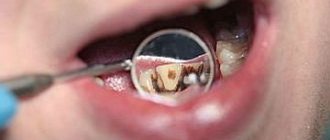
Dental injuries are a common problem in dentistry. Tooth dislocation is an injury that results in damage to the ligamentous apparatus and the tooth being displaced in its socket (photo below).
Tooth dislocation is accompanied by:
- severe pain
- bleeding
- soft tissue swelling
- appearance of tooth mobility
- change in enamel color
The causes of such injury may be:
- mechanical damage (due to impact from a fall, for example);
- biting hard food, hard objects in food;
- bad habits (crunching nuts in the shell, opening bottles with your teeth, etc.);
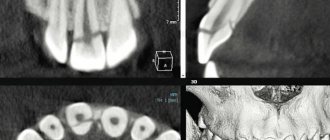
The diagnosis of tooth trauma (including tooth dislocation) is made based on symptoms and x-ray examination. The doctor not only determines the clinical picture, but also assesses the condition of the bone tissue at the site of dental injury. Tooth dislocation has its own types (complete, incomplete, impacted) and treatment features.
Tooth dislocation: photos and symptoms
Any injury has its own clinical picture. Tooth dislocation, photos of which can be viewed on dental websites, is also characterized by specific symptoms. During the examination, the dentist looks for signs to diagnose a luxated tooth.
The doctor also determines what type of tooth dislocation the resulting tooth is. The symptoms of each are slightly different. After analyzing the x-ray, treatment is usually prescribed.
Causes of dental injuries
Damage to baby teeth can be caused by any strong force applied to the jaw. For example, if a child was running and accidentally fell with his cheek on some object (chair, curb, step), this may well lead to a bruise or fracture of a tooth. Acute injuries also occur from blows to the face when children fight or play sports like boxing and karate.
Based on the nature of the acquisition, the reasons are divided into household, sports and travel. They are sudden and very painful. There are also chronic injuries that occur due to long-term bad habits. Biting nails, felt-tip pens, ballpoint pens, threads while sewing, or cutlery thins the enamel. Thin, fragile enamel and caries of baby teeth become the main factors of toothache in a child.
Types of tooth dislocations. Complete, incomplete and impacted tooth dislocation - what are the differences?
To determine what type of dislocation - complete, incomplete or impacted - the injury belongs to, you should pay attention to their differences in symptoms.
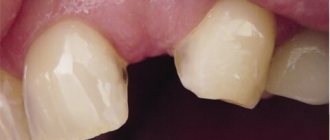
- Complete tooth luxation (photo below) is characterized by the tooth falling out of its socket. And if he is held in it, then only due to soft tissues.
- Incomplete tooth luxation is characterized by partial displacement of the root in the alveolus. Upon examination, it is noticeable that the tooth is tilted either towards the tongue, or back, or towards the cheek, or towards the lip.
- Impacted tooth dislocation is a rare type of such injury. With it, several teeth often suffer at once, which seem to go deep into the alveoli. An impacted tooth dislocation is visually recognized by a decrease in the height of its visible part (photo below). This injury leads to destruction of the jaw bone.
Complete tooth luxation, incomplete tooth luxation and impacted tooth luxation differ not only in symptoms, but also in the methods used in their treatment.
Prevention
Prevention of tooth dislocation includes:
- Explanatory work with employees of industries associated with increased injuries. Each employee is required to comply with safety regulations, which provide for an algorithm for performing certain actions and the use of protective devices.
- Explaining to parents and children the rules for arranging playgrounds and behavior on them, familiarizing themselves with possible types of injuries and methods of providing first aid if they occur. Parents should supervise young children during play.
- Educational work among the population about the need to comply with traffic rules by drivers and pedestrians, as this is necessary not only to reduce the level of injuries, but also to save lives.
- Compliance by medical personnel with the rules for performing dental procedures.
- Avoiding bad habits: you need to use special tools to open bottles and crack nuts.
- Avoiding situations that could lead to a fight; if it does occur, during it you need to tense your masticatory muscles and keep your teeth closed: this will help avoid not only dislocation of teeth, but also a fracture of the jaw.
- Providing a high level of protection for athletes involved in traumatic sports (hockey, boxing). For this purpose, helmets with full face protection and mouth guards are used (molded, which have a ready-made shape, and molded - after heating in hot water, they take the individual shape of the teeth).
Impacted, complete and incomplete tooth dislocation What treatment is needed?
Experts note that in most cases, injured teeth can be saved. The main thing is to see a dentist in time.
If an impacted tooth luxation is diagnosed, treatment is not always required, since the tooth often returns to its previous position on its own. But sometimes the damage is so severe that this does not happen. If just such an impacted tooth dislocation occurs, treatment is prescribed as for incomplete dislocation. Tactics for impacted dislocation can be different, it all depends on the degree of damage to the bone tissue and the severity of the injury.
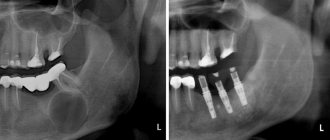
If a tooth is completely dislocated, treatment should begin immediately. It is advisable to insert the fallen tooth into the hole and get to the dentist as quickly as possible. The tooth must be placed in milk or held behind the cheek. If the replantation of a tooth after a complete dislocation is done within 2 hours, then the tooth will be completely engrafted without any consequences.
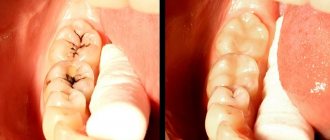
Treatment for incomplete tooth dislocation consists of repositioning the tooth to its previous position, fixing it with a splint; if the pulp dies, the canal is treated and filled.
If you still can’t save the tooth, you can get prosthetics or implantation.
Restoration of teeth after injury by our experienced endodontists:
- extended warranty
- saving 79% of teeth with injuries of various origins
- painless restoration of tooth integrity on the day of treatment
- treatment using modern equipment under magnification and a microscope (fillings last 10-15 years or longer)
- high-quality diagnosis, not treatment by eye
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Additional treatments
Drug therapy
- When carrying out manipulations to reposition a tooth after dislocation, local anesthesia is used, for this purpose Ultracaine D-S, Ultracaine D-S Forte, Cytokartin, Septanest, Bupivacaine are used. But the effect of the anesthetic stops after some time, so painkillers from the NSAID group are prescribed: ibuprofen, nimesulide, ketorolac, dexketoprofen. Children are prescribed ibuprofen and paracetamol.
- To improve the condition of the gums after injury, use: Dentol Gel - has a local anesthetic effect.
- Gel Metrogyl Denta - contains two antibacterial components, eliminates inflammation.
- Kamistad gel is a combined drug: lidocaine has a local anesthetic effect, chamomile flower tincture produces antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects, thymol has an antiseptic effect.
- Solcoseryl dental paste - stimulates regeneration processes in tissues, thereby shortening the healing period of wounds of the mucous membrane. The composition also includes polidocanol, a local anesthetic.
Physiotherapy
After acute phenomena have subsided, the following are used to stimulate healing processes and eliminate tissue swelling:
- UHF therapy is the effect on the body of an alternating electric field with ultra-high frequency.
- Microwave therapy – uses alternating electromagnetic oscillations of ultra-high frequencies of various ranges (centimeter, decimeter and millimeter).
- Magnetotherapy is the effect of a low-frequency magnetic field on the injured area.
- Magneto-laser therapy is a complex effect of magnetic and laser radiation.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Dislocation
Luxation is a displacement of the tooth relative to the socket. The upper incisors are more often susceptible to dislocation. They are:
- complete – the entire tooth falls out;
- incomplete - the root partially moves out of the recess, rupture of periodontal fibers occurs;
- impacted - the tooth is partially or completely displaced from the socket towards the jaw, the connective tissue is crushed.
Signs of a dislocation are severe pain, mobility of one or more teeth.
Fracture
Divided into crown and root fracture. A fracture of the crown of a tooth within the hard tissue, as a rule, does not cause discomfort or pain, and complaints are associated exclusively with the presence of an external defect. If the pulp is affected, it is accompanied by pain, bleeding from damaged vessels and swelling. The most common fracture is the front tooth.
The root fracture is localized in the area of the tooth base and can be longitudinal, transverse, diagonal, comminuted with or without displacement of the fragments. This injury has its own signs:
- severe pain when trying to touch the gums;
- bleeding from the gums;
- edema;
- mobility of the damaged tooth.
Diagnosis of a root fracture includes a history, examination, and x-ray.
Chronic injuries
The reasons lie in bite defects, habits of holding or gnawing various objects with teeth, and peculiarities of the profession. Systematic harmful effects on enamel lead to thinning, chipping and gradual destruction.
Content:
- Classification of injuries 1.1. Bruise 1.2. Traumatic dystopia 1.3. Complete dislocation 1.4. Crown fracture 1.5. Root fracture 1.6. Combined lesions
Children actively explore the world around them and most often do not think about safety measures.
Hence the frequent injuries. Moreover, not only the arms, legs and forehead suffer, but also the teeth. Statistics show that about 30% of visits to a pediatric dentist are related to injuries to temporary units. Let's look at what types of injuries occur in children's baby teeth and how to treat them correctly.
Tooth crown crack
If you enter “What is trauma” into a search engine, then any site gives the concept of “damage, disruption of the unity, completeness of a tooth, disruption of its functions.” With such an injury as a crack in the crown of a tooth, this statement is not entirely suitable. And now I’ll try to explain to you why. Firstly, the unity of the tooth (its completeness) when the tooth crown is cracked is not violated: there is simply a violation of the structure (structure) of the tooth enamel.
The main symptoms that patients diagnosed with a cracked tooth crown present with are: unsatisfactory aesthetics, teeth reaction to sour/sweet, cold/hot.
Cracked tooth crown clinic
The clinical picture of a cracked tooth crown is as follows: externally, both the doctor and the patient see visible lines running parallel to the surface of the tooth - cracks in the tooth crown; secondly, if a tooth has a crack, then it can perform its function. Of course, it is not a fact that it will be 100%.
A crack in the crown of a tooth can be single, paired, multiple or combined.
A crack in the crown of a tooth can be vertical or inclined. Most often, a crack in the tooth crown ends in the area of the enamel-dentin junction. But with significant force, a tooth crack can spread not only to the crown, but also to the root of the tooth.
The clinic also described cases where a crack in the crown of a tooth was located on teeth whose neighbors had more severe tooth trauma.
Diagnosis of a cracked tooth crown
Patients with a crown crack are not sent for an x-ray, as this is not necessary. But for high-quality diagnosis of tooth crown cracks, transillumination (transillumination) is currently used.
Treatment of a cracked tooth crown
Cracks in the crown of a tooth do not require treatment. But in such cases, the doctor needs to make sure that the pulp is vital. You can do repeated tests for control within 6 months.