A jaw fracture is one of the most common types of injuries among all injuries to the bones of the facial skeleton. According to statistics, damage to these bones (upper and lower jaws) accounts for more than 70% of cases of facial injuries. This can be explained by the anatomical structure and location of the bones, since they are large in size and have a high degree of mobility.
Maxillary fracture
Fractures of the upper jaw occur in 2–5% of cases of injuries to the facial bones of the skull. In half of the cases they are obtained due to mechanical influence from the outside.
The severity of the injury is related to the location of the bone damage: the higher the fracture line of the upper jaw, the stronger the separation of the jawbone from the skull bones, the more difficult the therapy and rehabilitation, the greater the likelihood of complications. Fractures of bones in the head area are considered one of the most dangerous to human health; they can provoke a number of complications from impaired functionality of the body in this area to concussion, meningitis, osteomyelitis and other types of lesions.
Severe forms of fractures of the upper jaw in this case are accompanied by:
- damage to the walls of the paranasal sinuses and the walls of the frontal sinus;
- damage to the nasal pharynx;
- injury to the middle ear;
- violation of the integrity of the meninges;
- injury to the anterior cranial fossa with pressing of the nasal bones into it;
- Emphysema of the subcutaneous tissues of the upper and middle third of the face (in the area of the eyes, forehead, cheeks) may occur;
- rupture of the soft tissues of the face (muscles, skin).
How long will it take for the injury to heal?
When asked how long it takes for a jaw fracture to heal, doctors answer that on average rehabilitation lasts up to 3 months. The trauma is significant, and only after the first month of treatment do patients begin to feel relief. Much of the relief is due to the fact that 21 days after the operation the fragments heal and doctors remove the splint, but sometimes this happens later, only on days 30–40.
On average, rehabilitation lasts up to 3 months
If you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations, in case of chronic diseases that disrupt tissue trophism (for example, diabetes), the healing process may take 2–4 weeks longer.
“I suffered a broken jaw in an accident. How many tears I shed while being treated!!! This whole thing heals quite slowly, you have to wear a splint, and it’s generally difficult to eat normally. If you want to lose weight and get rid of extra pounds, break your jaw. Black humor! This splint also constantly rubbed the mucous membrane on the cheeks and lips. All this time there was pain. After the splint was removed, there were sores and inflammation in my mouth. Then she replaced the teeth, since some were knocked out during the accident. In total, it took six months to recover. Now, thank God, the pain is gone, but it pulls and aches for any reason, for example, if the weather changes...”
Mi, fragment of review from otzovik.com
Symptoms
Based on characteristic signs (external and internal after radiography), it is possible to determine what type of injury the patient has. The most typical symptoms for fractures of the upper jaw are:
- there is blood coming from the nose and mouth;
- broken bite;
- feeling of pain when trying to close the jaw;
- hematomas “spectacles syndrome”;
- violation of some of the most important functions of the body: chewing, speech, breathing;
- general weakness, nausea, vomiting.
Painful sensations when palpating certain points on the face, as well as increased extensibility and compression of the bones are a clear sign of injury.
A particularly severe fracture of the upper jaw (base of the skull, zygomatic, nasal and lacrimal bones) may be accompanied by intense lacrimation and liquorrhea from the ears and nose.
Many patients have pronounced traumatic neuritis (damage to nerve fibers) of the infraorbital nerve.
Brief anatomy
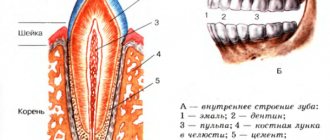
The upper jaw is a paired bone that has a body, in the thickness of which the Maxillary sinus is located, it communicates with the nasal cavity. Along the inner edge there is a pear-shaped notch, forming an opening of the same name. The processes extend to the sides, downwards - the alveolar, in which the teeth are located, from the outer surface - the zygomatic, upward - the frontal.
The bone has holes through which nerves emerge that innervate the face and, in fact, the teeth. The largest is the infraorbital foramen, from which a branch of the trigeminal nerve emerges. Bone is involved in the formation of the oral cavity, eye socket, and nose. Behind the zygomatic process is the maxillary tubercle, through which the nerves that innervate the teeth enter. A photo will help you visualize the above.
Fracture of the lower jaw
A person receives most of all jaw injuries after exposure to a strong mechanical force on the bone. In some cases, a violation of the integrity of bone tissue can occur spontaneously, due to a disease of the body, such as, for example, osteomyelitis, neoplasm and others. Among victims diagnosed with a fracture of the lower jaw, more men than women.
Such an injury can cause a lot of harm to a person’s health, so it is not advisable to delay visiting a doctor, or start treatment on your own, since fractures of the lower jaw with a high degree of severity, for example, shrapnel injuries or with displacement of the bone from the articular cavity, can cause:
- changes in normal bite;
- the lower jaw may begin to close poorly, which will lead to problems with chewing and the ability to speak;
- the addition of inflammatory processes due to infection of the affected areas of the oral cavity.
Causes
Jaw fractures are formed as a result of the influence of any traumatic factors, the force of which is higher than the strength of the bone. In many situations, the causes will be falls, impacts, road accidents, and industrial accidents.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
However, the outcome of injury often varies. This depends not only on the strength, but also on other reasons, which include the physiological integrity of the bone before the fracture.
The causes themselves differ depending on the type of injury.
Pathological fracture
Involves a situation in which the bone is damaged due to low-intensity trauma or everyday physical activity. It is based on the structural and functional pathological process of bone tissue, which provoked its significant weakening.
Today, many diseases are known that cause these types of defects. Also, such fractures occur due to the formation of malignant or benign growths on the bone.
Failure in the metabolism of certain substances, an unbalanced diet or inadequate supply of vitamins and minerals, persistent infectious lesions, hereditary diseases, therapy with medications that suppress cell division, other conditions and diseases that can provoke significant changes in the structure of the bone. These factors can weaken the bone and cause a fracture.
Traumatic fracture
It is a bone injury that develops as a result of any mechanical action of increased intensity. In many situations, this type of injury occurs as a result of a direct or indirect blow.
It can occur due to a fall, an accident, a gunshot wound, or many other possible factors. During such a defect, the state of the bone structure and its functioning before injury are normal.
Mostly, traumatic fractures are observed, which differ in the specific shape and physiology of the jaw from defects in other bones of the skeleton.
Symptoms
Depending on the degree of the fracture of the lower jaw and its type, the signs may be different; the form (closed or open) is of great importance, which will manifest themselves with varying degrees of severity. Often the affected person will experience the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the lower jaw;
- displacement and palpable movement of broken bones under the skin;
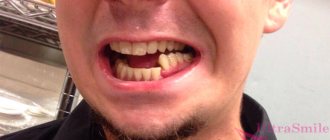
- deformation of the placement of both the upper and lower rows of teeth;
- visually noticeable facial deformation;
- change in bite;
- impaired breathing and slurred speech of the victim;
- dysfunction of chewing and swallowing;
- increased salivation;
- the appearance of gaps between teeth, especially in the injured area;
- numbness of lips and chin;
- general weakness of the body.
The presence of serious injuries due to a fracture of the lower jaw in the victim can be judged by the presence of the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- gagging;
- loss of consciousness;
- bleeding from the ear canals.
Diagnostic criteria for damage
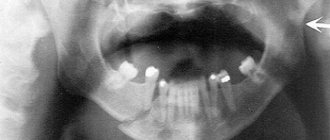
In order to confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform an x-ray of the skull bones. The diagnostic procedure is performed in two projections; special installations can be used. Using photographs of the skull bones, the doctor focuses on the contours of the main anatomical formations; if they are disturbed, we can talk about a fracture. Also, photographs can be taken when the teeth are closed; fragments may move, however, this is done with pain relief and minimal risk of damage to blood vessels and nerves.
Diagnosis of a jaw fracture
In case of fractures of the lower jaw, when the victim goes to a traumatologist, he will conduct the necessary set of diagnostic studies.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor needs to know the exact location and severity of the fracture. For this, the patient is prescribed radiography, visual examination and palpation of the injured jaw.
Without a detailed diagnosis, it will not be possible to determine the severity of the injury. But if you take into account the present symptoms, an experienced traumatologist will be able to provide emergency care in case of a serious patient’s condition.
Length of stay on sick leave
The length of a patient's stay on sick leave depends on the nature of the injury and the degree of complexity. On average, treatment time ranges from 2 months. If the alveolar process is damaged, the disability is 45 days; a fracture of the body will require 70 days of sick leave. Fractures of type Lefort 1 require on average 55 days, Lefort 2 – 66, Lefort 3 – 75 days.
Uncomplicated fractures require disability for 2 months, complicated ones from 120 to 130 days. After 120 days of being on sick leave, the patient must be referred to the MSEC (medical and social expert commission), which decides to extend the sick leave or recognize the victim as disabled.
Approaches to treatment and diagnosis can be very different, but they are all aimed at achieving maximum results. A dentist or maxillofacial surgeon will advise you on the intricacies of treatment. During the treatment process, prevention of complications is mandatory and a fracture may not leave any consequences.
Treatment
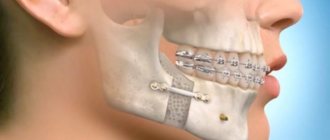
Methods for correcting fractures of the lower jaw are selected based on the severity of the injury that harmed his health. The treatment plan consists of the use of conservative methods (orthopedic methods, which are used in 90% of cases of injury), surgery, and hardware reposition. The main treatment measures include:
- performing an operation to reposition fragments;
- applying a splint to the lower jaw;
- creating and maintaining the necessary conditions for faster bone recovery;
- taking medications (antibiotics, drugs to strengthen the immune system);
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Surgical intervention - may include the following manipulations:
- installation of brackets on the upper jaw;
- fixation of the jaw with knitting needles;
- fixation with plates;
- fixation of the jaw with extraoral structures.
To cope with a fracture of the upper jaw, especially in the most severe forms, complex surgical interventions may be required.
Orthopedic methods are based on immobilization and fixation of the jaw at the fracture site using a splint.
What to do
If there is the slightest suspicion of a jaw fracture, you should seek help from a doctor, since self-therapy leads to dangerous consequences, including self-destruction of bone tissue.
Often, after injury, patients are unconscious and need to be transported to the hospital. In a relatively satisfactory condition, it is permissible to transport the patient on your own, but only after providing proper first aid.
It involves the following actions:
- cardiac and pulmonary resuscitation
- stopping bleeding;
- anesthesia;
- fixation .
Treatment and rehabilitation at the Center for Maxillofacial Surgery and Implantology
Our clinic specializes in the surgical treatment of high-complexity injuries of the zygomatic-orbital complex. Fractures of the zygomatic-orbital complex are dealt with by a team of highly qualified specialists - surgeons, anesthesiologists, resuscitators, medical personnel - who have extensive experience and knowledge to solve the most complex problems of maxillofacial surgery. Working together, they are able to develop and implement the most optimal and highly effective plan for a jaw fracture with a guaranteed high result.
Fractures of the zygomatic-orbital complex can have negative consequences of an aesthetic nature, worsen visual and respiratory function and lead to a number of complications. Characteristic of such cases are damage to the thin floor of the orbit, the restoration of which also requires surgical intervention. Therefore, correction of a jaw fracture should be carried out in a clinic with an exceptionally high reputation with highly qualified, experienced specialists who will help correct the consequences of both fresh and old injuries.
A jaw fracture is an injury to the zygomatic bone, which is an integral part of the orbit; therefore, injuries in this area are accompanied by:
- double vision
- displacement of the eyeball
- restriction of mouth opening
- swelling
- breathing problems
- the upper jaw may become numb
In order to accurately diagnose a fracture, its individual characteristics and predict the consequences, the Center’s experienced specialists have the opportunity to use the entire range of modern diagnostics, which will allow them to determine the nature of the damage, draw up the most effective treatment plan and accurately predict the future result.
Treatment of injuries of the zygomatic-orbital complex is carried out under general anesthesia in the inpatient setting of the Center for Maxillofacial Surgery and Implantology. It has the most modern operating rooms, equipped with the latest high-tech equipment and the ability to use innovative methods for correcting fractures of the zygomatic-orbital complex.
Consequences
To avoid adverse complications, you need to promptly seek the help of doctors. The following complications are likely:
- movement ;
- the appearance of gaps between teeth;
- deformation of the facial skeleton;
- formation of malocclusion.
To avoid adverse consequences, you should consult a surgeon.
In some situations, surgery is necessary to restore damaged parts of the face. In case of a minor fracture and timely consultation with a doctor, following all his instructions, jaw mobility will resume within 4 weeks.
Nutritional Features
For full rehabilitation after any injury, it is extremely important to provide the patient with a balanced diet containing all the vitamins and microelements necessary for cell regeneration.
In case of injuries to the upper jaw, this condition is difficult to fulfill due to the inability of the victim to chew food. To feed the patient, you will have to use special devices: tubes, bottles, straws, sippy cups.
The diet should consist of the following dishes:
- meat broths;
- raw eggs;
- pureed vegetable soups;
- natural juices with pulp;
- puree of vegetables and meat;
- liquid porridges;
- fermented milk products.
As bone tissue is restored, the patient should be offered more rigid dishes to develop the jaw. Crackers, hard fruits and other food components are prohibited until complete recovery. The process takes approximately one month.
The transition to solid food takes place gradually, under the strict supervision of the attending physician!
Food that is icy or too hot cannot be eaten; all dishes must be at room temperature. It is advisable to eat often, but little by little. After removal of the immobilizing structures, it is not recommended to quickly return to your usual diet. You should follow a gentle diet for some time to prevent gastrointestinal disorders.