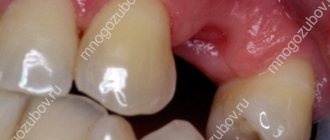
Possible reasons
Bleeding after dental surgery can be divided into two groups. In the first case, we are talking about primary bleeding, which cannot stop on its own after surgery. The second group includes situations where the problem arose only after a day or several days. Usually the reason is non-compliance with the post-operative period: heavy lifting, hot bath, non-compliance with the diet, alcohol, etc.
Let's consider the possible reasons for the first group:
- Violation of blood composition.
- Taking certain groups of medications that cause blood thinning.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Blood diseases.
- Nervous tension.
There are also reasons beyond the patient's control. For example, medical negligence. Some inexperienced dentists damage the tissue too deeply during tooth extraction. Due to deep trauma and damage to blood vessels, the wound does not heal.
Why might my nose bleed?
Nosebleeds are classified into “anterior” and “posterior.” In the first case, the cause is damage to small blood vessels, this type is usually easy to stop. The second case is considered more dangerous; bleeding occurs due to injury to large vessels located deeper in the nose, so it cannot be dealt with at home. If the blood is “spouting”, this is a reason to urgently call an ambulance.
Causes of nosebleeds include:
- nasal injuries;
- thinning of the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity;
- fragility of blood vessels, heart and blood diseases;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications (anticoagulants, NSAIDs, vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold).
What can you do at home?
If the problem has not resolved itself within three hours, then the following tips will help you:
- Apply a cold compress to your cheek. You can use a cold product or ice previously wrapped in cloth.
- Roll up sterile gauze, apply to the hole and bite for 10-15 minutes.
- Make strong tea. Soak a piece of bandage in liquid and apply to the damaged mucous membrane for 3-5 minutes.
- If you experience high blood pressure, you need to normalize it with medication. The specific drug and dosage are prescribed by the doctor.
When to seek medical help as soon as possible
Here are some signs of a Bleeding Cuts or Wounds wound that should be seen by a doctor. In some cases, your life may depend on it. Don't hesitate.
- The cut looks deep, bleeds a lot, and you can't stop the bleeding within 10 minutes. There are no options: either urgently go to the emergency room or call an ambulance.
- The wound can be described as “gaping.” The cut is deep and wide enough or has jagged edges.
- A deep cut is located on the face. Even if it is safe, if stitches are not applied in time, it may leave an unaesthetic scar.
- You have been bitten by an animal or person. If you are bitten by a pet and the scratch is minor, most likely there will be no trouble. But if we are talking about a bite from an unfamiliar animal, it is better to see a doctor. Rabies, once symptoms appear, is incurable by Rabies and 100% fatal. But if you get vaccinated in time, death can be avoided.
- You got a scratch or cut on the street, dirt got into the wound with it, and you don't have a tetanus shot. Or there is a vaccination, but more than 10 years have passed since the vaccination. Tetanus pathogens enter the wound along with dirt. The prognosis is more favorable than with rabies: in the absence of timely treatment, up to 80% of patients die, and not all 100%. But whether you will be lucky is another question.
- The wound was caused by a nail. Especially rusty Deep Cut First Aid. Such puncture wounds are the most dangerous in terms of tetanus.
- Signs of infection appeared. Reddened hot skin, swelling, purulent discharge from the wound, increased temperature, red stripes under the skin in the area of the cut - all this indicates an infection. There is a chance that the body will cope on its own. If not, you are at risk of blood poisoning. It's lethal, if anything.
However, no matter what the cut is - dangerous or safe - first aid begins with the same step. You must stop the bleeding. Well, or at least try to do it.
General recommendations
To avoid such problems, we strongly recommend that you follow the simplest rules of the rehabilitation period:
- Eating can be done no earlier than 3 hours after tooth extraction.
- Don't eat hot or cold foods.
- Give preference to liquid porridges and broths. Supam. Solid foods should be avoided until the hole is completely healed.
- Avoid taking hot baths and saunas.
- Avoid heavy lifting and exercise for a week.
- After tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth; this will significantly increase the healing time of damaged tissue.
- Limit brushing your teeth for the first 24 hours.
- You should not drink alcohol for a week after the operation.
- Never apply warm or hot compresses to your cheek.
Efficiency. Professionalism. Mercy
At yesterday's first aid courses, conducted by the Tyumen Emergency Medical Service, there were at least ten people. The courses are free. Everyone listened with interest to emergency doctor Andrei Rogotnev.
Useful tips based on practical experience
It is immediately worth noting that there is a lot of information on first aid on the Internet. The courses conducted by emergency doctors in Tyumen are valuable because the training is based on practical experience. Let's give a simple example. How long do you think it is possible to clamp an artery on the thigh or shoulder? Many will answer that no more than 1.5 hours. In fact, this recommendation has long been outdated, because after an hour and a half of compression, the blood below the tourniquet will clot in all vessels, and the limb will then have to be amputated. We are not at war, and we not only need to save a person’s life, but also try to save an injured arm or leg. However, first things first.
We find out where the blood is coming from - from a vein or from an artery
Before giving useful tips and recommendations for stopping bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev reminded that bleeding can be venous and arterial. We did not consider ordinary cuts, since they are not life-threatening. In venous bleeding, the blood comes from a vein; in arterial bleeding, the blood comes from an artery. It's generally simple. It is much more difficult for people far from anatomy and medicine to distinguish one bleeding from another. Meanwhile, it is important to understand this before you start saving a person. In fact, everything is simple here: blood from the artery flows like a fountain, but not in a continuous flow, but pulsates in time with the heartbeat, since blood from the heart enters all organs through the arteries. The blood flows back through the veins, so during venous bleeding there is no such pressure, the blood flows in a continuous stream, like water from a tap.
In case of arterial bleeding, you have no more than 3-8 minutes left
With arterial bleeding, the probability of death is greatest; with venous bleeding, death is unlikely; damage to large veins in the neck is dangerous. In case of bleeding from large arteries, those around you have no more than 3-8 minutes left. In such a short period of time, the ambulance will not have time to get there. Therefore, we drive away all fears, put plastic bags or rubber gloves on our hands if they happen to be nearby (so that in case something happens we don’t catch dangerous viruses), and look for points on the body to press the arteries with fingers. There are more than 10 such points on the body at which pulsation is felt on each side of the vertical axis of the body. We need to remember only three main ones: the carotid, brachial and inguinal arteries.
How to clamp the carotid artery
The carotid artery in the neck is to the right and left of the trachea. The pulse is clearly felt in this place. We feel and pinch this artery below the wound with our fingers. We compress the artery until the blood stops gushing out. If this happens, you did everything right. Do not under any circumstances reduce the pressure or remove your hand; the artery will be more difficult to find later.
And only after you have managed to stop the bleeding, Andrei Rogotnev advises you to do everything else: scream, call for help, ask passers-by to call an ambulance. If it is not possible to squeeze the artery with your fingers, you can secure a bandage (tourniquet, belt or piece of fabric) through the arm opposite to the wound. Thus, the artery will be compressed only on the side where the wound is. The most correct option is to compress the carotid artery until the ambulance arrives.
How to compress the brachial artery
We do the same with the brachial artery. The shoulder is the part of the arm from the elbow to the shoulder joint. Press your thumb against the inside of your shoulder to the bone and you will feel a pulsation. This is where you need to pinch the artery, clasping your hand with your thumb and forefinger until you find something to tighten it with. Motorists have a tourniquet in their first aid kit; in all other cases, you can use any available means - a shoe lace, a belt, a charger wire, etc.
How to clamp an abdominal artery
Bleeding from the abdominal artery (internal bleeding) can be stopped by pressing your fist on the abdomen in the navel area. You need to apply pressure towards the spine until the bleeding stops or decreases. Signs of internal bleeding: the person is pale and has a rapid heartbeat.
How to clamp the femoral artery
To stop arterial bleeding when the lower limb is damaged, you need to squeeze the inguinal fold between the thigh and lower abdomen with your fist. Here is another point of pressure on the artery.
The points for applying a tourniquet for injured limbs are the middle of the thigh or shoulder
If a limb is damaged, the artery should be pressed with a tourniquet above the wound. The points for applying the tourniquet are the middle of the thigh and shoulder. There is no point in applying a tourniquet to the lower leg or forearm (from the hand to the elbow), since here the arteries pass between two bones and stopping the bleeding is not guaranteed; significant force will need to be applied, which can damage the tissue.
If you are somewhere far from a populated area - in the forest or on the road - you should clamp the artery with a tourniquet for no more than 15 minutes. No more, otherwise a person risks losing an arm or leg. After 15 minutes, the tourniquet must be loosened without removing the last two rounds (turns of the tourniquet). We rest for the same amount of time as we walked, then tighten the tourniquet again and walk or drive further - to where we will receive medical assistance.
How hard should you squeeze the tourniquet?
Many people have a question: with what force should the artery be clamped with a tourniquet? We tighten the tourniquet until the bleeding stops, then fix it. It's better to try it yourself. The force should be minimal, as when squeezing with a tonometer cuff.
What to use instead of a tourniquet
Instead of a tourniquet, you can use fabric (scarf, shirt sleeve, trouser leg) or lace or bandage, with which you can make a “twist”. We wrap the bandage around the limb twice, tie a knot, but do not press it tightly to the hand, leaving a distance the size of a finger. Then insert a key, a pen or any stick and begin twisting until the bleeding stops.
Well, that’s actually all you need to know about stopping arterial bleeding. The main thing is not to faint at the sight of blood. Of course, you need to be mentally prepared for such situations in advance.
It is much easier to stop bleeding from a vein when the limbs are injured
With venous bleeding everything is much simpler. As soon as we understand that blood is running from the vein, we clamp the wound with a tight bandage, just as ordinary wounds are bandaged. The bleeding must stop.
If the tension of the tourniquet is weak, the blood flow from the vein will only increase
There are situations when people cannot understand whether blood is flowing from a vein or from an artery. At the same time they are trying to help. It should be remembered that when a tourniquet is applied, the bleeding should stop. If the tourniquet is loosely secured, the blood flow from the vein will only increase.
Yuri Shestak, Medical Information Agency NEDUGAMNET
What is the main danger of capillary bleeding?
First aid for capillary bleeding should not be called an unnecessary procedure. Compared to arterial and venous bleeding, capillary bleeding is not so dangerous, and in most cases the body copes with it on its own. But there are situations that are life-threatening:
- the skin is extensively damaged;
- the ambient temperature is increased;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- There is blood poisoning, oncology, hepatitis, arterial hypertension and other severe pathologies.
The most dangerous is bleeding as a result of damage to the blood vessels of internal organs. Prolonged bleeding provokes a decrease in blood pressure, oxygen starvation, and disruption of the cardiovascular system. If the blood loss is severe, the person dies without treatment. Hemorrhage in the brain affects important centers and also leads to a fatal outcome. Pleural bleeding disrupts breathing and puts pressure on the lung. In most cases, it is important to react in time to manifestations of capillary bleeding and provide first aid in a timely manner.
Some tips
It is not always possible to have the necessary solutions on hand to stop bleeding from a cut or to treat a wound. Therefore, you can use homemade remedies.
An ordinary leaf of forest plantain will help in case of a cut.
- You can apply ice from the refrigerator to the cut area.
- For multiple minor abrasions and cuts on the body, a hot shower will help. If you wash yourself carefully with soap, the bleeding will stop.
- Minor wounds after shaving in the armpits can be treated with deodorant.
- For a small abrasion or scratch, it is recommended to temporarily apply Vaseline or hygienic lipstick. A layer of wax will protect the wound from contamination.
- You can cover a razor cut with a piece of toilet paper instead of a napkin.
- Cuts on the face should not be treated with cologne, perfume or eau de toilette. They leave behind pigmentation.
- Traditional methods can be used in camping conditions, if you do not take a first aid kit with you: apply moss, cobwebs, use a thin film located under an eggshell, or a clean plantain leaf.
Don’t panic, but don’t overestimate your capabilities and knowledge in medicine. Consult your doctor.
Treatment
For treatment of this condition to be effective, the causes of the disease must be determined. It is very important to promptly identify and treat the main disorders - liver pathologies or oncological lesions.
Additional therapy methods include:
- injection of vitamin K;
- drugs to improve clotting;
- transfusion of frozen blood plasma;
- Other medications include hydroxyurea and oprelvekin, which help eliminate platelet problems.
The patient's diet should include foods high in calcium, folic acid, vikasol, and amino acids.
These include dairy products: cheese, cottage cheese, kefir. Fish and meat will also help eliminate the symptoms of pathology. It is equally important to eat leafy vegetables - green onions, spinach, cabbage.
When a cut becomes dirty
Incised wounds occur when working in the garden, when swimming in bodies of water (on glass or a shell at the bottom). Here the risk of infection increases significantly, even if the cut is shallow. The stronger the cut, the more careful you should be in processing.
Washing the wound with plain water is not enough. You need to use a weak solution of potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide. The small foam that forms causes dirt to be removed from the depths of the wound.
The edges are treated with brilliant green. Apply a sterile pressure bandage. Give the limbs rest, give it an elevated position.
If you are not sure about the complete cleanliness of washing a contaminated wound, you should consult a surgeon. He will check the condition of the wound and carry out additional treatment.
How to competently provide first aid for severe capillary bleeding?
First aid for capillary bleeding involves applying a tourniquet. The indication is extensive damage, impaired coagulation. Rules for applying a tourniquet:
- Wrap the tourniquet 2 times around the injured limb above the wound. Correct actions lead to the fact that the pulse under the wound will not be palpable.
- Place a piece of fabric under the tourniquet to avoid trophic changes.
- Be sure to record the exact time of application of the tourniquet. The skin condition is monitored.
- In the warm season, you can leave the tourniquet on the body for up to 2 hours, in winter - no more than 1 hour. Every 30 minutes you need to relax the rubber band for 30 seconds to avoid tissue death. If everything is done correctly, the limb does not turn blue or swell. And vice versa.
After applying a rubber tourniquet, the victim is quickly sent to the hospital for diagnosis and treatment. If you don’t have a rubber band at hand, use a belt, scarf, or tie.
How to stop bleeding from a deep cut and what to do next
Deep cuts are already dangerous. Large blood vessels may be affected, increasing the risk of serious blood loss or blood poisoning. Self-medication in such cases is prohibited. So act like this.
Call the doctor
If the cut bleeds heavily and/or causes significant pain to the victim, call 911. If the situation seems manageable and generally tolerable, go to the emergency room or try talking to your physician or surgeon over the phone.
Try to stop the bleeding
This should be done while you are waiting for an ambulance or preparing to go to the emergency room. Give the cut a quick rinse with water (soap is good) to remove any debris, and then, if there are no large pieces of debris left in the cut, apply a pressure bandage. You will need to hold a piece of clean gauze or cloth over the cut for about 5 minutes. Don't remove it early First AID: how to treat a cut: you can break a newly formed blood clot and the bleeding will only get worse.
If there are still large fragments in the wound and they cannot be washed off with water, do not try to pull them out - this may intensify bleeding. Let the doctor pull them out (who is already on his way to you or to whom you are in a hurry on your own). To make the bleeding weaker, in this case you can:
- Elevate the affected part of the body above the level of the heart.
- Apply a tourniquet to the injured limb, 7–10 cm above the wound. Both pharmaceutical tourniquets and tourniquets can be used, as well as homemade ones - for example, a belt or a rolled-up T-shirt. Mark the time of application of the tourniquet (with the same marker on the skin). You have 1–2 hours to see a doctor.
If the bleeding has been stopped, treat the wound with antiseptic ointment
Do not go deep into the cut: it is enough to process its edges. Then apply a sterile cloth - bandage or gauze - to the wound.
Superficial cuts from shaving
In a hurry, men, when using razors with an open blade, cause minor injuries to their facial skin in the form of shallow cuts. When inexperienced women treat their armpits, bikini area, and leg skin, they cause razor cuts.
- It is best to immediately treat such wounds with hydrogen peroxide and cover the cut with a band-aid.
- Men are advised to quickly use a piece of paper napkin, sticking it to the cut site. Only this method will cause re-bleeding when the dried blood comes off.
- Special hemostatic pencils containing astringents and disinfectants are available for sale. They are designed for use after shaving.
- For shaving, it is better to use special gels containing soaps and disinfectants.
Men are advised to keep a set of napkins nearby at all times.
Symptoms of bleeding
The main symptom is the appearance of blood from the nasal sinuses, its flow outward and inward (through the nasopharynx). Bleeding may also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- nausea;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- feeling of fullness in the ears;
- paleness of the skin of the face and hands.
Bleeding can be either light or heavy. Depending on the volume of blood lost, there are 3 degrees of severity:
- light – up to 500 ml;
- average – 500-1400 ml;
- heavy – more than 1400 ml.