Norm and pathology
The tooth extraction procedure involves violating the integrity of the soft tissues and mucous membranes, muscles and ligaments that surround the diseased tooth and are responsible for reliably holding the root in the gum. That is why it is quite logical that after the operation a slight inflammation may begin, characteristic of the wound healing period.
Its main symptoms are: moderate pain when speaking and opening the mouth, discomfort when trying to chew even soft food, discomfort at rest and during movement. Bleeding may also occur, which usually stops several hours after the tooth extraction procedure.
At the site of the gum incision, sharp pain may appear, which radiates to the head and can cause the onset of a migraine. Also considered normal is slight swelling, redness or slight bluish discoloration of the soft tissue. Sometimes a person experiences an increase in body temperature, and the injured area may “burn.” These symptoms usually go away on their own a few days after the intervention.
Possible consequences
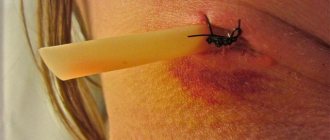
After tooth extraction, did a hematoma appear on the gum? This is a common consequence of surgery. The accumulation of blood in soft tissues occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the capillaries during surgery or during anesthesia of the jaw. The doctor cannot determine where the patient's blood vessels run, so the risk of damage cannot be ruled out.
A small bruise on the gum is a clot of coagulated blood that resolves within a few days. With a hematoma, moderate pain and swelling of the oral mucosa are also possible.
Possible complications
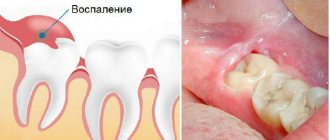
If serious inflammatory processes arise in the gum, then after surgery it may change its color to bright red, blue or black. If all this is accompanied by pain, the gums become loose to the touch, and purulent discharge appears, then you should immediately contact the clinic for an examination.
The most common complications include the appearance of cysts. They are small formations containing a small amount of clear liquid inside. If you seek help in a timely manner, treatment may be limited to drug therapy.
Other common pathological processes that occur against the background of gum inflammation include alveolitis, periostitis and gumboil. Flux appears due to infection in the periosteum tissue. Alveolitis manifests itself in the form of redness and significant swelling in the wound area. The patient may complain of acute pain, the appearance of pus, fever and poor health. Also, the pathology is often accompanied by bleeding, which cannot be treated with improvised means.
Treatment methods
Depending on the cause of gum swelling and accompanying pathological processes, the doctor may prescribe conservative treatment, or resort to surgical manipulation or tooth extraction. The clinical picture is determined by the results of examination and radiography.
Conservative therapy
When visiting a dental clinic, a specialist eliminates the cause of gum swelling and then begins to eliminate inflammation, symptoms and associated pathological processes.
The patient may be prescribed drug therapy, including:
- antiviral;
- painkillers;
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines.
Local therapy that has an antiseptic effect is required. The dentist may recommend the use of special ointments or gels, rinsing the mouth with medications or herbal decoctions.
Surgery
The help of surgical dentistry is necessary for certain indications. The need for surgical intervention arises with the development of a purulent process. The specialist will need to open the gum, fistula or root canal to release the pathological fluid. Next, the affected cavity is cleaned, treated with an antiseptic, and treatment of the underlying disease begins. Swelling of the gums can be a sign of a serious pathology that requires tooth extraction. The need for extraction or the possibility of saving the tooth is assessed by the doctor.
Blackening of the gums
A change in gum color does not always indicate the onset of inflammatory processes. If the gums at the site of the incision become whitish, this is considered one of the normal variants. This is how fibrin manifests itself, which tightens the wound and protects it from bacteria getting inside.
However, if the bed and adjacent fabrics have turned dark blue or black, this is a cause for concern. Blueness indicates the transition of inflammation to the third stage, which can lead to complete atrophy of the gum tissue.
The gums begin to turn black already when the irreversible process of decay has begun. This is usually accompanied by purulent discharge, a strong and very unpleasant odor from the mouth, and severe pain that cannot be controlled with conventional painkillers.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
What can you do
The first thing to remember: when the very first symptoms of an incipient inflammatory process in the oral cavity appear, it is important to contact a medical facility as quickly as possible. It is almost impossible to independently identify the cause and stage of development of the pathology, and treatment with folk remedies can lead to more serious consequences.
Inflammation at the initial stage is easily eliminated by rinsing. For this purpose, certain medicinal herbs may be prescribed, for example, thyme, sage or oak bark. They are ideal for regular rinsing, reduce pain and swelling, and have a powerful antibacterial effect.
The doctor may also prescribe analgesics, for example, Dolaren or Ketanov. Unfortunately, when the inflammatory process enters an advanced stage, such therapy will not bring the desired result. In this case, the dentist may prescribe washing the infected hole and treating it with medicinal applications. General recommendations include preventive rinsing of the mouth with antiseptics at home, for example, Chlorhexidine solution. It is also best to temporarily stop taking blood thinning medications, smoking, and drinking any alcoholic beverages.
previous post
How to make teeth whiter?
next entry
Expert advice
To avoid complications after tooth extraction, you must follow your dentist's recommendations.
- For the first week after surgery, do not eat solid foods or drink drinks through a straw.
- Do not take a hot bath or visit the bathhouse or sauna until the wound has completely healed.
- Use a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid damaging your oral tissues.
- If pain or other unpleasant symptoms occur, contact your doctor.
Reasons for the development of gingivitis in children
The abundance of causes of the disease can be divided into two large groups.
Common reasons include:
- colds, especially if they occur frequently;
- sore throat and chronic sinusitis;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Among the local reasons it is worth highlighting:
- poor-quality fillings, which, when destroyed, injure soft tissues;
- caries (infection from the cavity quickly enters the gums);
- crowded teeth;
- violations during the installation of braces;
- Tight lips that interfere with quality teeth cleaning.
Separately, it is worth noting the most important reason, since all of the above are only a catalyst for the development of the disease. So, the main reason why gingivitis begins to develop is poor oral hygiene, which can manifest itself both in improper brushing of teeth and in incorrectly selected toothpaste and brush.
Symptoms of the disease
Gingivitis has quite a few characteristic signs by which one can guess the onset of the disease:
- bleeding gums;
- pain during cleaning;
- swelling of the gums;
- severe redness of the gums in the case of an acute phase of inflammation;
- when the disease becomes chronic, the gums may acquire a bluish tint.
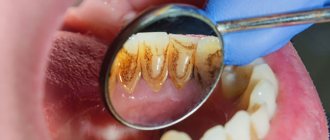
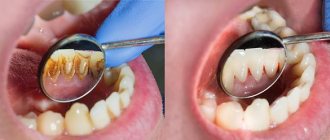
Often with the naked eye you can notice a large amount of accumulated plaque and tartar, and there may also be many teeth affected by caries.
In addition, gingivitis can be caused by diseases that have nothing to do with the oral cavity:
- heart and vascular diseases;
- disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
The above factors reduce immunity, as a result of which the gums lose their ability to resist toxins formed in plaque.
What is the best way to treat?
As was said a little above, gingivitis occurs due to accumulated soft plaque, so the first thing you need to do is get rid of it. Plaque can be removed using ultrasound - this is a simple and absolutely painless procedure. Using a special attachment, the dentist touches dental plaque, which is destroyed by ultrasound. By the way, ultrasound allows you to get rid of not only soft plaque, but also hardened formations on the teeth.
It is necessary to understand that plaque can be effectively removed, especially if inflammation has begun, only with ultrasound: rinsing with various means, using special toothpastes and gels with the addition of antibiotics can temporarily remove the symptoms of gingivitis, but these methods are not able to eliminate its cause. As soon as you stop using these medications, bleeding will return and the disease will continue to progress. Therapy aimed at reducing the inflammatory process is justified only after the deposits have been removed.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is usually prescribed as follows:
- Rinse with Chlorhexidine solution. The maximum duration of use of the drug is 10 days. Rinsing should be done twice a day for at least 30-40 seconds per procedure. The solution, which has a bitter taste, which not all children will like, has no contraindications based on the child’s age.
- Rinse with Miramistin (prescribed after the child reaches the age of 3 years). You need to rinse three times a day. The drug is inferior in its effectiveness to Chlorhexidine and is significantly higher in price.
- Rinse with infusions of chamomile or sage (it is not recommended to use oak bark).
In addition to rinses, many doctors prescribe ointments and gels. It is believed that the gel is more effective than ointment because, due to its consistency, it has the ability to remain on the gums for a long time, which promotes better absorption. In addition, the medicinal substances contained in the product penetrate much better into the tissues from the gel than from the ointment.
The most effective and proven gels on the positive side are the following:
- Cholisal is a drug that simultaneously has two effects: analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It is used for gingivitis and the beginning of teething (the drug is rubbed directly into the place where the tooth is emerging). There are no age restrictions. The gel can be used for a maximum of one and a half weeks, twice a day. After applying the product, it is recommended to eat within two, or preferably three, hours.
- Metrogil Denta. Used after 6 years. Apply directly with your finger or a cotton swab to the gums near all teeth; there is no need to rinse off the gel.
Many parents often decide to treat their child on their own, not wanting to see a dentist. But you need to understand that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs will have no effect if you do not get rid of the deposits, so you will still have to set aside time to visit the dentist. If you ignore the advice, then:
- symptoms of bleeding will disappear, but will reappear after completion of the course of therapy;
- gingivitis can become chronic, causing periodontitis.
In addition to anti-inflammatory therapy, oral cavity sanitation and silvering are carried out - a method that does not require drilling, but has a lot of disadvantages.
How to avoid the occurrence of gingivitis?
The following remedies will help prevent gum bleeding:
- High-quality oral hygiene. Parents should instill in their children oral care skills from an early age. Not all adults know that hygiene measures must begin before the first tooth begins to erupt.
- Using the right paste. If the child does not have gingivitis, then you can use any paste designed for children. If your child does not brush their teeth well enough, you can purchase a paste with amino fluoride.
- Stick to your diet - avoid snacking, limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates (carbonated drinks, sweets). Of course, you don’t need to completely deprive your child of sweets, but you can give them only immediately after the main meal, after which you should brush your teeth.
How to avoid complications
To avoid missing a cyst in the early stages, check with your dentist at least once every six months, especially if your child has chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. The occurrence of cysts is most likely between the ages of 6 and 12 years, especially during the formation of the first molars in the lower jaw.
Teach your child proper and regular oral hygiene. This will reduce the likelihood of inflammation and caries in both milk and permanent teeth. For this, use high-quality children's toothpaste for a specific age. Asepta has developed Baby, Kids and Teens pastes that take into account the dental needs of children of different ages. For the little ones, specialized Asepta wet wipes designed in the form of finger pads are suitable - wipe the gums after each feeding.
It is necessary to treat infections and caries in a timely manner so that they do not lead to the formation of a cyst in the future.
Differential diagnosis of gingivitis
It is based on the complaints presented to the patient, a visual examination of the patient, the results of functional tests and laboratory tests. The goal of differential diagnosis is to distinguish gingivitis from other periodontal diseases, such as periodontitis and periodontal disease.
The main feature that distinguishes gingivitis from other periodontal diseases is that the inflammatory process affects only the gum tissue, the remaining structures (muscle ligaments that hold the tooth in the jaw and bone tissue) remain unchanged.
Along with this symptom, gingivitis is not characterized by periodontal pockets, exposure of the necks of teeth, or their mobility. And the x-ray shows no signs of bone resorption.
Identifying gingivitis in a timely manner, determining its form and prescribing the correct treatment is the task of a periodontist. But not to forget about prevention and regularly visit the dental clinic is the maximum program for the patient. This is the only way to avoid a more serious periodontal disease – periodontitis.
What can you do as an emergency?
It was already mentioned above that the most common cause of symptoms in childhood is the process of teething or changing teeth. To help your baby endure this difficult and painful period more easily, special ointments and gels with an anesthetic effect will help: “Kalgel” or, for example, “Cholisal”. As a rule, such a problem does not require medical intervention - the process of “punching” the tooth out usually takes several days. To speed up this process, you can resort to the help of special baby teethers. The blue spots will gradually resolve on their own.
If the cause of the blue discoloration is a growing tooth, then the symptoms may resolve on their own
As for other causes of hematoma, including in adults, you cannot do without the help of a doctor. During a visual examination and examination of the clinical picture as a whole, the specialist will determine whether the symptom is a consequence of a disease of the oral tissues, a pathology of the body, or an incorrectly fixed crown. Only after this the doctor will be able to begin treatment. If the problem is gingivitis or stomatitis, then the patient will be prescribed a course of appropriate anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs - both for oral administration and for external treatment of the affected areas.
If the problem is the result of an incorrectly installed crown or prosthesis, you will have to completely remove the orthopedic device and undergo anti-inflammatory therapy. The prosthetic device is sent for correction or completely replaced with a new design, which is certainly the best option. When a bruise becomes the result of mistakes made by the doctor during filling, a temporary filling is applied and a course of anti-inflammatory drugs is also prescribed.
Cyst treatment
A dental cyst is treated either with therapeutic methods or with surgical intervention. The first ones are used in simple cases.
Surgery involves two types of operations - cystotomy and cystectomy. In both cases, local anesthesia is used. With cystomy, only the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. This is a less traumatic option, as it allows you to preserve the rudiments of permanent teeth during surgery on milk teeth.
Cystectomy is performed if the size of the cyst does not exceed 1.5 cm. This operation is more difficult, but postoperative recovery is much faster.
No matter how small and insignificant the swelling may seem to you, contact your dentist. This will avoid complications. And the problem will be resolved more easily and in a short time. Remember that no rinses, infusions or other folk remedies can guarantee recovery.
Types of hematomas
Hematoma in dentistry is classified depending on its location (subcutaneous hematoma, extensive hematoma), relationship to the lumen of the blood vessel (pulsating, non-pulsating), and the state of the escaping blood (clotted, infected, suppurating).
A subcutaneous hematoma is formed as a result of local hemorrhages into the subcutaneous tissue. The intensity of the hue of the hematoma depends on the depth of the bruise and the volume of blood shed. As hemoglobin is absorbed and destroyed, the hematoma changes color to greenish, yellow-green, or yellow. The formation of a subcutaneous hematoma is accompanied by pain, possibly increased temperature, and swelling of the tissues.
An extensive hematoma occurs as a result of rupture of large vessels; hematoma with signs of suppuration.
Causes and predisposing factors for hematoma formation
- Violation of vascular permeability
- Increased fragility of the vascular wall
- Impaired blood clotting
- Decrease in the body's defenses due to exhaustion, chronic disease, old age
- Immune system disorders
- Damage caused by dentist's instruments
- Bite pathologies
- Sharp edges of teeth
- Bridges and removable dentures
- Surgery
- Tooth extraction
- Damage to a vessel during the administration of anesthesia
- Hypertension
- Displacement of the neurovascular bundle of the lower jaw
- Domestic injuries
- Sudden injection of a large amount of anesthetic
A lump on the gum: what is it and what diseases can it indicate?
When taking care of your own health, you should remember that not only problems with teeth pose a potential threat: problems with gums can also signal the presence of serious problems in the body. We will devote this article to a fairly pressing issue - what to do if a lump (ball) appears on the gum? We will try to thoroughly study the issue, as well as understand what diseases this symptom may signal.
What is a lump on the gum?
In this case, we are talking about compaction of the soft gum tissue: visually this manifests itself in the form of the formation of a ball or lump - the problem is diagnosed through a visual examination, not to mention the fact that the affected area may hurt and cause discomfort.
Any change in the color of the gum tissue is always a reason to consult a dentist. If there is a lump (ball), you should go to the doctor immediately.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of such a lump - treatment tactics depend on the correct diagnosis, which the specialists of Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry can do. But generally speaking, there are two natures of the disease - infectious and non-infectious. Let's consider both factors separately.
Infectious causes of the formation of lumps on the gums in Kirov
Infection is always associated with the activity of pathogenic bacteria, which can infect absolutely any tissue of the human body. Gums are no exception: in this case, compaction is associated with infectious inflammation, which can occur for several reasons:
- Flux or periostitis. This phenomenon can be considered a complication of diseases such as caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. The infection may well affect not only the teeth, but also the adjacent tissues, that is, the gums. The result is the formation of a lump (or ball), which is noticeable even to the naked eye;
- Acid or granuloma, which can be classified as complications of periodontitis. The apex of the root is precisely the area where, due to various complications, an abscess often occurs - pus can penetrate into the periosteum area, and then under the mucous membrane. The insidiousness of this phenomenon lies in the fact that the tissues of this area are quite elastic, so at first a person may not notice negative symptoms and not experience discomfort. Only then, when the problem becomes serious, does a ball appear - this is a real fistula, which requires immediate contact with an experienced dentist;
Periodontitis and gingivitis. When inflammatory processes form in the periodontium, in almost 100% of cases the formation of various seals is observed. In the case of gingivitis, the ball acquires a red tint, and periodontitis is accompanied by the presence of a gray lump. If you do not seek high-quality or effective treatment, the disease transforms into a flux, which becomes even more noticeable and potentially dangerous to the general condition of the body.
This is exactly what the most common cases of infectious nature of the formation of a lump on the gum look like in Kirov. Next, we will look at the non-infectious cause of this problem.
Non-infectious causes of lump formation on the gums
There are also three most common options - we will again consider them individually:
- Epulis is a small growth. Visually, epulis resembles a tumor diagnosed with gingivitis, however, x-rays and/or histological examination will help to understand the true cause of the disease. This could be malocclusion, consequences of injuries, hormonal disorders, and even the result of unprofessional dental prosthetics;
- Ecostosis is a bone growth that occurs due to jaw abnormalities. Most often, this is observed due to genetic predisposition, however, the factor of injury should also not be excluded. The fact is that bone tissue can go beyond its usual limits, resulting in a noticeable lump. As a rule, inflammatory processes are not observed in this case, however, they may well appear during mechanical damage to the growths;
- A hematoma is a blood clot in the gum area, which is a direct consequence of the injury. Although, from time to time there are cases when a hematoma forms without external influence - this is also a reason to consult a dentist to solve the problem and prevent the development of complications.
So, we looked at the three most common causes of non-infectious origin of a lump on the gum in Kirov. Next, we will find out in what cases painful sensations occur in the presence of such a ball, as well as what methods of solving the problem exist today.
If the lump hurts?
If you suddenly find a lump on your gum, however, there are no pain symptoms, this does not mean that you should refuse professional diagnosis and treatment. Yes, it is likely that everything will go away on its own, however, in most cases this is not the case - there is a risk of tooth loss!
If the lump begins to hurt, you should immediately visit the dentist; however, even in this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
As for the most acute pain in the presence of a ball (bump) on a tooth in Kirov, this may signal periostitis. If the seal only bothers you when you apply pressure or eat warm or cold food, you can most likely diagnose gingivitis or periodontitis. In turn, epulis and ecostosis may go completely unnoticed, however, there may still be a slight feeling of discomfort.
Incorrect crown installation
Separately, I would like to pay attention to such a reason for the formation of a lump as incorrect installation of the crown (we have already mentioned this factor above). There are two possible factors to highlight here:
- Incorrect or poor-quality treatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, which can lead to periodontitis (we have repeatedly spoken about the complexity of the tooth depulpation procedure);
- Incorrect measurements or poor-quality prosthesis/crown. This is also very common, since an artificial element can injure the mucous membrane of the gums, causing irritation and the appearance of seals.
Treatment depends on the cause: in the first case, it is re-treatment of the tooth canals in Kirov, in the second - re-prosthetics (if, of course, it is possible).
Treatment of lumps on the gum in Kirov
And finally, a few words about how the ball is removed and the lump on the gum is treated. The order depends entirely on the nature of the disease. For example, infectious pathologies are treated by identifying and eliminating the root cause - this is done both through mechanical manipulation and with the help of medications. If periodontal inflammation occurs, measures such as sanitation and cleaning of the oral cavity, curettage, physiotherapy, etc. may well help. As for non-infectious manifestations, here the issue is resolved on an individual basis: sometimes the disease is simply observed without any active action, and in some cases surgical intervention is required.
We invite you to Doctor Efremov’s Dentistry: sign up for a consultation and get answers to all your questions! Information by phone: 8 (8332) 255-717 . Be healthy and take care of the beauty of your smile!
Pathogenesis
The occurrence of a hematoma in dentistry is usually caused by mechanical trauma to the oral cavity - unsuccessful surgery, tooth extraction, anesthesia injection. Domestic injuries are possible; people with poor blood clotting and older people are especially susceptible to this disease.
Stages of hemotoma development
- Red hematoma is bleeding into the surrounding tissue of red blood cells. Vascular rupture, thrombosis.
- Blue hematoma (2–3 days) - venous stagnation, changes in corpuscles.
- Green hematoma (4-5 days) - formation and release of hemasiderin.
- Yellow hematoma (6-7 days) - resolving therapy is recommended.
- If the process lasts for more than a month, ulcers and erosion may develop.
Symptoms
- Rising body temperature
- Pain on palpation
- Spontaneous throbbing pain
- Tissue compaction
- Tissue swelling
- Change in color of damaged skin
- Swelling of the mucous membrane