Your gums are swollen, it hurts to chew, your temperature has risen, but you still hope that it will go away on its own? You are most likely experiencing symptoms of a periodontal abscess, which is a medical emergency. The Renaissance Dent network of clinics provides services for therapeutic and surgical treatment of patients with periodontal diseases.
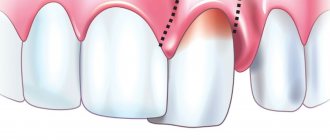
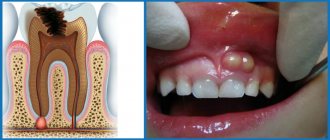
A periodontal abscess is a limited focus of purulent inflammation localized in the tissues surrounding the tooth.
Causes
The main cause of periodontal abscess is infection in the gum pockets, resulting in the development of purulent inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of periodontal abscess:
- Gum diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease.
- Injury to the soft tissue around the tooth by hard food or a crown.
- A foreign body gets into the gum pocket (the space between the tooth and gum): a piece of food, bristles from a toothbrush.
- Tooth diseases: caries, pulpitis.
How to relieve pain yourself
Before visiting a specialist, you can independently carry out a number of procedures to reduce pain:
- constantly rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution, for example furatsilin, miramistin or chlorhexidine, and the temperature of the liquid must be at room temperature (on average 20-25 degrees, but no more);
- It is also possible to rinse with well-filtered decoctions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, sage and St. John's wort;
- In no case should you heat the inflamed area or apply warming bandages and compresses, as this can provoke an increase in the inflammatory process and lead to complications;
- on the contrary, applying ice to the inflamed area helps reduce pain;
- It is recommended to try to carefully clean the diseased tooth and the surrounding space from food debris;
- You should not take strong painkillers without a doctor’s prescription; limit yourself to analgesics sold in pharmacies without a prescription;
- taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is contraindicated, because you can not only harm yourself, but also partially eliminate important symptoms by which the doctor determines the nature of the disease.
Types and symptoms of periodontal abscess
According to the flow, two types of periodontal abscesses are distinguished:
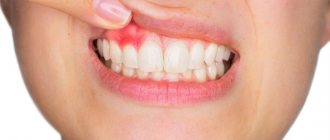
- Acute, which is characterized by vivid clinical manifestations in the form of severe pain, swelling of soft tissues, and the appearance of a formation filled with pus on the gum. The development of an abscess is combined with general malaise and fever.
- With chronic (cold) abscesses, the symptoms are erased: only bleeding and soreness of the gums are observed. Gradually, the roots of the teeth are exposed, the gum pockets are filled with pus and granulations. Chronic periodontal abscesses periodically worsen, especially against the background of decreased immunity after illness.
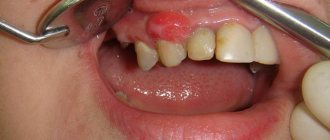
A gum abscess begins with the appearance of a swelling that is painful when pressed. The tumor gradually increases, chewing movements cause severe pain. Often pus seeps out from the gap between the tooth and gum. Pathological mobility of teeth appears. The patient’s general well-being worsens: loss of appetite, sleep disturbance, headaches, fever.
Diagnostics
The examination includes:
- patient interview,
- inspection,
- dental radiography,
- laboratory and instrumental methods.
During the examination, the doctor sees a painful local bulge and altered mucous membrane. There is no transitional fold from the periodontium to the tooth. The depth of the pockets is at least 3 millimeters.
X-ray shows:
- enlargement of the periodontal gap,
- destruction of the cortical plate,
- uneven resorption of spongy substance.
A blood test indicates nonspecific inflammation:
- high level of leukocytes,
- increase in ESR,
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
PCR allows you to accurately determine the composition of the microflora of the gum pockets. With an abscess, the number of bacteria increases 100 times. During the examination, doctors exclude:
- acute periodontitis or exacerbation of the chronic form,
- cyst with suppuration,
- periostitis,
- osteomyelitis.
First aid
- Before visiting the dentist, you can take painkillers to reduce pain: Paracetamol, Nurofen.
- It is recommended to rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions: furatsilin, potassium permanganate.
- It is forbidden to squeeze out the abscess, as well as use any thermal procedures in the area of the abscess: compresses, heating pads, as this can lead to the spread of the purulent process.
- In case of intoxication (fever, headache), it is necessary to increase the drinking regime to 2.5–3 liters per day.
Symptoms
As a rule, a periodontal abscess is easy to recognize by eye, but to make a more accurate diagnosis, dentists refer the patient for an x-ray. This inflammatory process has a specific list of typical symptoms that are similar in most patients:
- when pressing on the inflamed area, as well as in the process of chewing food, the patient experiences acute pain;
- when eating and drinking, sudden changes in temperature also cause a painful reaction;
- the inflamed area is usually a small spherical protrusion on the soft tissue;
- with frequent pressure on the damaged gum, the teeth may begin to loosen, and pus may begin to ooze from the resulting gap;
- in the absence of timely qualified medical care, the tumor grows to a noticeably noticeable and visually detectable size.
From the moment the tumor begins to increase in size, the patient’s general condition deteriorates sharply, severe headaches, nausea begin, body temperature rises, sleep and appetite are disturbed.
There are cases when the inflammation spontaneously opens up and almost all the pus flows out of the periodontal pocket, but this does not mean that you can no longer go to the dentist. After all, there are still particles of pus inside, which can re-provoke the inflammatory process. Moreover, the problem can go from acute to chronic. And, despite the fact that the pain and swelling of the gums will stop, the patient is strongly recommended to visit a doctor in order to completely clean the damaged gum area.
Treatment
The diagnosis of periodontal abscess is made based on the patient’s complaints, characteristic clinical picture and examination data. The abscess is not visible on an x-ray, but x-rays are performed to assess the condition of the bone tissue at the site of inflammation and the quality of root canal filling.
Surgical treatment consists of opening the periodontal abscess to ensure good drainage of purulent exudate.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
An incision is made in the gum mucosa at the site of the lesion, the cavity is cleared of pus, washed with antiseptics, and drainage is installed if necessary.
Antibacterial agents are prescribed for the entire postoperative period.
A periodontal abscess, the treatment of which must continue after the acute period, sometimes leaves behind deep gum pockets that require periodic rinsing with antiseptics in the dental office.
Purulent gum abscess
At the initial stage of the disease, the inflammation may contain only serous exudate and be accompanied by moderate pain and swelling. Treatment of this condition can be conservative (medication) without surgery. Over time, as a result of pathological processes, pus appears at the site of inflammation, the pain increases and often becomes pulsating. In the area of one or two teeth, a purulent abscess forms on the gum, the treatment of which requires surgical intervention.
Accumulating pus contains interstitial fluid, dead immune cells and microorganisms. As the disease progresses, the amount of pus increases and the pressure inside the abscess increases, microcirculation disorders worsen. Under such conditions, the risk of infection spreading to surrounding tissues and the development of complications increases.
Prevention
- Thorough dental hygiene: brushing your teeth in the morning and evening, rinsing your mouth after every meal, using various devices: dental floss, brushes. If there are dentures in the mouth, it is recommended to clean them of food debris using an irrigator - a special device that supplies water under pressure.
- Timely treatment of diseases of teeth and gums.
- Preventative dental examinations are necessary at least 2 times a year to assess the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. If there is hard dental plaque, use hardware teeth cleaning.
Clinic doctors
One of the services of the DentaBravo clinic is the treatment of periodontal abscess. Why is this disease dangerous? If left untreated, there is a risk of destruction and necrosis of periodontal tissue, the formation of a focus of chronic infection, loosening and tooth loss, the spread of inflammation to bone tissue and periosteum, osteomyelitis of the jaw, deformation of the jaw and distortion of the face, penetration of infection into other organs (for example, into the brain ).
What is a periodontal abscess?
This is a locally limited purulent inflammation of the gums (abscessus in Latin means “abscess”). It is a cavity filled with pus. Outwardly it looks like a rounded formation the size of a pea to a walnut.
What are the causes of periodontal abscess?
An abscess develops due to an infection that affects the periodontal pocket and gum tissue. The disease can be provoked by existing gum diseases (GINGIVITIS, PERIODONTITIS, PERIODONTOSIS, etc.). In addition, an abscess can appear as a result of mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries to the gums, as well as as a result of incorrect dental fillings or prosthetics.
What are the symptoms of periodontal abscess?
First, discomfort appears in the gum area. When chewing food or pressing on the gum with a finger, the patient feels pain. Gradually, the pain intensifies and leads to the inability to fully grind food with the teeth. After 1-3 days, a dense, reddened, spherical swelling forms in the area of inflammation. The tumor quickly increases in volume and is accompanied by pain radiating to the ear, jaw and cheek. The patient may also experience:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- insomnia;
- loss of appetite;
- decreased performance.
Sometimes a spontaneous opening of a periodontal abscess occurs, and then the pus flows into the oral cavity, and the pain and inflammation gradually subside. After this, the wound can heal, but without antiseptic treatment there is a high risk of re-infection of surrounding tissues.
How is a periodontal abscess diagnosed?
An experienced dentist can diagnose a periodontal abscess based on a visual examination. If the abscess is large and the gums are severely inflamed, an X-ray examination will be required to help determine whether the bone tissue is affected.
How is periodontal abscess treated?
Exclusively surgically. After local anesthesia, the doctor makes a precise cut in the gum and drains the abscess. The affected area can also be cleaned through the gum pocket, but this is not possible in all cases. Treatment of periodontal abscess includes the complete removal of pus and dead tissue, after which the wound surface is treated with antiseptic solutions. In case of significant inflammation, a course of antibacterial therapy is recommended, and in case of severe pain, analgesics are recommended.
What are the measures to prevent periodontal abscess?
The most effective methods of prevention are timely treatment of teeth and gums, high-quality oral hygiene care, prevention of gum injuries and treatment of oropharyngeal diseases.
How much does it cost to treat a periodontal abscess?
Prices for the services of the DentaBravo clinic can be viewed in the table below or in the price list. And if you need specialist advice, call us or fill out a special form by clicking on the “Make an appointment” button.
Cost of treating periodontal abscess
Prices for the treatment of periodontal abscess in branches of the Renaissance Dent clinic depend on the volume of pathology and the severity of the disease and the chosen technique. The sooner the patient addresses his problem, the cheaper the treatment will cost him. In any case, the patient will receive highly professional care, which will protect him from dangerous complications.
More detailed information about the prices and list of services for surgical periodontology at Renaissance Dent can be found in the price list on the official website of the clinic or by calling 242-10-20, daily from 9.00-21.00.
How a surgical autopsy is performed
Surgical opening (periostomy) can be complicated by the general condition of the patient and the size of the tumor. In some cases, it reaches such a size that it requires the installation of a drainage, a small tube that facilitates the outflow of purulent contents from the pocket. After opening such tumors, due to long-term suppression of the immune system, the patient is prescribed not only antibacterial drugs, but also immunostimulating therapy.
To avoid complications after surgery, dentists recommend their patients:
- refrain from smoking, drinking alcohol, and excessive food consumption;
- do not abuse sleeping pills and laxatives;
- do not take strong painkillers unless absolutely necessary;
- if the condition worsens, namely an increase in body temperature, the appearance of pus, redness around the incision, increased pain, incl. headache, muscle pain, immediately seek help from a doctor.
Acute periapical abscess
It is easiest to deal with visible sources of infection, but acute periapical abscess is very dangerous, since it is almost impossible to notice at an early stage of formation. In this case, the infection begins, literally, from the inside. The infection remaining in the tooth under a filling or in canals with dead pulp after insufficient treatment begins to spread through the roots of the tooth and alveolar bone to adjacent soft tissues. In this case, it is possible to identify the problem before the formation of an abscess or acute pain only with the help of photo X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
METROGYL DENTA® for periodontal abscess
METROGYL DENTA® has antibacterial activity and helps relieve inflammation caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The gel can be used to treat periodontal abscess in the postoperative period. Before using the drug, you must brush your teeth. Then a small amount of gel is carefully applied to the affected area of the gum using a cotton swab. The duration of action of the drug is 30 minutes; during this period you should refrain from drinking and eating. The duration of treatment is on average 7-10 days. Before using METROGYL DENTA®, we recommend consulting with your dentist.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.