Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes) is an acute or chronic inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can be caused by both cancer and infectious diseases. Antibiotics for swollen lymph nodes are used to treat a bacterial infection. To identify the root cause, histological methods, physical examination data and laboratory blood tests are used. The prognosis depends on the patient’s health status, concomitant diseases and the nature of lymphadenitis. Antibiotics are not always required for swollen lymph nodes.
Features of the disease
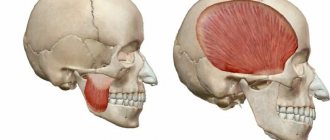
Lymphadenitis is a very common pathology, during which inflammation develops in the lymph nodes.
To understand the etiology of the disease, it is necessary to understand in more detail the physiological processes occurring in the human body. Lymph nodes represent a kind of barrier that restrains the spread of pathogenic microflora from the nearest focus of the inflammatory process throughout the system. However, there are cases when the lymph node itself becomes a source of infection in the event of suppuration. As a result, patients often require hospitalization and possibly surgery. It is quite difficult to obtain statistical data regarding the prevalence of pathology. The fact is that the disease often becomes a complication of other pathologies, for example, tonsillitis or purulent wounds, and its course is not very difficult. In such situations, therapy is aimed at the underlying disease, and lymphadenitis disappears without specific treatment. Therefore, patients with a very serious degree of pathology, which already requires serious medical and often surgical intervention, turn to a specialist.
Is it possible to use traditional methods for treatment?
The craze for traditional medicine is bearing fruit. People are trying to replace pills with natural remedies. Alas, advanced lymphadenitis cannot be cured by this. Traditional methods can become an additional way to treat the disease in the initial stages of lymphadenitis and only in consultation with a doctor.
If you are undergoing treatment at the dentist, then take on board the following remedies to help cope with inflammation:
- ginger tea;
- compress with echinacea tincture;
- blueberry drink before meals;
- beet juice;
- vitamin C.
These remedies will help strengthen the body and activate forces to fight the disease. At least they won't do any harm.
Important: do not use traditional medicine without medical supervision. Not a single folk remedy can cope with purulent inflammation. As a result, you will still see a doctor, but it will take longer to be treated.
In the worst case, self-medication will lead to the appearance of chronic lymphadenitis - the accumulation of disease in the lymph nodes. In this case, the lymph nodes will become dense and painless. But the inflammation has not gone away - it is “dormant” and waits for the hour to strike the body with an acute attack under favorable conditions.
Causes of pathology
As already indicated, in the vast majority of cases, inflammation occurs as a complication after an infectious process that has already been suffered.
This occurs for physiological reasons, when pathogens are carried by the lymph current to the nearest lymph node. If the body functions correctly and appropriate therapy is carried out, then the bacteria arrive there already in a weakened or killed state, or die directly in it. In this case, inflammation does not develop further. However, if the process is not stopped and the pathogen is very active, then inflammation is already developing in the node itself. In such a situation, lymphadenitis is secondary. However, there are cases when the pathology is primary.
This can occur as a result of trauma to the lymph node area, during which the strain penetrates through the site of injury. It should be noted that such pathologies are very rare and occur against the background of reduced immune defense. The cause of nonspecific lymphadenitis in most cases is staphylococcal and streptococcal infections .
The nodes enter through the flow of blood or lymph. The most common foci of primary inflammation include: carbuncles, boils, infected wounds, thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis and others. A specific type of pathology is caused by a special type of pathogen that provokes the appearance of specific diseases, for example, gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis, plague, anthrax and others. In such situations, the localization of the inflammatory process occurs in the node closest to the site of infection. So, in case of a sexually transmitted disease, the inguinal nodes are the first to react.
How to recognize lymphadenitis?
The inflammation initially develops asymptomatically. But soon, characteristic signs of lymphadenitis appear:
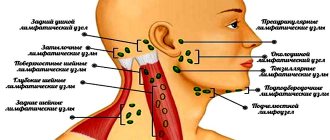
- enlarged lymph nodes under the lower jaw, pain when touched;
- redness of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- swelling;
- attacks of throbbing pain;
- insomnia;
- difficulty swallowing;
- heat;
- weakness;
- increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood.
Of course, these symptoms do not appear in 1 day. And many people ignore the appearance of mild pain. But if you do not consult a doctor at this time, the picture of the disease will become obvious in just 3 days. The lymph nodes will become inflamed, swollen, and the edema will gradually cover the entire submandibular surface. Patients become lethargic, complain of fatigue, weakness, and high fever. They cannot eat because the inflammation prevents them from opening their mouth normally and sleeping due to pain and fever.
If you continue to ignore the symptoms and postpone a visit to the doctor, the inflammation will become purulent, which will result in blue swelling and increased pain. To prevent this from happening, you should contact a dental surgeon at the DaVinci aesthetic dentistry studio.
The sooner the patient contacts the dentist, the easier it is to eliminate the infection. But many people themselves try to diagnose themselves and choose treatment, which leads to the spread of inflammation and aggravation of the above symptoms. Treating the disease in advanced stages is more difficult and takes longer.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes
To understand which antibiotics should be used for a particular pathology, it is necessary to pay attention to certain factors. There is clinical evidence that in most cases, nonspecific lymphadenitis is caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal microorganisms. That is why it is customary to prescribe antimicrobial agents that are most effective against them.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the severity of the disease, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Despite the fact that lymphadenitis has a very clear clinical picture, its features vary somewhat from patient to patient. Elderly people, young children and patients with chronic decompensated conditions are very prone to the formation of sepsis, which may well be fatal. Therefore, in such situations, a more powerful medication, or a combination of both, is often prescribed.
A characteristic feature of each type of antibiotic is the place where they accumulate. Due to the characteristics of the disease, it is preferable to use a product with a concentration in the human lymphatic system. For the best effect, it is also recommended to take into account the patient’s medical history and medication history. If a few months ago the patient already underwent antimicrobial therapy, then it is necessary to select a drug from a different group.
Modern tactics for treating pathology involve dividing drugs into first and second lines. Initially, safer drugs with a broad spectrum of action are prescribed. However, if they turn out to be ineffective or cause an allergic reaction, then you have to move on to second-line drugs.
For lymphadenitis use:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- lincosamides;
- aminoglycosides.
Penicillins
This class of antimicrobial agents was found earlier than others and has been widely used in medical practice for many decades. They have a very wide spectrum of bactericidal effects. However, due to long-term use, many pathogens have developed resistance to these medications.
Rules for taking antibacterial drugs
Antibiotics are among a number of drugs, the use of which is strictly prohibited without a doctor’s prescription, as they can lead to the development of serious side effects. In addition, the choice of antibacterial agent depends on the pathogen, so the patient cannot choose it independently.
Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed for lymphadenitis in a course. The minimum duration of therapy is five days, the maximum is four weeks. It is prohibited to discontinue the drug before completing the full course, because this can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of sepsis.
It is advisable to take the antibiotic at the same time, so that equal intervals are maintained between doses. If for any reason the time was missed, then the tablet must be taken as soon as possible and then continue the course as usual. You can take the drug only with clean water; any other liquid can affect the absorption of the active substance.
When is antibiotic therapy required?
First of all, you need to see a therapist
Antibiotics for severe inflammation of the lymph nodes are prescribed by a lymphologist, immunologist, oncologist or endocrinologist. First, you always need to contact your family doctor, who will write a referral to a specialist.
For patients with lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), treatment depends on the pathogen and may include watchful waiting, antibiotic therapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Waiting is used when the lymph nodes are smaller than 3 cm, are not characterized by redness of the skin and have been present for less than 2 weeks.
Antibiotics for severe inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck are used when the lymph nodes are more than 2-3 cm in size, thicken only on one side, and are characterized by excessive pain and redness. Antibiotics should target common infectious causes of lymphadenopathy: Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci.
Due to the increasing prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, antibiotic therapy with Clindamycin is recommended for enlarged lymph nodes.
What antibiotics can you take during pregnancy?
The period of waiting for the birth of a child is very important in the life of every mother, and the main task of the therapist when prescribing treatment is the safety of the fetus and the woman. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly understand what is prescribed for inflammation of the lymph nodes during pregnancy and lactation.
In most cases, penicillins are used for antimicrobial therapy. They are allowed to be used at any stage of pregnancy, including the first trimester. However, the prescription must have clearly defined indications.
For infections of the respiratory tract, urinary system and ENT organs, beta-lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins are used in most cases. In some cases, the use of Erythromycin is permitted.
What antibiotics are prescribed for children?
Lymphadenitis in children develops in childhood in most cases as a result of infectious lesions of the respiratory tract, and they, in turn, are accompanied by respiratory viruses.
Uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents for respiratory infections in children often leads to the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Due to the improper use of antibiotics, children may experience dyspeptic symptoms. In severe cases, it can lead to acute liver failure, enterocolitis or erythema multiforme.
Prescription of antibiotics is necessary for:
- bacterial pneumonia;
- meningitis;
- infections of the genitourinary system;
- purulent tonsillitis.
In childhood, the use of Cefuroxime and Amoxicillin is permitted. The first is used to destroy streptococcus, pneumococcus and staphylococcus, which often cause inflammation of the throat and mouth. The second belongs to the class of penicillins and is widely used in the treatment of tonsillitis, infections of the ears, nose and throat, as well as inflammation in bone tissue and the bloodstream.
How to prevent lymphadenitis?
Few people want to experience the symptoms of lymphadenitis. And to prevent inflammation from attacking you, follow simple rules:
- Treat all oral diseases in a timely manner, to do this, contact your dentist once every six months (online appointment) for a preventive examination;
- avoid injuries and scratches in the jaw area;
- treat all wounds with antiseptics.
DaVinci Aesthetic Dentistry Studio will help cure lymphadenitis at any stage. But we would be even more happy to help you warn him.
Add a comment