Baby teeth are considered temporary, so parents often treat them without due attention. Care, treatment, and concern for the health of the oral cavity are usually postponed until later - when the baby’s temporary bite is replaced by a permanent one. And this is a big mistake, dentists warn. The attitude towards the primary dentition from the moment of its appearance should be as attentive as to the permanent one.
Why can't we trust prejudices? Do baby teeth need to be treated? Is it possible to pull them out at home? And when should you definitely see a dentist? FAN journalist asked these questions to the head of the dental department of the Medsi children's clinic on Pirogovskaya, pediatric dentist Natalya Terentyeva .
Content:
- Do baby teeth really hurt?
- Why do baby teeth hurt in children?
- Pain in baby teeth after filling
- Treatment of dental diseases that cause painful symptoms
Many adults are surprised when they hear about the pain of baby teeth. They believe that temporary units that will soon fall out cannot hurt. Moreover, if a child complains of discomfort in the mouth, some parents do not take him to a dental clinic for examination. They expect that the problem will solve itself - the troubling molar, canine or incisor will soon become loose and fall out. Dentists do not agree with this attitude towards the problem of childhood toothache. Doctors say that if a child’s baby tooth hurts, it is necessary to treat it. In non-advanced cases, the bite can be kept intact. This is important for its correct formation.
Should I go to the dentist if my teeth are fine?
Regular preventative dental examinations are needed not only for adults, but also for children. Moreover, in childhood they are required even more often. If adults are advised to visit a doctor every six months, then children, due to the characteristics of tooth enamel and potential risks, should visit a doctor every three months.
In addition, parents should visit an orthodontist when their baby’s teeth begin to change. The specialist will conduct an examination,, if necessary, prescribe an x-ray of the oral cavity and recommend treatment that will help the permanent teeth grow evenly and in their places. This means your child’s smile will be beautiful and healthy.
Do baby teeth really hurt?
Temporary units can be just as painful as permanent ones. They have roots to which nerve endings go. In addition, the risk of painful sensations in preschoolers and primary schoolchildren is much higher. This is due to the specific structure of children's teeth. They are not sufficiently mineralized, and the dentin-enamel layer covering the crown is very thin. Because of this, even minor external problems can lead to caries. Pulp tissue in babies, on the contrary, is voluminous. It is quite easy for bacteria to reach them through expanded channels.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Those manipulations that an adult is able to calmly endure will become the strongest test for a child, both physically and psychologically. Pain management in pediatric dentistry is given a special place, because the psychological trauma from pain received in childhood at a dentist’s appointment will accompany a person throughout his life, and the fear of the dental office will turn into a real phobia. The use of anesthesia by pediatric dentists will remove pain and, accordingly, fear of procedures.
The use of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry has a number of features:
- for the youngest there are restrictions on the use of most products that can be used from 4 years old;
- the doctor must have experience and high qualifications to accurately calculate the active drug;
- children are afraid of treatment of baby teeth , and in general of all dental instruments, especially syringes and injections;
- Quite often, children experience allergic reactions to anesthetic drugs.
Why do baby teeth hurt in children?
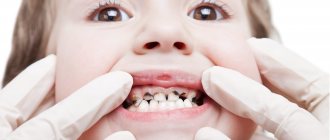
There are quite a few reasons. All of them are associated with various dental ailments. The prerequisites for any oral disease are poor hygiene, consumption of large amounts of sweets, and an unbalanced diet. Let's list the main reasons:
- advanced caries;
- progressive acute pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- flux;
- erosive damage to enamel tissue;
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis;
- increased sensitivity due to insufficient mineralization.
Unpleasant sensations in the mouth may occur due to the eruption of permanent units. Then the mucous membrane becomes injured and swells. This condition does not require dental treatment. In case of severe pain, inflamed tissues should be treated with special anesthetic gels. A popular cause of childhood toothache is jaw injury. Therefore, if an outwardly painful unit looks absolutely healthy, parents need to clarify whether the child has fallen or hit his face or chin on hard objects.
What is the reason?
It is generally accepted that the cause of pain is caries. In fact, there are many more sources of pain. Therefore, when a child has a toothache, it is important to understand what caused it:
- pulpitis, periodontitis – inflammation of internal tissues;
- flux - inflammation of the periosteum;
- gingivitis – inflammation of the gums;
- abscess – accumulation of pus in the tissues surrounding the tooth;
- enamel erosion;
- ulcer on the mucous membrane;
- fistulas;
- caries.
With caries, the pain is usually paroxysmal, does not last long - up to several minutes, and occurs when eating cold or hot food. In case of pulpitis, periodontitis - acute, lasts for hours, is not relieved by painkillers, therefore the child needs help immediately.
Pain in baby teeth after filling
It would seem that if there is a filling, then there should be no problems. But in practice, pain often occurs precisely in the area of the treated tooth. This is possible if the carious cavity was cleaned poorly, the root canals are not completely closed with a sealing compound, an inflammatory process has begun in the roots, and pulpitis has developed. It also happens that a small patient develops individual intolerance to the filling material installed for him. Regardless of the reason, most often the dentist removes the filling and examines the condition of the dental bottom. First, the doctor takes an x-ray to see if the roots are affected. It is dangerous to endure pain in a filled tooth. The inflammatory process occurring under the filling often spreads to adjacent soft tissues and the jaw bone. This is fraught with serious health problems.
First examination of a newborn
Immediately after birth, the baby is examined by specialists, including a dentist. This is important because an assessment of the general condition and reflexes is necessary, but the primary question is the size of the frenulum of the tongue. With a shortened frenulum, the child will not be able to grasp the nipple and suck normally. External examination and assessment of tongue movement does not always reveal abnormalities. This may appear in the next 5-15 days:
- smacking sounds appear during feeding;
- a long feeding process: the baby sucks, then pauses for a while and starts sucking again;
- Mom develops cracks and pain in her nipples;
- the child is capricious at the breast;
- is gaining weight poorly.
If such symptoms are noticed, you should make an appointment with a doctor so that he can examine the baby, determine the size of the frenulum and make the appropriate prescriptions.
Treatment of dental diseases that cause painful symptoms
What measures the dentist will take directly depends on the nature of the problem:
- At the initial stage of caries, you can even do without using a drill, which kids are so afraid of. The doctor simply treats the damaged tissue with fluoride and seals the fissures. If the carious cavity is large enough, you cannot do without removing the dark spot with a drill. Then, after cleaning the “hole,” it is treated with special medicinal compounds and sealed.
- In cases of pulpitis, children rarely have the entire pulp removed. Most often, it is sufficient to simply mummify the nerve. For this purpose, the dentist uses the vital amputation technique. It involves removing only the coronal part of the pulp. The root remains intact. In case of a severely advanced disease, they work with all damaged connective tissue.
- In case of inflammation of the periosteum - periostitis - surgical treatment is performed. The doctor opens the formed abscess and washes its cavity. The child is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures and rinses are prescribed. It is mandatory to treat the disease that led to the inflammatory reaction.
- An abscess involves draining the abscess and cleaning the root canals. The patient must be prescribed antibiotics. It is very important to block the spread of the abscess at an early stage. Otherwise, it may spread to surrounding tissues. Then the child will have to be hospitalized.
- Gingivitis requires complex therapy. The child undergoes professional oral hygiene and all plaque deposits are removed. Then medications and vitamins are selected. In some cases, physiotherapy is indicated.
- The fistula is opened immediately. The root canals are cleaned and filled. After the inflammatory reaction subsides, a permanent filling is placed.
The sooner the pain in primary teeth is treated, the more comfortable the therapy will be for the patient. Therefore, parents should not expect the disease to go away on its own. Only by taking the child to an appointment with the dentist can they be calm about his health.
What to do if a 6 year old child has a toothache?
Folk remedies can bring temporary relief. The main thing is that they do not cause an allergic reaction (herbs, honey) and do not lead to gum burns (tinctures, garlic). Dosages should be minimal. Children 6 years and older benefit from rinsing the mouth at intervals of 2-3 hours. The solution (not hot) must be kept in the mouth for up to a minute. Suitable for these purposes:
- saline solution (a glass of water + a teaspoon of salt);
- soda solution (a glass of water + half a teaspoon of soda);
- a decoction of chamomile, sage, lemon balm, oak bark, mint or other medicinal herbs.
So, what to do if your child has toothache? First of all, don't panic! Make an appointment with a pediatric dentist. After taking painkillers and rinsing, the baby will feel better. To prevent the situation from getting worse, offer your son or daughter soft or semi-liquid food, do not give anything cold or hot, and ask him to rinse his mouth with warm water after each meal. These measures are quite enough to survive the period until a visit to the pediatric dentist. Keep calm - and it will definitely be passed on to your child!
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry, types
1. Application of local anesthesia
Most often used. It is carried out in 2 stages - “freezing” with a gel or spray, after which the drug is injected. Typically, children of any age tolerate this type of anesthesia well. Sensitivity is not completely lost; minimum contraindications.
2. Use of sedation
A sedative is inhaled. The child relaxes, but remains conscious. This is not anesthesia in its “pure form”; there is no strong analgesic effect. It is often used with an injection of an anesthetic drug.
3. Use of general anesthesia
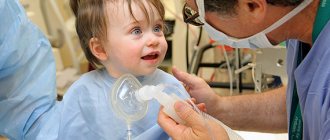
It is used in extreme cases, because the risk of complications after dental treatment under general anesthesia exceeds that with local anesthesia. The pediatric dentist must have good reasons for using general anesthesia, because this causes profound depression of the nervous system, which can be followed by complications. The primary thing is to correctly calculate the dosage and take into account the individual characteristics of the small patient.
The anesthetic drug is given by inhalation: by inhaling the vapor of the drug, the child falls asleep. The doctor gets the opportunity to quickly and calmly treat the tooth, and the child will not feel pain or get stressed.
Treat caries or remove a tooth?
Here, the recommendations of pediatric dentists agree: teeth need to be treated, although this is often associated with inconvenience. True, it is now much easier to persuade a child to calmly undergo treatment than it was before, when quality dentistry was unavailable. In a modern clinic, a calm and friendly atmosphere is important in a pediatric dentist's office. The doctor will first show the instruments, explain what he will do, and establish contact with the child. And drugs for pain relief will help carry out the treatment so that there are no negative impressions left from it.
Dental treatment is not scary! Especially if it doesn't hurt
It is best to treat tooth decay in its early stages. Then you can do without drilling at all - it will be enough to clean the surface of the tooth and apply a remineralizing composition. Small areas of caries can also be treated using a special device that uses a laser beam.
But even if a large carious cavity has already formed in the tooth, it is still recommended to install a filling. In some cases, crowns are even placed to save the tooth, which will last until the tooth falls out naturally. All this is justified in order to preserve the functionality of the tooth, which is extremely important for the formation of a correct permanent bite in a child.
Crowns can be installed to save teeth
Prevention is the best solution
So that you do not have to worry about treating or removing baby teeth, organize proper nutrition for your child and oral care.
Try to prevent your baby from consuming a lot of sweets; if possible, reduce the amount of sweet juices and carbonated drinks in the diet. And, of course, take care of regular and proper brushing of your teeth.
The child should brush his teeth 2 times a day: morning and evening. At the same time, do not allow any snacks after brushing your teeth in the evening. If your child is under two years old, brush his teeth yourself. At this age, by the way, be sure to use special toothpastes recommended for children over 0 years old, for example, ASEPTA baby.
Older children should brush their teeth themselves, but always under adult supervision. From the age of two, also visit the dentist at least 2 times a year. This is the only way you can prevent the development of serious dental diseases and ensure timely resolution of all emerging problems.
Alternative to general anesthesia
The safest alternative is sedation. Through a mask, the patient inhales a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide. A slight relaxation and drowsiness appears, and the feeling of fear disappears. At the same time, the child is conscious and able to do what the doctor says.
Sedation cannot be considered anesthesia in the full sense, but it still provides an analgesic effect, and in combination with an injection of an anesthetic it provides a good result. The gas composition is supplied through a device that controls the dose of the mixture, the time of sedation, allowing you to smoothly enter and exit “half-sleep”. After stopping the supply of the mixture, the effect lasts about 10 minutes.
Treatment of pulpitis of teeth with unformed roots
The root system of a baby tooth is formed over a long period of time after eruption, so there are often situations when caries begins to form on a tooth whose roots have not yet closed the apex. This leads to some treatment difficulties:
- short roots and wide channels;
- the upper part of the root is the “growth” zone, injury to which is an obstacle to root formation;
- the likelihood of infection of the permanent tooth germ;
Treatment of pulpitis of teeth with immature roots in children requires special care. The doctor must carefully monitor that the filling material is not carried beyond the expansion of the root apex. It is worth noting that complete removal of the pulp and treatment of the canals is impossible - the optimal solution here is vital and devital extirpation. Pulp amputation may also be used. The biological method, which consists in preserving a viable pulp and relieving inflammation, is also practiced quite often. Its essence is to prepare the tooth, apply a medicinal paste with calcium hydroxide, after which the tooth is filled with temporary material. A few days later, if there are no complications and the unpleasant symptoms disappear, the doctor installs a permanent filling.