Reasons for the development of atheroma
Atheroma develops in those places where there is an accumulation of a large number of sebaceous glands - in the area around the nose, on the eyelids, neck, scalp, chest, back and earlobe. Atheroma behind the ear is the most common of all types of atheroma, and, as a rule, affects both men and women equally.
The occurrence of atheroma of the earlobe is characterized by an unpredictable course and frequency of occurrence due to constant rubbing of the tumor with foreign objects - various hats, scarves, headphones, collars of shirts and blouses. In medical practice, cases of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one are described, which occur in cases where proper surgical treatment is not carried out.
Diagnostics
Consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary first of all to exclude ear, nose and throat diseases. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient to specialists.
At your appointment, the ENT doctor will conduct a survey and examine the lump. To collect anamnesis, the doctor will check whether there is pain when pressing, whether there have been infectious diseases. In addition, he will take into account whether the bump behind the ear is soft or hard, whether it is pedunculated or tightly adjacent.
Next, the doctor will order a blood test to diagnose inflammation. To determine the cause of the tumor, an ultrasound or x-ray is performed.
What does atheroma behind the ear look like?
The reasons for the development of atheroma include the following factors:
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body.
- Harmful factors of external and internal ecology.
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Diseases of the endocrine system and hormonal imbalance.
- Increased production of sebum by the glands and oily skin.
- Infection of the sebaceous gland duct (during ear piercing, for example).
- Presence of acne and seborrhea of the scalp.
Factors that can trigger the appearance of atheroma include improper and insufficient hygienic care and hypothermia of the body.
Main causes of pain
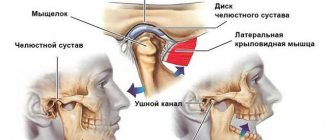
The human jaw is considered one of the most complex joints found in the human body. It represents the front part of the skull, consists of bones and nerve endings, and is involved in the process of chewing food, swallowing, and speaking. Therefore, when the jaw joint near the ear hurts, this can be a sign of a variety of pathologies.
There is a lymph node on both sides of the jaw; more precisely, they represent a paired symmetrical network, but it is in this area that the nodes responsible for the head and neck are located. If they increase in size and begin to hurt, you can suspect the development of an inflammatory process in the body.
Closer to the place where the upper and lower jaws meet, there is another organ - the ear. This organ is paired and is also penetrated by nerve endings and blood vessels. That is why, when the ear and jaw hurt on one side, this is not surprising.
The affected joint radiates pain into the auditory tube, and from there it is transmitted directly to the tissues of the jaw. In addition, pathologies of the teeth, trachea, internal organs, nasopharynx and larynx can cause discomfort. Being one of the most powerful and complex joints in the body, the jaw joint can become diseased due to degenerative changes in the osteochondral tissue (such changes are observed in osteoporosis).
Similar symptoms may be accompanied by inflammatory processes in the tissues of muscle fibers, which cause muscle spasms and pain when moving the head and jaw. There are many reasons why the jaw near the ear hurts, each of them requires its own treatment tactics.
Neuralgia and vascular diseases
Pain in the jaw joint, which is provoked by damage to the nerve plexuses, occurs for the following reasons:
Jaw displacement
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve - accompanied by burning pain, mainly on the right side and radiating to the ear;
- damage to the superior laryngeal nerve - occurs with severe pain in the lower jaw;
- inflammation of the glossopharyngeal nerve - accompanied by a sharp pulsation throughout the lower part of the face, starting from the root of the tongue and ending with the jaw;
- pathology of the occipital nerve - this disease is characterized by the fact that the pain is deceptive, radiating to the jaw when chewing and to the back of the head, closer to the ear.
Pain in the ear area, accompanied by radiation to the neck and lower jaw, also occurs due to vascular disorders. This affects the carotid artery, neck and half of the face on the right or left side.
Damage to the facial artery occurs against the background of sharp pain in both jaw bones at once, it is localized in the areas of the wings of the nose, lips, ears
Arteries are responsible for a complete blood supply to brain tissue, for the supply of necessary microelements and nutrients there, so any vascular disease can provoke blood flow dysfunction. Pain in the jaw area, radiating into the tissues of the face and ears, but in some cases becomes a harbinger of an upcoming cerebral hemorrhage - a stroke.
Dental diseases and injuries
If it hurts a person to chew, the gum tissue is swollen, and discomfort radiates to the ears, the cause may be periodontal and molar diseases:
- carious process;
- inflammation of pulp tissue;
- periodontal abscess;
- wisdom tooth growth;
- atrophic and necrotic changes in the gums, which led to the development of a purulent process;
- adaptation period after installation of removable dentures, braces and other structures;
- poor-quality treatment, removal or prosthetics of teeth.
Sometimes simultaneous pain under the ear and when opening the mouth appears after mechanical trauma to the jaw joint, for example, after a blow, bruise, dislocation or fracture. Dislocation can be caused by opening the mouth too wide while yawning, laughing, coughing or vomiting.
If the lower jaw is dislocated on the left side, then pain will be transmitted to the entire left half of the face, and, conversely, if the joint on the right is affected, sharp discomfort will be felt on the opposite side.
The most common cause of dislocation is weakness of the ligamentous muscles of the jaw.
Muscle weakness occurs when there is a lack of calcium in the body and due to age-related changes in cartilage tissue. Osteomyelitis often occurs when the jaw joint is dislocated. After mechanical damage to the jaw, during purulent processes and the formation of phlegmon in the soft tissue, when the tissues of the face are strongly blown in the cold, pain often occurs, radiating to the ear.
Diseases of the ENT organs
What to do if your jaw hurts near your ear, and the discomfort is accompanied by an increase in temperature? First of all, you need to visit an otolaryngologist, since such symptoms are typical for sinusitis and sinusitis. In this case, pain occurs in the eye sockets, temples and forehead, photophobia, and discharge of mucopurulent contents from the nasal passages.
Also, in addition to dental diseases and sinusitis, ear pathologies can provoke intense pain in the jaw area. However, the symptoms here can be deceptive, for example, in a disease called erythrootalgia, or red ear syndrome, redness of the paired organs is caused not by an inflammatory process, but by a displacement of 3–4 cervical vertebrae.
Pain in the left corner of the jaw can be caused by angina pectoris or an impending heart attack, and in the right corner - by an infectious process in the throat or sinus cavity. In addition to the source of infection, such symptoms are characteristic of a tumor (osteogenic sarcoma) located inside the bone tissue.
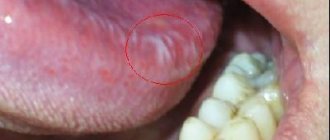
In addition to other ENT diseases, pain in the ear and jaw can be caused by glossitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue), sialolithiasis (damage to the salivary glands), hypersensitivity of the tongue and neoplasms in the larynx
Joint pathologies
Pain in the temporomandibular region can also be caused by pathologies treated by an orthopedist - arthritis, arthrosis and osteoporosis. During a comprehensive diagnostic examination of the body, pathological changes in bone tissue will be recorded not only in the jaw, but also in the elbow and knee joints.
This fact will make it possible to differentiate pain in the jaw near the ear, caused by arthrosis and arthritis, from that caused by dental or neurological problems.
Arthritis is a pathology that develops when there are disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Disease of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint) is usually of an inflammatory nature. But arthrosis occurs against the background of degenerative changes in osteochondral tissue.
These changes do not always occur due to age; sometimes the culprit is a serious pathological process of damage to the intervertebral discs and other joints. In this case, pain appears in the morning or during physical activity.
Symptoms of atheroma
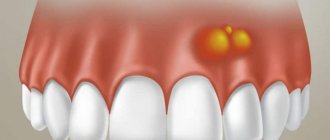
Typically, atheroma reaches from 5 to 40 mm in size. In the initial stages, until infection sets in, atheroma may not bother patients. If suppuration occurs or the atheroma increases in size, the following symptoms may occur:
- Pain and redness in the area of atheroma.
- Swelling and increased body temperature.
- Burning and itching in the area where the atheroma is located.
- Feeling of free fluid when pressed.
In some cases, these symptoms of inflammation disappear within 10-15 days, after which the nature of the tumor changes. It becomes more dense, homogeneous and immobile. This occurs due to the replacement of the secretion of the sebaceous glands with connective tissue cells. At this stage, atheroma can give active growth, but can also remain in an unchanged position for several years. Metastasis to other organs is not observed in atheroma.
If a person’s immunity has enough strength to cope with the infection, then the atheroma spontaneously opens, as a result of which its contents drain from the cavity. This may be secretion from the sebaceous glands mixed with blood and pus. There is nothing wrong with this, except for the fact that after the autopsy, unsightly scars and scars remain on the body.
Of course, the presence of tumors such as atheroma of the earlobe or other area of the body should be an indication for surgical intervention and removal, since the tumor can grow into adjacent tissues and organs, as well as become inflamed as a result of a secondary infection.
Does your child need specialist help?
You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone
8-(4822)-33-00-33
or using the online registration system on the website
To make an appointment with a doctor
Read also: Dermatitis in children
Parotid fistula
Occurs when there is an intrauterine disorder in the formation of the hearing organ. A fistula is a canal that opens behind the ear in the area of the cartilaginous part of the auricle, and the other end goes into the oral cavity, middle ear or neck area. A lump at the site of the fistula outlet is formed only when the tissues of the canal become inflamed.
Treatment and prevention of atheroma
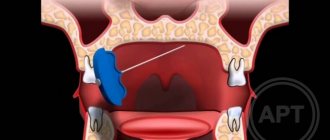
Treatment of atheroma is predominantly surgical, with removal of the cavity along with its contents. To do this, a small skin incision is made on the body, through which access to the atheroma is provided. After removing the contents, the cavity is washed, and if necessary, a turunda is inserted for several days to facilitate the release of blood, pus and fat.
The operation is performed not in a hospital setting, but on an outpatient basis. Local anesthesia is used for pain relief. For small atheromas, sutures are not applied, since the skin incision heals on its own after 5-6 days. For large atheromas, cosmetic sutures are applied, which are regularly processed after 1-2 days. The operation itself is painless for the patient, but the danger is that without eliminating the causes that caused the appearance of atheroma, there is a high probability of relapses (almost 50% of all cases). That is why it is so important not only to eliminate the cause of atheroma, but also to take measures to prevent the disease. These include personal hygiene measures and early consultation with a doctor. It is not recommended to treat atheroma on your own.