Splashes from under the tongue)))
Today at a meeting at work I yawned and splashed all the documents))) It was so awkward))). Who knows what this is and is it possible to learn to splash like this on purpose?
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Nikulina Marina
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Sheludyakov Sergey
Psychologist, Clinical psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Trifonova Maria Anatolyevna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Gundertailo Yulia Danilovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Vyacheslav Potapov
Psychologist, consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Zinovieva Natalya Yurievna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Wrzecinska Eva
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Natalya Maratovna Rozhnova
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Tropina Natalya Vladimirovna
Psychotherapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Kokunina Tatyana Viktorovna
Psychologist, Psychodrama-therapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Was it so awkward or do you want to learn? In general, when you yawn, you need to cover yourself.
Is there a fountain in your mouth? ))
geeyyy, I yawned for nothing)))) If I had sneezed, well, it didn’t go well, I could have splattered the documents, but when yawning, you still need to manage it. The author needs to cover his mouth, they told you correctly here.
This happened to me too)))) only not on documents, but on the face of the interlocutor)))
I have a friend who, when she talks, splashes fly at her interlocutor. ugh :((
Related topics
5, 6. you probably know each other
It’s just your glands that produce saliva working hard. It's okay, but when you yawn, cover your mouth anyway.
Thick saliva
The salivary glands produce a multicomponent fluid (secret), which mainly consists of water. Only 5% of saliva is enzyme compounds, amino acids, acidic salt residues and various trace elements. This secret performs a lot of important functions in the human body:
- protective (moisturizes the oral mucosa, protects it from attacks by pathogenic bacteria);
- allows you to taste the food.
digestive (ensures the formation of a food bolus);
In a healthy person, saliva is a transparent, odorless liquid, which upon contact with the mucous membrane does not cause irritation, burning or other discomfort.
Why is there a problem?
Thick saliva is a symptom that many patients may experience. The viscous, foamy liquid is the result of a failure in the production of mucin glycoprotein (high molecular weight components responsible for the formation of the food bolus). Other causes of thick saliva are disorders of the autonomic nervous system, eating foods with strong odors and strong tastes (increase salivation).
Pathological factors causing the appearance of white mucus in the mouth:
- Sinusitis. These are active inflammatory processes in the nasal sinuses, which “make themselves known” with thick and viscous sputum and bad breath. Snot from the nose enters the oral cavity, from there into the pharynx, flows down the back wall of the throat, and ends up in the stomach. The chronic course of sinusitis, in addition to local symptoms, can be complicated by regular severe headaches, fever, and weakness.
- Xerostomia. In this case, viscous saliva and mucus in the mouth are a consequence of disruption of the salivary glands themselves. Additional symptoms: swelling, hardness of the tongue, dryness, irritation, burning sensation on the mucous membrane. The throat may be sore, sore, and the functioning of the taste buds may be impaired.
- Fungal candidiasis. A disease of an infectious nature that develops against the background of an immune failure in the body. Thus, saliva becomes sticky in patients who take medications on a long-term basis - corticosteroids (hormones) or antibiotics. In addition, the candida fungus enters the oral cavity through contact (through a kiss, when sharing personal hygiene items). Associated discomfort: dysphagia, metallic taste in the mouth, burning and itching of the mucous membranes.
Common respiratory diseases such as tonsillitis, laryngitis, and pharyngitis also lead to the appearance of foamy saliva. The infection affects the tonsils, causing the formation of purulent blisters on the back wall of the throat - when they resolve themselves, purulent exudate flows into the oral cavity, causing the appearance of a putrid odor (taste), the feeling of thick mucus in the mouth. In addition, the course of such diseases is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, dehydration, and dysfunction of the salivary glands - the amount of secretion produced decreases, and saliva in the mouth thickens.
Splashes of saliva from under the tongue. Four techniques, or the spitting phenomenon
But then the Chief Boss came, and everything changed.
He spat there, spat here, and the sky parted before Him, and from the spitting the stars, the Sun, the Moon and the Earth were born. The sky gave birth to Wind, the Sun gave birth to Fire, and Fire was ready to incinerate everyone and everything, but Godfather spat again, and Water appeared. This is how four elements arose and complemented the overall picture of the World. A boy subsequently emerged from them, taking a drop from each.
He borrowed a warm heart from Fire, and from then on Fire became his essence. He took over the memory of his ancestors from the Earth, learned to respect authorities, remember his mother and father with a kind word, and the boy stood up for the District, and the boy became clear-headed.
The wind gave the boy a strong connection with Nishtyak, the god of relaxation, and the boy became even. Water rewarded the boy with the ability to heal and heal - to pour a competent market, in short - and the boy stood up for a divorce, and Luck was lucky for him.
And then the Chief Boss appeared again: he came to leave forever. But, before disappearing behind the scenes of eternity, He left the boy for edification his Mastery - Four spitting techniques or the Art of spitting in four different ways.
Spitting helps you focus and get to the heart of things.
Method One: Fire Technique
The most famous method of spitting is “through the teeth.”
Articulation: The anterior upper edge of the surface of the tongue is firmly pressed against the upper front teeth. Saliva accumulates in the hollow formed by the bend of the middle part of the tongue. At the moment of spitting, the tip of the tongue slides down, slightly moving outward, and a stream is sprayed out from the gap between the front teeth.
The spitting is accompanied by a characteristic sound “TZYRK”, for which this method is sometimes simply called “Tsvirk”.
The fluttering spitters are always fast and short-ranged.
This technique symbolizes expression, aggression, treachery, because it is born from the best Zhigan (that is, fiery) qualities of a boy.
Prevention
Preventing the development of hypersalivation is:
- Commitment to a healthy lifestyle without smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Timely treatment of any common diseases.
- Regularly visiting doctors to monitor your health.
- Compliance with hygiene rules to avoid helminthic infections.
- Maintaining hygienic oral care.
- Timely prosthetics for tooth loss. Read more about prosthetic methods→
- Good nutrition.
When sialorrhea appears, there is no need to self-medicate by taking medications uncontrollably. Only a doctor, after an examination, can decide how to reduce salivation and prescribe effective treatment that relieves unpleasant symptoms.
Method two: Earth Technique
A common dynamic method of spitting through tightly pursed lips, it is performed in most sitting poses, especially in the Courts and Bench poses.
Articulation: Lips tightly compressed. Saliva accumulates on the tip of the tongue, pressed against the roof of the mouth. At the moment of performance, the tip comes off the palate, the lower lip slides slightly forward and down, the cheeks, like blacksmith’s bellows, sharply compress, and a portion of saliva, usually quite copious, falls to the ground.
This technique symbolizes loyalty to tradition and closeness to Mother Earth.
Causes of the phenomenon
Hypersalvation is considered a common manifestation only in children under six months; after this period, increased salivation is considered a disease that results in inflammation of the oral cavity.
Most often, increased secretion of saliva is caused by epidemic encephalitis, cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease, stomatitis, stomach ulcers, and amyotrophic sclerosis.
This phenomenon is also observed during pregnancy and brain oncology.
Alternative causes include intestinal infection, lead or mercury vapor poisoning, liquid iodine poisoning, etc.
Yellow coating on the tongue, how to remove it and what are the reasons for its appearance on the tongue can be found out by reading one of our articles.
You can find out how to treat bumps in the corners of your mouth by studying this article. Very useful and valuable material, available to absolutely everyone!
Here, the cost is indicated, as well as instructions for using chlorhexidine.
Types of hypersalivation
The production of increased amounts of saliva is divided into the following types
, which are associated with the manifestation and symptoms:
- Salivation due to taking pharmaceutical drugs
. A very large part of pharmacological drugs, especially in the treatment of a runny nose or sore throat, leads to increased salivation. In this case, hypersalvation is a side effect of treatment and is very easily eliminated by lowering the dosage of the drug that caused it; - Hypersalvation as a consequence of stress
. This phenomenon is very rare and does not always go away after the stress stops; sometimes the period of inclusion of the salivary glands in normal functioning lasts for a very long time. There are often cases when, due to an increase in saliva levels, the patient had to wear special reservoirs for collecting saliva indoors; - Increased salivation during belching
. Gastrointestinal diseases, such as ulcers or various forms of gastritis. The occurrence of sour belching, as one of the manifestations of the disease, can lead to the production of saliva and mucous acidic fluid in the oral cavity. When swallowing is impaired, this manifestation is also observed as an attempt by the body to cope and push a bolus of food down the esophagus. These reasons are a very serious fact that requires examination in a medical institution. - Increased salivation with sore throat
. Lacunar tonsillitis is one of the most common causes. In this case, salivation occurs in conjunction with an increase in temperature, fever, malaise, and headache. The disease can also be complicated by vomiting. The lymph nodes become enlarged, and the tonsils are evenly covered with a gray coating, as well as a coating on the tongue, which becomes an indirect cause of salivation; - Increased salivation during communication
. This reason is the most unfavorable, as it can affect a person’s communication skills. Impaired functioning of the oral muscles leads to this disease, as a rule, it is a symptom of cerebral palsy and other neurological lesions. Diabetes mellitus and endocrine disorders of the thyroid gland are another reason for increased drooling when talking; - Increased salivation in females
. Flushes and sweating that accompany menopause can be enhanced by increased secretion of saliva from the glands. Doctors explain this by hormonal changes in the body. This does not require treatment and goes away on its own over time, when all hormonal processes settle down; - Increased salivation in pregnant women
. In this case, the increase may be caused by impaired blood circulation in the thin films of the brain, which is disrupted during pregnancy. In this case, heartburn occurs. A decrease in the body’s immune capacity and vitamin deficiency also contribute to the development of hypersalvation in pregnant women; - Worms
. The vital activity of worms and their presence in the body also leads to profuse salivation. In this case, it is caused by the formation of a special toxin that circulates in the blood, absorbed through the colon; - Orthodontics
. The presence of “crooked teeth”, tartar and gum inflammation in the oral cavity is a very rare but obvious cause.
Third method: Water Technique
This method largely repeats the previous one, but is characterized by an incomparably large amount of saliva released. The spitting is done slowly, lazily, often through the use of mind-altering substances. The boy bends over and looks for a long time at the heavy and viscous drop of saliva coming out of his mouth, thoughtfully admiring how beautifully it stretches and finally reaches the ground.
The highest art is to hit a puddle left by another spit or a seed coat with such spit.
Articulation: Similar to the previous method, but less dynamic; movements of the tongue and cheeks are smoother.
This technique symbolizes complete relaxation, but at the same time composure, concentration and perseverance.
How to spit a stream from under your tongue. Four techniques, or the spitting phenomenon
But then the Chief Boss came, and everything changed. He spat there, spat here, and the sky parted before Him, and from the spitting the stars, the Sun, the Moon and the Earth were born. The sky gave birth to Wind, the Sun gave birth to Fire, and Fire was ready to incinerate everyone and everything, but Godfather spat again, and Water appeared.
This is how four elements arose and complemented the overall picture of the World. A boy subsequently emerged from them, taking a drop from each.
He borrowed a warm heart from Fire, and from then on Fire became his essence. He took over the memory of his ancestors from the Earth, learned to respect authorities, remember his mother and father with a kind word, and the boy stood up for the District, and the boy became clear-headed.
The wind gave the boy a strong connection with Nishtyak, the god of relaxation, and the boy became even. Water rewarded the boy with the ability to heal and heal - to pour a competent market, in short - and the boy stood up for a divorce, and Luck was lucky for him.
And then the Chief Boss appeared again: he came to leave forever. But, before disappearing behind the scenes of eternity, He left the boy for edification his Mastery - Four spitting techniques or the Art of spitting in four different ways.
Spitting helps you focus and get to the heart of things.
Fourth method: Wind Technique
This is a long-range and fast-firing grub. The flight range can reach several meters and is determined, first of all, by the severity of the “charge”: mucous deposits from the nasopharynx are used for spitting.
Source: https://dens1995.ru/uhod/kak-plevatsya-iz-pod-yazyka.html
Diagnosis and treatment
It is quite possible that the increased thickness of saliva in the morning is the result of hormonal changes in the body, so the problem may resolve on its own after some time, the salivary glands will restore their normal functioning. If such an abnormal phenomenon persists for a long time, it is necessary to visit a dentist, assess the condition of the teeth and oral mucosa, and exclude local inflammatory processes. The doctor will give directions for studies to assess the “health” of the salivary glands.
Important! The first thing that needs to be done in case of increased viscosity of saliva is to cope with dry mouth and “wash out” pathogens that begin to attack the mucous membrane when local immunity is reduced. To do this, experts recommend rinsing your mouth with decoctions of herbs with anti-inflammatory properties (chamomile, calendula) and a soda-salt solution (½ teaspoon of each powder per glass of warm boiled water).
For laryngitis, pharyngitis and other respiratory diseases, it is advisable to use gels, sprays, and solutions with antiseptic properties. The dentist may prescribe artificial saliva or a spray humidifier for the oral cavity. Such products also have antibacterial properties and fight bad breath.
Bromlane, Acetylstein are mucolytic drugs that thin saliva well and help remove mucus in infectious respiratory diseases. Inhalation is another method of dealing with the problem. Pharmaceutical compositions or decoctions, infusions of medicinal plants well moisturize the mucous membrane, provide an anti-inflammatory effect, and make the consistency of saliva more liquid.
Types of pain
“Anything can hurt: the back wall of the pharynx, the tonsils, the hypopharynx, the nasopharynx, the epiglottis with the root of the tongue,” says Vladimir Zaitsev. The main thing is to understand that there is a difference in sensations with one or another localization of pathogenic microorganisms.
1. Pain worsens when swallowing
One of the options for soreness in the throat area is pain, which intensifies when swallowing. At the same time, it is not sharp, diffuse, but intensifies when swallowed and swallowed. Here doctors usually talk about the most common situation: acute pharyngitis. “When a person became hypothermic, the back wall of the throat became cold, and it became inflamed. At the same time, there is no mucus flowing down the back wall, the throat just hurts,” notes the ENT doctor. You can go to the mirror, shine it with a flashlight and see redness on the back wall. And it will also be spilled all over the back wall.
Article on the topic
Throat hazard. Why does laryngeal cancer develop?
Here it is worth understanding, the otolaryngologist emphasizes, that if a person ignores this situation and does not begin to be treated, then the disease may progress to the chronic stage. “In this case, the pain will also change its character: instead of acute pain when swallowing, there will be a feeling of dryness of the back wall, its complete dryness, then there will be a feeling of rawness, soreness, burning, and there may be a desire to drink something or even put oil drops in the nose, to soften the wall of the pharynx,” says Vladimir Zaitsev. He emphasizes that the condition cannot be ignored. You can also see that the mucous membrane is suffering from dryness by looking in the mirror: it will be noticeable that it is not filled with water.
2. Sore throat is associated with the nose
Another type of pain appears when, for example, the tonsils are removed, or if a person has problems with the nose that lead to sleep apnea, snoring and the fact that his mouth is constantly open during sleep. “Such a situation will sooner or later lead to subatrophic pharyngitis. Due to the constant drying of the back wall of the pharynx, the mucous membrane will stop working as it should,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
It makes noise, itches, it doesn't breathe. Non-serious symptoms of serious ENT diseases Read more
3. Aching pain on the right and left
There may also be a problem when there is bad breath, weakness, lethargy and an aching sore throat, discomfort in the throat. This is what the condition of chronic tonsillitis or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis looks like. “When there is a history of it, pain and discomfort do not appear in the center of the pharynx, but the pain will be localized on the sides: on the right and left. Also, against the background of such pain, low-grade fever appears: its values rise to 37.3-37.5 degrees. At the same time, plugs in the tonsils will be visible, such small white curdled grains,” notes Vladimir Zaitsev.
Article on the topic
Viral throat infections: symptoms, treatment
4. Throat hurts sharply and constantly
If the pain in the throat is unbearable and sharp, the temperature jumps above 38.5, and a scarlet throat is visible, very painful, then with a high degree of probability we are talking about acute catarrhal sore throat. “The temperature is high, the pain is very strong, sometimes it doesn’t even allow you to swallow saliva, as a result of which it just starts flowing from the mouth, it even gets to this point,” says the otolaryngologist.
5. Pain in the neck area
When hoarseness appears, this indicates that the inflammation has moved from the oropharynx just below, to the larynx, says the ENT doctor. “When there is acute inflammation of the larynx, acute laryngitis develops. However, it will not necessarily be accompanied by a complete absence of voice (aphonia); dysphonia may also be present. Here, too, against the background of incomplete closure of the ligaments, pain will appear. But it will not be localized at the level of the palate or along the back wall of the pharynx. It will be marked slightly lower, at neck level. The person himself will even point to his neck, describing his condition,” says Vladimir Zaitsev. Laryngitis, as the otorhinolaryngologist emphasizes, can be subacute, acute and chronic.
And it definitely needs to be treated. “If laryngitis is not treated, the inflammation may go away, but hoarseness may remain. The vocal cords will get stuck in this state, settle down, and the person will continue to live with this hoarseness forever,” says the specialist.
Killer bones, melted plasticine. How to kill foreign bodies in the throat and ear Read more
6. Pain in the epiglottis area with suffocation
“The epiglottis is a kind of flap, a petal that closes the entrance to the trachea, and, for example, when taking a sip of water or swallowing food, it protects the organ from water and food entering further into the trachea, lungs and bronchi,” notes the doctor. At the same time, there are situations when this well-coordinated system fails. This could be:
- against the background of decreased immunity;
- during extreme heat;
- in case of injury.
In all these cases, the epiglottis can become inflamed and noticeably increase in size. “Here a characteristic pain appears, which cannot be confused with anything: suffocation, squeezing pain not at the level of the oropharynx, but slightly below, there is a feeling of lack of air. This is a bright moment, it’s called epiglottitis,” says Vladimir Zaitsev. In an acute situation, they say that the epiglottis increases in size, swells, is tense and red; naturally, therapy is required, usually with antibiotics.
There is also a situation when an abscess of the epiglottis develops: this is already a purulent process, when opening of the formation and its cleaning is required.
Article on the topic
Mushroom place. How to get rid of mycoses in the throat and ears?
7. The root of the tongue hurts
There is also such an option as inflammation of the root of the tongue. There is a lingual tonsil on it, notes the otorhinolaryngologist, which is part of the lymphoid tissue. The root of the tongue may become inflamed on its own. A lingual sore throat develops. “The temperature is as high as with a sore throat, but a person reflexively feels pain at the level of the tongue, but not at the tip or from the sides, but in the very depths. A feeling of suffocation may also develop because the airways are nearby,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
It is also worth remembering that there is a condition when it is not so much pain that develops, but a burning sensation, itching, a desire to scratch, and there may also be slight soreness. In such a situation, notes Vladimir Zaitsev, they talk about pharyngomycosis, that is, a fungus in the throat.
Prevention
To avoid problems such as increased viscosity of saliva, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day, with preference given to purified water. It is better to limit the intake of carbonated, caffeinated drinks (they dehydrate the body). Quitting alcoholic beverages and smoking also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the salivary glands.
It is useful to rinse your mouth with a warm saline solution from time to time, avoid hypothermia and stress, do not buy sugar-containing chewing gum, and humidify the air in the room. A well-structured, balanced diet with plenty of fiber (vegetables, fruits) and cereals is the best prevention of any problems with the digestive organs, including the salivary glands.
So, foamy, sticky and viscous saliva is a signal notifying about certain problems in the body. The cause of the anomaly may lie in a malfunction of the salivary glands themselves, hormonal or metabolic disorders, bad habits or chronic diseases (“the respiratory organs, gastrointestinal tract, and oral cavity suffer”). A dentist will help determine the cause of the problem and select the appropriate treatment, who, if necessary, will involve other specialists (immunologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, etc.).
How to teach a child to chew solid food?
Bring the spoon to your mouth, play with the food, twirl the food with your tongue, spit it out, bite it, try to chew it and finally swallow a piece... What children don’t do to cope with adult food, which at first seems so “difficult”! We tell you how to teach your child to chew solid food so that it does not become a family problem. Nutritionist Anastasia Ivanovna Shalunova advises.
— Anastasia Ivanovna, let’s talk about how to teach a child to chew and swallow solid food. Why is age important here?
— It is important not to miss the right moment when chewing skills are most easily formed. The most optimal period is from 6 to 10 months, when introducing complementary foods with pieces. However, the boundaries of the norm are arbitrary, because a child can only eat liquid food even at one and a half years old.
Children begin to chew due to the formation of the physiological and neuropsychological processes of the body - this is individual for each child. And here the influence of cesarean section and natural childbirth is also very important, how the birth process proceeded and how the baby developed from birth.
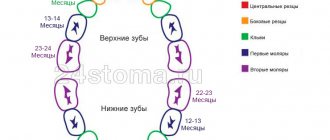
When to give your baby solids
| 4-5 months | The first chewing movements are observed, the reflex of pushing food out with the tongue disappears. The child’s first solid food—porridge and vegetable purees—helps support these changes. |
| 7-8 months | The child is ready for vegetable, fruit, meat purees with small pieces, chopped fruits and berries. |
| Up to 12 months | Biting and chewing skills are strengthened, lateral movements of the tongue develop, and the child consciously and confidently moves food to the teeth. As the baby approaches one year of age, food pieces become larger. |
How can parents understand that their child is ready to chew solid food?
— Food interest is formed conditionally from 4 to 6 months, when the child pulls the plate, spoon towards himself, asks for food. During this period, complementary feeding begins, gradually moving from homogeneous puree-like dishes to denser ones, with pieces.
The child is ready to chew food if:
- he confidently takes and holds the spoon;
- sits without adult support;
- receives complementary foods for three to four weeks.
From 6 to 10 months, it is easier to teach a baby to eat and chew food in pieces. If the child does not chew, but sucks or licks what was given to him, there is no need to prohibit him - perhaps he is not hungry or he is interested in something else at that moment in time.
If there is no interest in food for up to a year, you may need to work with psychologists, neuropsychologists, and neurologists. Each of them will look at the child’s problem from their own perspective and give recommendations.
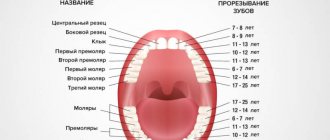
— How many teeth are enough to start chewing?
— You can “chew” food without teeth, grinding the pieces with your gums. Some children develop teeth late but are still given solid foods to develop chewing skills. Chewing can stimulate blood circulation and tooth growth.