will need to consult a qualified doctor. Before drawing up a treatment plan, the dentist will examine the oral cavity and, if necessary, recommend instrumental examinations - x-rays, panoramic photographs. Severe cases of the disease require an integrated approach - antibiotic therapy, the use of products for local treatment of inflamed areas and traditional medicine recipes.
Medicines for local treatment of the mouth
What to do if there is inflammation of the soft tissues of the mouth? The pharmacological industry offers a wide range of products to combat the problem, which are available in the form of sprays, ointments, gels and applications. All drugs are supplied with instructions for use. The specialist can adjust the frequency of use of the medicine, which is indicated in the instructions, depending on the severity of the problem and the form of its course.
If the gums are swollen and accompanied by bleeding, then antiseptic rinses are recommended for therapeutic purposes:
- Listerine. Use 2 times a day for 30 seconds. The course of treatment is 5-10 days.
- Stomatophyte. Use up to 4 times a day for up to 15 days.
- Furacilin - up to 3 times a day.
- Chlorhexidine. For periodontitis in adults, a solution at a concentration of 0.2% is prescribed; in children, swollen gums are treated with a 0.05% solution. Rinse your mouth after eating until the unpleasant symptoms disappear completely.
- Chlorophyllipt. Effectively acts against streptococcal infections. Before use, the solution is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1 tbsp. l. medications per 200 ml of liquid.
The effect of rinses is enhanced by simultaneous applications of healing ointments and gels.
The purpose of the applications is to apply medicinal agents to the gums under the film. The drugs create a protective layer on reddened areas and contribute to the death of pathogenic flora
Among the effective means for applications are:
- Periodontocyte, consisting of mint, oregano and sage;
- Gengigel with hyaluronic acid, due to which enhanced regeneration of lesions occurs;
- Stomatofit for pain relief of inflamed gums;
- Cholisal for the treatment of periodontitis in children and adults;
- Solcoseryl for pain relief in damaged areas and their speedy healing.
You can treat gum inflammation with special toothpastes. They are also used for preventive purposes. These drugs contain anti-inflammatory herbs and antimicrobial components. Among the best pastes, we should highlight: Lakalut, Mexidol phyto; The president. It is recommended to use these products for brushing your teeth for no more than 1 month.
Antimicrobial agents are used in rare cases, for example, when signs of intoxication of the body appear. Antibiotics not only suppress the signs of periodontitis, but also help restore the functions of all systems. Taking medications from this group is possible only with the permission of the dentist. The doctor selects the appropriate remedy and determines its dosage.
Traditional medicine recipes are used as additional drugs to medications in the treatment of gum inflammation
Natural remedies are allowed for both adults and children. For the latter category of patients, one-component recipes and products that do not contain bee products are selected.
Red gums are treated with the following recipes:
- Concentrated soda solution: 1 tsp. The product is dissolved in 200 ml of water. The mixture is used every 2 hours to treat red spots.
- Linden blossom: 1 tbsp. l. linden flowers are poured with 250 ml of cold water and left for 5 hours. The medicine is used every 4 hours to rinse the mouth.
- Fir oil. Used if there are bumps or bleeding wounds on the surface of the inflamed gum. A gauze swab dipped in oil is applied to problem areas for 15 minutes 2 times a day.
- Linden honey and a rusty nail. The recipe is used to remove boils and purulent abscesses. To do this, the nail is heated until red and placed in honey. A black substance forms around the nail and is used to lubricate the gums.
What to do with it: remove or treat
Epulis on the gums is considered a serious pathology that requires specialist help as early as possible. Delaying a visit to the doctor can cause complications. What treatment will be carried out depends on the type of disease and clinical picture.
Treatment always begins with identifying and eliminating the provoking factor. If the cause lies in internal processes, then therapy is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of epulis. When a tumor is caused by orthopedic or orthodontic structures, tooth damage, poor-quality restoration, etc., the cause is first eliminated. Professional teeth cleaning using a gentle method is mandatory. The dentist may prescribe the use of local antiseptics, hormonal drugs, antibiotics and other types of medications depending on the cause of the pathology.
In most cases, angiomatous and fibromatous epulis of the gums can be cured conservatively. After the causes of the pathology are eliminated, the tumor may begin to decrease in size and even disappear completely. Giant cell epulis is an indication for surgical treatment.
Emergency help for inflammation
What to do if your gums hurt? First aid to relieve symptoms is provided at home. It is recommended to regularly (once every 2 hours) rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions - furatsilin, baking soda, chlorhexidine.
To treat redness of the gums, ointments with an antiseptic and hemostatic effect are used.
The basic rule of emergency care is the exclusion of radical methods of treatment: such therapy leads to serious consequences. To stop the proliferation of pathogenic flora, herbal tinctures sold in pharmacies without a prescription are suitable - Givalex, Stomatodin, Mevalex. The products are used according to the instructions for use.
Removal of epulis on the gum
The need to remove the supragingival tissue occurs when the tumor is large, is growing rapidly, or is at risk of cancer. The procedure is complex and can only be performed by an experienced oral or maxillofacial surgeon.
Removal of epulis on the gum takes place under local anesthesia or sedation. The essence of the operation is to remove the lump and excise the affected tissue. Excision of the epulis itself can be done with a scalpel or laser. Dentists prefer a laser that can instantly stop bleeding and make precise “cuts.”
If the pathological process has penetrated deeply, it is possible to remove a section of bone using a cutter or bur. If teeth are damaged in the area where the tumor is located (loose teeth, exposed roots, etc.), the surgeon removes these teeth as well.
After the operation, the patient is covered with iodomorphic gauze. If there is a large area of dissection, the surgeon will apply sutures. A sterile bandage is applied over it.
In case of angiomatous and fibromatous appearance, removal of epulis on the gum can also be carried out if conservative therapy has not yielded results or the patient seeks help in the presence of complications.
Dentists' recommendations
Epulis is a gum tumor that poses a great danger to the health of teeth and the entire body. Treatment of the pathology is complex and lengthy, but even with high-quality treatment, the risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
It is not always possible to prevent the occurrence of epulis on the gums of a child or an adult, but with timely consultation with a specialist, complications, complex treatment, long recovery and aesthetic defects that remain after surgery can be avoided.
The best prevention is to visit the dentist every 6 months. If you are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of rubbing of the mucous membranes or gums, you should immediately consult a dentist, without waiting for a tumor or other pathologies to occur.