04.05.2018
The oral cavity connects the body with the environment and can therefore be subject to a variety of negative influences. Such influences include the influence of too hot or too rough food, the influence of pathogenic microorganisms. In such cases, the first protective barrier is the mucous membrane, which lines the entire oral cavity and has, in addition to protective ones, many other functions. The mucous membrane is well supplied with blood, and its cells divide quickly and frequently. Therefore, wounds on the mucous membrane heal faster than on other parts of the body. However, for a number of reasons, the mucous membrane can be subject to inflammatory processes called stomatitis. Stomatitis is considered separately from such inflammatory processes in the oral cavity as gingivitis (inflammation of the gums; they have their own characteristics) and periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium). The causes of stomatitis are very diverse.
Infectious causes
Stomatitis can be caused by infection with viruses or bacteria. In these cases, stomatitis is usually considered as an independent disease.
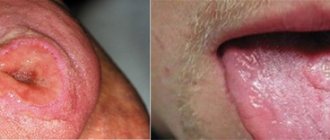
This is especially true for infection with herpes simplex viruses, which leads to very painful inflammation of the mucous membrane. There are two types of herpetic stomatitis - acute herpetic stomatitis (with primary infection) and recurrent herpetic stomatitis (which can pass through the acute stage or manifest itself as a general infection of the body in the presence of provoking factors). Herpetic stomatitis can lead to an aphthous form, in which erosions, aphthae, and even painful ulcers appear on the mucous membrane.
A specific type of stomatitis is chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, which begins almost immediately with the formation of aphthae, and the nature of which is not yet clear. But viral and bacterial infections and vitamin imbalances are also suggested as initiating factors.
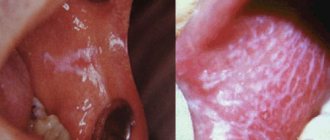
The specific infection that causes stomatitis includes a fungal infection (fungi of the genus Candida) and the disease itself is called candidiasis (thrush). Thrush is characterized by the formation of whitish dots on the mucous membrane, and as the fungal infection multiplies, a whitish coating. Candidiasis develops, as a rule, as a result of violations of hygiene rules, physiological disorders in the body, and the use of certain medications. It is often observed in children and its danger cannot be underestimated. This infection, which initially appears on the oral mucosa, can be spread to all organs and systems of the body, and in this case already poses a significant threat to health.
Purely bacterial causes of stomatitis are less common. As a rule, bacterial infections affecting the oral mucosa accompany viral types of stomatitis (for example, streptostaphylococcal lesions).
Dental pathologies
The infection can be acquired by not following the rules of personal hygiene, as well as by contact with an already sick person. The most common pathologies are listed below.
Stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis that can cause pain in the oral mucosa.
| Type | Description |
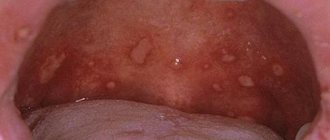
| Catarrhal | Mild inflammation of the oral mucosa. Appears due to lack of oral hygiene and the formation of tartar. It also occurs as an allergic reaction to certain medications. With it, the oral mucosa becomes red and swollen, and may be covered with a whitish coating. If you eat anything hot/spicy, pain, itching, and burning occur in the mucous membrane. |
| Acute herpetic | Occurs due to the herpes virus. The younger and younger generations are at risk. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. Sores covered with a yellowish coating form on it. Pain is felt in the mouth, saliva begins to be produced more abundantly. The patient feels unwell, does not want to eat, and feels worse. If the pathology takes a severe form, the temperature rises to 40 degrees. Then the patient begins to feel sick, vomit, and have a headache. The mucous membranes in the mouth become covered with ulcers. |
| Ulcerative-necrotic | Appears due to microorganisms - spindle-shaped rods, as well as spirochetes. They are found in periodontal pockets and under the gum near wisdom teeth that have not fully erupted. If the immune system does not work at full strength, the pathology becomes active, resulting in stomatitis. It first touches the gums, after which it is possible that it will spread to the entire oral mucosa. Large ulcers appear, diseased areas of the mucous membrane die off. A gray-green coating appears on the gums and ulcers. In this case, the patient feels pain in the mouth, which becomes stronger during eating. The gums begin to bleed, an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, salivation becomes more abundant, the patient feels worse, and the temperature rises to 38-40 degrees. |
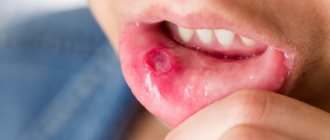
| Aphthous | It develops due to allergies to certain foods, stressful situations, hormonal imbalance, insufficient intake of certain substances by the body (iron, vitamin B12, folic acid), systemic pathologies, injuries, for example, damage to the mucous membrane by one or another “chemical”, failures in the functioning of the immune system. The slightest trauma to the mucous membrane is enough for stomatitis to begin to develop. In this case, single/multiple ulcers appear on the tongue, floor of the mouth, soft part of the palate, as well as on the inner surface of the lips and cheeks. Before the formation of visible signs of aphthous stomatitis, the patient feels pain. Ulcers also create discomfort. Moreover, it is so strong that a person cannot eat or swallow normally, even speaking causes pain. |
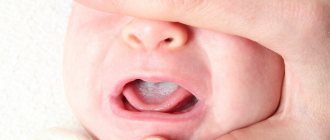
| Traumatic | The cause is mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa. This usually affects the gums and tongue. Redness and swelling appear in the injured area. Among the forms of this type of disease are Bednar's aphthae, also known as aphthae (ulcers) of newborns: in a baby up to one year of age, small round ulcers appear on the mucous membrane approximately in the center of the palate. The reason for their occurrence lies in the careless actions of adults: lack of caution when wiping the mouth or causing injury with a rough nipple while bottle-feeding. If the case is severe, some of the ulcers may merge, creating a large wound surface resembling a butterfly. A yellow coating often appears on it. Now medicine knows methods to prevent complications. |
Gingivitis
This disease is inflammation of the gums. They hurt while eating, talking, and the pain is felt even when at rest. The likelihood of contracting this pathology does not depend on age category.
With gingivitis, the gums turn red and bleed, pain appears in the mouth, and it begins to smell unpleasant. This disease is treated in a dental clinic.
Herpes
This pathology, which occurs in the mouth, is a consequence of the spread of the herpes virus throughout the body. No part of the mucous membrane in the human body is protected from it. But usually this disease manifests itself on the lips.
Small ulcers form on the mucous membrane of the mouth and in the throat, causing pain. At first these are bubbles with yellow liquid. When they burst, they leave behind wounds. They also cause discomfort.
The same sensations are felt at any degree of damage. It is very painful to touch the source of the pathology, to eat, or just to drink. Herpes is treated by an infectious disease specialist.
Here it is important to first remove the inflammation, and only then begin the actual treatment. At home, it is useful to rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile and calendula. It would not be superfluous to use Miramistin and chlorhexidine solution.
To defeat the disease, the doctor prescribes specific medications for external or internal use. Self-medication here, as with many other health problems, is harmful.
Important ! Only a specialist has the necessary experience needed to correctly diagnose the disease and determine how far it has gone.
Neuralgia
If inflammation damages nerve endings, the pain spreads widely. With neuralgia of the muscles of the face and jaw, discomfort in the mouth is also possible. Then the pain is felt when the jaw works, which happens while eating, speaking or yawning.
In this case, symptoms include more pain during certain activities. The source of pain is inside the tissue, in the muscle, not on the mucous membrane. A visual inspection will not show anything here.
With this problem, therapy comes down to restoring damaged nerves and muscles. To make a correct diagnosis, you should undergo an x-ray of the affected area of the face, and also consult with an oral surgeon.
Next, the specialist prescribes therapy, focusing on how severe the case is. Neuralgia is usually treated using antibiotics, as well as some specific remedies.
Worth knowing ! It happens that patients are hospitalized.
Sialometaplasia
Benign lesion of the palatine salivary glands. At first, you can suspect something is wrong by noticing not too large seals on the hard palate, similar to nodules. The growth of the affected areas occurs quickly, and their dimensions can reach up to 20 mm. With this pathology, the patient feels aching pain and pulsation where the ulcers are localized.
People aged 40-50 years are susceptible to this pathology. Moreover, more than half of the patients are men. The disease occurs due to one of the following reasons:
- damage to the mucosa;
- vasospasm;
- injections for dental procedures.
Important ! With this pathology, the most important thing is to make a correct diagnosis. This is because its symptoms can easily be confused with other ailments.
Be that as it may, you should always identify the very cause of pain in the oral cavity. Only then can a specialist prescribe the necessary therapy and give certain recommendations on how to keep the mouth clean and prevent relapses.
Other causes of stomatitis
In addition to infections, there is a whole range of other causes that can cause inflammation of the oral mucosa: • allergic reactions of a local and general nature (for example, to certain foods, medications, filling materials, oral care products) • the presence of soft and hard dental plaque, multiple caries • incorrectly installed dentures or orthodontic devices (braces) • irritation and trauma to the mucous membrane (mechanical injuries, burns) • deficiency conditions in the body (vitamins A, B and C, iron, folic acid); • intoxication with nicotine, alcohol, metal compounds.
Stomatitis can be manifestations and side effects of common infectious diseases (measles, diphtheria) or internal and general diseases and pathologies (blood and skin diseases, hormonal fluctuations, metabolic disorders).
Inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs especially often when the body's immune system is weakened and due to insufficient oral hygiene. The danger of stomatitis may also be associated with increased and constant dryness of the mouth, in which the protective functions of the mucous membrane are sharply weakened. The salivary glands produce on average up to 1.5 liters of fluid per day, and its deficiency leads to an imbalance in the acidity of the environment, an imbalance of inorganic components and, ultimately, has a depressing effect on the immune defense of the mucous membrane.
How to get rid of stomatitis and other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
Treatment of stomatitis and other inflammatory diseases is usually comprehensive, aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition, eliminating the root cause and risk factors.
Often, inflammation of the oral cavity is painful, accompanied by itching, irritation, and swelling of the mucous membrane. Because of this, patients have difficulty eating. To alleviate the condition, the affected areas are treated with various anesthetic and antiseptic rinses, powders, and solutions. This also prevents possible complications of diseases, for example, the transition of aphthae or foci of inflammation into ulcers, which require more time to heal.
Another important area of treatment is the elimination of local causes of inflammation of the oral mucosa. These include local foci of infection, for example, caries , dental plaque (tartar), traumatic chipped teeth, protruding parts of fillings or dentures [1]. For this purpose, appropriate treatment and professional hygiene are carried out.
And finally, a significant part of therapy is devoted to the diagnosis and elimination of a general disease that can provoke inflammation of the oral cavity (for example, endocrine disorders or chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract) [1]. In special cases, antiviral drugs [5], antimycotics [6] and antibiotics [1] are used.
Prevention of stomatitis and other inflammatory diseases includes [7]:
- treatment of major systemic diseases;
- strengthening general immunity: adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, nutrition, giving up bad habits, eliminating hypo- and avitaminosis;
- strengthening local immunity: regular careful hygiene, avoiding injury and irritation of the mucous membrane in the mouth.
Regular individual and professional oral hygiene is a key way to prevent intraoral inflammation. It must include:
- brushing your teeth twice a day, after breakfast and before bed, with a soft-bristled brush and toothpaste;
- the right choice of toothpaste: if you are prone to inflammation of the mouth and gums, as prescribed by a specialist, you should give preference to pastes with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties;
- use of antibacterial rinses with anti-inflammatory effects;
- cleaning interdental spaces with dental floss or tape;
- regular visits to the dentist (once every 6 months) for a preventive examination and professional removal of dental plaque.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms of stomatitis depend on its type and form, are very diverse and specific. General symptoms include redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, burning and pain in the mouth (including when eating hot, sour or spicy foods), an increase (or, conversely, a decrease) in salivation, bad breath, as well as the manifestation, in depending on the severity of the disease, specific lesions - erosions, af, ulcers.
Organization of diagnostics
If a person goes to the hospital with complaints of discomfort and pain in the oral cavity, the doctor first conducts a survey to diagnose associated lesions. Then tests are prescribed:
- allergy test;
- bacterial culture from the site of inflammation to identify the type of infection - viral, fungal or bacterial.
A general blood test and blood serum test are required. If necessary, a referral for diagnostics from specialists of a different profile is issued.
Only after a full examination, identification of the etiology and type of the disease is it prescribed how to treat inflammation in the mouth. Independent actions will only aggravate the condition and provoke complications.
- Diseases of the tongue and oral cavity: photos and names of diseases of the mucous membrane in adults, methods of treatment
Treatment
The primary diagnosis of the disease based on clinical manifestations is carried out by a dentist, who also carries out local symptomatic treatment based on the primary diagnosis. But in complex and unobvious cases, laboratory diagnostics are carried out, and doctors of other specialties (allergists, dermatologists, immunologists) are brought in for treatment.
Local symptomatic treatment usually involves the use of rinses with solutions of painkillers and antiseptic drugs (including herbal origin), the use of drugs for tissue regeneration (after the acute phase subsides), if necessary, the elimination of irritating and provoking factors (removal of dental plaque, hard deposits, treatment dental caries).
Local drug treatment is carried out only after an accurate diagnosis has been established (the cause of stomatitis) and usually includes treatment with antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal drugs in the form of ointments and applications.
General treatment is carried out, as a rule, in a hospital and is aimed at eliminating the internal causes of stomatitis (treatment of internal pathologies), taking therapeutic drugs according to special regimens, and physiotherapy.
How to treat?
Before choosing a course of treatment for stomatitis, the specialist finds out where this pathology came from in this case. To save a patient, for example, from catarrhal stomatitis, tartar is removed, teeth are treated and filled. To relieve him of ulcerative stomatitis, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the body for problems with the blood, gastrointestinal tract, heart and blood vessels. And with aphthous stomatitis, the sick person is examined for allergies and rheumatism.
Along with treating the disease, the specialist prescribes local therapy, which means rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine - 0.05% or 1% solution. The following drugs are also used when rinsing:
- aminocaproic acid;
- herbal decoctions;
- methylene blue.
A gentle diet will help speed up treatment.
Here are the foods to avoid:
- spicy;
- roast;
- rough food.
Here are some things you should increase your consumption of:
- porridge;
- pureed soups;
- vitamins (special emphasis on A and C).
Important ! After eating, you should rinse your mouth thoroughly. First with clean warm water, then with medicine.
Treatment for stomatitis usually takes from five days to one and a half weeks. But if the disease is started, it will last longer, becoming more and more severe.
Prevention
In general, it is quite difficult to avoid this disease in the presence of predisposing causes; you can only take some general measures to possibly prevent the disease or complication in the form of stomatitis.
Since the herpetic virus, especially in acute primary forms, is extremely contagious, a certain isolation of the patient is required to prevent the spread of infection by airborne droplets and contact. The difficulty here is that there is a rather long incubation period, up to 26 days, and the first signs of stomatitis may escape attention.
Other preventive measures are of a general nature and consist of proper and complete oral hygiene, regular professional cleanings in a dental clinic (removal of soft and hard plaque), timely treatment of mucosal injuries, and measures to generally strengthen the immune system.
Posted in Useful information | Tags: teeth, diabetes, care
Mucosal injury
For any person, the cause of pain in the mouth can be ordinary injuries.
For example:
- eating something too hot/cold. This injures the mucous membrane, and pain quickly appears in it. Inflammation indicates the presence of injury to the mucosa, caused by temperature exposure, and at the same time incompatible with its integrity. Eating something very hot can cause injury to both the palate and the tongue, as well as the throat;
- rough food, which can leave scratches on the roof of your mouth and on the inside of your cheeks. This causes pain and burning to appear after a day or two;
- A child has more ways to damage his or her mucous membrane than an adult. The baby can scratch it with his thin nail or put something in his mouth, for example, a toy. And if the child is somewhat older, his mucous membrane can be damaged by lollipops and chips.
When choosing a remedy for pain, it is very important to pay attention to the nature of the injury:
- in case of a burn, it is useful to rinse your mouth with warm water and then use Metrogil Denta dental ointment;
- In case of mechanical damage, it is recommended to immediately use antiseptics by rinsing your mouth with them. For an adult, it is useful to rinse your mouth with a mixture: 10-15 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide per glass of water. Decoctions of calendula and chamomile are also good. Also good are the drugs “Rotokan” and “Miramistin”, which fight infection as well as inflammation.
The main rule: no self-medication! Therapy must be prescribed by a specialist. Otherwise, you can make the situation even worse. So if symptoms appear, it is recommended to visit a doctor. He will prescribe the best treatment for a particular situation.
Traditional therapy
Herbal decoctions, used mainly for rinsing, have some anti-inflammatory and at the same time anesthetic effects for stomatitis.
First. Onion peel infusion:
- chop dry onion peel;
- 3 tsp. pour the resulting mixture with 500 ml of hot water;
- boil;
- leave for 7-8 hours;
- strain
Second. Horse sorrel decoction :
- chop horse sorrel roots;
- 1 tbsp. l. pour the resulting mixture with 1 tbsp. water;
- boil for 15 minutes;
- strain.
Third. Calendula decoction:
- Pour boiling water over calendula flowers in the proportion of 1 tbsp. l. flowers for 1 tbsp. water;
- leave for 15 minutes;
- strain.
Fourth. Nettle infusion:
- finely chop nettle leaves;
- 1 tbsp. l pour 2 tbsp. boiling water;
- let stand for half an hour;
- strain;
- use if the gums are bleeding and the oral cavity is “decorated” with ulcers.
Fifth:
- Pour 1 part of onion juice into an enamel-coated container;
- dissolve 1 part honey in a hot bath;
- pour onion juice with 2 parts water and honey;
- cool;
- Make lotions and compresses from the result in case of inflammation of the gums and oral mucosa.
Sixth:
- 2 tbsp. l. St. John's wort and 1 tbsp. l. pour chamomile into porcelain dishes;
- pour boiling water;
- stir, close the lid;
- hold for 1.5 hours;
- strain through a sieve.
Seventh:
- 1 tbsp. l. chop sage leaves and calendula flowers;
- put them in a pan covered with enamel;
- pour one and a half cups of boiling water;
- stir;
- put in a water bath;
- Cook over medium heat for 10 minutes, covering with a lid;
- cool to ambient temperature;
- strain through cotton cloth.
Eighth:
- 1 tsp each fresh onion juice and Kalanchoe juice, as well as 3 tbsp. l. pour water into porcelain dishes;
- stir.
Ninth:
- 1 tbsp. l. Brew one and a half cups of boiling water for green tea;
- wait 40 minutes;
- at this time dissolve 1 tbsp. l. honey in the bath;
- strain the tea;
- add honey;
- mix.
Tenth:
- 2 tbsp. l. plantain pour 1 tbsp. boiling water;
- close the lid;
- hold for 15 minutes;
- strain through a fine sieve;
- cool.
Important ! You need to rinse your mouth with such decoctions every two hours every day.