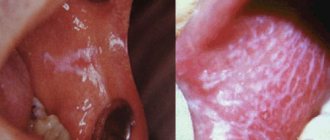
Stomatitis of various etiologies
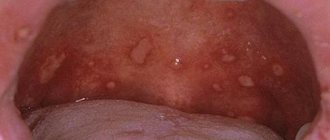
The oral mucosa becomes inflamed with stomatitis. Whitish spots are located on the inner sides of the cheeks, on the gum tissue. Without therapeutic measures, painful ulcers will quickly appear. Such children exhibit restless behavior, fever, loss of appetite, and disturbed sleep. The disease may be:
- Viral, when it occurs against the background of influenza, chickenpox, bronchitis and other diseases;
- Allergic, if the baby develops asthma, atopic dermatitis appears;
- Bacterial, when the little one picks up some kind of infection, for example, a fungal one;
Purulent cyst
A white spot on a child's gum may indicate the development of cysts. They look like beads. Occurs against the background of infection of the body. A formation with purulent contents is detected on x-ray. Most often, the disease is caused by bacteria that penetrate into the chewing organs or soft tissues. This happens with complicated caries. When the accumulated pus begins to come out, swelling appears. If you do not visit the pediatric dentist on time, the pus accumulates, then the abscess breaks out, and the little one develops a fistula. Don't ignore rashes in your child's mouth! Contact your doctor promptly!
Lipoma and leukoplakia
With leukoplakia, keratinization of the mucous membrane is noted. This process is influenced by the following stimuli:
- sharp edges of affected teeth;
- hanging uneven fillings;
- hot and spicy food;
- malocclusion;
- improperly fitted dentures;
- crowns made of various materials;
With this disease, whitish plaques may have clearly defined edges or blurred ones. There is no discomfort. The rash may be rough, cracks and ulcers may appear. The doctor will take a sample of this tissue to send for a biopsy. Often the formation turns out to be a harmless lipoma, that is, a wen. It requires medical supervision. It is important that its size does not increase.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
This is an infectious viral disease that occurs in response to primary contact with the herpes simplex virus.
Infection occurs
- by airborne droplets;
- through contact and household means (through toys, dishes, etc.);
- from persons suffering from recurrent herpes.
Children aged 6 months to 3 years are most often affected.
Main signs of the disease:
redness of the oral mucosa and blisters appear, which quickly open and form multiple painful round ulcers (erosions), bleeding gums; increased body temperature, general weakness, intoxication; the child eats and sleeps poorly.
To prevent the spread of infection
a child with acute herpetic stomatitis is not allowed to visit a child care facility, even if the disease occurs in a very mild form.
Prevention of infection with the herpes simplex virus upon contact with sick people involves lubricating the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth with 0.25% oxolinic ointment for 5 days.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
Treatment of white spots on gums
The first thing parents need to do is visit a pediatrician. If necessary, the child will be referred to a dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the factors that provoke the disease are determined. Depending on your age, the doctor will carry out therapeutic measures.
- In case of improper hygiene, the mother will receive professional recommendations.
- When pimples are a consequence of vitamin deficiency, the nutrition of the mother and child is adjusted. You should drink enough liquid.
- Congenital masticatory organs, if they are mobile, are removed.
- Pathological diseases are treated with modern methods.
- The toddler should be protected from anxiety and stress.
- Stomatitis is treated with antiseptics, for example, Miramistin. The drug is prescribed by a doctor.
- Candida fungus is eliminated with drugs such as Flucostat. The baby's mouth is treated with chlorhexidine.
- If there is a lack of calcium, the necessary minerals are prescribed.
You cannot puncture the blisters yourself. The gum tissue may be damaged. After all, with such a procedure, infection can easily occur.
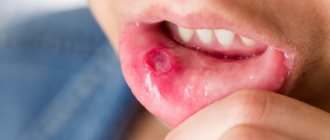
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis
This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, characterized by periodic exacerbations and remissions.
Causes of the disease:
- allergic reactions in a child;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory infections;
- functional disorders of the central and autonomic nervous system;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx (otitis, sinusitis, etc.)
School-age children and adolescents are more often affected.
Main signs of the disease:
on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (usually lips, cheeks, transitional folds of the upper and lower jaws, the lateral surface and back of the tongue) one or several areas of redness with rounded painful aphthae covered with a yellowish coating appear; the child’s general condition may deteriorate, the child refuses to eat; healing occurs with adequate treatment after 5-7 days without a scar.
In order to prevent exacerbations of the disease, it is necessary:
- regular visits to the dentist (at least 2 times a year);
- elimination of foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity (treatment of carious teeth and periodontal diseases);
- systematic hygienic oral care.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
Reasons for appearance
Opportunistic bacteria are part of the oral microflora of every person. Age doesn't matter here. Thrush appears when fungi, like yeast, become active and exceed the permissible number. Also, pathology is formed when pathogenic strains enter the patient’s body. The reason that leads to problems may be internal. Also, negative environmental factors influence deterioration of health. Often, anomalies are caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, intestinal problems and others.
To prevent serious complications, you should consult a doctor promptly. A dental clinic that has modern equipment and uses the latest technologies will help you understand the problem and eliminate it. Advances in dentistry allow you to achieve results quickly. Having identified the true cause of the problem, the dentist will draw up a treatment plan. The problem will be solved when the provoking factor is eliminated.
Candidiasis in the oral cavity
This inflammatory disease is often diagnosed in children. It can affect a newborn. The basis of the disease is pathogenic fungi. They provoke damage to the mucous layer, and the uvula suffers. Candidiasis is suppressed by the defenses of a healthy toddler. But when fungi multiply quickly, the immune system cannot cope with them, as it weakens. The pathology progresses against the background of the following problems:
- Inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- Colds;
- Hormonal instability;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics;
Children's fragile immunity cannot withstand negativity. All this leads to imbalance. White palate in a baby’s mouth can appear due to severe stress, which reduces the body’s immune strength. The growth of fungi is provoked by excessive dryness of the mucous membranes and an imbalance of acid balance. The first sign of damage to the mucous membrane is itching. At risk are those guys who wear braces, are treated with hormonal drugs, and do not clean their chewing organs well. The disease develops especially quickly when unfavorable factors are combined. The baby's mucous membrane is covered with a cheesy film. Whitish crumbs are difficult to remove; ulcers form underneath them. They may bleed.
Infectious lesions
When the body's resistance decreases, the appearance of pathogenic bacteria is often associated with the appearance of one or another infection. As a result, white spots develop on the palate.
- Fungal strains are highly infectious. Pathogenic microbes quickly colonize the damaged mucosa.
- With scarlet fever, the baby's mouth turns red, a rash appears, and the temperature rises.
- With diphtheria, the film has dirty inclusions.
- With whooping cough, a putrid odor from the mouth is clearly heard.
- With dysentery, the layer is dense, and erosions appear underneath it.
Oral diseases
Oral problems cannot be ignored. Parents should immediately show the toddler to the pediatrician, who will refer the child to the dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the exact cause of the disease is determined and a treatment regimen is developed. Specialists know how to work even with the smallest children. Problems in infants can develop due to dental diseases. Most of them are characterized by inflammation, swelling, the appearance of a film and ulcers. The source of infection is pathogenic bacteria. The main diseases include:
- Stomatitis, in which whitish sores with clearly defined edges appear. Children experience discomfort and refuse to eat. The disease progresses when the mucous membrane is damaged, there are not enough vitamins, allergies develop, and the body's defenses decrease.
- Gingivitis, when the gums and other soft tissues of the mouth are affected.
- Caries, with the active development of which white matter is diagnosed in the oral cavity in large quantities.
Stomach and intestinal problems
In pediatric practice, white spots on the palate of a child are quite common. The provoking factor is diseases of the digestive tract:
- Gastritis, which is characterized by inflammatory processes of the gastric mucosa. In addition to whitish deposits, patients experience pain, spasms, and stool disturbances.
- Dysbacteriosis, which is manifested by bloating, weight loss, problems with stool.
- Enterocolitis, in which, in addition to a film in the oral cavity, accumulation of gases and spasms of the gastrointestinal tract are diagnosed.
Candidiasis (thrush)
This is a fungal disease that occurs as a result of the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida on the oral mucosa.
Transmission of a fungal infection to a child is possible:
- during passage through the birth canal of a mother suffering from candidomycosis;
- through contact and household means (through pacifiers, underwear and other items for caring for the newborn).
Weak children in the first weeks of life are more likely to get sick.
Main signs of the disease:
the disease begins asymptomatically, and then the child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly. Regional lymph nodes may be enlarged, body temperature is normal, but may also be elevated, a plaque in the form of white dots appears in the oral cavity on the mucous membrane of the cheeks along the line where the teeth meet; on the palate, lips, and tongue; As the fungus multiplies, the plaque increases in size, forming a film resembling curdled milk.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary to promptly treat thrush in women during pregnancy and maintain a healthy gastrointestinal tract in a young mother; observe sanitary and hygienic measures in maternity hospitals and at home, sterilize pacifiers and bottle nipples.
Prevention
in children is the timely detection and treatment of dysbiosis, and with long-term prescription of antibiotics - timely administration of probiotics.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
Treatment of white plaque on the palate of a child
The white spots will disappear if the cause of the problem is eliminated. If you regurgitate frequently, for example, you should change your feeding method and sterilize your utensils. A small area of fungal infection is treated with topical preparations. Severe forms of the disease are treated medicinally using complex drugs. Fungal diseases are dealt with:
- Clotrimazole;
- Candide;
- Pimafucin;
- Fluconazole;
- Diflucan;
A sterile gauze ball is moistened with the solution. They gently wipe the oral cavity several times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the complexity of the situation. Treatment usually lasts 7-10 days. Irrigation or lubrication is also prescribed. To boost the body’s defenses, doctors recommend vitamin complexes and probiotics for children. This will restore the natural microflora in the intestines.
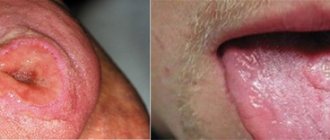
Afta Bednara
This is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, occurring in weak, bottle-fed infants in the first months of life.
Causes of the disease:
- permanent mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the palate due to a nipple that is too long and too hard;
- may occur in breastfed children if the mother's nipple is very rough.
Main signs of the disease:
round or oval erosions, covered with loose plaque and located symmetrically at the border of the hard and soft palate, redness of the surrounding mucous membrane. The child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary
promptly replace the pacifier or pacifier if irritation occurs on the oral mucosa.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
If any changes appear on the oral mucosa, you should visit a pediatric dentist to avoid complications and conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment!!!
Symptoms
The origin of a particular sign can be established based on a complete picture of what is happening. And it can be compiled during a comprehensive examination, the first stage of which will be a survey, examination and other physical methods (for example, palpation). This will provide an opportunity to make a preliminary conclusion and reassure worried parents.
Bon's knots
Bohn's nodules are small (up to 3 mm in diameter) cysts formed from the rudiments of the salivary glands. They have a spherical shape and are located on the soft palate. One or more similar formations are detected in the baby, but over time they will disappear on their own. The nodules do not cause any discomfort.
Prevention
Everyone who gives birth should know how important hygienic cleaning of the child’s oral cavity is. This procedure cannot be ignored. It can prevent many dental diseases. Therefore, do not miss visits to the dentist! Only a doctor can notice problems at an early stage. Treatment started on time will be faster and easier.
Compliance with preventive measures minimizes the risk of pathology. During the period of bearing a child, the expectant mother needs to take care of her health, pay close attention to oral hygiene procedures, and not introduce into the diet those foods that create a favorable atmosphere for the activation of fungi. Prevents problems:
- Refusal of artificial feeding, transition to breastfeeding;
- Before feeding the baby, the breasts should be treated with a solution of baking soda;
- Pacifiers, pacifiers, and bottles should be sterilized;
- After the baby has eaten, you need to give him boiled warm water to drink, which will wash away the remaining milk from the mucous membrane.
Causes of black plaque on the tongue in adults
“Stick out your tongue” - probably everyone has heard this phrase in the doctor’s office. “Why is it so important for a doctor to see a patient’s tongue?” – patients are lost in conjecture. The doctor will determine whether the tongue is clean or coated, and can suggest a diagnosis based on the nature and color of the plaque. Dark coating on the tongue is a sign of what disease? Do not be afraid of the appearance of a strange shade of the mucous membrane of the tongue. The reasons for the color change may be temporary and completely harmless.
Causes of black plaque on the tongue in adults:
- changes in bacterial flora after a course of antibiotics;
- poor oral hygiene;
- xerostomia;
- glossitis;
- regular use of mouthwashes containing irritating oxidizing agents;
- smoking or chewing tobacco;
- drinking excessive amounts of coffee or black tea;
- alcohol abuse.
What does brown coating on the tongue mean? Discoloration usually occurs when the papillae on the surface of the tongue grow larger than normal. The waste products of microorganisms accumulate between them, which leads to an unpleasant tint of the tongue. If the root of the tongue is covered with a green coating, the cause may be oral candidiasis (thrush). When taking antibiotics or eating “colored” foods, the white-gray coating characteristic of thrush can turn different shades of green.
What does a red coating on the tongue mean:
- about a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12, which causes a reddish tint;
- about “geographic tongue” (benign migratory glossitis), which is characterized by the appearance of reddish spots on the surface of the tongue;
- about scarlet fever, one of the symptoms of which is “strawberry tongue.” Read more about the symptoms and treatment of scarlet fever on our website Dobrobut.com;
- about Kawasaki syndrome, observed in children under the age of five and characterized by damage to the blood vessels. The syndrome is accompanied by redness of the tongue (“strawberry tongue”).
How to deal with tongue coating
Thorough cleaning of the tongue is the main hygienic measure aimed at eliminating plaque. Clinical trials have shown that regular tongue cleaning reduces bacteria and bad odor by 75%.
How to get rid of dry mouth and white coating on the tongue:
- use a special scraper - effective tongue cleaning reduces plaque by 40%;
- drink enough water;
- eat foods containing coarse fiber (for example, apples, carrots);
- quit smoking;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages;
- Healthy food;
- rinse your mouth after eating.
By following these simple rules, you can forever “say goodbye” to the coating on your tongue and forget about bad breath.
Related services: Pediatrician consultation