X-ray of the jaw in children
Problems with teeth, as well as with the development of bite, begin to bother a person from a very early age. Pediatricians constantly monitor the teething process in very young children. Parents can also seek advice from pediatric dentists if there is a suspicion that something is going wrong.
A procedure such as an x-ray of a child’s jaw is prescribed quite often today. There is no need to be afraid that X-rays can negatively affect the child’s health - the modern equipment used for the study is characterized by minimal radiation exposure. X-ray can be considered a safe diagnostic method.
Indications for x-rays of primary teeth
X-rays for children are carried out as prescribed by a doctor, at least 2 times a year. The image allows the doctor to recognize the following dental disorders and diseases:
- condition of dental roots and soft tissues, including gums;
- determine the rudiments of the roots of permanent teeth;
- inflammatory processes;
- deep caries;
- nerve damage;
- pathological changes in tooth roots;
- purulent processes;
- anomalies in the structure of the teeth and jaw;
- impacted and supernumerary teeth;
- malocclusion;
- damage to the jaw bones.
Indications for dental X-rays in children may include other conditions - diseases of the teeth, jaw apparatus, but in any case, the image should be taken on the recommendation of a specialist who needs a complete clinical picture.
When is a child's jaw x-rayed?
So, an X-ray of the jaw of a child with baby teeth: when can it be prescribed? There are a number of situations in which this procedure is necessary:
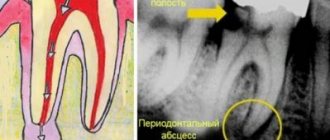
- A dental examination reveals pockets of caries, and it is necessary to determine how deep the lesion has spread. An X-ray of the jaw will allow you to see how damaged the roots of baby teeth are and whether the rudiments of permanent teeth are affected by caries.
- During examination, anomalies were revealed in the dentition. For example, milk teeth erupted with displacement, rotation, tilt, and so on. An X-ray of the jaw
will allow you to see the location of the rudiments of permanent teeth, predict possible pathology of eruption and begin to plan orthodontic treatment. - Various types of malocclusion have been diagnosed. That is, if the lower jaw protrudes forward and overlaps the front one, or, conversely, the lower jaw is pushed deeper than it should be normally, an x-ray will help identify the degree of development of the pathology and understand its causes.
- After the loss of milk teeth, the eruption of permanent teeth is not observed. It may not happen often, but it happens. The most common cause of this problem is the position of the permanent tooth buds too high. X-rays will allow you to see exactly at what height the teeth are currently located and predict the approximate time of their eruption.
- Suspicion of an abscess - an x-ray will help translate this suspicion into an accurate diagnosis or refute it.
- Various jaw injuries. To assess how much a blow, bruise, fall or other mechanical impact has affected the integrity of the teeth and jaw bones, an x-ray may also be prescribed.
What does an X-ray of a child’s jaw with baby teeth show?
An X-ray of a child’s jaw before the loss of temporary baby teeth will show:
- the degree of reduction in dental mass in the event of inflammatory gum disease;
- changes in the roots of teeth;
- foci of caries, including those located in the interdental space;
- abscesses;
- anomalies in the structure of the upper and lower dentition;
- location of permanent tooth buds.
When is an X-ray prescribed for a child?
If X-rays in adolescents and adults do not cause concern, then X-ray diagnostics of young children worries many parents.
The devices used in modern medicine do not harm the body, but the study is still carried out only if indicated. Dental X-rays are recommended for children for the following indications.
- Deep caries. The procedure is carried out to determine the lesions and affected area. The image allows the specialist to assess whether the roots and rudiments of permanent teeth are damaged.
- Developmental anomalies. X-rays make it possible to determine the causes and characteristics of irregular teething, as well as delays in their growth.
- Control of permanent teeth. Diagnostics allows you to see all the features of the rudiments of permanent teeth, as well as predict the period of their eruption and identify possible pathologies.
- Malocclusion. X-ray is the most accurate diagnostic method for determining abnormalities in tooth growth and jaw position.
- Abscess. The study is aimed at confirming or refuting the development of an abscess if signs are present.
- Jaw injuries. In case of mechanical damage, an x-ray is taken to assess the damage to bone tissue that has occurred.
X-rays are often used to monitor the treatment being carried out. Diagnostics is also used when restoring teeth using temporary prosthetics or installing orthodontic structures.
Methodology
There are several ways to take an X-ray of a child's jaw or lower skull.
Intraoral radiography
Intraoral x-rays are carried out using special dental devices, which help take targeted images of one or more adjacent teeth (one to four). Such an examination allows us to assess the condition of the hard tissues of primary and permanent teeth, periodontal and periodontal tissues, jaw bones for the diagnosis of retention and follicular cysts, oncological tumors, anomalies in the location and number of erupted teeth and rudiments, etc.
When performing a study, a blank of x-ray film is placed in a special paper envelope, which is inserted into the oral cavity and placed in the area of the desired tooth. The X-ray machine is brought to the face from the outside and placed as close as possible to the tooth/teeth being examined.
In pediatric dentistry, intraoral radiography is often prescribed to diagnose pathologies of the palatal suture. Although, it must be said that if we are talking about a very young patient (2-3 years), it is quite difficult to carry out such an x-ray, because it can be difficult to explain to a child why it is needed and that it will not hurt.
Extraoral methods
The most common method of performing extraoral x-rays is a panoramic photograph, or orthopantomogram. In such photographs, you can see in a direct projection the entire upper and lower dentition, as well as the structure of the patient’s jaw. Orthopantomogram images allow you to make a detailed interpretation and description of the condition of teeth and gums, to recognize even hidden pathologies or those that have just begun to develop (for example, periodontal disease, caries).
You can see what a panoramic x-ray of a child’s jaw looks like in a photo on the Internet.
Types of X-rays for examining children
Examinations of the teeth and jaw may require different areas to be examined or results obtained from different types of images. Depending on the indications for x-rays, a certain type of procedure is used.
Types of x-rays of a child's teeth and jaw.
- Sight shot. Obtaining an image that displays a separate area (one or two teeth with closely spaced soft tissues).
- Panoramic shot. An image showing a large area of the dentition along with the jaw bone and the rudiments of molars.
- 3D pictures. A modern method of obtaining three-dimensional images of the upper and lower jaw.
There are also differences in technique. There are internal or external diagnostic methods. If it is necessary to obtain a targeted image, internal x-rays are used; in other cases, the external method is used.
How safe is an X-ray of a child's jaw?
X-rays of the jaw for children, including infants, are a relatively safe procedure. The radiation exposure during imaging is negligible and cannot negatively affect the further development of the dental system. At the same time, it must be said that taking X-rays without indications, for prevention, is still not worth it.
Contraindications for
Contraindications to X-raying a child’s jaw are:
- unsatisfactory general condition of the child;
- bleeding;
- pathologies in the thyroid gland.
Features of baby teeth
The structure of baby teeth is similar to permanent teeth: in the jaw there are such types of teeth as incisors, canines, premolars and molars - all like in adults. Only their number differs: for children – 20, for adults – 32.
Baby teeth are formed in the sixth week while still in the womb. After the birth of a child, teeth erupt at about 6 months and grow in by 3-4 years. The exact age depends on the individual's rate of development.
However, there are some differences from permanent teeth:
- baby teeth have long roots that are easily absorbed over time
- greater distance between teeth - so that falling out for replacement is easy
- thinner and more delicate enamel
- softer dentin and surrounding tissues
Decoding the results
The finished images must be deciphered by a specialist. It is possible that several doctors will be present during the decoding, for example a radiologist
, dentist, otolaryngologist.
The photographs are used to assess how symmetrically the teeth and jaws are positioned. If a focus of any pathology is detected, it is important to determine its exact location and size.
When diagnosing a jaw fracture, you need to determine its complexity, consider whether there are fragments and how they are located.
If a tumor-like neoplasm is detected, it is important to assess its size, consider its boundaries (clear or blurred), and determine its location.
X-ray safety
There is often a belief among patients and parents that dental x-rays, and in particular, children’s panoramic dental photographs, are harmful to health and “unnecessarily expose them to radiation.”
Of course, you shouldn’t do an X-ray thoughtlessly and without the appropriate doctor’s testimony. Ionizing radiation affects the body, but only in large doses.
When X-rays are taken for children at NovaDent, the amount of radiation is strictly dosed and does not exceed the permissible level, so you don’t have to worry about the health safety of the procedure.
Contact NovaDent pediatric dentistry for a consultation. Prices for x-rays in our clinic are quite affordable and start from 450 rubles.
Expert of the article you are reading: Lapshina Maria Aleksandrovna Dentist, pediatrician
20 years
Clinical experience
Krasnogorsk
Moscow region, Krasnogorsk, Podmoskovny Boulevard, 5
+7
Free consultation with this specialist