Treatment of dental pathologies in children is a complex process that requires extensive practical experience and knowledge of child psychology. Especially when it comes to baby teeth. In order not to damage the rudiments of permanent units, the doctor must perfectly know the technique of performing manipulations and act very carefully.
Children's doctors at the Levoberezhnaya Dental Clinic try to save teeth even with extensive damage and remove them only as a last resort. You can make an appointment by calling the phone number listed on the website or using the online form.
Why does caries occur in childhood?
It is known that caries is a pathological process that occurs in the hard tissues of teeth under the influence of internal and external factors. Carious lesions arise as a result of the “work” of cariogenic bacteria living in the oral cavity.
In this article
- Why does caries occur in childhood?
- Features of caries of milk teeth
- Symptoms of carious lesions in baby teeth
- Why is caries treated for young children?
- How is caries treated in children?
- Methods for treating childhood caries without drilling
- Invasive treatment of caries
- Do they give anesthesia to children?
- Prevention of childhood caries of primary teeth
By processing carbohydrates that enter the mouth with food, these bacteria produce acid. It is this that contributes to the destruction of enamel, dentin and other tooth tissues. Several factors contribute to the proliferation and active activity of cariogenic bacteria, which ultimately leads to the development of caries in children.
- Improper dental hygiene.
Insufficient cleaning from plaque, infrequent cleaning.
- Eating high in carbohydrates.
Children who eat a lot of sweets and flour, drink sweet compotes at night, and snack on chocolates are more susceptible to developing caries. A favorable breeding ground for microbes is formed in their mouth.
- Reduced immunity.
Weakened immune defense does not allow the body to effectively resist negative influences, so children with weak immunity develop caries more often.
- Features of intrauterine development.
The formation of teeth occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy, and it can be affected by the lifestyle, health, and previous diseases of the expectant mother.
These factors contribute to the fact that tooth enamel begins to lose mineral substances, cariogenic microbes multiply in the mouth, and as a result, dental caries develops.
Gum inflammation
The most common inflammatory gum diseases in children are stomatitis and gingivitis. Stomatitis, or, as it is usually called, thrush, is an infectious inflammatory process provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. Treatment is antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy, always carried out under the supervision and recommendations of a dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous, as some children may have allergic reactions to certain medications or antiseptics.
Gingivitis most often occurs due to plaque on baby teeth and insufficient general hygiene, but the reasons for their development can also be trauma to the gums during teething or other injuries, untreated caries. With this problem, you also need to contact a doctor, who will select the optimal treatment regimen and prevent gingivitis from developing into childhood periodontitis.
Features of caries of milk teeth
Saliva at an early age does not have sufficient antiseptic properties, and microbes easily multiply in the oral cavity. At the same time, the degree of enamel mineralization in baby teeth is less than in permanent teeth. In this regard, childhood caries spreads very quickly. If in an adult a carious lesion on permanent teeth can develop from an early stage to a deep one over several years, then in children the same process takes only a few months.
In a child, dental caries often affects several teeth at once. Only children have such types of caries as ring-shaped and planar. The condition of the dental system is also affected by various infectious diseases to which children are susceptible.
How to choose a doctor for your child
A child's first visit to the dentist is a very important event that should be taken very seriously. It is imperative to find a doctor who gets along well with children and to whom the child will go with great pleasure. This will determine whether he will have a fear of dentists in the future.
It is recommended that you spare no expense for the first time and take your child to a paid clinic . In such institutions, treatment is accompanied by a friendly attitude from the staff; children are often shown cartoons and given toys to play with.
Symptoms of carious lesions in baby teeth
The manifestations of caries depend on what stage the process is at.
For early caries (the so-called stain stage), a characteristic sign is a light spot or thin line on the surface of the tooth enamel. This is an area of demineralization - the focus of carious lesions. At this stage, it is difficult to notice caries without the help of a dentist, because the child does not show anxiety or complain of pain or discomfort.
When the process enters the superficial stage, a dark pigmented spot forms on the tooth enamel, which has a rough structure. The tooth may react to sweets, and during the examination the doctor discovers areas of softening of the enamel.
At the next stage of middle caries, dentin is damaged - the bone tissue of the tooth, in which a cavity is formed. The lesion looks like a darkened area, food gets stuck in the hole, and the child complains of pain when eating cold or hot food.
At the stage of deep caries, it is painful for the child to chew, the tooth reacts to any irritants, it can hurt on its own, and partial or complete destruction of the crown occurs. A characteristic type of childhood caries is the bottle form. It affects the dental neck and occurs in infants who often feed from a bottle for a long time. Depending on the form, stage of the disease, and the age of the child, the dentist will decide how to treat teeth affected by caries.
Why is caries treated for young children?
There is a myth that baby teeth with caries do not need to be treated, as they will fall out anyway. In fact, dentists unanimously say that treatment of childhood caries at any age, both on milk and permanent teeth, is mandatory.
There are several reasons why caries of baby teeth should be treated before the age of 5-6:
- The baby tooth preserves space for the permanent tooth and stimulates its growth.
- It takes part in the chewing function and, therefore, in the digestion process.
- Baby teeth affected by caries are a source of chronic infection in the child’s body. In addition, the root of the baby tooth is located next to the germ of the permanent tooth. If caries in children is not treated, the inflammatory process can affect permanent teeth even before they erupt.
- Healthy baby teeth are necessary for a child to develop high-quality speech skills and correct pronunciation of sounds.
- If parents do not treat their child's caries, this can lead to untimely loss of baby teeth. Because of this, other teeth in the row shift, permanent teeth begin to cut in the wrong place, which leads to malocclusion.
- Early loss of a baby tooth can delay the eruption of a permanent one.
This is why it is so important to preserve baby teeth until they fall out naturally. And this can only be done if baby teeth are treated properly in a timely manner.
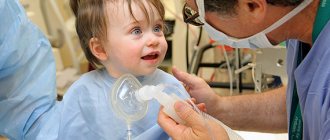
Dental treatment under anesthesia
In most cases, treatment is carried out after the introduction of anesthesia, which is divided into two types - application with local application of medication and injection, which involves the administration of an injection. The second option is safer and more effective.
If a child has panic fear or is simply restless, anesthesia is used, but before using it, a number of diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- biochemical blood test;
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood to determine sugar levels;
- electrocardiography to assess the state of the heart.
You should not eat food 5–6 hours before anesthesia, and drink water and other liquids 4 hours before.
Sleep is induced very gradually using sevoflurane-based gas. If the child needs to be woken up, the doctor increases the amount of oxygen supplied, and this can be done at any time. After waking up, all reflex functions are fully restored within the first 15 minutes. As a rule, there are no complications.
How is caries treated in children?
What to do if a child has caries? Parents often ask dentists this question. And the answer is to treat. It is not so important when a child develops caries, whether he is one year old, 5 years old or 12 years old; dental disease is treated at any age. The only difference is how exactly dental caries are treated.
Different treatment methods are divided into two main groups - conservative and surgical. Conservative ones allow you to quickly and painlessly stop the carious process without drilling the tooth. Such techniques are most suitable for children, but they are effective only in the early stages of caries.
Surgical treatment involves drilling the carious cavity with a drill, removing the affected tissue and installing a filling. In case of deep or moderate caries, it will not be possible to cure a tooth without preparation.
Methods for treating pulpitis in adolescents under 14 years of age, and how do they differ from treatment for adults?
Before starting treatment, the dentist’s main task is to determine whether the patient’s permanent tooth has roots, what stage of formation they are in, and also to find out the condition of the tooth, the location of the source of inflammation, the shape and length of the root canals. To do this, the patient must undergo an x-ray.
Treatment will be different for teeth with formed and unformed canals.
There are 3 main methods of treating pulpitis.
- A conservative method of treating pulpitis is without removing the pulp; during the treatment, the canal is washed with an antiseptic, a calcium-containing paste is applied to the pulp chamber and filled.
- Partial pulp removal
This method involves removing the infected coronal part of the pulp, cleaning and rinsing the cavity, which is then filled with a drug. After the inflammation subsides, the tooth is filled.
- Surgical method with complete removal of the pulp (depulpation). In this case, the pulp is removed, the canals are expanded and washed, and then filled.
We do not use arsenic pastes to treat pulpitis - the same popularly known “arsenic” to “kill” the pulp. Modern technologies and materials make it possible to treat pulpitis using more humane methods for patients of all ages.
Read more about these techniques in our articles:
Treatment of pulpitis of baby teeth
Treatment of pulpitis (in adults)
When and what methods of treating pulpitis of a permanent tooth in a child can be used?
- A child’s diseased permanent tooth has unformed roots.
In this case, during treatment ONLY gentle methods of treating pulpitis are used - a conservative method of treatment or partial removal of the pulp while preserving its living root part.
Depulping – i.e. Complete removal of the pulp is not applicable for such teeth, because their pulp connects to the tissues of the growth zone, which will be injured, and this is not allowed. It is necessary to preserve the living growth zone until the formation of the tooth and periodontal tissues is completed.
In the process of treating permanent teeth with developing roots, all manipulations are aimed at relieving inflammation and preserving the growth zone of the tooth. Subsequently, to avoid relapses, it is recommended to regularly monitor the patient using radiography until the tooth root is completely formed, and then carry out high-quality endodontic canal treatment.
- A child’s diseased permanent tooth has already formed roots.
When treating such a tooth, any of the above methods can be used, including complete removal of the pulp (depulpation). The latter is preferable, but the dentist chooses a technique based on the specific situation.
- Conservative treatment is carried out in case of “early” stage of the disease and in case of injuries.
- Partial pulp removal is effective in treating chronic and onset acute forms of pulpitis.
- The indication for depulpation is any form of pulpitis with severe pain and if other methods do not produce results.
Methods for treating childhood caries without drilling
A child has been diagnosed with a carious spot, that is, initial caries - what to do in such a situation. The doctor may offer several options.
- Fluoridation.
A special composition with a high concentration of fluoride is applied to the surface of the tooth enamel. The mineral substance helps strengthen the enamel, restore its structure, and helps stop the further process of tissue destruction.
- Remineralizing therapy.
The teeth are coated with compounds containing phosphorus, calcium, magnesium and other minerals. The treatment promotes the remineralization of enamel, restoring its strength and structural characteristics.
- Ozone therapy.
Another modern non-invasive method in which children's teeth are treated with ozone. It destroys different types of cariogenic bacteria, preventing their proliferation in the oral cavity.
- Silvering.
Previously, this method was very popular, today it is used less frequently due to the fact that it affects the aesthetics of the teeth. After silvering, white baby teeth acquire a distinct dark color. The essence of the method is that tooth enamel is coated with compounds containing silver. They have an antiseptic and bactericidal effect, forming a protective film on the surface that prevents the spread of infection. Silvering does not cure caries, but it helps slow down the process of tooth decay.
How is the treatment carried out?
First of all, doctors prepare the baby - they get to know him, tell him about teeth beaming in a playful way, turn on the baby’s favorite cartoons so that he can relax and stop being afraid. Next, the baby is allowed to breathe oxygen - they put on a mask so that he gets used to it and understands that there is nothing to worry about. After a couple of minutes, Sevoran gas is supplied. Since the gas is highly concentrated, the immersion in anesthesia occurs very quickly - literally in the first few breaths.
After putting the little patient under anesthesia, the doctor begins treatment. Throughout the entire treatment period, the assistant monitors vital signs using special equipment - temperature, pulse, blood pressure, heart function. After treatment is completed, the little patient is gently brought out of anesthesia. After recovery from anesthesia, breathing is restored immediately, the baby wakes up, and within 15-30 minutes leaves the clinic in a good mood and feeling well.
Invasive treatment of caries
If there is a hole in a tooth, it is treated as if it were permanent, using an invasive method. First, using a drill, the dentist prepares the carious cavity and removes softened, pigmented tissue. Rinses, dries and disinfects the tooth.
After sanitation, a filling is placed inside the cleaned cavity. Today, light-curing filling composites are the most popular. They are applied in layers, and at each stage they are illuminated with a special lamp for curing. Light-curing fillings have good strength, long service life and do not shrink, which reduces the risk of developing recurrent caries under the filling.
After installing the filling, the doctor adjusts it to the bite, grinds and polishes it, giving it the correct anatomical contours.
Other important features of the treatment of pulpitis in permanent teeth for children under 14 years of age:
In order for the treatment of pulpitis to be successful and the patient to have no relapses or complications, it is necessary to:
- Strictly maintain sterility to avoid infection during treatment.
- Use a rubber dam to isolate the patient’s oral cavity from the manipulation field.
- Carry out a thorough filling of the canals - the voids left in them will provoke the re-development of inflammation.
- Monitor the quality of canal filling after treatment using repeated x-ray diagnostics.
- Do not forget that not only adults, but also children need high-quality fillings and dental restoration, and, sometimes, even prosthetics with ceramic inlays.
Do they give anesthesia to children?
Many parents are concerned about how to painlessly treat teeth in children under 5 years old.
Non-invasive methods are absolutely painless. If a cavity needs to be prepared, anesthesia may be required. Children most often undergo two-stage anesthesia. First, the gum area is treated with an anesthetic gel, which numbs the injection site, and then an anesthetic injection is given.
In some cases, it is advisable to use sedation - when the child is introduced into a relaxed state of half-asleep using a special gas. Choosing the optimal method of pain relief and treatment is the responsibility of the dentist.
Prevention of childhood caries of primary teeth
Caries of primary teeth can be prevented if you listen to the recommendations of dentists and follow preventive measures for this dental disease.
- Take care of your oral cavity from the moment the first tooth appears.
Previously, it was believed that young children needed to brush their teeth from about one year old, when they grew eight front incisors. Modern dentistry has revised this approach, and today it is recommended to brush children’s teeth as soon as the first baby tooth has erupted. This usually occurs between 6-9 months of age. It is clear that a baby cannot take care of the oral cavity on his own, so this task falls on the shoulders of the parents. The first teeth are cleaned with special fingertips or a baby brush without toothpaste. The brush should have a small cleaning head and ultra-soft bristles. As they approach the age of one year, they begin to brush their teeth with fluoride-free toothpaste. As the child gets older, the size of the head and the stiffness of the bristles may change. For example, for a child aged 5 years, you can purchase a toothbrush with medium-hard bristles.
- Follow the rules for brushing your teeth.
A child may develop caries even with regular brushing if this process is left to chance. Children under about 7 years old cannot brush their teeth properly, so parents should help them and monitor the process. Proper oral care involves brushing your teeth twice - in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed. The hygiene procedure should not take less than 2-3 minutes. It is important to ensure that the child thoroughly cleans each tooth on both sides and cleans the chewing surfaces. A large number of bacteria accumulate on the tongue and the inside of the cheeks, so at the end of cleaning you need to teach your child to remove plaque from these surfaces.
- Routine visit to the dentist.
Few children like to treat tooth decay. Modern methods make it possible to do this quickly, painlessly and without drilling, but only if the disease is detected at an early stage. This is why it is so important to take your child to the dentist twice a year, even if the child has no complaints. The doctor will check the condition of your teeth and give recommendations for care. Regular visits accustom your child to visiting the dentist and help get rid of fear. In the future, such children sit in the dental chair without any problems and have their teeth treated.
Follow these preventive measures and you may not have to treat your child’s caries.
Experts' opinion
The complex composition of ASEPTA Baby toothpaste allows you to simultaneously care for your gums and teeth. The product has:
- Certificate of state registration;
- Certificate of conformity No. ROSS RU. AG81.H01070.
The paste does not contain fluoride and does not require consultation with a doctor before use. The product is safe if swallowed, as it does not contain components harmful to the health of the baby.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)